Symptoms Of Lobular Breast Cancer
Lobular breast cancer sometimes begins without symptoms. It may show as an abnormal area on a mammogram, which leads to further examination.
Spotting ILC on a mammogram can be difficult because the cancer cells spread in a line rather than in a distinctive lump, as in IDC. Magnetic resonance imaging imaging is reported to provide more sensitive images that may show the cancer better.
The first symptom of ILC is sometimes a thickening or hardening of a portion of the breast. This thickening can be felt by touch, but it feels different from the classic lump associated with IDC, the more common breast cancer.
Other symptoms of ILC may include:
- swelling or fullness in a part of the breast, or in the whole breast
- a change in the skin texture in a part of the breast
- dimpling in the breast
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rates
Survival rates for cancer are typically calculated in terms of how many people live at least 5 years after their diagnosis. The average 5-year survival rate for breast cancer is 90 percent, and the 10-year survival rate is 83 percent. This is an average of all stages and grades.
The stage of the cancer is important when considering survival rates. For instance, if the cancer is only in the breast, the 5-year rate of survival is 99 percent. If it has spread to the lymph nodes, the rate decreases to 85 percent.
Because there are many variables based on the type and spread of cancer, its best to talk with your doctor about what to expect.
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 cancer means the breast cancer has extended to beyond the immediate region of the;tumor;and may have invaded nearby lymph nodes and muscles, but has not spread to distant organs. Although this stage is considered to be advanced, there are a growing number of effective treatment options.
This stage is divided into three groups: Stage 3A, Stage 3B, and Stage 3C. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and surrounding tissue.
Read Also: What To Do When You Get Skin Cancer
Certain Breast Cancer Subtypes Have A Better Statistical Prognosis
In general, tubular, mucinous and medullary breast carcinomas have a better prognosis than the other sub-types.
The table below gives a very general approximation of the survival rates that may be associated with the different breast cancer subtypes.
However, please bear in mind that these figures are a rough generalization only and survival will always be determined by the individual characteristics of each breast cancer and each patient.
Nonetheless, the relative aggressiveness of the different breast cancer subtypes can be interpreted from the table.
and is almost always near 100% curable.)
| breast cancer sub-type | |
| Inflammatory breast carcinoma | 65% 35% |
What Is Ductal Carcinoma In

For an in-depth look at Ductal Carcinoma visit our latest post.
Basically, ductal carcinoma in-situ is a very early form of breast cancer, whereby cancer cells, of various grades, are present in the milk ducts of the breasts.
The reason ductal cancer is named in-situ at this early phase, is that the abnormal cells have not yet spread outside of the milk ducts. This explains the reason for the very good prognosis for this type of breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Cure Melanoma
Understanding Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Prognosis varies by stage of breast cancer.
Non-invasive and early stage invasive breast cancers have a better prognosis than later stage cancers .
Breast cancer thats only in the breast and has not spread to the lymph nodes has a better prognosis than breast cancer thats spread to the lymph nodes.
The poorest prognosis is for metastatic breast cancer , when the cancer has spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes to other parts of the body.
Learn more about breast cancer treatment.
What Are The Treatment Options For Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Another way a doctor may describe stage 3 breast cancer is if its operable or inoperable. This will determine further treatments.
If a cancer is operable, this means a doctor believes most or all of the cancer can be removed with surgery.
Inoperable cancer is still treatable with systemic therapy, but surgery isnt the right option because doctors feel they cant remove enough cancerous cells.
Treatment options for stage 3 breast cancer may include:
- Surgery: known as a mastectomy, to remove cancerous tissue and also to remove lymph nodes
- Hormone therapy: to slow or stop the growth of cancerous cells, if hormones are driving their growth
- Chemotherapy: involves taking medications to kill fast-growing cancer cells
- Targeted therapy: uses your genes to attack cancer cells without harming healthy cells
Your doctor may also recommend a combination of two or more treatments.
Don’t Miss: What Do Skin Cancer Sores Look Like
What Is The Rate Of Survival For Stage 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Breast Cancer Survival Rates Are Affected By Tumor Grade
Breast cancer grade refers to the size and shape of the malignant breast cancer cells. If the breast cancer cells look very different than normal breast tissue cells, and somewhat random in appearance, they are called poorly differentiated and described as high grade.
There are three main breast cancer grades and these are as follows:-
- Grade 1: The cancer cells are well differentiated and look the most like normal cells. These type of cancers tend to be slow-growing.
- Grade 2: These cancer cells are moderately differentiated. This means that the cells look less like normal cells and tend to grow faster.
- Grade 3: Poorly differentiated cells do not appear like normal cells at all and tend to be very fast growing. Hence, the affect on prognosis.
Microscopic Images of Ductal cell carcinoma in Situ Grades 1, 2 and 3
Higher grade breast cancers tend to have a poorer prognosis.
You will be able to find the Grade of your tumor on your pathology report.
Also Check: How To Remove Skin Cancer Yourself
Patient Characteristics Between Ilc And Idc
The SEER tumor registry database was used to identify 1,097,908 patients diagnosed with ILC and IDC. After selecting patients based on specific inclusion and exclusion criteria, the remaining 318,406 patients were included in our research. Table 1 shows the patient selection process. Finally, 30,190 patients were assigned to the ILC group and 288,216 patients were assigned to the IDC group. Table 2 summarizes the clinical characteristics of the ILC and IDC groups.
Table 2 Comparison of clinical characteristics between invasive lobular carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma group in unmatched population.
People diagnosed with ILC tended to be older , exhibit poorly differentiated and larger lesions, be ER/PR positive and were administered less radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Given the surgical procedures, ILC had a higher percent of mastectomy compared to IDC cases . A lower rate of radiation therapy and chemotherapy was observed in the ILC group .
How To Improve Your Breast Cancer Survival Rates
While some things that influence breast cancer survival rates cannot be changed , there are several ways a patient can potentially improve his or her outcomes. For instance:
- Studies suggest that outcomes tend to be better for patients who undergo radiation therapy after surgery. Even though surgery by itself can be effective, radiation therapy can destroy residual cells that were not visible or accessible during an operation.
- Hormone therapies can help prevent recurrences in patients whose tumors are found to be hormone-receptive. Some of these therapies are only available through clinical trials; patients can discuss the potential risks and benefits of participation with their treatment teams.
- The outcomes for stage 0 breast cancer are generally more favorable than the outcomes for more advanced stages of breast cancer. Although ductal carcinoma in situ does not always progress into a more invasive malignancy, treating it early before it progresses to a more advanced stage of cancer can improve a patients outcome.
Not only are there several ways to improve survival outcomes, but also quality of life outcomes as well. For instance, reconstructive surgery can be performed to improve aesthetic results after a lumpectomy or mastectomy. Women who hope to breastfeed can discuss possible breast-tissue-sparing techniques with a surgeon. Additionally, supportive care services are available to help patients better manage the side effects of breast cancer treatment.
Don’t Miss: How Do You No If You Have Skin Cancer
Oncogene Expression May Negatively Affect Breast Cancer Outcome
A relatively new addition to the discussion of breast cancer survival statistics and prognosis is oncogene expression.
An oncogene is a tiny fragment of genetic material which is carried in a chromosome and can cause normal cells to become malignant.
The oncogene HER-2, in particular, has been linked to more aggressive breast cancers.
Around one-third of all breast tumours produce the HER-2 oncogene, and these patients tend to have higher rates of recurrence and lower overall breast cancer survival rates.
According to a 2013 Canadian scientific study, the overall 5-year survival rate of HER-2 positive breast cancer is 88.6%. Furthermore, the relapse-free survival rate for 5 years is 79.4%.
What Is The Prognosis For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
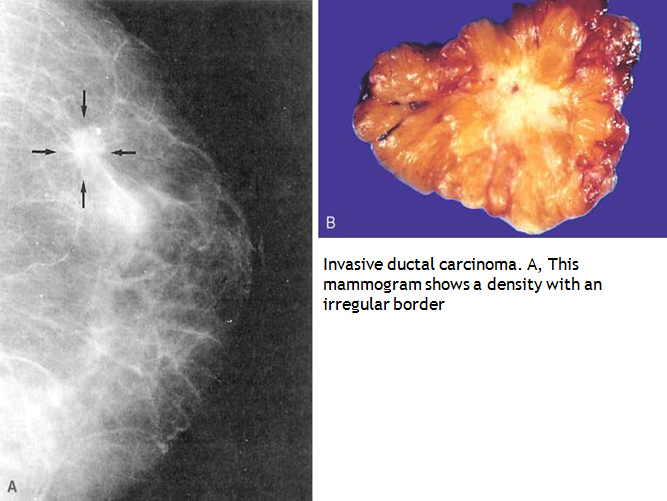
Based on individual markers and prognostic factors, including the staging of your tumor, your physician will work to give you a prognosis. At Johns Hopkins Medicine, our team of breast cancer specialists is dedicated to developing cutting-edge techniques for surgery, breast reconstruction, chemotherapy, biologic targeted therapy, radiation therapy and other hormonal therapies. Our research allows us to make great strides forward for patients with breast cancer.
You May Like: Can Skin Cancer Be Cured
Relative Survival Rate By Stage
The survival rates by stage are based on the stage at the time of diagnosis. Youve probably been given a number and letter for your cancer stage. Here, the terms localized, regional, and distant are used instead of numbers and letters. Heres what they mean and the 5-year relative survival rates for each:
- Localized breast cancer is only in the breast. This includes stage IA , some IIA , and some IIB . The 5-year relative survival rate is 99%.
- Regional breast cancer has spread to nearby tissue or lymph nodes. This includes stage IB , some IIA , some IIB , and all stage III . The 5-year relative survival rate is 86%.
- Distant breast cancer has spread to other parts of the body. This includes stage IV, pronounced stage 4). The 5-year relative survival rate is 28%.
Tumor Size Or Clinical Features On Diagnosis
Tumor size, as a single prognostic factor in DCIS, has remained controversial amongst medical experts.
Whilst many cases of DCIS are diagnosed by mammography and are not palpable on diagnosis some present as a clinical, palpable mass .
Narod, following a 2014 medical study, asserts that:-;
Tumour size and palpability are risk factors for breast cancer recurrence and mortality.
;One small, 2006 medical study concluded that higher rates of invasive caner were detected according to tumor size. Progression to invasive cancer occurred in 10% of DCIS patients with a tumor size between 2.5 to 3.5 cms, 57% for tumor size 3.6 to 4.5 cms and 71% for tumors between 4.5 and 6 cms.
This study concluded that tumors over 2.5 cms have a higher risk of progressing to invasive cancers. However, the study stresses the correlating importance of axillary node involvement.
Recommended Reading: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
Are Women Opting Against Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treatment
Its no surprise that these results were met with some raised eyebrows and of course concerns in the medical community, especially considering DCIS is almost exclusively diagnosed by mammography and some women may view these findings as a green light to cancel those appointments or ignore a diagnosis of DCIS.
Yet, there is no right way to treat DCIS. Like any cancer, there are a variety of factors at play ranging from the biology of the tumor and patients age to menopausal status and lifestyle.;;
The most common type of non-invasive breast cancer, DCIS, is considered non-invasive because it has not yet spread beyond the milk ducts to the surrounding tissue. While this type of breast cancer isnt life threatening, having DCIS can increase a womans chance of later developing invasive breast cancer.
So the question remains: does it matter if I have DCIS? Should I opt for a double mastectomy, no mastectomy, lumpectomy? Or should I do nothing? Of course, there is no simple answer when it comes to the treatment of breast cancer and that logic holds true for women facing a DCIS diagnosis. We are all unique individuals armed with a vast array of biological characteristics and risks and physicians must treat your cancer with this same multi-faceted approach.
What Affects Prognosis
There are a number of factors that affect breast cancer prognosis. These include:
- the;type;of breast cancer
- the;grade;of the breast cancer
- the;size;of the breast cancer
For more information see our booklet;Understanding your pathology results;or visit our;pathology report;page.
Other factors that may affect your prognosis include your age, menopausal status , lifestyle factors and your general health.
All of these factors will be considered when estimating your prognosis and deciding what;treatment;youre offered.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Cancer Is Skin Cancer
What Is Stage 0 Dcis
Stage 0 breast cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ is a non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. In Stage 0 breast cancer, the atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts or lobules into the surrounding breast tissue. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ is very early cancer that is highly treatable, but if its left untreated or undetected, it can spread into the surrounding breast tissue.
Additional Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma:
There are four types of invasive ductal carcinoma that are less common:
- Medullary Ductal Carcinoma This type of cancer is rare and only three to five percent of breast cancers are diagnosed as medullary ductal carcinoma. The tumor usually shows up on a mammogram and it does not always feel like a lump; rather it can feel like a spongy change of breast tissue.
- Mucinous Ductal Carcinoma This occurs when cancer cells within the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma carries a better prognosis than more common types of IDCs.
- Papillary;Carcinoma ;This is a very good prognosis breast cancer that primarily occur in women over the age of 60.
- Tubular Ductal Carcinoma ;This is a rare diagnosis of IDC, making up only two percent of diagnoses of breast cancer. The name comes from how the cancer looks under the microscope; like hundreds of tiny tubes.; Tubular breast cancer has an excellent prognosis.
Show me more…
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Basal Cell Carcinoma
How Is Prognosis Estimated
Prognosis is estimated by looking at what has happened over many years to large groups of people diagnosed with a similar cancer. However, everyones situation is different so no one can say for certain what will happen to you. Also, treatments and survival rates are constantly improving, which affects the accuracy of estimates for people being treated today.
Prognosis is described in different ways. It may be put into words or numbers. Its often expressed as a five- or ten-year survival rate. This is an estimate of how many people are likely to be alive five or ten years following their diagnosis.;
A 90% five-year survival rate means that 90 out of 100 people diagnosed with breast cancer are likely to be alive five years after their diagnosis. It doesnt mean these people will only live for five years; it just states how many people are likely to be alive at that point.
Cancer Research UK has general statistics on five- and ten-year breast cancer survival rates on;their website. Remember, these statistics are based on large groups of patients and cannot predict what will happen in your individual case.
Some Cases Of Dcis Will Progress Towards Invasive Breast Cancer If Left Untreated
There is a general consensus that DCIS may represent a transitional stage between the normal breast tissue and invasive breast carcinoma.
However, it is still largely unknown which types of DCIS are non-progressing towards invasive breast cancer if left untreated.
One recent study estimated that only between 100 to 270 cases of DCIS per 100000 will not progress to invasive breast cancer if left untreated.
A medical study from the United Kingdom examined 84 breast cancer screening units. This large research study looked at DCIS diagnoses between the years of 2003 and 2007 for women aged 50 to 64 years.
Data from over 5,243,658 was analyzed. The average frequency of DCIS detected was 1.60 per 1000 women. The study found that for every 3 cases of DCIS detected on screening there was one less case of invasive cancer in the next 3 years.
Don’t Miss: What Does Skin Cancer On Your Lip Look Like
Data Acquisition And Patient Selection
We used the SEER dataset that was released in April 2015, which included data from 18 population-based registries and covered approximately 28% of U.S. cancer patients. Data for tumour location, grade and histology were recorded according to the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology Version 3 . The inclusion criteria used to identify eligible patients were the following: females aged between 18 and 79, unilateral breast cancer, breast cancer as the first and only cancer diagnosis, diagnosis not obtained from a death certificate or autopsy, only one primary site, pathological confirmation of infiltrating ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified and papillary carcinoma with invasion , surgical treatment with either mastectomy, breast-conserving surgery or unknown type, known ER and PR statuses, American Joint Committee on Cancer stages IIII and known time of diagnosis from January 1, 2003 to December 31, 2012. Patients diagnosed with breast cancer before 2003 were excluded because the World Health Organization did not recognize IPC as a distinct pathological entity until 2003. In addition, patients who were diagnosed with breast cancer after 2012 were not included because the database was only updated up to December 31, 2012 and we wanted to ensure adequate follow-up time. A total of 233,171 patients were included. Of these patients, 524 were diagnosed with IPC and 232,647 were diagnosed with IDC.