What Tests Are Used To Stage Melanoma
There are several tests your doctor can use to stage your melanoma. Your doctor may use these tests:
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Patients with melanomas deeper than 0.8 mm, those who have ulceration under the microscope in tumors of any size or other less common concerning features under the microscope, may need a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes to determine if the melanoma has spread. Patients diagnosed via a sentinel lymph node biopsy have higher survival rates than those diagnosed with melanoma in lymph nodes via physical exam.
- Computed Tomography scan: A CT scan can show if melanoma is in your internal organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan: An MRI scan is used to check for melanoma tumors in the brain or spinal cord.
- Positron Emission Tomography scan: A PET scan can check for melanoma in lymph nodes and other parts of your body distant from the original melanoma skin spot.
- Blood work: Blood tests may be used to measure lactate dehydrogenase before treatment. Other tests include blood chemistry levels and blood cell counts.
Treating Stage Ii Melanoma
Wide excision is the standard treatment for stage II melanoma. The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma.
Because the melanoma may have spread to nearby lymph nodes, many doctors recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy as well. This is an option that you and your doctor should discuss.
If an SLNB is done and does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If the SLNB finds that the sentinel node contains cancer cells, then a lymph node dissection will probably be done at a later date. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
Treatment Of Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancers By Type And Stage
Most of the time, treatment of nasal cavity or paranasal sinus cancer is based on where it is and its stage . But other factors, such as a persons overall health and personal preferences, could also affect treatment options. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about the treatment plan he or she recommends.
The staging of nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancer is very complex. At this time, staging systems have only created for the most common cancers maxillary sinus and nasal cavity/ethmoid sinus cancers. Treatment choices for less common cancers of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses are tailored to each patient depending on the tumor type, size, location, and the patients general medical condition and wishes.
Because nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancers are rare, they’ve been hard to study well. Most experts agree that treatment in a clinical trial should be considered for anytype or stage of nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancer. That way people can get new treatments that are being studied.
Don’t Miss: Can Someone Die From Skin Cancer
Treatment Of Stage Iii Melanoma That Cannot Be Removed By Surgery Stage Iv Melanoma And Recurrent Melanoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage III melanoma that cannot be removed by surgery, stage IV melanoma, and recurrentmelanoma may include the following:
- Radiation therapy to the brain, spinal cord, or bone.
Treatments that are being studied in clinical trials for stage III melanoma that cannot be removed by surgery, stage IV melanoma, and recurrent melanoma include the following:
- Immunotherapy alone or in combination with other therapies such as targeted therapy.
- For melanoma that has spread to the brain, immunotherapy with nivolumab plus ipilimumab.
- Targeted therapy, such as signal transduction inhibitors, angiogenesis inhibitors, oncolytic virus therapy, or drugs that target certain genemutations. These may be given alone or in combination.
- Surgery to remove all known cancer.
- Systemic chemotherapy.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Where Else Does Melanoma Spread To
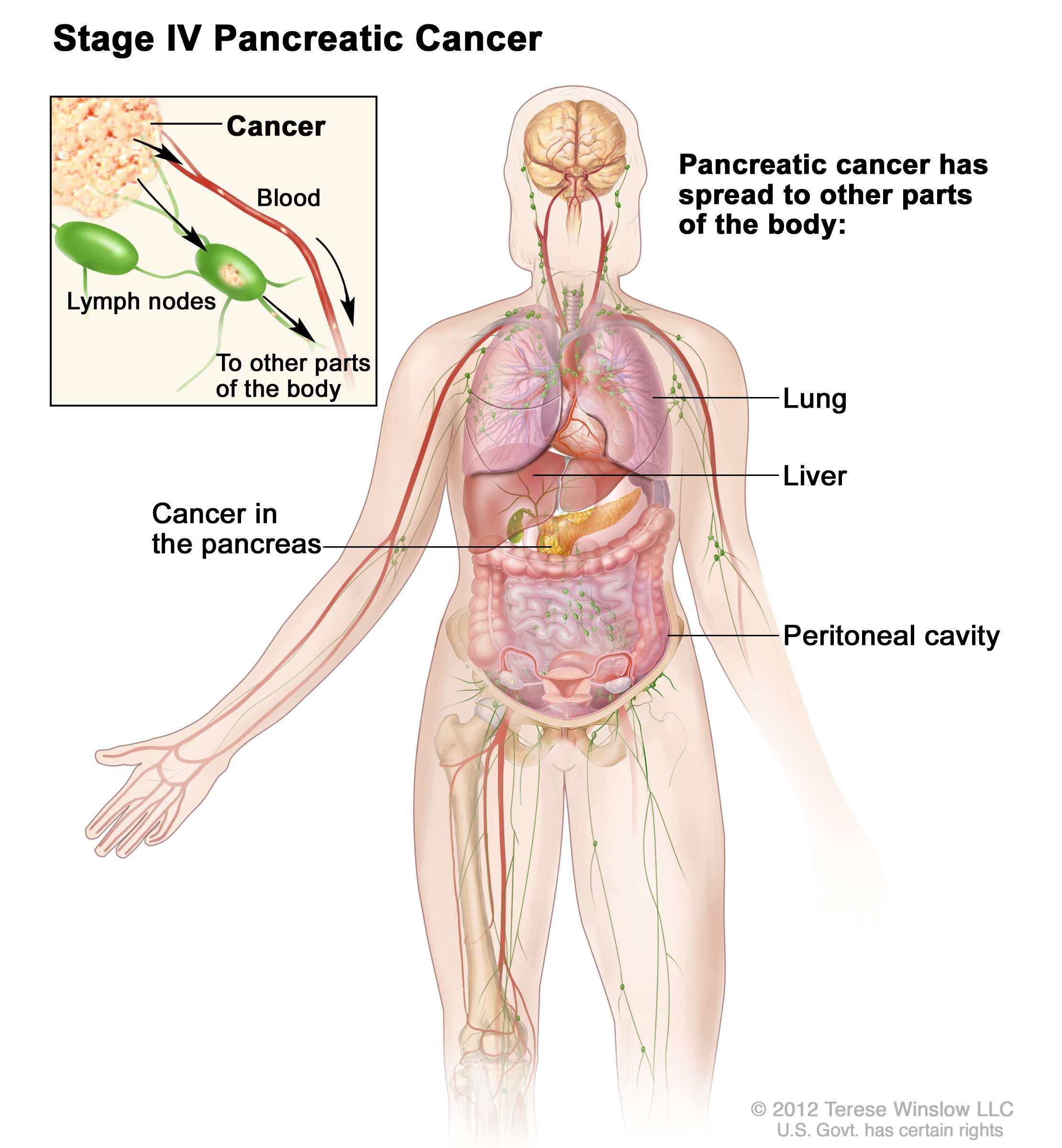
When melanoma advances to stage 3, it means the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes or the skin around the primary tumor and lymph nodes. In stage 4, the cancer has moved to other areas far beyond the lymph nodes, like your internal organs. The most common places melanoma spreads to are the:
- lungs
- brain
- stomach, or abdomen
These growths will cause different symptoms, depending on which areas it has spread to. For example, you may feel breathless or constantly cough if the cancer has spread to your lungs. Or you may have a long-term headache that wont go away if it has spread to your brain. Sometimes the symptoms for stage 4 melanoma may not appear for many years after the original tumor was removed.
Talk to your doctor if youre feeling new pains and aches or symptoms. Theyll be able to help diagnose the cause and recommend treatment options.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To Die From Melanoma
Symptoms Of Metastatic Cancer
Metastatic cancer does not always cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, what they are like and how often you have them will depend on the size and location of the metastatic tumors. Some common signs of metastatic cancer include:
- pain and fractures, when cancer has spread to the bone
- headache, seizures, or dizziness, when cancer has spread to the brain
- shortness of breath, when cancer has spread to the lung
- jaundice or swelling in the belly, when cancer has spread to the liver
Discussion Of Pathological Response
Assessment of pathological response to chemotherapy has played an important role in head and neck carcinomas, esophageal carcinoma, osteogenic sarcoma, and small cell lung carcinoma. Pathological complete response is defined as fibrosis or fibro inflammation without microscopic evidence of carcinoma and histologically negative nodes. Non-pCR is defined as any evidence of viable carcinoma, either at the primary site or at the resected regional LN. Those patients who achieve complete pathological response have long-term survival advantage. Junker et al. found that in NSCLC patients, not only complete responders but also extensive responders with < 10% residual tumor also had good long-term survival.
The common histological features of tumor regression are coagulative necrosis, fibrosis, foam cell/giant cell reaction, as well as mixed inflammatory infiltrate. The amounts of fibrosis correlate well with extent of tumor regression, which in turn is a surrogate marker of tumor response. Squamous carcinoma was associated with a higher probability of treatment response than adenocarcinoma.
To conclude, pathological response can be of two types: Responder and non-responder groups. The common histological changes seen are fibrosis, necrosis, and foam cell/giant cell reaction in some cases, increase in residual tumor nuclear grade is seen. The radiological assessments may not correlate well with the pathological response.
Recommended Reading: What Type Of Cancer Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
How Is Melanoma Treated
Your melanoma treatment will depend on the stage of the melanoma and your general health.
Surgery is usually the main treatment for melanoma. The procedure involves cutting out the cancer and some of the normal skin surrounding it. The amount of healthy skin removed will depend on the size and location of the skin cancer. Typically, surgical excision of melanoma can be performed under local anesthesia in the dermatologist’s office. More advanced cases may require other types of treatment in addition to or instead of surgery.
Treatments for melanoma:
- Melanoma Surgery: In the early stages, surgery has a high probability of being able to cure your melanoma. Usually performed in an office, a dermatologist numbs the skin with a local anesthetic and removes the melanoma and margins .
- Lymphadenectomy: In cases where melanoma has spread, removal of the lymph nodes near the primary diagnosis site may be required. This can prevent the spread to other areas of your body.
- Metastasectomy: Metastasectomy is used to remove small melanoma bits from organs.
- Targeted cancer therapy: In this treatment option, drugs are used to attack specific cancer cells. This targeted approach goes after cancer cells, leaving healthy cells untouched.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy includes treatments with high-energy rays to attack cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Immunotherapy: immunotherapy stimulates your own immune system to help fight the cancer.
Role Of Cytology In Lung Cancer
Conventional cytologies such as sputum examination, bronchial lavage, bronchial brushings, fine-needle aspiration biopsy have played an important role in the diagnosis of primary and metastatic lung cancers. Immunohistochemical stains can be applied on cytological material. The immunohistochemical markers such as TTF-1, CK7, CK20, 4A4, 34 E12, and p63 help to classify further subtypes in Non-small cell lung cancer . In addition, epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation studies can also be done on the blocks prepared from cytological material, which helps in choosing appropriate targeted therapy. Thus, cytology plays an important role not only to subclassify tumors but also to individualize treatment strategy with the advantage of easy availability and minimum invasiveness.
Thus, the patient was diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, T3N2M1a, stage IV.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Skin Cancer On Your Leg
Treatments For Stage I Melanoma
Your doctor will most likely treat stage 1 melanoma with surgery called wide excision, which cuts out the melanoma along with a margin of healthy surrounding skin. The amount of healthy skin removed is determined by the location and the thickness of the melanoma being treated.
While wide excision surgery is often the only treatment necessary, in some cases a doctor may also choose to check for cancer in nearby lymph nodes by performing a sentinel lymph node biopsy. If cancer cells are found in the lymph nodes, further treatment will become necessary, such as a lymph node dissection , chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapies.
What Is Metastatic Cancer
In metastasis, cancer cells break away from where they first formed , travel through the blood or lymph system, and form new tumors in other parts of the body. The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor.
Cancer that spreads from where it started to a distant part of the body is called metastatic cancer. For many types of cancer, it is also called stage IV cancer. The process by which cancer cells spread to other parts of the body is called metastasis.
When observed under a microscope and tested in other ways, metastatic cancer cells have features like that of the primary cancer and not like the cells in the place where the metastatic cancer is found. This is how doctors can tell that it is cancer that has spread from another part of the body.
Metastatic cancer has the same name as the primary cancer. For example, breast cancer that spreads to the lung is called metastatic breast cancer, not lung cancer. It is treated as stage IV breast cancer, not as lung cancer.
Sometimes when people are diagnosed with metastatic cancer, doctors cannot tell where it started. This type of cancer is called cancer of unknown primary origin, or CUP. See the Carcinoma of Unknown Primary page for more information.
You May Like: Is This Skin Cancer App
Stages 0 I And Ii Maxillary Sinus Cancer
The first step in treating most stage 0, I, or II maxillary sinus cancers is surgery to remove the cancer. In most cases, a maxillectomy is done. Lymph nodes in the neck aren’t removed.
Radiation might be needed after surgery for people with stage I and II cancers, if the cancer has features that make it more likely to come back, such as positive margins , or cancer growing into the area around the nerves .
Radiation is often recommended after surgery for adenoid cystic cancers, even if the margins are negative and there’s no perineural invasion, because they have a high chance of coming back after treatment.
For some aggressive types of maxillary sinus tumors, such as undifferentiated cancer or esthesioneuroblastoma, chemotherapy might be recommended along with radiation treatment.
In cases where surgery to remove the cancer would be risky because of other medical problems, treatment may be radiation therapy alone or chemo given with the radiation.
What Are Treatment Options For Recurrent Nasal Cavity Or Paranasal Sinus Cancer

Cancer is called recurrent when it comes back after treatment. Recurrence can be local , regional , or distant . Options for treating recurrences depend on the location and type of cancer, as well as the treatment used the first time.
For a local recurrence, if radiation was the first treatment for the cancer, surgery may be used. If the first treatment was surgery without radiation, radiation therapy may be tried. Chemo and/or targeted therapy may be used with radiation, or it may be used by itself to treat recurrences that are not controlled by radiation therapy or surgery.
In a regional recurrence, the cancer comes back in the lymph nodes in the neck. This is often treated with surgery to remove many lymph nodes in the neck that are on the same side as the cancer. This may be followed with radiation to the neck, sometimes combined with chemo and/or targeted therapy.
Recurrent melanomas or sarcomas of the nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses are treated by surgery, if possible. Depending on the exact type of cells forming the cancers, chemo or other treatments may also be given.
When a nasal cavity or paranasal sinus cancer comes back in other organs, it’s often treated with chemo, targeted therapy, and/or immunotherapy, although radiation could also be an option if it wasnt given before.
Because these cancers are hard to treat, clinical trials of new treatments are a good option for some people.
Recommended Reading: Do Skin Cancer Spots Appear Suddenly
Signs Of Melanoma Include A Change In The Way A Mole Or Pigmented Area Looks
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by melanoma or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- A mole that:
- changes in size, shape, or color.
- has irregular edges or borders.
- is more than one color.
- is asymmetrical .
- itches.
- oozes, bleeds, or is ulcerated .
For pictures and descriptions of common moles and melanoma, see Common Moles, Dysplastic Nevi, and Risk of Melanoma.
Five Types Of Standard Treatment Are Used:
Surgery
Surgery to remove thetumor is the primary treatment of all stages of melanoma. A wide local excision is used to remove the melanoma and some of the normal tissue around it. Skin grafting may be done to cover the wound caused by surgery.
Sometimes, it is important to know whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. Lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy are done to check for cancer in the sentinel lymph node . It is the first lymph node the cancer is likely to spread to from the primary tumor. A radioactive substance and/or blue dye is injected near the tumor. The substance or dye flows through the lymphducts to the lymph nodes. The first lymph node to receive the substance or dye is removed. A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells. If cancer cells are found, more lymph nodes will be removed and tissue samples will be checked for signs of cancer. This is called a lymphadenectomy. Sometimes, a sentinel lymph node is found in more than one group of nodes.
After the doctor removes all the melanoma that can be seen at the time of the surgery, some patients may be given chemotherapy after surgery to kill any cancer cells that are left. Chemotherapy given after the surgery, to lower the risk that the cancer will come back, is called therapy.
Surgery to remove cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes, lung, gastrointestinal tract, bone, or brain may be done to improve the patients quality of life by controlling symptoms.
Also Check: What To Do To Prevent Skin Cancer
What To Ask Your Doctor About Stage Iv Melanoma
When your doctor tells you that you have Stage IV melanoma, it can be frightening and overwhelming. But it is important to use the time with all of your doctors to learn as much about your cancer as you can. Your doctors will provide you important information about your diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment options.
It is often helpful to bring a friend or family member with you to your doctor appointments. This person can lend moral support, ask questions, and take notes.
The following questions are those you may want to ask your doctors. Some of the questions are for your medical oncologist, some are for your surgical oncologist, and some for your dermatologist. Remember, it is ALWAYS okay to ask your doctor to repeat or clarify something s/he has said so that you can better understand it. You may find it helpful to print out these questions and bring them with you to your next appointment.
It Usually Starts With Suspicious Spot
Maybe you noticed a mole that stood out from the rest . Its edges were irregular, maybe it was asymmetrical in shape, unevenly pigmented, noticeably large , or rapidly changing . These are the spots that concern dermatologists. If you had one, your doc did a biopsy on your own ugly duckling. During this in-office procedure, your doctor either shaved off a layer of your mole, punched it out with a hole-punch-like tool, or removed it with surgical excision, along with a margin of healthy skin to check for wandering cancer cells.
Recommended Reading: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest