Genetics Of Melanoma And Metastasis
Despite ongoing efforts to characterize additional genetic mutations mediating melanoma formation and progression, quite a bit is already known . BRAF, a mitogenic Ser/Thr kinase in the MAPK/ERK pathway, has an activating mutation, V600E, in at least 50% of melanomas and is thought to be a central oncogenic driver in melanoma. The effect of BRAFV600E mutational status on melanoma metastasis is still somewhat unclear, though some data do exist. BRAF-mutant tumors have been reported to have a worse prognosis than, for example, NRAS mutants , another oncogenic mutation that is thought to drive melanoma formation in a smaller subset of tumors. Though, the association of BRAF-mutation with poor outcome compared to NRAS-mutants was not replicated in other studies . Some preliminary evidence suggests that inhibition of targets downstream of mutant BRAF in melanoma can inhibit lung metastasis . Evidence from thyroid cancer, in which the BRAF V600E mutation is also common, suggests that this mutation can increase invasiveness . However, a recent study in an orthotopic mouse model of melanoma has suggested that RAS/RAF mutational status does not have a role in determining metastasis . The discrepancies in these early studies suggest the implications of the BRAFV600E mutational status with respect to survival and metastasis in melanoma are likely complex.
Treatment Of Metastatic Melanoma
Metastatic melanomas can be difficult to treat. The five-year survival rate for people diagnosed with melanoma that has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 66 percent, according to the American Cancer Society. When cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, there may also be other metastases too small to detect by scans. For people diagnosed with stage 4 melanoma, or melanoma that has spread to distant parts of the body, the five-year survival rate is 27 percent.
For stage 3 and 4 melanomas, the following treatments may be used:
Multiple therapies can be used at any given time, and your care plan is a dynamic process. You and your care team should discuss all the options and decide on a treatment plan. Each treatment has different side effects, and its important to feel fully informed of all the associated risks. Other medications and options may help manage the symptoms of your cancer treatment, so you can live the highest quality of life possible throughout the course of your treatment and disease.
Expert
Recognizing The Signs And Symptoms
The most noticeable sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole or birthmark. People should be aware of any pigmented areas on the skin that appear abnormal in color, shape, size, or texture.
People with stage 4 melanoma may also have ulcerated skin, which is skin with tiny breaks on the surface. These ulcerations can bleed.
Another sign is swollen or hard lymph nodes, which a doctor can confirm by carrying out a physical examination. Other tests include blood tests and imaging scans to confirm the presence of cancer and check how much it has spread.
Also Check: How Serious Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Complementary And Alternative Treatments
It’s common for people with cancer to seek out complementary or alternative treatments. When used alongside your conventional cancer treatment, some of these therapies can make you feel better and improve your quality of life. Others may not be so helpful and in some cases may be harmful. It is important to tell all your healthcare professionals about any complementary medicines you are taking. Never stop taking your conventional treatment without consulting your doctor first.All treatments can have side effects. These days, new treatments are available that can help to make many side effects much less severe than they were in the past.
Haematogenous Spread Of Melanoma
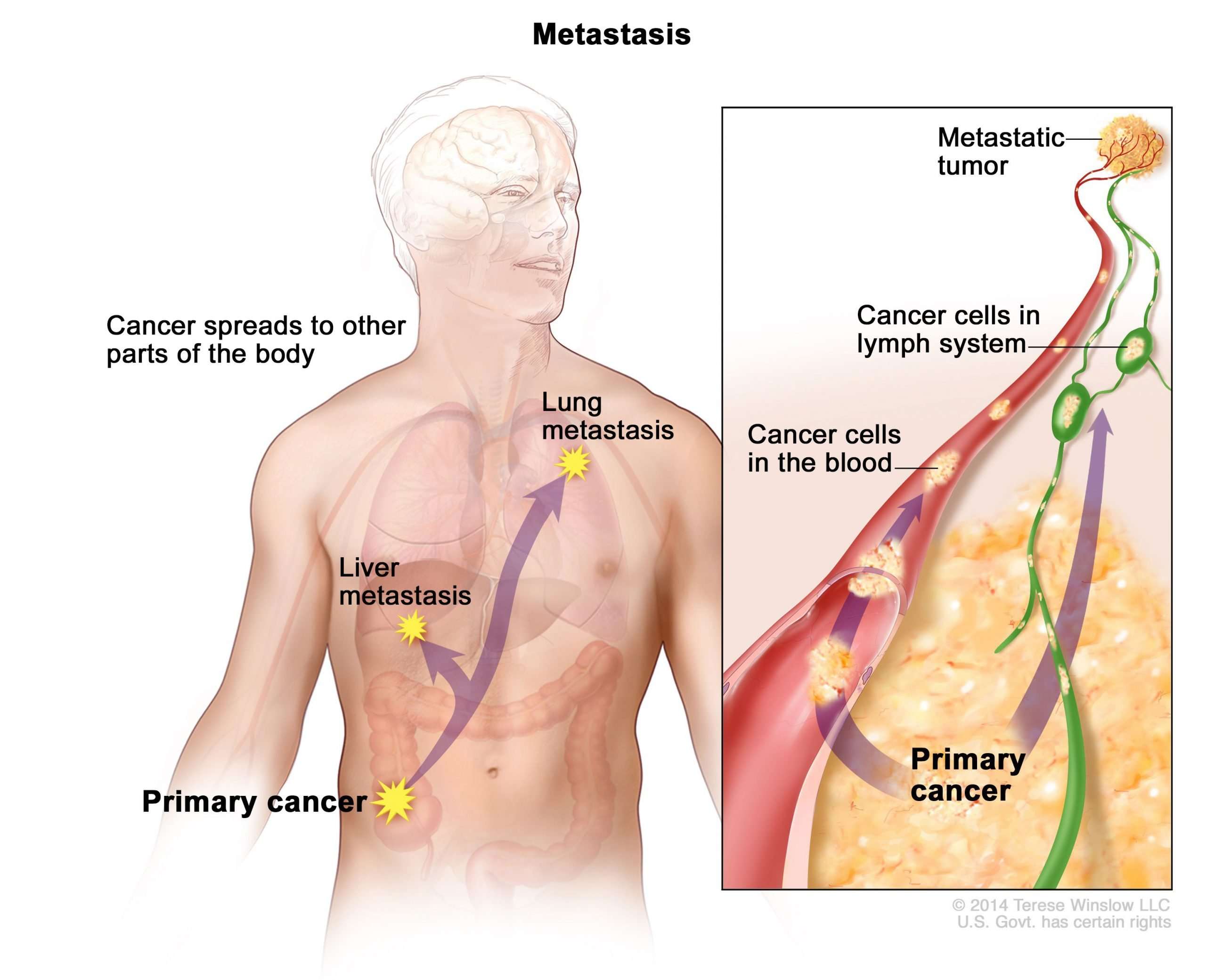
Haematogenous spread is spread of melanoma cells in the bloodstream, which can happen either by a tumour invading blood vessels or secondary to lymph node involvement. Once in the bloodstream, melanoma cells can travel to distant sites in the body and deposit. It can proliferate in any tissue but most often grows in the lungs, in or under the skin, the liver and brain. Many patients also develop metastases in bone, gastrointestinal tract, heart, pancreas, adrenal glands, kidneys, spleen and thyroid.
Read Also: Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Malignant
Red Flag #: Bone Pain Or Fractures
The bones are considered a late-stage site of melanoma metastasestypically, it doesnt spread to the bones until its already spread to another area of the body first. Melanoma can cause pain in the bones where its spread, and some peoplethose with very little body fat covering their bonesmay be able to feel a lump or mass. Metastatic melanoma can also weaken the bones, making them fracture or break very easily. This is most common in the arms, legs, and spine. If you feel any sharp, sudden, or new pains that wont go away, talk to your doctor.
Common Places For Melanoma To Spread
Melanoma can spread from the original site on your skin and form a tumor in any organ or body tissue, but its most likely to metastasize to the lymph nodes, liver, brain, lungs, and less commonly, the bones. Melanoma really likes the brain and the liver, says Lisa Zaba, M.D., dermatologic oncologist at Stanford Medical Center in San Jose, CA. If you notice any of the following red flags, it might mean your melanoma has spread and warrants a call to your doctor right away.
Don’t Miss: How Long Until Melanoma Spreads
Symptoms Of Metastatic Melanomas
Melanoma usually is found in early stages, before its become metastatic. If you notice any abnormal moles or discolorations on your skin, dont hesitate to reach out to your doctor. This is especially important for those with many risk factors. Melanoma is more treatable at early stages, so early identification may prevent metastatic melanoma from developing.
Though a primary tumor is typically found, its possible that metastatic melanoma is detected elsewhere in the body and causes symptoms without any signs of a primary tumor.
Metastatic melanoma symptoms and signs may include:
- Fatigue
Metastatic Melanoma Life Expectancy
The 5-year survival rate for a metastatic melanoma is about 15% to 20% 7). The 10-year survival is about 10% to 15% 8). The outlook is better if the spread is only to distant parts of the skin or distant lymph nodes rather than to other organs, and if the blood level of lactate dehydrogenase is normal.
- The survival differences among M categories will be useful for clinical trial stratification however, the overall prognosis of all patients with stage IV melanoma remains poor, even among patients with M1a. For this reason, the Melanoma Staging Committee recommended no stage groupings for stage IV.
Table 2. American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system for Stage 4 Melanoma
| M |
|---|
- A sore that doesnt heal
- Spread of pigment from the border of a spot into surrounding skin
- Redness or a new swelling beyond the border of the mole
- Change in sensation, such as itchiness, tenderness, or pain
- Change in the surface of a mole scaliness, oozing, bleeding, or the appearance of a lump or bump
Be sure to show your doctor any areas that concern you and ask your doctor to look at areas that may be hard for you to see. Its sometimes hard to tell the difference between melanoma and an ordinary mole, even for doctors, so its important to show your doctor any mole that you are unsure of.
Metastatic melanoma in the brain
Figure 2. Metastatic melanoma in the brain
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Skin Cancer At Home
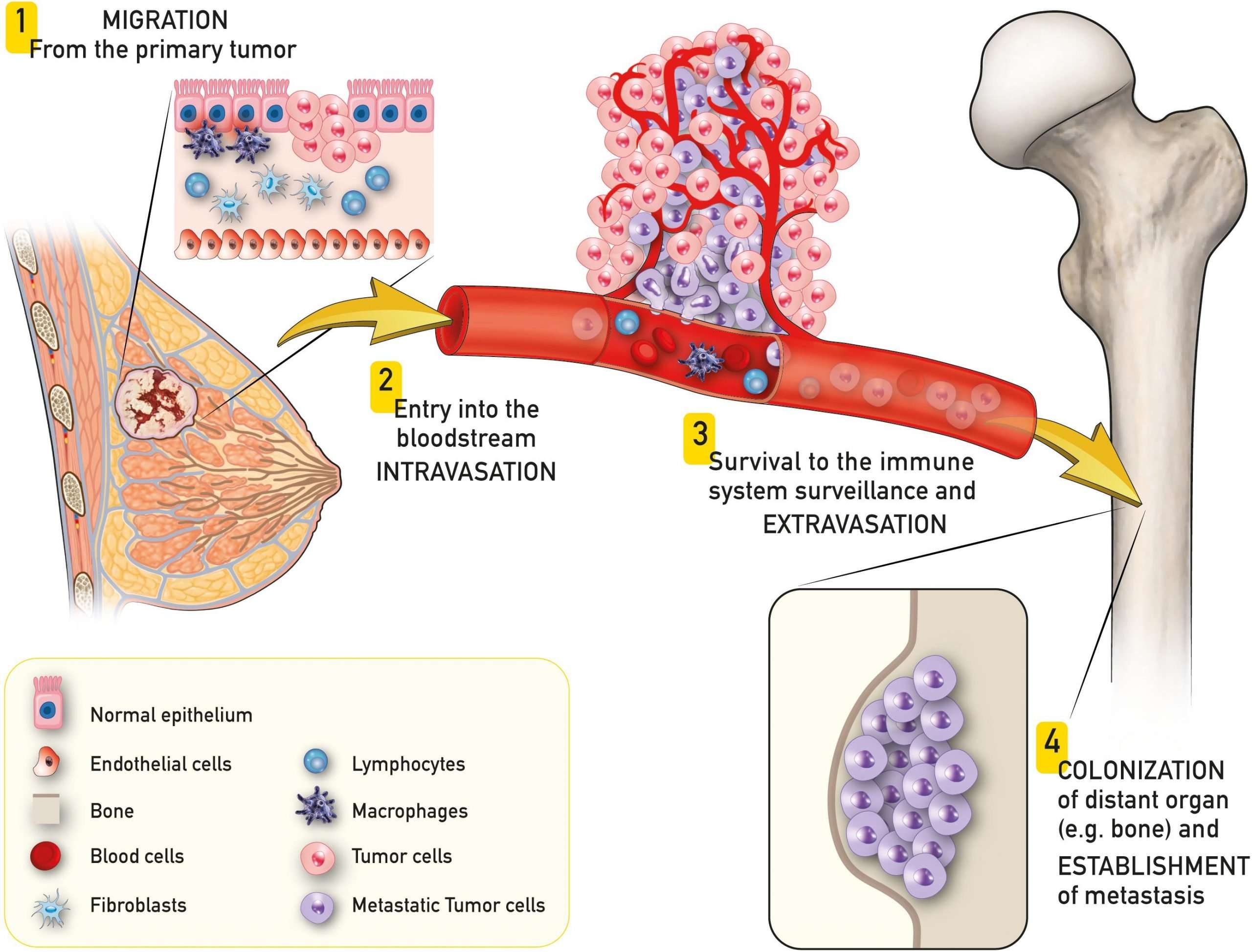
Temporal And Spatial Complexity Of Metastasis
Metastasis involves a series of steps which must be completed before the emergence of clinically meaningful metastatic disease . These steps are further complicated by additional observations from human melanoma patients which add temporal and spatial complexity to metastasis. Many melanoma patients are cured after excision of their primary tumor however, some are not, and will have disease recurrence. Melanoma recurs less frequently at the site of the original primary tumor, instead more commonly recurring at different sites in the body as metastatic lesions. These recurrence patterns suggest that melanoma cells had already spread before excision of the primary tumor, even though this spread might not have been clinically apparent at that time. In melanoma patients, metastatic recurrence can occur within a relatively short period of time, but takes > 5 years in about 40% of patients., , , The period in between initial excision of the primary tumor and subsequent metastatic recurrence is often referred to as metastatic dormancy, where previously disseminated tumor cells are thought to persist in a relatively non-proliferative state.
How Is Metastasis Detected
If your doctor suspects that your melanoma may have spread, there are several tools available to verify the diagnosis. These include a blood test for lactate dehydrogenase , which increases when melanoma metastasizes, and imaging studies, such as chest X-ray, computed tomography , magnetic resonance imaging , positron emission tomography and ultrasound.
The doctor may also need to take a sample of your lymph nodes, using a procedure called “sentinel lymph node mapping.” If confirmed, there are many treatments available, including chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery.
Don’t Miss: Are There Stages Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
How Much Time Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasis
Uveal melanoma represents nearly 80% of all eye cancer and approximately 40% of patients ensue metastatic tumors. Metastases are often confined to the liver and, a small number of patients undergo a theoretically curative operation, this is linked with a poor diagnosis.
In the Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study the liver was the most common site with several patients diagnosed with metastasis with increased mortality rate following the statement of tumor metastasis was 80% at 12 months and 90% at 24 months
There is presently little available data for the optimum management and treatment of metastatic uveal malignancy and the lack of efficient treatments in this scenario has directed to the common use of systemic therapies for patients with cutaneous tumors.
A rare case of a patient of choroidal tumor left eye who acquired very early liver metastasis within just 7 months even after primary therapy completion of leading cancer comprises of enucleation and 3-dimensional conformal radiation treatment. Hence, metastasis should be intensely sought following the treatment of a primary lesion.5,6
Melanoma Formation And Progression
Progression from normal melanocytes to melanoma has classically been divided into a series of progressive steps . Although there are several histologic subtypes of melanoma, this model best describes superficial spreading melanoma, the most common variant, but is useful in understanding other subtypes as well. Melanoma is thought to arise in one of two ways: with no visible precursor lesion or in association with a benign melanocytic proliferation called a nevus . Although only 2030% of melanomas are thought to arise in association with a nevus precursor , this model is also useful in understanding the progression of de novo melanoma .
Although the model described above provides a foundation for understanding melanoma formation and progression, the critical events that occur between local tumor expansion and metastatic spread are complex and not addressed by the model. Additionally, there is compelling evidence that progression does not always occur in such a neat, step-wise fashion. In fact, there is evidence to support the notion that melanocytic cells can spread to distant sites in earlier stages of tumor progression. Lastly, melanomas show a predilection for metastasis to particular organs. Much work has been done to explain these phenomena at a molecular level and these issues will be the focus of this review.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Most Serious Type Of Skin Cancer
Risk Factors For Metastatic Melanomas
You cannot get metastatic melanoma without first having melanoma, though the primary melanoma may be so small its undetectable. Major risk factors for melanomas include:
- Light skin, light-colored hair or light-colored eyes
- Skin prone to burning easily
- Multiple blistering sunburns as a child
- Family history of melanoma
- Frequent exposure to sun or ultraviolet radiation
- Certain genetic mutations
- Exposure to environmental factors, such as radiation or vinyl chloride
Other factors have been connected with increased metastasis. In a 2018 study in the Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia and a 2019 study in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, the following factors were associated with higher levels of metastasis:
- Male gender
- Primary tumor thickness of more than 4 mm
- Nodular melanoma, which is a specific subtype that a care team would identify
- Ulceration of the primary tumor
How Fast Does Melanoma Spread
Melanoma is a deadly form of skin cancer because of its ability to metastasize to local lymph nodes and other organs. It is estimated that melanoma kills, on average, over 10,000 people in the United States every year.
The first sign of flat melanoma is usually a new spot or an existing mole or freckle that changes in appearance. Some changes can include:
- A spot that has grown in size
- A spot where the edges are looking irregular versus smooth and even
- A spot that has a range of colors such as brown, black, blue, red, white or light gray.
- A spot that has become itchy or is bleeding
According to Dr. Andrew Duncanson, board-certified dermatologist at Forefront Dermatology, It is important to know that melanoma can appear on areas of the skin not normally exposed to the sun such as under the arm, chest, and buttocks. It can also appear in areas that you are not able to see easily on your own including the ears, scalp, back of legs, and bottom of feet. I always recommend to my patients to look for the ugly duckling spot the new spot that doesnt look like any others. Additionally, ask a family member to look over the hard to see areas monthly, while also getting an annual skin cancer exam by a board-certified dermatologist to detect skin cancer early.
Recommended Reading: Does Melanoma Skin Cancer Itch
What Is Metastatic Melanoma
Melanoma is a cancer that begins in the melanocytes . Metastatic melanoma is considered to be a late form of stage IV of melanoma cancer and occurs when cancerous melanoma cells in the epidermis metastasize and progress to other organs of the body that are located far from the original site to internal organs, most often the lung, followed in descending order of frequency by the liver, brain, bone and gastrointestinal tract 1). The two main factors in determining how advanced the melanoma is into Stage IV are the site of the distant metastases and whether or not the serum lactate dehydrogenase level is elevated. LDH , an enzyme found in your blood and almost every other cell of your body, turns sugar into energy, and the more you have in your blood or other body fluid, the more damage has been done to your bodys tissues.
It is crucial to diagnose melanoma in its early stages before it metastasizes, as once it has spread, it is difficult to locate its origin and so treatment and patients survival rate tends to be hindered 2).
An estimated 178,560 cases of melanoma will be diagnosed in the U.S. in 2018 3). Of those, 87,290 cases will be in situ , confined to the epidermis , and 91,270 cases will be invasive, penetrating the epidermis into the skins second layer 4).
Melanomas can develop anywhere on the skin, but they are more likely to start on the trunk in men and on the legs in women. The neck and face are other common sites.
What Causes Metastatic Melanoma
Anyone can get melanoma, but most cases of melanoma are caused by UV radiation from sunlight some studies even put incidences of skin cancer caused by sun exposure at around 95%. The UV rays from the sun damage skin cells ability to repair DNA. When this happens, gene mutations can occur and the risk of cancer increases.
The risk of melanoma is higher in fair-skinned people as they have less melanin in their skin to protect from the suns rays. Risk is also higher if there is a history of melanoma in the family as gene mutations are often passed down from one generation to the next.
Also Check: Does Medicare Cover Skin Cancer
Red Flag #: Swollen Lymph Nodes
If melanoma spreads, it often goes to the lymph nodes first, says Melinda L. Yushak, M.D., assistant professor of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta. The cancer cells will first travel to the nodes closest to the original tumor, she says. Lymph nodes are located throughout your entire body, but large clusters are found in the neck, underarms, chest, abdomen, and groin. If the cancer has made its way to the lymph nodes, it usually wont be painful, but theyll feel swollen or even hard to the touch, Dr. Zaba says.
The Spread Of Melanoma Metastasis
If you or a family member or friend have recently been diagnosed with melanoma, you may be wondering, just where and why can melanoma spread?
With surgery, melanoma confined to the skin has a 5-year survival rate in 98% of cases. Unfortunately, if the lesion recurs , gets thicker, or spreads from the skin to the lymph nodes or distant organs, it becomes much more dangerous. This occurs in stage III and IV melanoma and is called melanoma metastasis.
Don’t Miss: Is Melanoma Painful Or Itchy
Molecularly Targeted Therapy For Melanoma
- Ipilimumab is a monoclonalantibody that targets CTLA-4. It can increase survival in metastatic melanoma.
- Vemurafenib, sorafenib and dabrafenib target the BRAF protein which is mutated in some metastatic melanomas. Trametinib inhibits the MAPK signalling pathway in melanoma with BRAF mutations. Cobimetinib is a MEKinhibitor that is taken in combination with vemurafenib. These new drugs can lead to a very good initial improvement but eventually, the metastatic melanoma progresses.
- Pembrolizumab targets the programmed death 1 receptor and can be used in patients with all forms of melanoma. Favourable response rates were demonstrated in clinical trial data from 173 patients with melanoma in the KEYNOTE-001 study.
- Nivolumab is a human programmed death receptor-1 blocking antibody. The Check-Mate studies indicated clinical benefit in metastatic melanoma.
- Therapies which block the formation of new blood vessels can also be helpful as additional treatments.
- A number of vaccines for melanoma have been developed with the aim of stimulating the immune system to fight the melanoma cells. Unfortunately, these have had disappointing results to date.
With a range of new therapies being developed and studied for melanoma, some patients choose to participate in a clinical trial. This can mean having access to a treatment that wouldnt otherwise be possible.