Adjuvant And Neoadjuvant Therapy
Adjuvant therapy, which refers to therapy given after a primary surgery, has not been found to be beneficial in renal cell cancer. Conversely, neoadjuvant therapy is administered before the intended primary or main treatment. In some cases neoadjuvant therapy has been shown to decrease the size and stage of the RCC to then allow it to be surgically removed. This is a new form of treatment and the effectiveness of this approach is still being assessed in clinical trials.
Renal Cell Carcinoma Tissues
All formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded renal tumors were from the archive of the Institute for Surgical Pathology, Zurich University Hospital, and were reviewed by one pathologist . A total of 20 ccRCCs and 9 pRCCs were selected for this study and diagnosed according to the 2004 WHO classification.Dominant architectural patterns were recorded for all ccRCCs. In total, 8 cases were dominantly solid/nested, 10 alveolar/acinar, and 2 tumors were mixed solid, alveolar, and papillary. This study was approved by the local commission of ethics .
What Causes Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer is caused when DNA in cells in one or both kidneys mutate, which may lead to uncontrolled cell division and growth. While the exact cause of a persons kidney cancer may not be known, certain risk factors are strongly linked to the disease, including smoking tobacco and obesity. Also, people with certain hereditary cancer syndromes or a family history of kidney cancer have a high risk of developing the disease.
Known risk factors for kidney cancer include:
Recommended Reading: Where Does Skin Cancer Metastasis To
How Renal Cell Carcinoma Spreads
Renal cell carcinoma can spread from the kidney to other areas of the body. It can enlarge within the kidney and grow into the adrenal glands, which are adjacent to the kidneys. Adrenal glands are small organs that make and release hormones. Each kidney has one adrenal gland located right above it.
Cancer cells can also enter into the bloodstream or the lymphatic vessels, spreading to other areas of the body. The cancer can then grow in other organs, such as the lungs, bones, or brain, causing serious harm to these areas.
Evaluation Of Metastatic Disease

Renal cell carcinomas are adenocarcinomas that usually arise from the epithelial cells of the proximal convoluted tubule.
| Overview of the most important types of renal cell carcinoma | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Non-clear cell renal cell carcinomas | |||
| Collecting duct carcinoma | ||||
| Relative frequency | ||||
|
||||
| Microscopic appearance |
|
|
|
|
| Prognosis |
|
|
Rule of 3: A mutation in the VHL gene on chromosome 3 causes RCC .
You May Like: What Causes Small Cell Carcinoma
How Common Is Kidney Cancer
Each year an estimated 75,000 patients are found with a kidney tumor. Approximately 65,000 of these are ultimately found to be renal cell carcinoma .
The most common type is clear cell carcinoma. Renal cell cancer is not one disease but rather a collection of 15-20 types of renal tumors that can arise from the kidney. Kidney cancer is among the 10 most common cancers in both men and women, and the risk for developing kidney cancer is higher in men than in women. More information about kidney cancer risk factors >
What Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
It’s the most common type of kidney cancer. Although itâs a serious disease, finding and treating it early makes it more likely that youâll be cured. No matter when youâre diagnosed, you can do certain things to ease your symptoms and feel better during your treatment.
Most people who have renal cell carcinoma are older, usually between ages 50 and 70. It often starts as just one tumor in a kidney, but sometimes it begins as several tumors, or itâs found in both kidneys at once. You might also hear it called renal cell cancer.
Doctors have different ways to treat renal cell carcinoma, and scientists are testing new ones, too. Youâll want to learn as much about your disease as you can and work with your doctor so you can choose the best treatment.
Also Check: How Long Before Melanoma Is Deadly
Met And Egfr Inhibitors
In addition to VEGF-TKI data on MET inhibition with tivantinib in comparison to a combination of tivantinib with the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib were recently published . Although an earlier study with erlotinib as monotherapy indicated promising results with an ORR of 11%, the more recent study was stopped permanently after the interim analysis due to a lack of efficacy in both treatment arms. So far, the use of MET inhibitors or erlotinib is not recommended outside clinical trials.
Other Types Of Kidney Cancer
Other less-common types of kidney cancers include:
-
Transitional cell carcinoma. This is also known as urothelial carcinoma. It starts where the ureter and kidney meet. This area is called the renal pelvis. This type of kidney cancer can act and look like bladder cancer.
-
Wilms tumor. This cancer most always occurs in children. It’s very rare in adults.
-
Renal sarcoma. This is a very rare type of kidney cancer. It begins in the blood vessels and connective tissue around the kidneys.
Recommended Reading: How Does Skin Cancer Work
What Is The Prognosis For People With Ccrcc
The estimate of how a disease will affect you long-term is called prognosis. Every person is different and prognosis will depend on many factors, such as
- Where the tumor is in your body
- If the cancer has spread to other parts of your body
- How much of the tumor was taken out during surgery
If you want information on your prognosis, it is important to talk to your doctor. NCI also has resources to help you understand cancer prognosis.
Doctors estimate ccRCC survival rates by how groups of people with ccRCC have done in the past. Because there are so few pediatric ccRCC patients, these rates may not be very accurate. They also dont take into account newer treatments being developed.
With this in mind, ccRCC patients with smaller tumors have a better chance of survival than patients with larger tumors. The 5-year survival rate for patients with ccRCC is 50-69%. When ccRCC is already large or has spread to other parts of the body, treatment is more difficult and the 5-year survival rate is about 10%.
Related Resources
What Are The Types Of Kidney Cancer
Renal Cell Carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer, accounting for approximately 85% of all malignant kidney tumors. In RCC, cancerous cells develop in the lining of the kidney tubules and grow into a mass called a tumor. Like many other cancers, the growth begins small and grows larger over time. RCC typically grows as a single mass. However, there are cases where a kidney may contain more than one tumor, or tumors are found in both kidneys at the same time.
Also Check: How To Get Tested For Skin Cancer
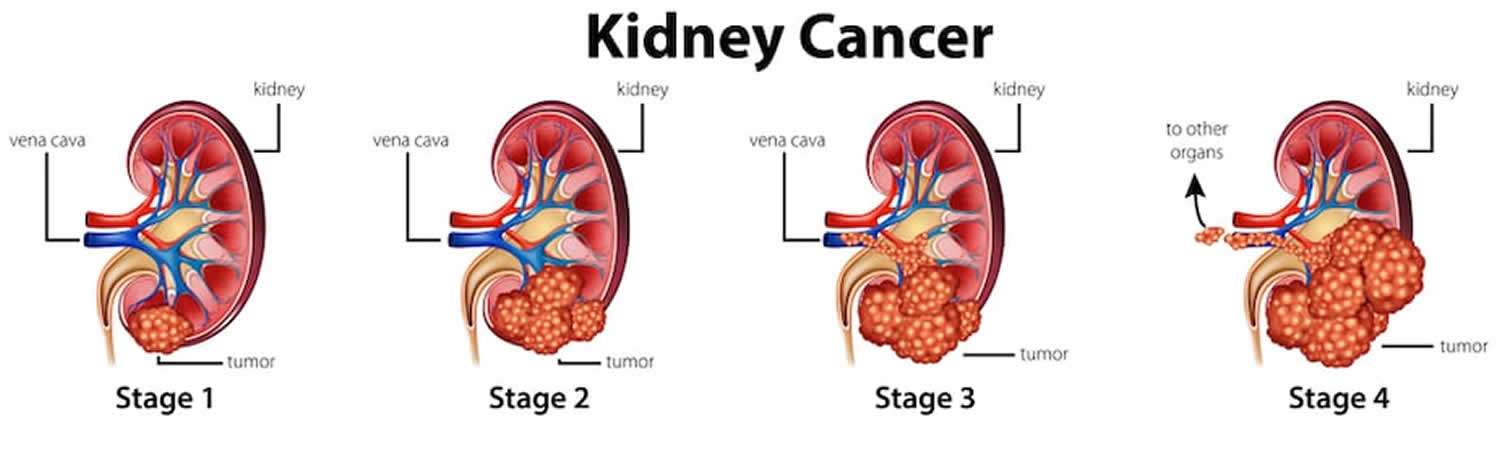
What Are The Stages Of Rcc
Doctors use staging to determine if cancer has spread beyond the kidneys. RCC may spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body through tissue, the lymph system, or the blood. Doctors determine cancer stage based on tumor size and whether the cancer has spread beyond the kidneys and to other organs.
RCC is staged from I to IV. Stage I means cancer is only in the kidney, and stage IV indicates it has spread to other organs and lymph nodes.
Renal Cell Carcinoma Tumor Stages
- Stage 1: The tumor is only in the kidney and it is smaller than 7 centimeters in size.
- Stage 2: The tumor is only in the kidney and it is larger than 7 cm in size.
- Stage 3: The tumor has spread beyond the kidney to adjacent areas, such as the adrenal gland.
- Stage 4: the tumor has spread beyond the kidney and adjacent structures to at least one other area of the body.
You May Like: Can You Get Rid Of Skin Cancer
The Role Of Lipid Droplets In Ccrcc
As the most significant pathological feature of ccRCC, the existence of lipid droplet accumulation not only reveals the abnormal lipid metabolism of ccRCC, but also indicates some death pathways of ccRCC cells. It has been pointed out that lipid droplets in ccRCC cells can be used as bioenergy fuel and raw materials for cell membrane generation, and can also be involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress . Therefore, we are very interested in the formation and role of lipid droplet itself.
Fatty acids are substrates for the synthesis of various lipid types. Diacylglycerol acyltransferase catalyzes diacylglycerol to synthesize triacylglycerol with FAs and plays an important role in lipid synthesis . DGAT1 and DGAT2, two genes encoding DGAT, have been identified, and their main functions have been recognized in the past ten years. Researchers have used molecular tools to study the metabolic changes in mice lacking these two enzymes, revealing the function of DGAT1/2 . Currently, DGAT1/2 is known to play a positive regulatory role in many cancers related to lipid accumulation . Inhibitors targeting DGAT activity have also made significant progress . Related studies have tentatively confirmed the important role of DGAT in cancer, and we hope that more relevant studies can describe the detailed mechanism of DGAT in ccRCC, including other types of RCC.
Symptoms Of Renal Cell Carcinoma
cases of kidney cancer. RCC usually manifests as one tumor, but it may include two tumors. If there are two, they can both be in the same kidney or there can be one tumor in each.
Risk factors for this type of cancer include:
- a family history of RCC
- some hereditary kidney diseases, such as polycystic kidney disease
- smoking
- obesity
Surgical treatment for RCC is often recommended, depending on what stage the cancer is at. The survival rate is fairly high if the cancer is caught early, with a five-year survival rate of
Recommended Reading: Can Skin Cancer Be Inherited
How To Manage Your Symptoms
Palliative care can relieve symptoms like pain, fatigue, and nausea. This treatment won’t cure your cancer, but it can help you feel better. You can still get your other cancer treatments while you’re getting palliative care.
Palliative care can include:
- Pain relievers and other medicines
- Relaxation techniques
How Is Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated
Based on the type and stage of RCC, your doctor will recommend a treatment plan. The plan may include one or more of the following approaches:
-
Surgery: This is the most common treatment for kidney cancer. Surgery can often cure early-stage RCC.
-
Radiation therapy: Also called radiotherapy, this treatment uses beams of intense energy to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
-
Thermal ablation: Your doctor inserts a needle into the tumor and applies heat to kill cancer cells.
-
Cryosurgery: Cold liquid nitrogen is delivered directly to the tumor through a needle kill cancer cells
-
Immunotherapy: Leading-edge immunotherapy drugs prompt your own immune system to fight the cancer.
-
Targeted therapy: Thesemedications attack specific parts of cancer cells to stop them from growing and multiplying.
-
Chemotherapy: Oral or intravenous medications stop cancer cells from growing.
Recommended Reading: How Can Skin Cancer Kill You
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Renal cell carcinoma arises from the renal cortex or the renal tubular epithelial cells. Overall, the incidence has been steadily increasing, and currently, it is the seventh most common cancer among men. Among the genitourinary cancers, RCC has the highest mortality rate. The prognosis of metastatic ccRCC is poor, with a median survival of about 13 months and 5-year survival under 10%. However, with newer therapies, overall survival has improved. Usually, the patients are asymptomatic until the malignancy has advanced, which is the biggest challenge for early diagnosis. The classic symptoms include flank pain, hematuria, and palpable renal mass is seen in only 9% of the cases. Higher rates of diagnosis of RCC are due to an incidental diagnosis. The treatment involves an interprofessional team consisting of a urologist, medical oncologist, nephrologist, and a genetic counselor. Patients with a family history should be educated about the possibility of acquiring cancer.
Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Papillary RCC is the second most common form of kidney cancer and makes up about 15% of all cases. Papillary RCC is a non-clear cell renal carcinoma which is different from the more common clear cell type. There are two main types of papillary RCC: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 tumors tend to be slower growing, and type 2 tumors tend to be faster growing and are more likely to spread. Papillary RCC can be The passing of genetic information from parent to child through parental genes.hereditaryor non-hereditary.
Read Also: How Do You Die From Melanoma
Rcc In End Stage Renal Disease Patients
The benefit of early detection of RCC in ESRD would be that the RCC would be less likely metastatic and hence ultimately fatal. ESRD patients are not routinely scanned for RCC unless there are other issues. Transplantation also carries an increased risk for kidney cancer this is estimated to be 15-fold over the first three years following transplantation, and this risk increases with extent of exposure to immunosuppressive agents . The prevalence of RCC in native kidneys after transplantation is around 5% overall but 19% in ACKD patients or 54% in patients with complex cysts . The life expectancy of a transplant recipient has improved and cancer may soon be the leading cause of death late after transplantation. A marker of aggressiveness of RCC developing after transplantation could also aid in establishing priority for transplantation.
Rare Non Clear Cell Rcc Subtypes
- Collecting duct carcinoma: A very rare and aggressive type of RCC. At initial diagnosis, it is usually metastatic and has spread to other parts of the body. It is more common in younger people.
- Translocation RCC: A rare type of kidney cancer. This cancer can be identified by seeing mutations, or changes, in a gene called TFE3. This type affects children and young adults but can also affect older adults.
- Renal medullary carcinoma : This is a very rare type of kidney cancer. It affects young people who carry the sickle cell trait or have sickle cell disease. These cancers are usually metastaticspread to other parts of the bodyat diagnosis.
- Unclassified RCC: Less than 1% of RCCs are unclassified. They are very rare and do not easily fit into one of the more common subtypes. They tend to be more aggressive.
Also Check: What Color Is Skin Cancer Ribbon
Overview Of Origin Cell Type Stage And Grade
Human RCCs are thought to arise from a variety of specialized cells located along the length of the nephron. RCC is comprised of several histological cell types. Both clear cell and papillary RCC are thought to arise from the epithelium of the proximal tubule. Chromophobe RCC, oncocytoma, and collecting duct RCC are believed to arise from the distal nephron, probably from the epithelium of the collecting tubule. Each type has differences in genetics, biology and behavior. The most common histological type is clear cell carcinoma, also called conventional RCC, which represents 7580% of RCC. Papillary , chromophobe and other more rare forms such as collecting duct carcinoma comprise the remainder. Oncocytomas represent 37% of renal masses but are invariably benign and their exclusion from classification as RCC has been recommended . Distinct tumors of different cell types can occasionally be seen in the same kidney. An individual tumor can have mixed histologies. The pathologist differentiates cell types routinely by morphology and immunohistochemical markers as well as by cytogenetic and molecular genetic analysis particularly when the cell type is equivocal. Three to five per cent of RCC cannot be classified and are termed RCC, unclassified. Sarcomatoid RCC is no longer considered as a true subtype since sarcomatoid change represents undifferentiated cells associated with progression of disease in all RCC cell types .
Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma
Chromophobe RCC is a rare form of kidney cancer that makes up approximately 5% of all cases. It is a non-clear cell renal carcinoma that starts in the cells that line the tubes in the kidney that help filter waste from blood. Chromophobe RCC can be The passing of genetic information from parent to child through parental genes.hereditary or non-hereditary.
Also Check: Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Kill You
How Is Ccrcc Treated
Treatments for people with ccRCC include surgery and immunotherapy. Treatment will depend on how much the cancer has grown.
Surgery: Once ccRCC is diagnosed, you may have surgery to remove the cancer and part of the kidney surrounding it. In early stage ccRCC, part of the kidney with the cancer is taken out. If ccRCC is in the middle of the kidney, or if the tumor is large, sometimes the entire kidney must be removed. In later stage ccRCC, removal of the kidney is controversial but may be appropriate in some patients.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy helps the bodys immune system fight the cancer cells.
Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy targets the changes in cancer cells that help them grow, divide, and spread. Some targeted therapies that are used to treat clear cell renal carcinoma include cabozantinib, axitinib, sunitinib, sorafenib, and pazopanib.
Other treatments can be used that do not involve removing the kidney, such as:
- Radiation therapy, which uses radiation to kill the tumor cells
- Thermal ablation, which uses heat to kill the tumor cells
- Crysosurgery, which uses liquid nitrogen to freeze and kill the tumor cells