Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for melanoma skin cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread beyond the skin where it started.
- Regional: The cancer has spread beyond the skin where it started to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the lungs, liver, or skin on other parts of the body.
You May Like: Can Melanoma Be Treated Successfully
Number Of Metastatic Lymph Nodes Involved
If the melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes the risk of spread to other parts of the body is higher. The greater the number of lymph nodes containing melanoma, the less favourable the prognosis.
A sentinel node biopsy is a technique used to determine whether melanoma cells have spread to lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis of the skin primary lesion. The procedure involves the injection of a radioactive tracer by a radiologist , to show where the site and lymph node where the lymph fluid from the skin at the primary melanoma will flow. Afterwards, at the same time as the extra surgery for the primary melanoma a blue dye is injected around the site of the primary lesion. Using the guide from the radiologist a surgeon looks for the first lymph node to take up the dye. The lymph node is removed and sent to be examined by a histopathologist to determine if the node tests positive for melanoma. The procedure is considered when the Breslow thickness of the melanoma is more than 0.8mm.
Patients may develop lumps in the lymph node regions such as the neck, armpit and groin. This is lymph node metastasis.
Tnm Categories And Subcategories For Stage Iii Melanoma
T means Tumor. This category is related to your primary melanoma tumor.
T0 means no evidence of a primary tumor.
The T1 category includes tumors that are less than 1.0 mm thick. T1 subcategories:
- T1a tumors are less than 0.8 mm thick and are not ulcerated.
- T1b tumors are less than 0.8 mm thick and are ulcerated or are 0.8 to 1.0 mm thick and can be ulcerated or not.
The T2 category includes tumors that are greater than 1.0 mm and up to 2.0 mm thick. T2 subcategories:
- T2a tumors are greater than 1.0 mm and up to 2.0 mm thick and do not have ulceration.
- T2b tumors are greater than 1.0 mm and up to 2.0 mm thick and are ulcerated.
The T3 category includes tumors that are 2.0 to 4.0 mm thick. T3 subcategories:
- T3a tumors are 2.0 to 4.0 mm thick and are not ulcerated.
- T3b tumors are 2.0 to 4.0 mm thick and are ulcerated.
The T4 category includes tumors that are greater than 4.0 mm thick. T4 subcategories:
- T4a tumors are greater than 4.0 mm thick and are not ulcerated.
- T4b tumors are greater than 4.0 mm thick and are ulcerated.
N means Node. This category is related to the regional spread of your melanoma, beyond the primary tumor.
The N1 category comprises spread to only one lymph node OR there is in-transit, satellite, or microsatellite metastasis. N1 subcategories:
The N2 category comprises spread to two or three lymph nodes OR that there is in-transit, satellite, or microsatellite metastases AND one positive lymph node. N2 subcategories:
Don’t Miss: What Kind Of Cancer Causes Skin Rashes
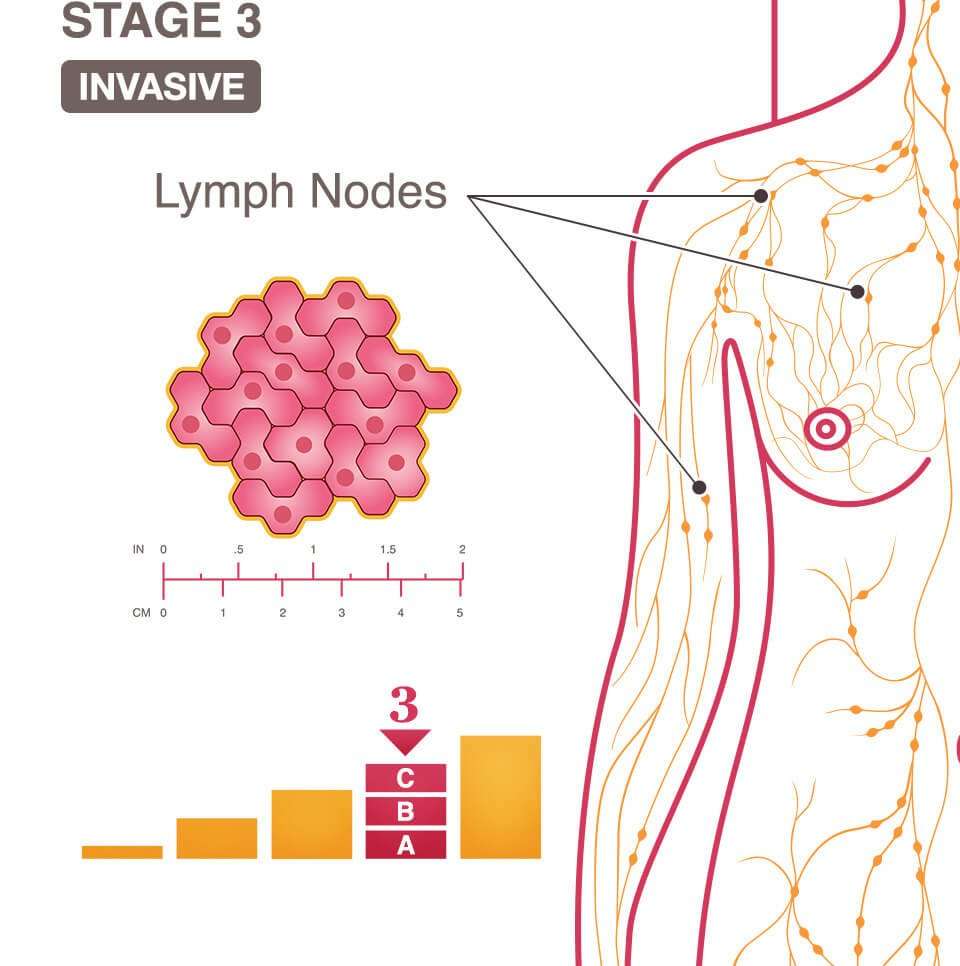
What Does Stage 3 Cancer Mean
Stage 3 usually means the cancer is larger. It may have started to spread into surrounding tissues and there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes nearby. Stage 4 means the cancer has spread from where it started to another body organ. For example to the liver or lung. This is also called secondary or metastatic cancer.
Read Also: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
Treating Stage Ii Melanoma
Wide excision is the standard treatment for stage II melanoma. The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma.
Because the melanoma may have spread to nearby lymph nodes, many doctors recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy as well. This is an option that you and your doctor should discuss.
If an SLNB is done and does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If the SLNB finds that the sentinel node contains cancer cells, then a lymph node dissection will probably be done at a later date. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
Recommended Reading: How To Detect Melanoma Early
Skin Exam And Physical
If youve been diagnosed with melanoma, youve already had a skin biopsy. This biopsy was taken when you had part of the suspicious spot removed. After it was removed, a doctor looked at the spot under a microscope to find out if it contained cancer cells. This is currently the only way to tell if someone has skin cancer.
After getting the diagnosis, the next step is to get a complete skin exam and physical.
During the physical, your dermatologist will feel your lymph nodes. This is where melanoma usually goes when it begins to spread. It usually travels to the lymph nodes closest to the melanoma.
If there is a risk the cancer could have spread, your dermatologist may recommend that you have a lymph node biopsy. If a sentinel lymph node biopsy is recommended, it can be performed at the time of your surgery for melanoma.
After the skin exam and physical, your dermatologist may recommend testing, such as a CAT scan, MRI, or a blood test. These can also help detect spread.
Treating Stage 0 Melanoma
Stage 0 melanoma has not grown deeper than the top layer of the skin . It is usually treated by surgery to remove the melanoma and a small margin of normal skin around it. The removed sample is then sent to a lab to be looked at with a microscope. If cancer cells are seen at the edges of the sample, a second, wider excision of the area may be done.
Some doctors may consider the use of imiquimod cream or radiation therapy instead of surgery, although not all doctors agree with this.
For melanomas in sensitive areas on the face, some doctors may use Mohs surgery or even imiquimod cream if surgery might be disfiguring, although not all doctors agree with these uses.
Don’t Miss: Who Do You See For Skin Cancer Screening
Treating Stage 1 To 2 Melanoma
Treating stage 1 melanoma involves surgery to remove the melanoma and a small area of skin around it. This is known as surgical excision.
Surgical excision is usually done using local anaesthetic, which means you’ll be awake, but the area around the melanoma will be numbed, so you will not feel pain. In some cases, general anaesthetic is used, which means you’ll be unconscious during the procedure.
If a surgical excision is likely to leave a significant scar, it may be done in combination with a skin graft. However, skin flaps are now more commonly used because the scars are usually less noticeable than those resulting from a skin graft.
Read more about flap surgery.
In most cases, once the melanoma has been removed there’s little possibility of it returning and no further treatment should be needed. Most people are monitored for 1 to 5 years and are then discharged with no further problems.
Immunotherapy & Clinical Trials
Voluntary research studies may provide the best hope for stage 3 mesothelioma patients. Immunotherapy and gene therapy are two constantly evolving areas in cancer treatment. In 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved multiple immunotherapies for mesothelioma.
Specialists at specific treatment centers offer mesothelioma clinical trials and experimental treatments to improve prognosis and extend life expectancy. Patients should ask their mesothelioma specialists about appropriate clinical trials in their area and the requirements for enrolling in a research trial.
You May Like: What Is Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma
Treating Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage IV melanomas have already spread to distant lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
Metastases in internal organs are sometimes removed, depending on how many there are, where they are, and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab are typically the first drugs tried, especially in people whose cancer cells do not have BRAF gene changes. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Ipilimumab , a different type of checkpoint inhibitor, is not typically used by itself as the first treatment, although it might be combined with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. This slightly increase the chances that the tumor will shrink, although itâs also more likely to result in serious side effects, which needs to be considered carefully. People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects..
Itâs important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.
What Are The Stages Of Melanoma
When a melanoma has been diagnosed, the pathology report provides information to determine thestage of the disease.
The prognosis of melanoma and the treatment options available depend on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed.
One of the most common areas of confusion is the difference between the levels of melanoma and the staging of melanoma. The level of melanoma relates to the depth of the melanoma in the skin and the staging of melanoma refers to how limited or advanced the melanoma is at the time of diagnosis.
The stages of melanoma are determined by reviewing different factors including:
Read Also: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
Read Also: Who Can Diagnose Skin Cancer
Strategies To Improve Treatment
The progress that has been made in the treatment of melanoma has resulted from patient participation in clinical trials. Currently, there are several areas of active exploration aimed at improving the treatment of melanoma.
Precision Cancer Medicines & Immunotherapy: As promising as all of the new, medicines are they typically stop working at some point because melanoma cells find another pathway that lets them start growing again. In many cancers, combination therapy improves survival and leads to cures when compared to single agent treatment. In addition to developing new precision cancer medicines and immunotherapies, researchers are testing various combinations of two or more drugs with encouraging results.
BRAF & MEK*:* The combination of a novel BRAF inhibitor Braftovi with a MEK Mektovi significantly delayed cancer recurrence compared to treatment with Zelboraf alone. Zelboraf was the first BRAF inhibitor approved for treatment of advanced melanoma and represented a breakthrough by significantly improving survival compared with chemotherapy, replaced the latter as a treatment option.
Vaccines: Currently, no vaccine has been approved for the treatment melanoma. Melanoma vaccines produce responses, often dramatic, in some patients, but effects are far from consistent.
References:
A Word About Survival Rates By Stage
You may feel frightened by the survival rates listed above, but keep the following in mind. Statistics are numbers, not people. They predict what the average outcome may be, but they say little about how you, as an individual, will respond to treatment. In addition, treatments are improving. Newer treatments have been approved, and more are currently being tested in clinical trials. Statistics are often several years old, and they may not reflect how someone will respond to treatment today.
Also Check: How Can You Get Skin Cancer From The Sun
Survival Rates For Melanoma Skin Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
Read Also: How To Identify Skin Cancer
Where To Find Support For Stage 3 Melanoma
With a melanoma diagnosis, its important to reach out to those close to you during your treatment. In addition to family and friends, there are many support groups and resources who can help answer questions or provide a listening ear.
Find a melanoma support group. The American Melanoma Foundation maintains a list of support groups throughout the country find them by .
Join an online support group. If you feel more comfortable participating in an online support group, the AIM at Melanoma Foundation offers a support community as well as counseling.
Seek financial assistance, if needed. The Melanoma Research Foundation has developed a central resource for patient assistance programs and government entities that offer financial assistance for those with melanoma. For more information, please .
Sign up for a mentoring program. Olympic figure skater Scott Hamiltons charity, 4th Angel, offers a mentoring program for those with cancer. This telephone-based program is designed to provide support and encouragement to those with cancer.
Many organizations provide professional and supportive services when youve been diagnosed with melanoma. Other organizations that provide support for those with skin cancer include the:
Don’t Miss: What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
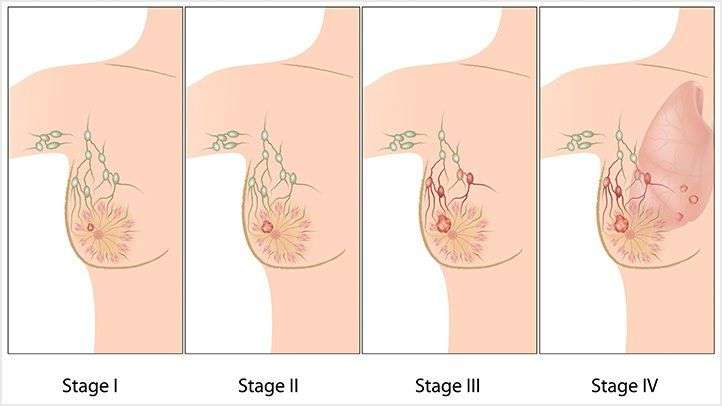
Stages Of Melanoma Skin Cancer
Staging describes or classifies a cancer based on how much cancer there is in the body and where it is when first diagnosed. This is often called the extent of cancer. Information from tests is used to find out the size of the tumour, which parts of the skin have cancer, whether the cancer has spread from where it first started and where the cancer has spread. Your healthcare team uses the stage to plan treatment and estimate the outcome .
The most common staging system for melanoma skin cancer is the TNM system. For melanoma skin cancer there are 5 stages stage 0 followed by stages 1 to 4. Often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the Roman numerals I, II, III and IV. Generally, the higher the stage number, the more the cancer has spread. Talk to your doctor if you have questions about staging.
When describing the stage, doctors often use the words early stage, locoregional or metastatic.
Early stage means that the cancer is only in where it started and has not spread to other parts of the body. It includes stage 0, stage 1A, stage 1B, stage 2A, stage 2B and stage 2C melanoma skin cancers.
Locoregional means the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, or it has spread to nearby areas of skin or lymph vessels. It includes stage 3 melanoma skin cancer.
Metastatic means that the cancer is in a part of the body farther from where it started. It includes stage 4 melanoma skin cancer.
Find out more about .
Mitotic Rate Of Your Melanoma
The staging system has been recently updated. It no longer includes the mitotic rate to work out your stage. But your doctor may still use it to work out how likely your cancer. is to spread.
Mitotic rate means the number of cells that are dividing in a certain amount of melanoma tissue. Higher mitotic rate may mean that the melanoma is at greater risk the spreading because more cells are dividing more.
Also Check: How To Remove Skin Cancer On Face
How Is Melanoma Staged
Melanoma stages are assigned using the TNM system.
The stage of the disease indicates how much the cancer has progressed by taking into account the size of the tumor, whether its spread to lymph nodes, and whether its spread to other parts of the body.
A doctor can identify a possible melanoma during a physical exam and confirm the diagnosis with a biopsy, where the tissue is removed to determine if its cancerous.
But more sophisticated technology, such as PET scans and sentinel lymph node biopsies, are necessary to determine the cancers stage or how far its progressed.
There are five stages of melanoma. The first stage is called stage 0, or melanoma in situ. The last stage is called stage 4. Survival rates decrease with later stages of melanoma.
Its important to note that survival rates for each stage are just estimates. Each person with melanoma is different, and your outlook can vary based on a number of different factors.