Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
SCC is generally faster growing than basal cell cancers. About 20 out of every 100 skin cancers are SCCs. They begin in cells called keratinocytes, which are found in the epidermis.
Most SCCs develop on areas of skin exposed to the sun. These areas include parts of the head, neck, and on the back of your hands and forearms. They can also develop on scars, areas of skin that have been burnt in the past, or that have been ulcerated for a long time.
SCCs don’t often spread. If they do, it’s most often to the deeper layers of the skin. They can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other parts of the body, but this is unusual.
Who Is At Risk
Much like with BCC, the more time you spend in the sun, the more at risk you are for developing SCC. About 90% of nonmelanoma skin cancers are caused by sun exposure, and people who have tanned indoors have a 67% higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma.
Your risk for SCC is higher if you:
- Have a history of skin cancer
- Have a history of unprotected exposure to the sun or tanning beds
- Have a weakened immune system due to a chronic condition or medication
- Are over age 50
- Have a history of chronic skin infections, precancerous skin growths or human papillomavirus
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin depends mostly on the following:
- Stage of the cancer.
- Whether the patient is immunosuppressed.
- Whether the patient uses tobacco.
- The patient’s general health.
Treatment options for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin depend on the following:
- The type of cancer.
- The stage of the cancer, for squamous cell carcinoma.
- The size of the tumor and what part of the body it affects.
- The patients general health.
Don’t Miss: Does Melanoma Skin Cancer Itch
Signs Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Like BCC, SCC is most commonly found in areas with frequent sun exposure like the face, ears, neck, scalp, and hands. The growths can also occur in scars or sores and look like open sores, red patches, warts or thickened skin. They can also appear in areas not affected by the sun, such as the genitals.
The skin around an SCC growth may show signs of sun damage like wrinkling and darker pigment. They can bleed or itch as well.
Determining If The Cancer Has Spread
As part of your diagnosis, your doctor will also determine what stage the cancer is in. The different stages refer to whether and how far the cancer has spread in your body, on a Roman numeral scale of I to IV. A stage I cancer is small and contained to the body part where it originated, whereas a stage IV cancer has spread aggressively to other parts of the body.
Depending on the type of skin cancer that a person has, it may be more or less likely that it has spread through the body. For instance, basal cell skin cancer rarely spreads beyond the skin where it starts. However, melanomas and large squamous cell carcinomas are more likely to spread into other regions of the body. Cases of melanoma, in particular, may call for further tests to determine the specific stage theyre in.
Your doctor may evaluate multiple factors in order to stage the cancer. Using biopsies and imaging tests, your doctor may take a look at:
-
The size and thickness of the tumor, and whether it has grown into surrounding tissues
-
Nearby lymph nodes, to check for signs of cancer spread
Recommended Reading: How Fast Can You Get Skin Cancer From The Sun
Recurrent Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas are the most common type of skin cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. These cancers develop within the basal cell layer of the skin, in the lowest part of the epidermis.
Patients who have had basal cell carcinoma once have an increased risk of developing a recurrent basal cell cancer. Basal cell cancers may recur in the same location that the original cancer was found or elsewhere in the body. As many as 50 percent of cancer patients are estimated to experience basal cell carcinoma recurrence within five years of the first diagnosis.
Basal cell carcinomas typically grow slowly, and it is rare for them to metastasize or spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. But early detection and treatment are important.
After completing treatment for basal cell carcinoma, it is important to perform regular self-examinations of the skin to look for new symptoms, such as unusual growths or changes in the size, shape or color of an existing spot. Skin cancers typically develop in areas of the body that are exposed to the sun, but they may also develop in areas with no sun exposure. Tell your oncologist or dermatologist about any new symptoms or suspicious changes you may have noticed.
- Have a history of eczema or dry skin
- Have been exposed to high doses of UV light
- Had original carcinomas several layers deep in the skin
- Had original carcinomas larger than 2 centimeters
Preparing For Your Appointment
If you have any concerns about the health of your skin, it is important to share them with your doctor. After making an appointment, there are steps you can take to prepare yourself and make the most of your time with your doctor.
Here are some things to consider and be prepared to discuss before visiting the clinic or hospital:
-
What symptoms are you experiencing ?
-
When did you first notice your symptoms?
-
Have there been any major changes or stressors in your life recently?
-
What medications and/or vitamins are you taking?
-
What questions do you have for your doctor?
You May Like: Do You Die From Skin Cancer
Knowledge Is Your Best Defense
What Is Skin Cancer?
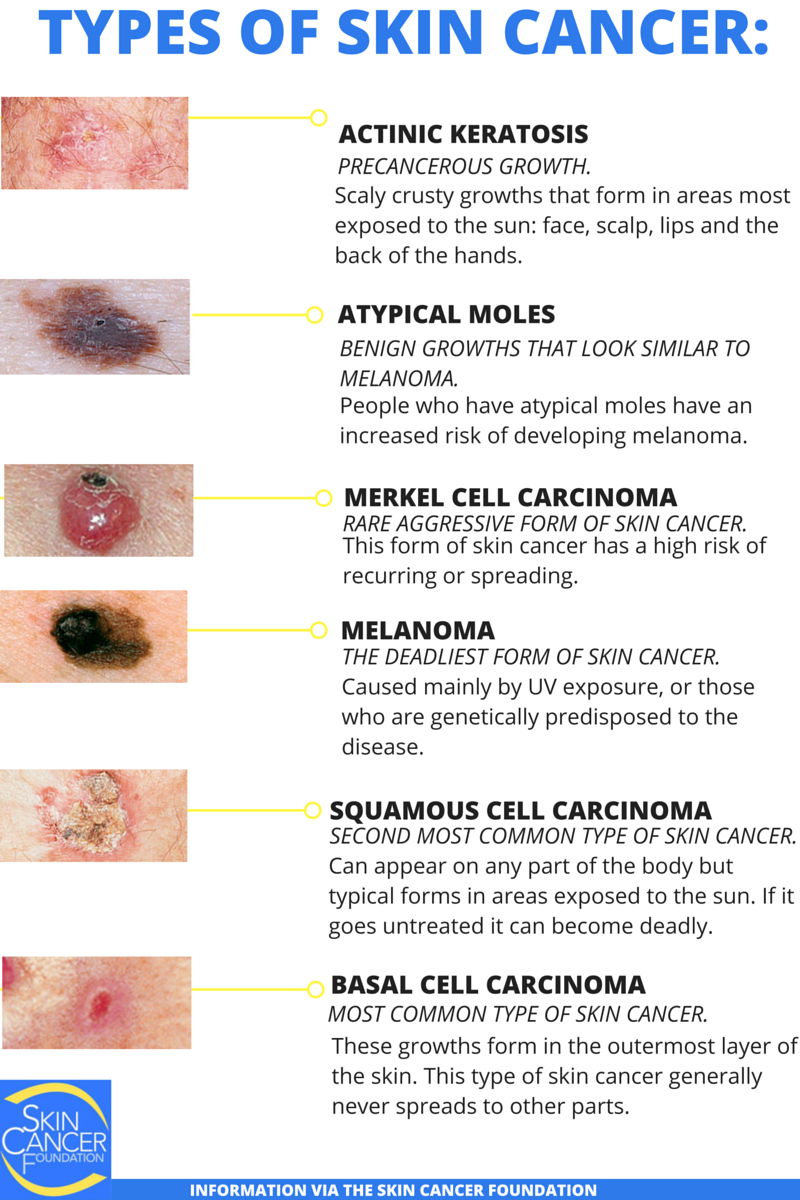
Skin cancer is the out-of-control growth of abnormal cells in the epidermis, the outermost skin layer, caused by unrepaired DNA damage that triggers mutations. These mutations lead the skin cells to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumors. The main types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma , squamous cell carcinoma , melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma .
The two main causes of skin cancer are the suns harmful ultraviolet rays and the use of UV tanning beds. The good news is that if skin cancer is caught early, your dermatologist can treat it with little or no scarring and high odds of eliminating it entirely. Often, the doctor may even detect the growth at a precancerous stage, before it has become a full-blown skin cancer or penetrated below the surface of the skin.
Americans will develop skin cancer by age 70.
Squamous Cell Carcinomas Are More Likely To Spread
Like basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas are curable and can usually be removed completely when caught in time. They are, however, more dangerous than BCC because of their higher likelihood to spread. SCC is more likely to grow into the deeper layers of skin and other tissues in the body than BCC. While basal cell carcinoma usually does not grow into other areas of the body, it can rarely grow into a large tumor on the skin.
Also Check: What Are The Stages Of Malignant Melanoma
Skin Cancer Types: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Overview
All content solely developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology gratefully acknowledges the support from Sanofi Genzyme and Regeneron.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
What is squamous cell carcinoma of the skin?A common type of skin cancer, squamous cell skin cancer can develop from a pre-cancerous skin growth called an actinic keratosis .
Is it contagious? No
How Concerning Is Each Type Of Skin Cancer
As with all cancers, it depends very much on how soon you catch it and whether it has spread. “Skin cancer occurs when a previously normal cell undergoes a transformation and begins to grow abnormally and multiply,” says Dr Arun. “As these cells multiply, they form a mass or tumour. If the tumour is benign, it is non-cancerous and is unlikely to spread, if it is malignant, cells are cancerous and can spread to other tissues and organs.
“When it comes to skin cancer, melanoma cancer is by far the most aggressive and more commonly known. It is found in areas most exposed to the sun and the risk of getting skin cancer grows with age.”
If you keep a regular check on your moles, you should be able to spot any chances quickly. “Non-melanoma cancers can be treated if identified early cure rates for type BCC is high, around 90%,” says Dr Arun. “Patients who have been treated for non-melanoma cancers will need to monitor the affected area after their treatment and seek advice from their GP or dermatologist if they spot any further changes.”
Read Also: How Serious Is Skin Cancer On The Face
Precancerous Types Of Skin Cancer
Some precancerous growths, often attributable to sun exposure, can lead to skin cancer over time. However, if they are recognized and removed early, you could avoid a cancer diagnosis. These growths include:
- Actinic keratosis: About 40-60% of squamous cell cancer cases began as actinic keratosis. Anywhere between 2-10% of these growths will develop into SCC, sometimes in as little as a couple of years. Actinic cheilitis is a type of actinic keratosis that appears on the lower lip, and is at higher risk for developing into skin cancer
- Bowens disease: This early, noninvasive form of SCC is at high risk of becoming skin cancer if not addressed. It presents as an eczema-like scaly patch and is usually red or brown in color. These growths have been linked to sun exposure, radiation, carcinogen exposure, genetics, and trauma
- Leukoplakia: These white patches on the lips, tongue, and gums may be caused by alcohol and tobacco use, and can turn into squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer sites on the lips may be caused by sun damage
- Keratoacanthoma: This dome-shaped growth is usually found on sun-exposed skin and usually grows quickly at first, then slows down. Many shrink and go away on their own, but if they continue to grow, this tumor can turn into squamous cell carcinoma. They are usually removed surgically
Keeping Cancer In Check
Chronic exposure to the sun or intermittent sunburns can lead to skin cancer. Skin cancer risk doubles with five or more sunburns in a lifetime, but just one bad sunburn can double the risk of melanoma. While skin cancer is uncommon in African Americans, Latinos and Asians, it can also be more deadly because they are often diagnosed later in the course of the disease.
Its important to examine your skin regularly. You should report any changes in an existing mole or any new moles to your physician. People with fair complexions have the highest risk of developing skin cancer, but everyone should avoid the sun and practice safety measures to protect their skin.
The American Cancer Society recommends the Slip, Slop, Slap and Wrap policy. When you go out in the sun, slip on a shirt, slop on sunscreen, slap on a hat and wrap on sunglasses to protect your eyes and the sensitive skin around them.
Exposure to the UV rays of tanning lamps is not safe. Tanning lamps give out UV rays, which can cause long-term skin damage and can contribute to skin cancer. Tanning bed use has been linked with an increased risk of melanoma, especially for people under 30. Most doctors and health organizations recommend not using tanning beds and sun lamps.
Also Check: What Is The Best Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Skin Cancer
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. About 75 out of every 100 non melanoma skin cancers are BCCs. They develop from basal cells and these are found in the deepest part of the outer layer of the skin .
They develop mostly in areas of skin exposed to the sun, including parts of the face such as the nose, forehead and cheeks. Also, on your back or lower legs.
They are most often diagnosed in people who are middle aged or older.
Doctors might also call a basal cell cancer a rodent ulcer.
There are a number of different types of BCC. Each type can look and behave differently. They include:
- nodular basal cell skin cancer
- superficial basal cell skin cancer
- morphoeic basal cell skin cancer – also known as sclerosing or infiltrating basal cell skin cancer
- pigmented basal cell skin cancer
Nodular basal cell cancer is the most common subtype.
It’s very rare for basal cell skin cancer to spread to another part of the body to form a secondary cancer. It’s possible to have more than one basal cell cancer at any one time and having had one does increase your risk of getting another.
What Is The Staging For Skin Cancer
There is no specific staging system for basal cell carcinoma. If the tumor is wider than 2 cm , it is probably a more serious tumor. Basal cell carcinomas of the ears, nose, and eyelid may also be of more concern, regardless of the size.
There is a staging system for squamous cell carcinoma. Large tumors that are thicker than 2 mm, invade the nerve structures of the skin, occur on the ear, and have certain worrisome characteristics under the microscope are of more concern. If the tumor metastasizes to a site at some distance from the primary tumor, the cancer is likely to be a dangerous tumor.
You May Like: What Does Stage 4 Skin Cancer Look Like
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Squamous cells are found throughout the human body. These cells line organs, such as the lungs, throat, and thyroid. We also have squamous cells in our skin.
The job of squamous cells is to protect what lies beneath. In our skin, these cells sit near the surface, protecting the tissue beneath.
Anywhere we have squamous cells, we can develop a type of cancer called squamous cell carcinoma .
In the skin, this cancer is usually not life-threatening. It tends to grow slowly, but it can grow deep. When the cancer grows deep, it can injure nerves, blood vessels, and anything else in its path. As the cancer cells pile up, a large tumor can form.
Most people who develop this skin cancer have fair skin that they seldom protected with sunscreen or sun-protective clothing. Before developing this skin cancer, they tend to notice signs of sun damage on their skin, such as age spots, patches of discolored skin, and deep wrinkles.
Anyone can develop squamous cell carcinoma
While anyone can develop this skin cancer, you have a greater risk if you live with a transplanted organ, use tanning beds, or have fair skin that you seldom protected from the sun.
Another sign of sun-damaged skin is having one or more pre-cancerous growths on your skin called actinic keratoses . Some AKs progress, turning into squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
To find out what this skin cancer can look like and see pictures of it, go to: Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Signs and symptoms.
ImageGetty Images
Prognosis For Skin Cancer
It is not possible for a doctor to predict the exact course of a disease. However, your doctor may give you the likely outcome of the disease. If detected early, most skin cancers are successfully treated.
Most non-melanoma skin cancers do not pose a serious risk to your health but a cancer diagnosis can be a shock. If you want to talk to someone see your doctor. You can also call Cancer Council 13 11 20.
Read Also: How Bad Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Skin Cancer Symptoms And Signs
Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer and has a predilection for sun-exposed skin. Tumors may appear as a pearly or waxy bumps usually with visible blood vessels , or as a flat scaly reddish patch with a brown border, or as a hard or scar-like lesion . Frequently BCCs can be itchy, often bleed, or in more advanced cases, ulcerate.
Different Types Of Skin Cancer
On this page
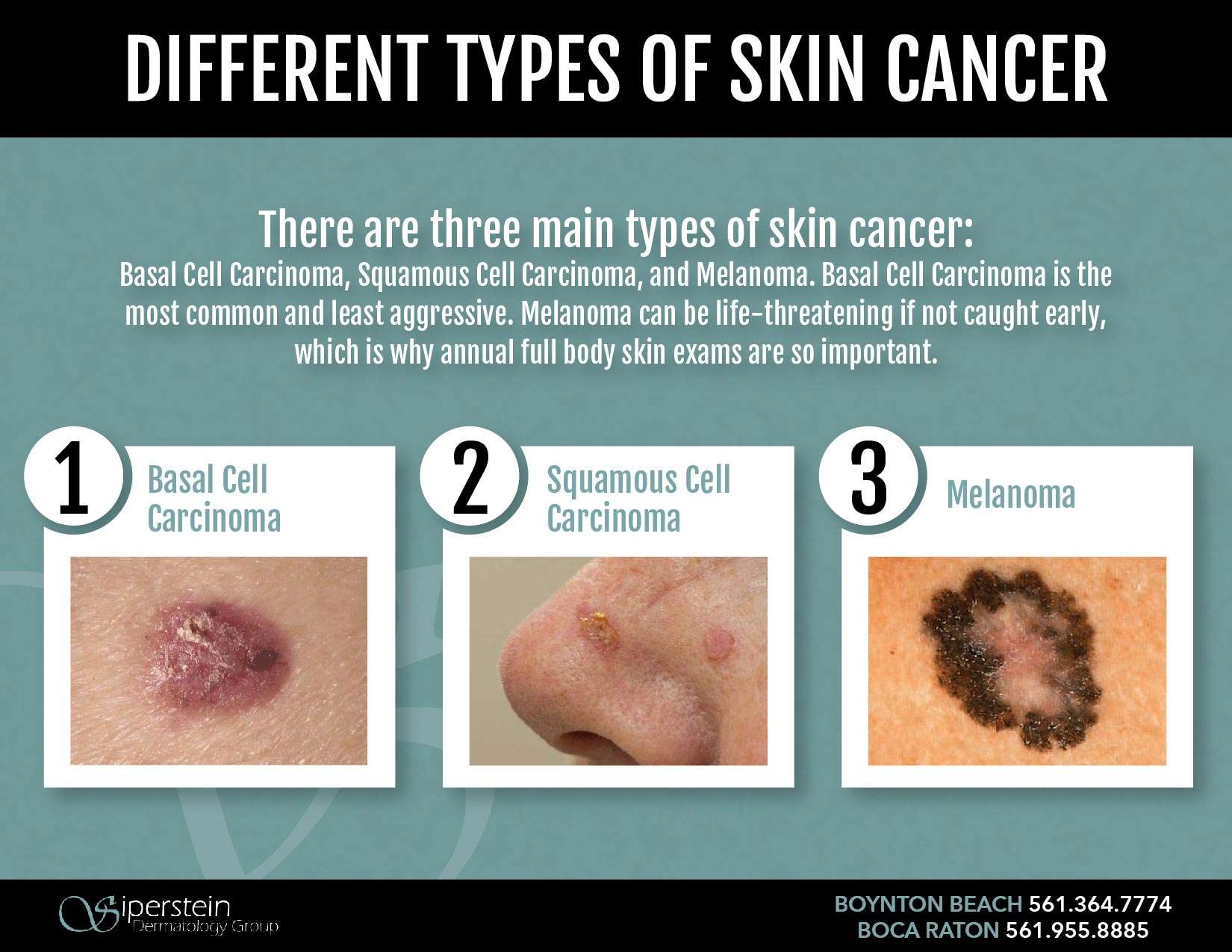
The different types of skin cancer are named after the type of skin cell they start from. There are three main types of skin cancer:
- basal cell carcinoma
- squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
- melanoma.
BCCs and SCCs are different from melanoma. They are called non-melanoma skin cancers.We have separate information about melanoma.
See also
The skin does many things. It:
- protects the body from injury and infection
- helps to control body temperature
- helps to control fluid loss
- gets rid of waste substances through the sweat glands.
The skin is divided into 2 main layers. The outer layer is the epidermis and the layer underneath is the dermis. Below these is a deeper layer of fatty tissue.
The epidermis contains several types of cells. Most of the epidermis is filled with cells called keratinocytes, also called squamous cells.
The lowest layer of the epidermis is called the basal layer. It contains rounder cells called basal cells.
The basal layer also contains skin cells called melanocytes which produce melanin. Melanin gives skin its natural colour.
Read Also: How Deadly Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
After Squamous Cell Cancer Of The Skin Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Skin Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the skin or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
Basal cell carcinoma of the skin rarely spreads to other parts of the body. Staging tests to check whether basal cell carcinoma of the skin has spread are usually not needed.
The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: