What Causes Squamous Cell Carcinoma
95% of Squamous Cell Carcinomas in Australia are the result from skin damage caused by
- Cumulative long-term sun exposure
- Intermittent overexposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun
Most Squamous Cell Carcinomas occur on parts of the body exposed to the sun especially the face, ears, neck, bald scalp, shoulders, and back, but many can be found in areas that are only burned or exposed occasionally such as the abdomen or upper thighs
It is not possible to pinpoint a precise, single cause for a specific tumour, especially tumours found on a sun-protected area of the body or in an extremely young individual. Some Squamous Cell Carcinoma can also result from less common causes such as:
- contact with arsenic,
- exposure to ionising radiation such as X-rays
- open sores that resist healing,
- chronic inflammatory skin conditions, and
- as complications of burns and scars.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
According to the Moffitt Cancer Center, squamous cell carcinoma is classified into stages from 0-4 according to how far it has spread throughout the body. Stage 0 means it hasnt spread beyond the top layer of skin. Stage 1 squamous cell has spread deeper into the skin but has not spread into healthy tissue or lymph nodes. Stage 2 squamous cells have grown deeper into the skin and have spread to additional skin layers or nerves. Stage 3 means that the cancer has spread to lymph nodes, and Stage 4 squamous cell has spread to at least one organ, such as a separate area of the skin, the lungs, or the brain.
How Fast Does Oral Cancer Spread
About one half of people with oral cancer will live more than 5 years after they are diagnosed and treated.
If the cancer is found early, before it has spread to other tissues, the cure rate is nearly 90%.
More than half of oral cancers have spread when the cancer is detected.
Most have spread to the throat or neck.17 Oct 2017
Don’t Miss: Can Renal Cell Carcinoma Be Benign
Conditions Related To Keratoacanthoma
These conditions are extremely rare, but they can cause multiple keratoacanthomas to grow on your skin. There can be so many that doctors canât remove them all with surgery.
Ferguson-Smith. This can cause as many as 100 keratoacanthomas at one time. Itâs the most common type of multiple keratoacanthoma. Itâs a condition you can get through your genes and may start as early as age 8.
You may take retinoid medicine to try to reduce the number of additional tumors.
Grzybowski syndrome is even more rare. It causes tumors that are smaller but itch intensely. They may even show up in the mouth.
Journal of Investigative Dermatology: âAre Keratoacanthomas Variants of Squamous Cell Carcinomas? A Comparison of Chromosomal Aberrations by Comparative Genomic Hybridization.â
Medscape: âKeratoacanthoma.â
Cleveland Clinic Center for Continuing Education: âNonmelanoma Skin Cancer.â
James Spencer, MD, dermatologist in private practice in St. Petersburg, FL, and clinical professor of dermatology at Mount Sinai School of Medicine.
Skin Cancer Foundation: âSquamous Cell Carcinoma.â
American Academy of Dermatology: âSquamous Cell Carcinoma.â
DermNet New Zealand: âKeratoacanthoma,â âMultiple Self-Healing Squamous Epitheliomas of Ferguson-Smith,â âGrzybowski Generalized Eruptive Keratoacanthomas.â
Ronald Davis, MD, dermatologist in private practice adjunct professor of dermatology, University of Texas Medical School San Antonio.
Recommended Reading: How Severe Is Skin Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
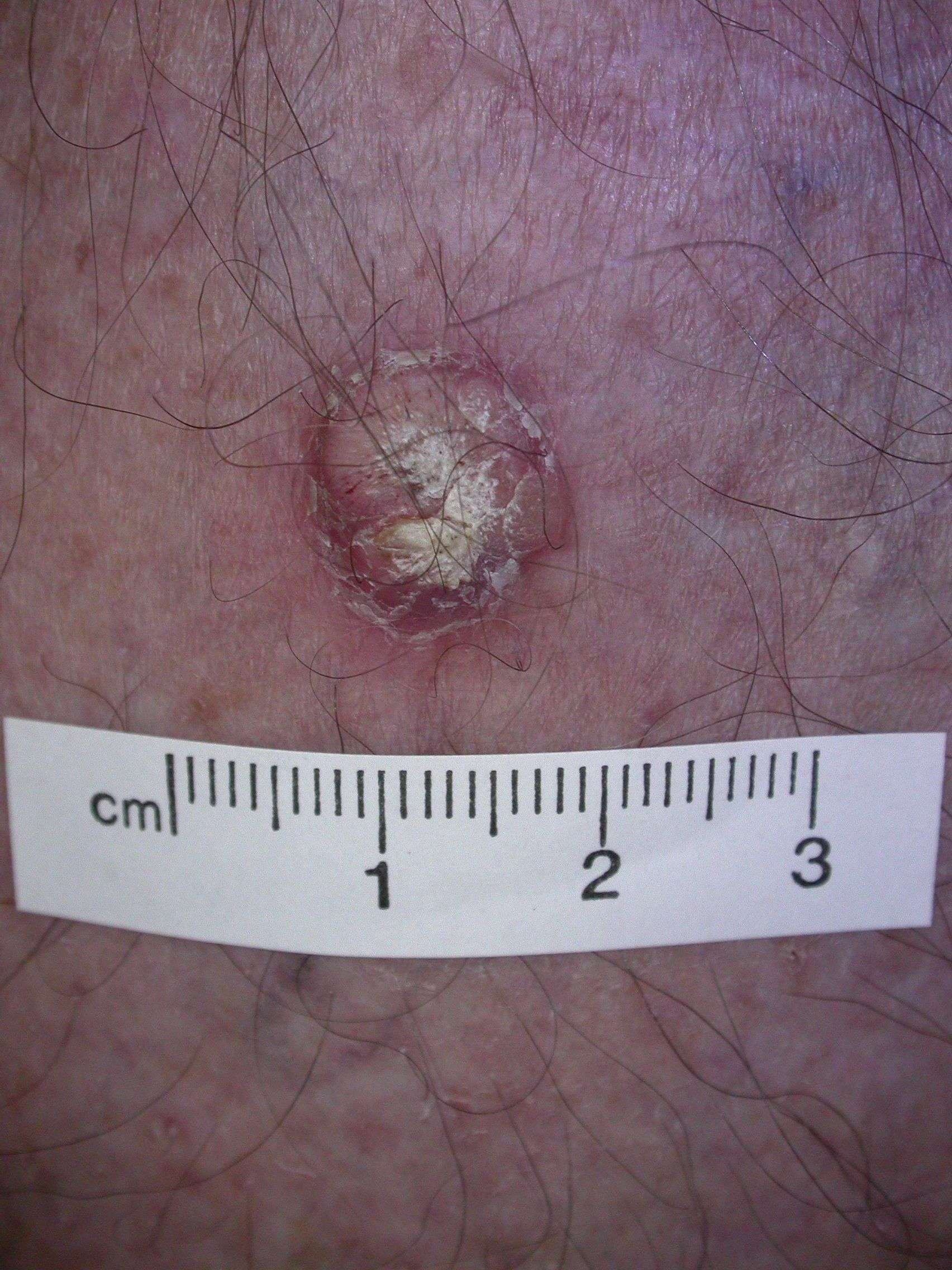
Certain things make you more likely to develop SCC:
- Older age
- Blue, green, or gray eyes
- Blonde or red hair
- Spend time outside, exposed to the sun’s UV Rays
- History of sunburns, precancerous spots on your skin, or skin cancer
- Tanning beds and bulbs
- Long-term exposure to chemicals such as arsenic in the water
- Bowens disease, HPV, HIV, or AIDS
Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist who specializes in skin conditions. They will:
- Ask about your medical history
- Ask about your history of severe sunburns or indoor tanning
- Ask if you have any pain or other symptoms
- Ask when the spot first appeared
- Give you a physical exam to check the size, shape, color, and texture of the spot
- Look for other spots on your body
- Feel your lymph nodes to make sure they arent bigger or harder than normal
If your doctor thinks a bump looks questionable, theyll remove a sample of the spot to send to a lab for testing.
Continued
Also Check: How To Know If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer
What Causes Squamous Cell Cancer
Skin cancer is caused by mutations that occur in skin cell DNA. These changes cause abnormal cells to multiply out of control. When this occurs in the squamous cells, the condition is known as SCC.
UV radiation is the most common cause of the DNA mutations that lead to skin cancer. UV radiation is found in sunlight as well as in tanning lamps and beds.
While frequent exposure to UV radiation greatly increases your risk of skin cancer, the condition can also develop in people who dont spend much time in the sun or in tanning beds.
These people may be genetically predisposed to skin cancer, or they may have weakened immune systems that increase their likelihood of getting skin cancer.
Those who have received radiation treatment may also be at greater risk of skin cancer.
Risk factors for SCC include:
- having fair skin
- having light-colored hair and blue, green, or gray eyes
- having long-term exposure to UV radiation
- living in sunny regions or at a high altitude
- having a history of multiple severe sunburns, especially if they occurred early in life
- having a history of being exposed to chemicals, such as arsenic
Visit Us Dermatology Partners
Whether youre worried a spot youve noticed is cancerous or youre just ready for your annual professional skin exam, the U.S. Dermatology Partners team would love to hear from you. You can get started scheduling your visit by completing our online request form. Once we receive your scheduling request, one of our local team members will be in touch to finalize the details of your office visit.
Find a location near me
Sign Up for Our Newsletter!
Get the latest updates on news, specials and skin care information.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
Do You Need Chemotherapy For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Because just about all squamous cell carcinoma is usually localized it is typically not treated with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is used for widespread cancer cell eradication, not localized growths. Chemotherapy could be used for a very small percentage of these cases, typically if the cancer has spread.
About 95 percent of squamous cell carcinomas are detected early, and this makes them easy to treat. All treatment options are highly successful, but Mohs micrographic surgery is the most successful while taking the least amount of healthy skin.
How Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Treated
Although squamous cell cancers usually grow slowly, it is important to see a dermatologist quickly. “The sooner you see your doctor and the cancer is diagnosed and treated, the less complicated the surgery to remove it will be, and the faster you will make a complete recovery, Dr. Leffell explains. The treatment for squamous cell cancer varies according to the size and location of the lesion. The surgical options are the same as those for basal cell cancer:
- Surgical excision: Removing a squamous cell lesion is a simple procedure that typically takes place in the dermatologist’s office. After numbing the cancer and the area around it with a local anesthetic, the doctor uses a scalpel to remove the tumor and some of the surrounding skin to make sure all cancer is eliminated. Estimating how much to take requires skill and expertise, Dr. Leffell notes. The risk of taking too little tissue is that some cancer remains taking too much leaves a larger scar than is necessary. Shaped like a football, the wound is stitched together, using plastic surgery techniques. If dissolvable stitches are used, they will disappear on their own as the area heals. Though the procedure leaves some redness and a small scar, it tends to become less noticeable over time. “The cure rate for this type of excision is typically about 90 to 93 percent,” says Dr. Leffell. But, of course, this is dependent on the skill and experience of the doctor.”
Don’t Miss: Does Aflac Cancer Policy Cover Skin Cancer
Factors That Could Affect Your Prognosis
Certain aspects of your health or cancer could affect your outlook. For example, people who have a weakened immune system from a disease like HIV or a medication they take tend to have a less positive outlook.
The location of the tumor also matters. Cancers on the face, scalp, fingers, and toes are more likely to spread and return than those on other parts of the body. SCC that starts in an open wound is also more likely to spread.
Larger tumors or ones that have grown deep in the skin have a higher risk of growing or returning. If a cancer does recur after treatment, the prognosis is less positive than it was the first time around.
Ask your doctor if you have any risk factors that can be managed or controlled. You may need more aggressive treatment, or to be monitored more closely for recurrence.
When Your Cancer Comes Back
Finishing your treatment can come as a huge relief, especially if your doctor tells you youre in remission. Yet your cancer can come back. This is called a recurrence.
See your doctor for regular follow-up visits to catch any recurrence early, when its most treatable. The doctor who treated your cancer will let you know how often to get check-ups. You may see your doctor every 3 months for the first year, and then less often.
Read Also: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
What Are The Causes Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Lip
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Lip is caused when skin cells are burnt or damaged from prolonged exposure to the ultraviolet component of the sun, over many decades
- The source of UV may be from lamps and other such devices, apart from the sun, and their effect on the skin may cumulatively add-up
- Smoking and tobacco chewing may strongly influence development of SCC of Lip
- Sometimes, individuals working in certain industries may be exposed to chemicals or x-rays for a long duration. This may also contribute to its formation
- Scientific research has indicated that the human papillomavirus along with other risk factors, such as sun-exposure, skin color, and an advancing age, seem to greatly multiply the chance of an individual being affected by oral SCC. Nevertheless, the reason behind how the virus is responsible for influencing the conditions development is not well-established
Read Also: What Is The Deadliest Type Of Skin Cancer
What Is Squamous Cell Cancer
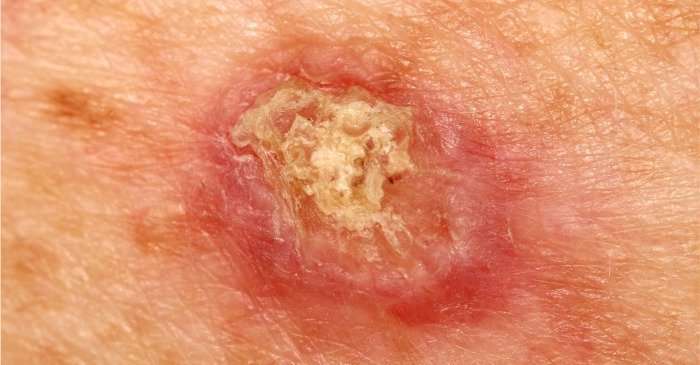
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is a common skin cancer that typically develops in chronic sun-exposed areas of your body. This type of skin cancer is usually not nearly as aggressive as melanoma and is uncontrolled growth of cells in the epidermis of your skin.
It can become disfiguring and sometimes deadly if allowed to grow. Squamous cell carcinomas are at least twice as frequent in men as in women. They rarely appear before age 50 and are most often seen in individuals in their 70s.
An estimated 700,000 cases of SCC are diagnosed each year in the United States, resulting in approximately 2,500 deaths.
Read Also: What Does Skin Carcinoma Look Like
Learn More About Squamous Cell Carcinoma And How It Is Diagnosed And Treated
Accounting for only a fraction of a percentage of all head and neck tumors, cancer of the ear and temporal bone is considered rare. Yet a common place for squamous cell carcinoma to develop when it does affect the ear is within the temporal bone.
- Squamous cell carcinoma is a form of skin cancer that develops within the middle and outer layer of skin in the ear canal
- This condition is life-threatening as the tumor can spread to the brain and the nerves around the ear.
How To Improve Your Odds
Even if youve exhausted all of your treatment options, you dont have to give up. Researchers are always testing new SCC treatments in clinical trials. Getting into one of these studies could give you access to a drug or therapy that might slow or stop your cancer.
To avoid the worsening of your skin cancer or a new cancer in a different area, protect yourself from the suns damaging UV rays. Wear sun-protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat whenever you go outdoors. Apply a layer of broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
Also check your own skin for any new growths on a regular basis. Report any skin changes to your doctor right away.
Read Also: How To Get Tested For Skin Cancer
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
The best way to prevent SCC is to avoid sunburn. Avoid going outin the sun when the UV Index is higher than 3, such as in the middle of theday. Seek shade, wear a hat, sunglasses and clothing that protects you from thesun, and always use an SPF30+ sunscreen. Do not go to tanningsalons.
If you are at very high risk of developing another skin cancer, yourdoctor may prescribe you specific vitamins.
How To Tell If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has Spread
While its not common for squamous cell carcinoma to spread, it is helpful to be mindful of the signs. First, there are certain known risk factors to be aware of, as these characteristics have been associated with a higher stage of squamous cell carcinoma. Risk factors for squamous cell spreading include:
- The tumor is thicker than 2 millimeters.
- The tumor has grown into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin.
- The tumor has grown into the nerves in the skin.
- The tumor is present on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip.
Knowing the stage of your cancer will help your medical team understand how serious it is and how best to treat it. Staging squamous cell carcinoma is based on a physical exam, detailed history, skin biopsy, lymph node biopsy, and imaging studies.
To determine if your cancer has spread, your physician may recommend several diagnostic tests. A skin or lymph node biopsy can show how far cancer cells have spread in the region of the primary tumor. Your medical team may also recommend a computed tomography scan to determine the spread.
You may also be able to recognize squamous cell carcinoma spreading by its appearance. Possible symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma include:
- A thick, red, scaly patch of skin
- An open sore or scar
- An elevated growth that is usually pink, red, or the color of your flesh.
- A wartlike nodule with raised edges
While most squamous cell carcinoma lesions are painless, it is possible to experience pain or numbness at the site.
Also Check: Can You Get Skin Cancer On Your Ear
Melanoma Skin Cancer Growth Rate
Melanoma skin cancer is the most dangerous and aggressive type of skin cancer, but it is significantly less common than other, non-melanoma types of skin cancer like Squamous cell carcinoma and Basal cell carcinoma. Melanoma skin cancer has a rapid growth rate, which is what makes it so dangerous it can turn life-threatening in just six weeks and poses a high risk of spreading to other parts of the body if left untreated. The early form of squamous cell carcinoma is known as Bowens disease.
What Are The Possible Complications Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity
The possible complications due to Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity could be:
- Severe discomfort while eating, chewing, or swallowing food this can even lead to weight loss
- A partial of complete loss of taste sensation
- They can metastasize to the lymph nodes SCC of Oral Cavity has a higher chance of metastasis than if they are at other locations
- Tumors that invade into nerves have higher chances of recurrence and metastasis
- Tumors that are over 2 cm in size have a higher incidence of recurrence and metastasis, than tumors that are less than 2 cm in size
- Severe emotional and psychological stress
- Complications that arise from cancer therapy
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Effective Treatment For Melanoma
How Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity Be Prevented
A few methods to prevent Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity include:
- Maintain proper oral hygiene
- Avoid chewing tobacco and smoking
- Avoid prolonged and chronic exposure to the sun
Regular medical screening at periodic intervals with blood tests, scans, and physical examinations, are mandatory, due to its high metastasizing potential and possibility of recurrence. Often several years of active vigilance is necessary.
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity
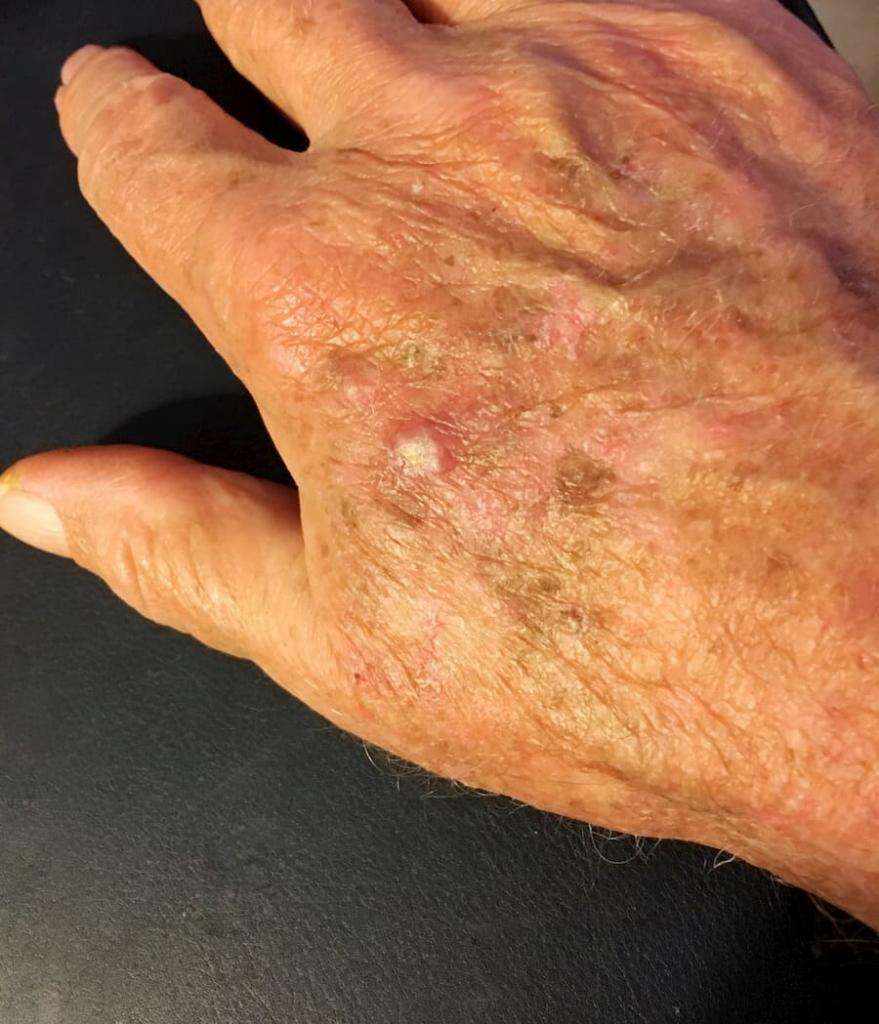
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity is a common malignant tumor of the mouth that typically affects elderly men and women. It is more aggressive than conventional squamous cell carcinoma affecting other body regions
- The cause of the condition is unknown, but genetic mutations may be involved. Factors that may influence its development include smoking and chewing of tobacco, radiation treatment for other reasons, and exposure to coal tar and arsenic
- The squamous cell carcinoma may appear as slow-growing skin lesions. The lesions may ulcerate and cause scarring of the oral cavity. It may be difficult to eat, swallow food, or even to speak
- The treatment of choice is a surgical excision with clear margins followed by radiation therapy or chemotherapy, as decided by the healthcare provider. In majority of the cases, the prognosis is good with appropriate treatment
- Nevertheless, the prognosis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity depends upon many factors including the stage of the tumor and health status of the affected individual. There is a possibility of local or regional metastasis, which can involve the lymph nodes. This may dictate the course of the condition
Read Also: How To Tell If Skin Cancer Is Melanoma