A Positive Sentinel Node Biopsy: What Happens
If the lymph-node biopsy finds melanoma cells, there are two options. If many cancer cells are present in many lymph nodes, then all the lymph nodes in that area may be surgically removed. If there are only a few cancer cells, your doctor may instead opt to monitor the lymph nodes through ultrasound every few months and start you on immunotherapy or targeted therapy, says Melinda L. Yushak, M.D., assistant professor in the department of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta.
How Does Stage 2 Melanoma Affect The Body
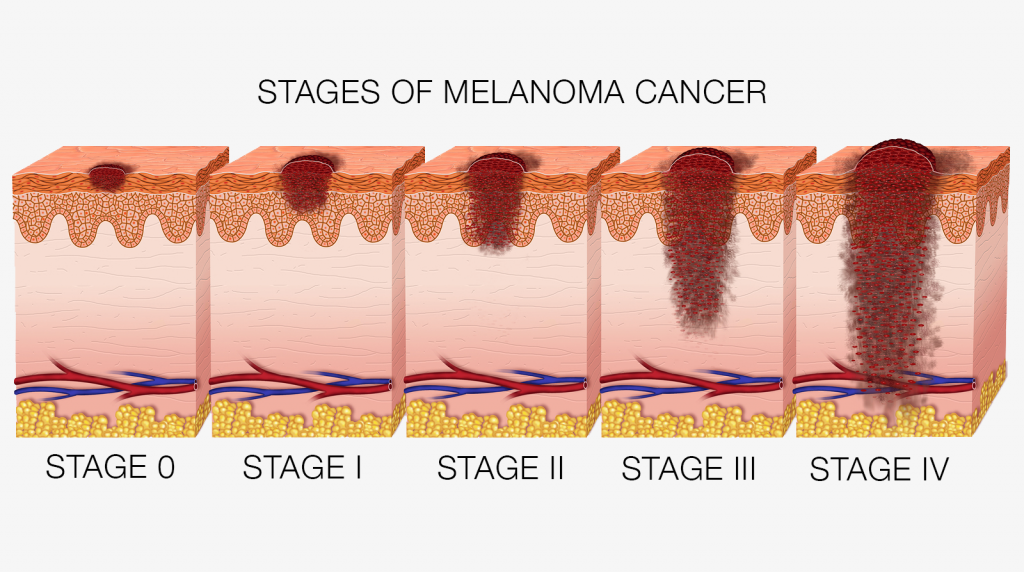
Stage 2 melanoma is caused by the overproduction of certain skin cells called melanocytes, which are the cells that produce skin pigment. This cell overgrowth usually starts on an existing mole on the skin or as a new skin growth. Generally, these growths are found in areas of skin that are exposed to sunlight, although they may be found in other parts of the body, including internal mucous membranes like those found in the esophagus and urinary tract. Stage 2 melanoma is the third stage of skin cancer, so growths have spread from the epidermis down through the dermis and in some cases, into the underlying fat and tissue. Sometimes, cells have begun to spread through the skin and enter other parts of the body. If left untreated, stage 2 melanoma can continue to spread rapidly throughout the body.
Mouse Models Mimic Metastasis Of Human Melanoma
Metastasis is a highly inefficient process in that the vast majority of cancer cells that try to migrate die before they ever have an opportunity to form a tumor, Dr. Morrison said.
Dr. Morrisons team found previously that one factor limiting the survival of melanoma cells circulating in the blood is that the cells experience a high level of oxidative stress. Oxidative stressan imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the bodycauses chemical reactions that can damage proteins, DNA, and lipids in cells and disrupt normal cell processes. However, precisely how oxidative stress kills circulating melanoma cells was not known.
For their studies, the team used a mouse model of metastasis created by transplanting melanoma cells from humans beneath the skin of specially bred mice with weakened immune systems. These mice were used to avoid having the transplanted human cells seen as foreign and attacked by the immune system. The team also used a second mouse model created by transplanting mouse melanoma cells into mice with normal immune systems.
Comparing these two mouse models let the researchers control for potential effects of the immune system on the spread of melanoma, Dr. Salnikow explained.
The study was supported in part by NCIs Patient-Derived Models of Cancer program, which promotes the development of animal models that more closely mirror how tumor cells behave in humans.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Deadliest Type Of Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2;basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage;3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones;or other organs in the body.
Skin Exam And Physical
If youve been diagnosed with melanoma, youve already had a skin biopsy. This biopsy was taken when you had part of the suspicious spot removed. After it was removed, a doctor looked at the spot under a microscope to find out if it contained cancer cells. This is currently the only way to tell if someone has skin cancer.
After getting the diagnosis, the next step is to get a complete skin exam and physical.
During the physical, your dermatologist will feel your lymph nodes. This is where melanoma usually goes when it begins to spread. It usually travels to the lymph nodes closest to the melanoma.
If there is a risk the cancer could have spread, your dermatologist may recommend that you have a lymph node biopsy. If a sentinel lymph node biopsy is recommended, it can be performed at the time of your surgery for melanoma.
After the skin exam and physical, your dermatologist may recommend testing, such as a CAT scan, MRI, or a blood test. These can also help detect spread.
Also Check: How Often Does Melanoma Spread To Lymph Nodes
Treatment Of Stage Iii Melanoma That Can Be Removed By Surgery
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage III melanoma that can be removed by surgery may include the following:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and some of the normal tissue around it. Skin grafting may be done to cover the wound caused by surgery. Sometimes lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy are done to check for cancer in the lymph nodes at the same time as the surgery to remove the tumor. If cancer is found in the sentinel lymph node, more lymph nodes may be removed.
- Surgery followed by immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors if there is a high risk that the cancer will come back.
- Surgery followed by targeted therapy with signal transduction inhibitors if there is a high risk that the cancer will come back.
- A clinical trial of immunotherapy with or without vaccine therapy.
- A clinical trial of surgery followed by therapies that target specific gene changes.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Treating Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage IV melanomas have already spread to distant lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
Metastases in internal organs are sometimes removed, depending on how many there are, where they are, and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab are typically the first drugs tried, especially in people whose cancer cells do not have BRAF gene changes. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Ipilimumab , a different type of checkpoint inhibitor, is not typically used by itself as the first treatment, although it might be combined with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. This slightly increase the chances that the tumor will shrink, although itâs also more likely to result in serious side effects, which needs to be considered carefully. People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects..
Itâs important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.
Also Check: What Is The Leading Cause Of Skin Cancer
I’ve Been Diagnosed With Melanomawhat Happens Next
Doctors use the TNM system developed by the American Joint Committee on Cancer to begin the staging process. Its a classification based on three key factors:
T stands for the extent of the original;tumor, its thickness or how deep it has grown and whether it has ulcerated.
What Is Breslow depth?
Breslow depth is a measurement from the surface of the skin to the deepest component of the melanoma.
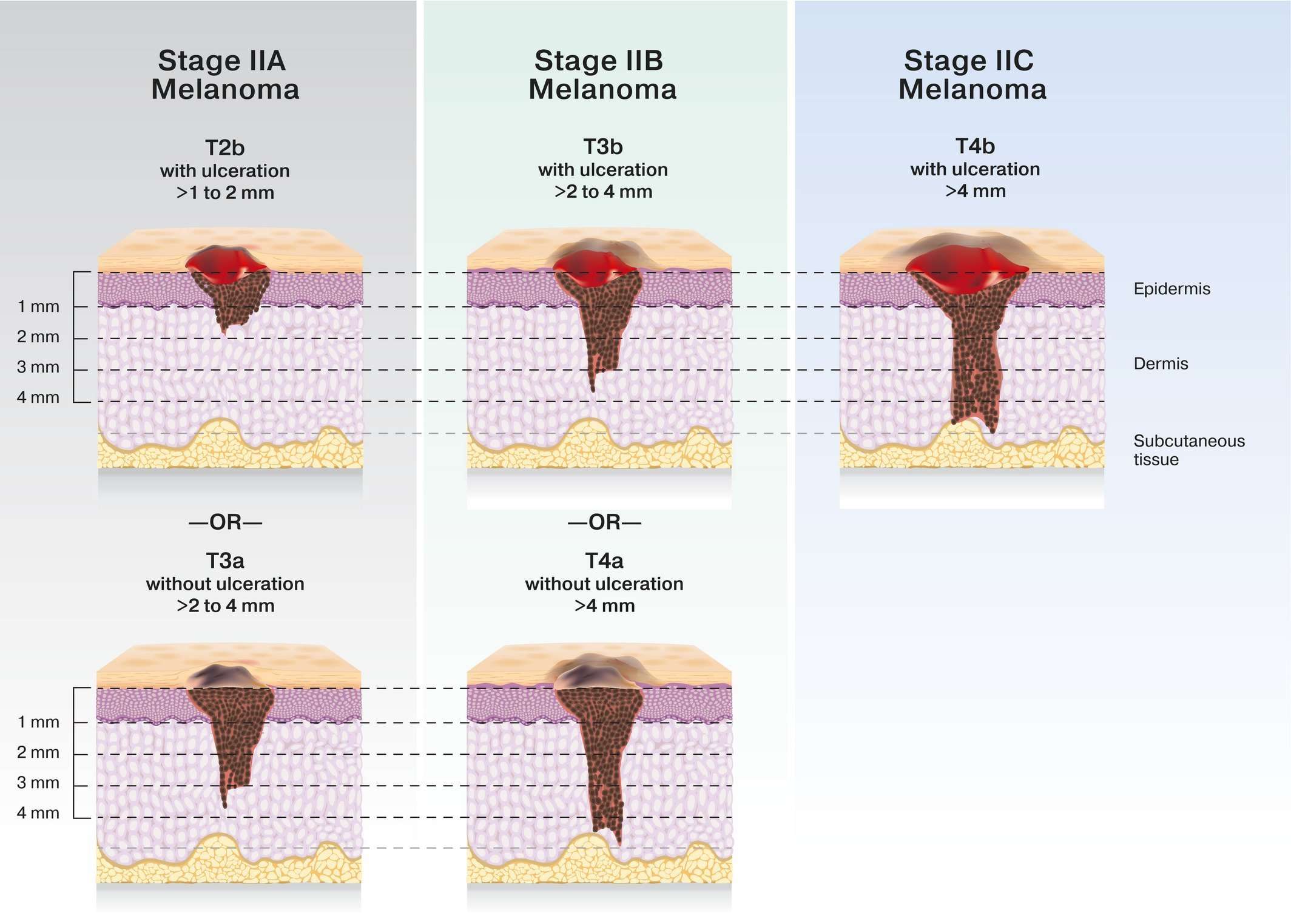
Tumor thickness: Known as Breslow thickness or Breslow depth, this is a significant factor in predicting how far a melanoma has advanced. In general, a thinner Breslow depth indicates a smaller chance that the tumor has spread and a better outlook for treatment success. The thicker the melanoma measures, the greater its chance of spreading.
Tumor ulceration: Ulceration is a breakdown of the skin on top of the melanoma. Melanomas with ulceration are more serious because they have a greater risk of spreading, so they are staged higher than tumors without ulceration.
N indicates whether or not the cancer has already spread to nearby lymph nodes. The N category also includes in-transit tumors that have spread beyond the primary tumor toward the local lymph nodes but have not yet reached the lymph nodes.
M represents spread or metastasis to distant lymph nodes or skin sites and organs such as the lungs or brain.
After TNM categories are identified, the overall stage number is assigned. A lower stage number means less progression of the disease.
Why Are There Melanoma Stages
There is a lot to say whether or not this is at a point in time where it can be treated by simply removing the freckle and never hearing of it again. Then again, if it spread to a more important organ in the body, there might not be a chance in saving yourself. How do you distinguish between one and the other?
- Choroidal Melanoma: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
- Amelanotic Melanoma Cytology, Treatments, Diagnosis, Pictures
Recommended Reading: How To Identify Skin Cancer
Stage I And Stage Ii Melanomas
Making a melanoma diagnosis means gathering as much information about your skin cancer as possible. One key step is determining the cancers stage, which is a measure of the amount and severity of cancer in the body. Staging helps your doctor understand how best to treat the cancer, and is used when discussing survival rates.
Following stage 0 , the degrees of melanoma range from stage I through stage IV, with higher numbers indicating further spreading of the cancer throughout the body.
There are three factors commonly used to determine melanoma staging, and theyre represented by the TNM system. The first factor is the severity of the primary tumor , which includes how thick the tumor is and whether the skin covering it has broken. The second factor is whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes . The third factor is whether the cancer has spread, or metastasized , to lymph nodes farther away in the body or other organs.
How Is Melanoma Treated
Your melanoma treatment will depend on the stage of the melanoma and your general health.
Surgery is usually the main treatment for melanoma. The procedure involves cutting out the cancer and some of the normal skin surrounding it. The amount of healthy skin removed will depend on the size and location of the skin cancer. Typically, surgical excision of melanoma can be performed under local anesthesia in the dermatologist’s office. More advanced cases may require other types of treatment in addition to or instead of surgery.
Treatments for melanoma:
- Melanoma Surgery: In the early stages, surgery has a high probability of being able to cure your melanoma. Usually performed in an office, a dermatologist numbs the skin with a local anesthetic and removes the melanoma and margins .
- Lymphadenectomy: In cases where melanoma has spread, removal of the lymph nodes near the primary diagnosis site may be required. This can prevent the spread to other areas of your body.
- Metastasectomy: Metastasectomy is used to remove small melanoma bits from organs.
- Targeted cancer therapy: In this treatment option, drugs are used to attack specific cancer cells. This targeted approach goes after cancer cells, leaving healthy cells untouched.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy includes treatments with high-energy rays to attack cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Immunotherapy: immunotherapy stimulates your own immune system to help fight the cancer.
Also Check: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like On Your Head
Diagnosis And Staging What It Means For You
How is melanoma diagnosed?
To diagnose melanoma, a dermatologist biopsies the suspicious tissue and sends it to a lab, where a dermatopathologist determines whether cancer cells are present.
After the disease is diagnosed and the type of melanoma is identified, the next step is for your medical team to identify the stage of the disease. This may require additional tests including imaging such as PET scans, CT scans, MRIs and blood tests.
The stage of melanoma is determined by several factors, including how much the cancer has grown, whether the disease has spread and other considerations. Melanoma staging is complex, but crucial. Knowing the stage helps doctors decide how to best treat your disease and predict your chances of recovery.
Number Of Metastatic Lymph Nodes Involved
If the melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes the risk of spread to other parts of the body is higher. The greater the number of lymph nodes containing melanoma, the less favourable the prognosis.
A sentinel node biopsy is a technique used to determine whether melanoma cells have spread to lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis of the skin primary lesion. The procedure involves the injection of a radioactive tracer by a radiologist , to show where the site and lymph node where the lymph fluid from the skin at the primary melanoma will flow. Afterwards, at the same time as the extra surgery for the primary melanoma a blue dye is injected around the site of the primary lesion. Using the guide from the radiologist a surgeon looks for the first lymph node to take up the dye. The lymph node is removed and sent to be examined by a histopathologist to determine if the node tests positive for melanoma. The procedure is considered when the Breslow thickness of the melanoma is more than 0.8mm.
Patients may develop lumps in the lymph node regions such as the neck, armpit and groin. This is lymph node metastasis.
You May Like: How To Remove Skin Cancer Yourself
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage squamous cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is assigned to one of the five squamous cell carcinoma stages, which are labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of squamous cell cancer are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage;1 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high risk features.
Stage 3;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
How Is Melanoma Staged
Melanoma stages are assigned using the TNM system.
The stage of the disease indicates how much the cancer has progressed by taking into account the size of the tumor, whether its spread to lymph nodes, and whether its spread to other parts of the body.
A doctor can identify a possible melanoma during a physical exam and confirm the diagnosis with a biopsy, where the tissue is removed to determine if its cancerous.
But more sophisticated technology, such as PET scans and sentinel lymph node biopsies, are necessary to determine the cancers stage or how far its progressed.
There are five stages of melanoma. The first stage is called stage 0, or melanoma in situ. The last stage is called stage 4. Survival rates decrease with later stages of melanoma.
Its important to note that survival rates for each stage are just estimates. Each person with melanoma is different, and your outlook can vary based on a number of different factors.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Difference Between Skin Cancer And Melanoma
After Melanoma Has Been Diagnosed Tests May Be Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Skin Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out whether cancer has spread within the skin or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment.
For melanoma that is not likely to spread to other parts of the body or recur, more tests may not be needed. For melanoma that is likely to spread to other parts of the body or recur, the following tests and procedures may be done after surgery to remove the melanoma:
The results of these tests are viewed together with the results of the tumor biopsy to find out the stage of the melanoma.