Can You Die From Skin Cancer If Youre Diagnosed With Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer. It is classified as a non-melanoma form of the condition, and accounts for about 75 percent of all skin cancer cases. It almost never spreads beyond the original tumor site, but can do serious damage there if not treated. Mohs surgery is considered the most effective treatment technique.
Limiting sun exposure is the single most important measure for prevention of any kind of skin cancer, including BCC. The risk when outside can further by reduced by using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 to 50, wearing pants, long skirts, long-sleeved shirts, and wide-brimmed hats that provide adequate protection.
Melanoma Skin Cancer Mortality By Age
Melanoma skin cancer mortality is strongly related to age, with the highest mortality rates being in older people. In the UK in 2016-2018, on average each year almost half of deaths were in people aged 75 and over. This largely reflects higher incidence and lower survival for melanoma skin cancer in older people.
Age-specific mortality rates rise steeply from around age 55-59. The highest rates are in the 90+ age group for females and males. Mortality rates are significantly lower in females than males in a number of age groups.The gap is widest at age 90+, when the age-specific mortality rate is 2 times lower in females than males.
Melanoma Skin Cancer , Average Number of Deaths per Year and Age-Specific Mortality Rates per 100,000 Population, UK, 2016-2018
You May Like: What Is Braf Testing In Melanoma
Uv Exposure And Overexposure
UV exposure stimulates melanocytes to produce melanin, often resulting in a tan or sunburn, both of which indicate overexposure and damage to the skin, skin cells, and DNA within those skin cells., The underlying biology of skin cancer risk is directly related to damage to the skin and its genetic material. Although all UV exposures can affect skin cancer risk, entirely avoiding UV rays from the sun is neither realistic nor advisable for most Americans. Spending time outdoors is associated with positive health benefits, such as increased levels of physical activity and improved mental health.-
Read Also: How To Treat Melanoma Skin Cancer
Don’t Let Skin Cancer Sneak Up On You
Do you know how to spot skin cancer? In this video, the American Academy of Dermatology used an ultraviolet camera to show people the sun damage hidden underneath their skin. While you cant see all the sun damage on your skin, its important to check the spots you can see before its too late.
Can you spot skin cancer?
Anyone can get skin cancer, regardless of skin color. It is estimated that one in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. When caught early, skin cancer is highly treatable.
Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma

The most common sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new;mole or a change in an existing mole.
This can happen anywhere on the body, but the;most commonly affected areas are;the back in men and the legs in women.;
Melanomas are uncommon in areas that are protected from sun exposure, such as the buttocks and the scalp.
In most cases, melanomas have an irregular shape and are more than 1 colour.
The mole may also be larger than normal and can sometimes be itchy or bleed.
Look out for a mole that gradually changes shape, size or colour.
Superficial spreading melanoma are the most common type of melanoma in the UK.
They’re more common in people with pale skin and freckles, and much less common in people with darker skin.
They initially tend to grow outwards rather than downwards, so they do not pose a problem.
But if they grow downwards into the deeper layers of skin, they can spread to other parts of the body.
You should see a GP if you have a mole that’s getting bigger, particularly if it has an irregular edge.
You May Like: What Does Skin Carcinoma Look Like
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of cancer, but also the least likely to spread. In particular, BCCs rarely spread beyond the initial tumor site. However, left untreated, BCCs can grow deeper into the skin and damage surrounding skin, tissue, and bone. Occasionally, a BCC can become aggressive, spreading to other parts of the body and even becoming life threatening. Also, the longer you wait to have your BCC treated, the more likely it is to return after treatment. Like BCCs, SCCs are highly curable when caught and treated early. However, if left to develop without treatment, an SCC can become invasive to skin and tissue beyond the original skin cancer site, causing disfigurement and even death. Over 15,000 Americans die each year from SCCs. And even if untreated carcinomas dont result in death, they can lead to large, open lesions on the skin that can cause discomfort, embarrassment, and infection.
A Rapidly Changing Treatment Landscape
Starting in 2011, two new types of drugs started to change the treatment landscape for metastatic melanoma.
One was a group of targeted therapies called BRAF inhibitors and MEK inhibitors. The BRAF and MEK proteins are both part of a cell signaling pathway that commonly drives the growth of melanoma. The other was a type of immunotherapy called immune checkpoint inhibitors, which encourage the bodys own immune system to attack cancer cells.
In 2011, the Food and Drug Administration approved the immune checkpoint inhibitor ipilimumab , the first drug to improve how long people with metastatic melanoma lived.
And in a very short amount of time since then, more than 10 drugs have been approved , which have now been shown to improve overall survival in a very meaningful way, said Dr. Olszanski.
Both BRAF and MEK inhibitors, which are typically used in combination, and immunotherapies can cause dramatic and sometimes long-lasting tumor responses in some people with advanced melanoma. However, the overall impact of these drugs on survival in people with melanoma was not clear.
Because more than 90% of melanomas occur in white men and women, the researchers only had enough data to analyze these groups.
But from 2013 to 2016, the trends in mortality reversed. Overall, the melanoma mortality rate declined by 17.9% during the 4-year period. The reduction in deaths was seen in nearly every age group, but was greatest in men aged 50 and older.
Don’t Miss: What Is Grade 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Dietary Sources Of Vitamin D
The best natural sources of vitamin D in the diet include fatty fish and fish liver oils. Small amounts of vitamin D are also found in egg yolks, beef liver, some mushrooms, ricotta cheese, and some cuts of pork. Vitamin D-fortified foods and beverages provide most of the vitamin D in the U.S. diet. Almost all of the milk in the United States is fortified with vitamin D, and many of the ready-to-eat breakfast cereals provide a small amount of added vitamin D. In addition, specific brands of soy beverages, orange juice, yogurt, margarine, and other foods are also fortified with vitamin D.
Medical Uses of UV Exposure
Dermatologists and other doctors sometimes use UV light to treat health conditions, such as psoriasis, rickets, and eczema. These providers are advised to carefully weigh the risks and benefits of UV treatment for individual patients and carefully monitor doses.,-
Benefits of Being Outdoors
Risks of Indoor Tanning Outweigh Any Potential Benefits
Low levels of sunlight in the winter months may contribute to seasonal affective disorder , and as a result, some indoor tanners may attempt to self-treat SAD with UV exposure through indoor tanning., Medical treatment of SAD frequently incorporates light treatment, but UV wavelengths are not generally recommended .,, In addition, light is thought to affect SAD through the retina, not the skin.
Leaving Squamous Cell Carcinoma Untreated
The third type of skin cancer we have to be cautious of in Australia is squamous cell carcinoma. This is potentially life threatening and is most dangerous when found on the face, lips, ears or neck. As it grows, there is the chance it may spread to the lymph nodes and internal organs, and while it isnt as fast growing as melanoma, it still requires treatment.
You may notice squamous cell carcinoma in the top layer of your skin and it will likely be red and scaly. Surgery is often used for removal, but if it has progressed significantly some reconstruction to the face may be needed. This is the second most common form of skin cancer, and can be quite painful to touch.
All skin cancer has the potential to be fatal, and regular checks and any necessary treatment is recommended. Melanoma is by far the most serious form of skin cancer, and if suspected you should seek an urgent skin check. Please contact My Skin Centre to book your appointment in the Perth region.
Don’t Miss: What Is Melanoma In The Brain
Stages Of Skin Cancer
If you receive a skin cancer diagnosis, the next step is to identify its stage.
Staging is how doctors determine whether the cancer has spread to other parts of your body. Staging is common with melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma, because these cancers are more likely to spread.
Typically, basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas dont involve staging. These skin cancers are easily treated and dont usually spread. However, your doctor may recommend staging for larger lesions.
Staging is based on the size of the growth and whether it has high-risk features. High-risk features include:
- larger than 2 millimeters thick
- spreads into the lower levels of the skin
- spreads into the space around a nerve
- appears on the lips or ears
- appears abnormal under a microscope
Heres a general breakdown of skin cancer stages:
- Stage 0. The cancer hasnt spread to surrounding areas of the skin.
- Stage 1. The cancer is 2 centimeters across or less, with no high-risk features.
- Stage 2. The cancer is more than 2 cm across and has a least two high-risk features.
- Stage 3. The cancer has spread to the bones in the face or nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 4. The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or internal organs.
Why Not To Leave Skin Cancer Untreated
Skin cancer has two sides. On the one hand, it is fairly easy to detect and treat when done so at an early stage. On the other hand, when left untreated, skin cancer can cause disfigurement and even death. This is the dark side of skin cancer. Find out the sobering consequences of allowing skin cancer to develop into later stages.
Also Check: How To Know You Have Skin Cancer
Leaving Basal Cell Carcinoma Untreated
Basal cell carcinoma is a slow growing cancer, but this doesnt mean it can be ignored. This is the least dangerous form of skin cancer and rarely spreads to other internal parts of the body. While death is a rare consequence there is the potential for disfigurement. Over time basal cell carcinoma can expand and cause ulcers and damage the skin and tissues.
Any damage could be permanent and have an impact on the way you look. Depending on how long the basal cell carcinoma has been present, radiotherapy may be required. This is the most common form of skin cancer and is often found on the face. You may notice a small lump which is shiny or pearl like and this is a sign you should get checked. This type of cancer generally does not cause any pain.
Exams And Tests For Skin Cancer
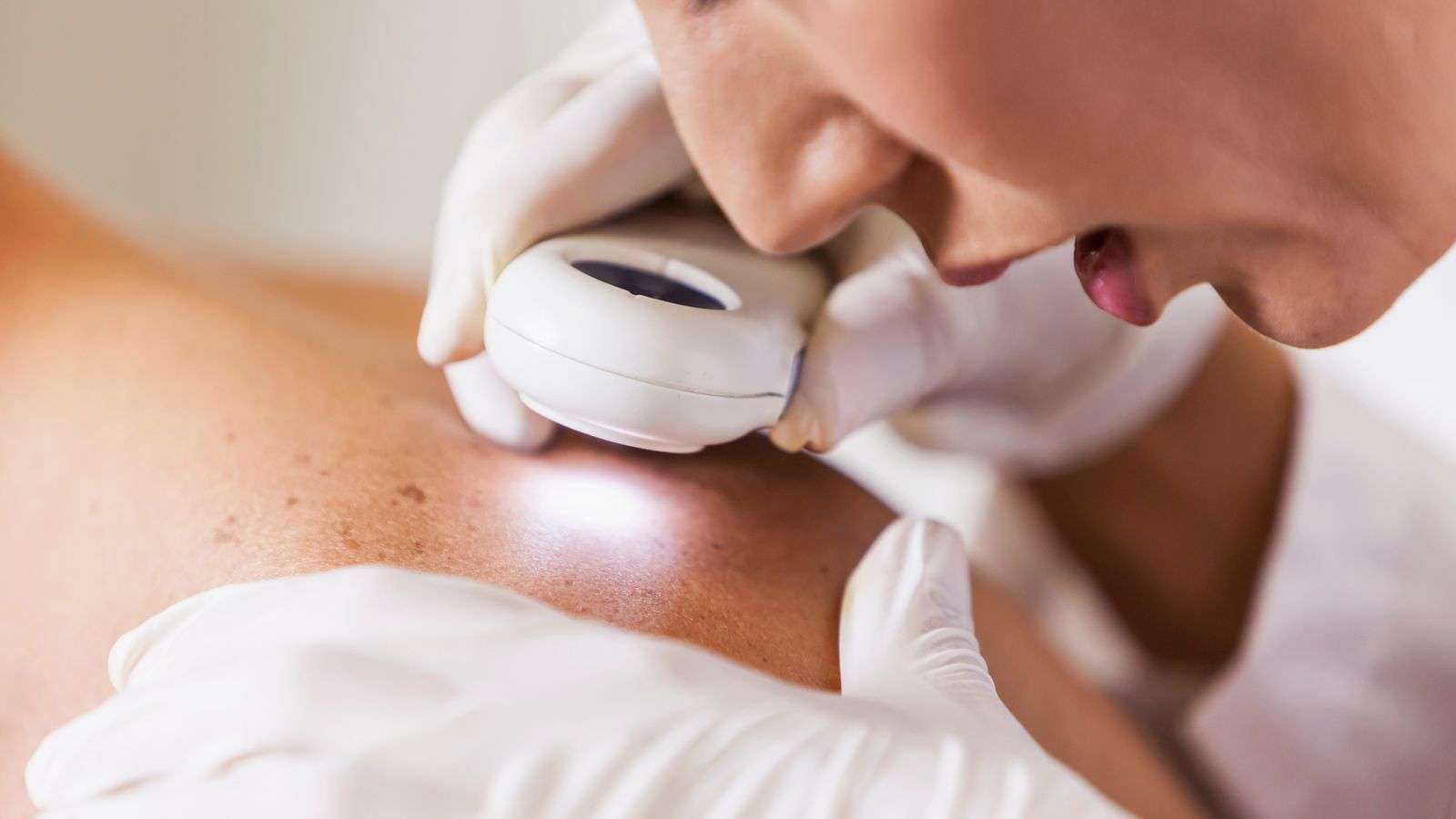
If you think a mole or other skin lesion has turned into skin cancer, your primary care provider will probably refer you to a dermatologist. The dermatologist will examine any moles in question and, in many cases, the entire skin surface. Any lesions that are difficult to identify, or are thought to be skin cancer, may then be checked. Tests for skin cancer may include:
- The doctor may use a handheld device called a dermatoscope to scan the lesion. Another handheld device, MelaFind, scans the lesion then a computer program evaluates images of the lesion to indicate if it’s cancerous.
- A sample of skin will be taken so that the suspicious area of skin can be examined under a microscope.
- A biopsy is;done in the dermatologist’s office.
If a biopsy shows that you have malignant melanoma, you may undergo further testing to determine the extent of spread of the disease, if any. This may involve blood tests, a chest X-ray, and other tests as needed. This is only needed if the melanoma is of a certain size.
Continued
Also Check: What Does Early Squamous Skin Cancer Look Like
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Medical Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of skin cancer treatment for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more information, see Surgery.People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the use of a small beam of radiation targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy can cause irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It can also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, topical chemotherapy creams have been FDA approved for the treatment of certain low-risk nonmelanoma skin cancers. Patients with advanced or many basal cell carcinomas are sometimes prescribed oral pills to block the growth of these cancers. Side effects include muscle spasms, hair loss, taste changes, weight loss and fatigue.
In advanced cases of melanoma, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work better than existing therapies.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize
Skin Cancer Undiagnosed For Over 10 Years
The patient had neglected his illness for more than 10 years, says a case report in the International Open Access Journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons .
The patient was a man, 48, living in a U.S. city. The medical attention was sought out due to the insistence of a family member, continues the paper.
The cancer was basal cell carcinoma that had grown to 10 centimeters on his scalp. Somehow this patient didnt mind living with an ulcerating, oozing and bleeding growth on his head.
Had he not sought treatment, he could have lived many more years barring death from an unrelated cause such as a heart attack or car accident.
With that all said, there is no data on what the record is for how long a person lived with an undiagnosed skin cancer.
Certainly you can imagine there must be many cases of people all over the world, living in undeveloped societies with scant medical care, let alone skin cancer awareness, whove been living for over 20 years with a slowly growing bump or patch.
This would describe basal cell carcinoma.
But a person will not get away for too long with an undiagnosed melanoma, as it WILL spread and cause symptoms of that spread, such as respiratory problems or ongoing severe headaches .
Dr. Musick says that the following are common ways that skin cancer shows up:
red bump that bleeds easily a scab or wound that just wont heal slowly enlarging pink or red patch of skin a dark irregularly-bordered bump or spot
Steven Musick, MD
.
How Do You Treat Skin Cancer On The Scalp
The methods for treating skin cancer on the scalp vary depending on the type of cancer. The earlier it is, the better.
The most common form of treatment for basal cell and squamous cell cancers, as well as some types of melanoma, is minor surgery to cut out the cancerous portion of skin. NextGen OMS offers comprehensive head and neck surgery options, which are ideal for removing many types of early-stage skin cancer on the head.
This is why the five-year survival rate for many types of skin cancer is so high when theyre treated early. When it reoccurs, its usually because it went through metastasis before removal, in which case youll need further treatment.
If surgery is not available as an option, your doctor may suggest radiation therapy instead. This isnt used very often on the scalp because surgery is almost always possible for skin cancer on head and scalp areas, but doctors occasionally use it for skin cancer on nearby regions like the nose and ears.
Also Check: How Dangerous Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Also Check: What Are The Risk Factors Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Rare Skin Cancer On The Rise
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare type of skin cancer that affects about 2,000 people in the United States each year.
Though its an uncommon skin cancer, cases of Merkel cell carcinoma have increased rapidly in the last couple of decades.
This type of cancer starts when cells in the skin, called Merkel cells, start to grow out of control.
Merkel cell carcinomas typically grow quickly and can be difficult to treat if they spread.
They can start anywhere on the body, but Merkel cell carcinomas commonly affect areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and arms.
They may look like pink, red, or purple lumps that are firm when you touch them. Sometimes, they can open up as ulcers or sores.
Risk factors include: