How Does The Doctor Know I Have Skin Cancer
Basal and squamous skin cancer may look like:
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas that look a lot like a scar
- Raised reddish patches that might itch
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Small, pink or red, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas
- Pink growths or lumps with raised edges and a lower center
- Open sores that dont heal, or that heal and then come back
- Wart-like growths
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Turn Into Melanoma
Basal cell carcinoma does not progress into melanoma. Each is a separate and distinct type of skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer and one of two major nonmelanoma skin cancer types . The cancerous cells originate in the lower layers of the epidermis, grow slowly and rarely spread to other parts of the body.
Melanoma is a rare but aggressive type of skin cancer that originates in the melanocytes. These skin cells, which are found in the deepest part of the epidermis, produce melanin, the pigment that gives the skin its color.
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas, similar to a scar.
- Raised reddish patches that might be itchy.
- Small, pink or red, translucent, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas.
- Pink growths with raised edges and a lower area in their center, which might contain abnormal blood vessels spreading out like the spokes of a wheel.
- Open sores which may have oozing or crusted areas that dont heal, or that heal and then come back.
Read Also: Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Curable
What To Do If Your Dog Has A Tumor On His Leg
Likewise, if your dog has a tumor on one of its legs, your veterinarian will want to take x-rays of the leg to see if the tumor has spread to the bone underneath it. Standard biopsies will be taken of the growth or sore. This is the best way to determine exactly what kind of tumor your dog has.
Recent Posts
How Is Actinic Keratosis Diagnosed
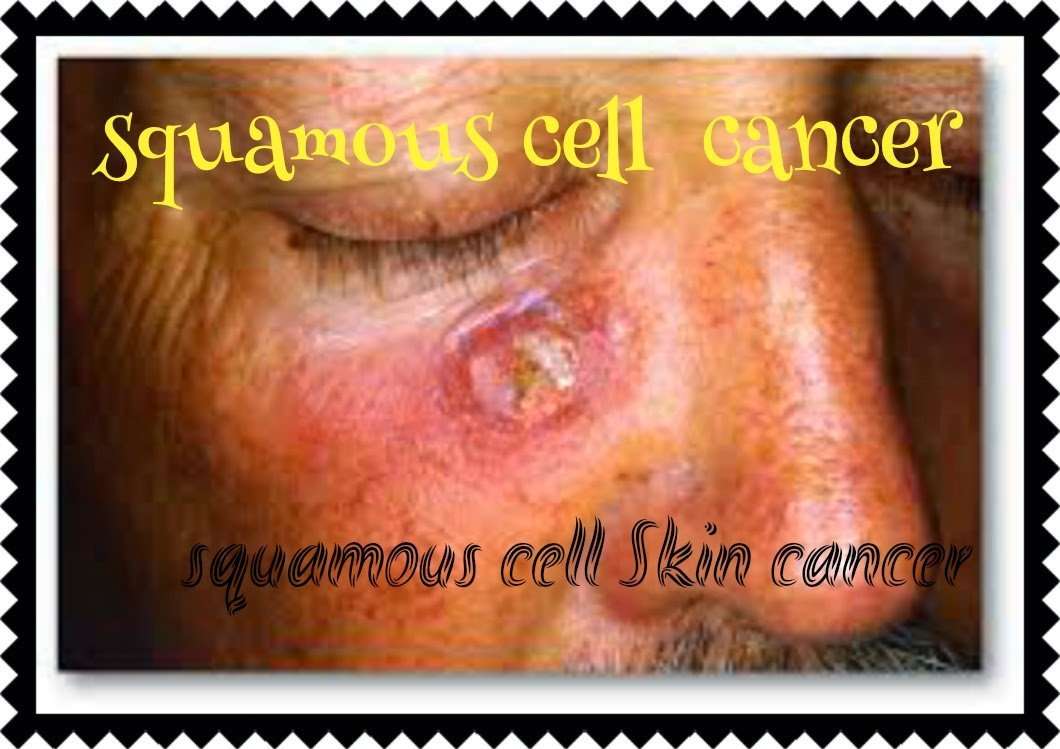
Healthcare providers can often diagnose an actinic keratosis by looking at and feeling the area on your skin. But sometimes an actinic keratosis can be hard to tell apart from skin cancer. Your healthcare provider might remove the area of skin to have it checked under a microscope. This is known as a skin biopsy.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Scientific Name For Skin Cancer
What Causes Squamous Cell Cancer
Most squamous cell skin cancers are caused by repeated and unprotected skin exposure to ultraviolet light from sunlight and tanning beds.;
Risk factors for developing squamous cell skin cancer include:;
- Ultraviolet light exposure
- Having light-colored skin
- Excisional biopsy: removes the entire tumor
- Incisional biopsy: removes only a portion of the tumor
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
SCC is generally faster growing than basal cell cancers. About 20 out of every 100;skin cancers are SCCs. They begin in cells called keratinocytes, which are found in the epidermis.
Most SCCs develop on areas of skin exposed to the sun. These areas include parts of the head, neck, and on the back of your hands and forearms. They can also develop on scars, areas of skin that have been burnt in the past, or that have been ulcerated for a long time.
SCCs don’t;often spread. If they do, it’s;most often to the deeper layers of the skin. They;can spread to nearby;lymph nodes;and other parts of the body, but this is unusual.
Read Also: How To Know You Have Skin Cancer
What Happens If Precancers Go Untreated
As the name suggests, precancers are damaged skin cells that arent considered cancerous, but if they are left untreated, these lesions are at high risk to become skin cancer. There are two main types of precancerous skin conditions: actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi. Actinic keratosis looks like a rough, scaly patch of the skin that is usually red or brown. This condition may develop into squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Nevi are moles, and dysplastic nevi is a term that means a mole is abnormal. Dysplastic nevi may develop into melanoma without proper treatment. While precancerous skin cancers are not malignant on their own, the potential to develop into life-threatening forms of this condition means they need to be evaluated regularly.
You May Like: Can Skin Cancer Look Like Psoriasis
Understanding Your Stage Of Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
The stage is based on the size of the tumor, how deeply into the skin it has grown, and whether cancer has spread beyond the tumor to the lymph nodes. Your doctor will look at the results of the biopsy to determine the stage. If you have squamous cell skin cancer, your doctor may also recommend imaging such as CT or PET-CT scan, or testing lymph nodes near the tumor to see if the cancer has spread beyond the skin.
Most non-melanoma skin cancers are Stage 0 or Stage 1. Stage 3 and 4 are relatively rare. Based on the type of cancer, the stage of cancer, your overall health, and other factors, your doctor works with you to develop a treatment plan.
Read Also: How Fast Does Melanoma Metastasis
What It Looks Like
Squamous cell cancer involves the runaway growth of keratinocytes, cells in the outermost layer of skin, which produce the protein keratin. Squamous means scaly; in 60%80% of cases, the lesions emerge on or near scaly patches called actinic keratoses that develop from sun-damaged skin.
To continue reading this article, you must log in.
- Research health conditions
- Prepare for a doctors visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
What Is Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell skin cancer is one of the most common types of skin cancer that occurs when cells in the top layer of skin grow out of control.;
There are 3 main types of cells in the top layer of the skin where cancer can form:
- Squamous cells
- These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, that constantly shed as new ones form
- These cells can develop into squamous cell skin cancer;
- About 20% of skin cancers are squamous cell carcinomas;
Squamous cell cancer cannot turn into melanoma since each type of cancer arises from different types of cells in the skin. It is possible, however, to have both squamous cell skin cancer and melanoma skin cancer at the same time.
You May Like: What Type Of Skin Cancer Is Deadly
How Do You Tell The Difference Between Skin Cancer And A Bug Bite
Its not always easy. A painful patch on your skin could be a sign of skin cancer, but it could also be an insect bite.; If its an itchy spot, it could be a sign of skin cancer, but it could also be an insect bite or an allergic reaction to something.
The Skin Cancer Foundation provides a list of five warning signs of skin cancer1:
- A scar-like area that is white, yellow or waxy, with the skin appearing shiny and taut.; This may indicate the presence of an invasive basal cell carcinoma.
- An open sore; this area may bleed or ooze, scab over, then continue the process and never fully heal. This is a very common sign of basal cell carcinoma.
- A reddish patch or irritated area. These areas are frequently found on the face, chest, shoulders, arms or legs. They may itch or hurt, or there may be no discomfort.
- A shiny bump or nodule; this can be pearly or clear in color, but can also be pink, red, or white, or even tan, black or brown in dark-haired people and can be confused with a mole.
- A pink growth with an elevated border and crusted indentation in the middle, which slowly grows larger. Blood vessels may appear on the surface as the area grows.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Causes
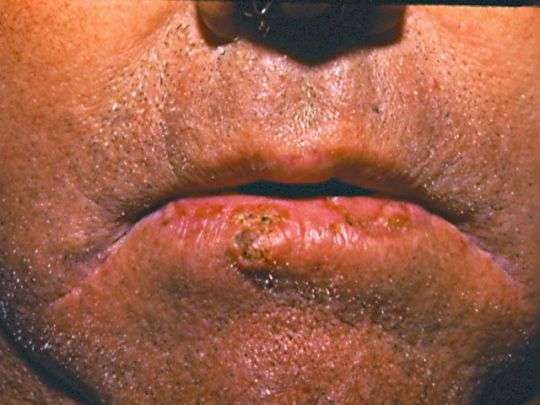
Exposure to ultraviolet rays, like the ones from the sun or a tanning bed, affects the cells in the middle and outer layers of your skin and can cause them to make too many cells and not die off as they should. This can lead to out-of-control growth of these cells, which can lead to squamous cell carcinoma.
Other things can contribute to this kind of overgrowth, too, like conditions that affect your immune system.
Recommended Reading: How To Say Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Melanoma: The Deadliest Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, because it tends to spread if its not treated early.
This cancer starts in the melanocytes cells in the epidermis that make pigment.
About 100,350 new melanomas are diagnosed each year.
Risk factors for melanoma include:
- Having fair skin, light eyes, freckles, or red or blond hair
- Having a history of blistering sunburns
- Being exposed to sunlight or tanning beds
- Living closer to the equator or at a higher elevation
- Having a family history of melanoma
- Having many moles or unusual-looking moles
- Having a weakened immune system
Melanoma can develop within a mole that you already have, or it can pop up as a new dark spot on your skin.
This cancer can form anywhere on your body, but it most often affects areas that have had sun exposure, such as the back, legs, arms, and face. Melanomas can also develop on the soles of your feet, palms of your hands, or fingernail beds.
Signs to watch out for include:
- A mole that changes in color, size, or how it feels
- A mole that bleeds
RELATED: The Difference Between Chemical and Mineral Sunscreen
What Are The Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is classified into the following stages, which are partly based on how far the cancer has spread throughout the body:
- Stage 0 Squamous cell carcinoma develops in the squamous cells, which are located in the epidermis . During Stage 0, the cancer hasnt spread beyond the epidermis.
- Stage 1 When squamous cell carcinoma progresses to Stage 1, it means that the cancer has spread deeper into the skin, but not into any lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 2 A Stage 2 classification means that, in addition to progressing deeper into the skin, the cancer also displays at least one high-risk feature. This might include metastasizing to the lower skin layers or the nerves. However, at this stage, the cancer still hasnt spread to lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 3 Once squamous cell carcinoma reaches Stage 3, the cancer has spread into lymph nodes but not any other tissues or organs.
- Stage 4 This is the final stage of squamous cell carcinoma, where the cancer has spread to at least one distant organ, whether that be the brain, the lungs or a separate area of skin.
If you think you might have squamous cell carcinoma, its important to seek prompt medical attention to minimize the risk of cancer spread. The specialists in Moffitt Cancer Centers Cutaneous Oncology Program can provide you with the comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services you need. Call or complete our new patient registration form online to request an appointment.
- BROWSE
Recommended Reading: How Serious Is Melanoma Cancer
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Keeping Cancer In Check
Chronic exposure to the sun or intermittent sunburns can lead to skin cancer. Skin cancer risk doubles with five or more sunburns in a lifetime, but just one bad sunburn can double the risk of melanoma. While skin cancer is uncommon in African Americans, Latinos and Asians, it can also be more deadly because they are often diagnosed later in the course of the disease.
Its important to examine your skin regularly. You should report any changes in an existing mole or any new moles to your physician. People with fair complexions have the highest risk of developing skin cancer, but everyone should avoid the sun and practice safety measures to protect their skin.
The American Cancer Society;recommends the Slip, Slop, Slap and Wrap policy. When you go out in the sun, slip on a shirt, slop on sunscreen, slap on a hat and wrap on sunglasses to protect your eyes and the sensitive skin around them.
Exposure to the UV rays of tanning lamps is not safe. Tanning lamps give out UV rays, which can cause long-term skin damage and can contribute to skin cancer. Tanning bed use has been linked with an increased risk of melanoma, especially for people under 30. Most doctors and health organizations recommend not using tanning beds and sun lamps.
You May Like: What Is Stage 4 Malignant Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinomas Topical Treatment
Topical treatments can be successful on superficial basal cell carcinomas with little depth. These drugs work by inflaming the area where they are applied. The body responds by sending white blood cells to attack the inflammation. These white blood cells go after the mutated basal cells. Aldara, Efudex, and Fluoroplex are three of the most used drugs.
If You Are Experiencing An Emergencyplease Call 911 Immediately
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | ||
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category “Analytics”. |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category “Functional”. |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category “Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category “Necessary”. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category “Performance”. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Types Of Skin Cancers Are Deadly
Skin cancers are some of the most complex and serious conditions treated by dermatologists, and the U.S. Dermatology Partners team takes our role in preventing and treating all types of skin cancers very seriously. While some forms of skin cancer are not typically life-threatening, without proper treatment, there are serious health risks associated with all forms of skin cancer. According to Dr. Jessica Dorsey of U.S. Dermatology Partners in Cedar Park, Texas, Most skin cancers are slow-growing and unlikely to spread to other parts of the body, but without treatment, just about any form of skin cancer has the potential to be destructive or even fatal. Keep reading to learn more about the importance of regular screenings to catch skin cancer in the earliest stages and prevent the severe repercussions of untreated skin cancers.
What Is The Treatment For Squamous Cell Cancer
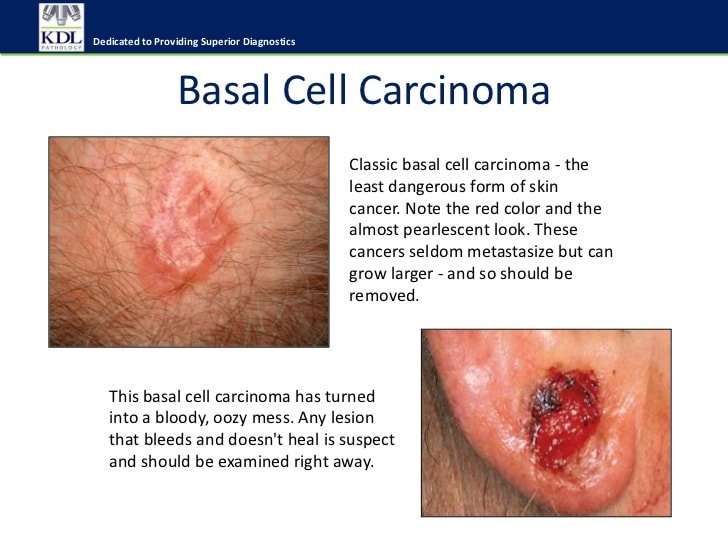
Treatment for squamous cell cancer may include one or more of the following:
- Surgery;
- Excision: removes the entire tumor
- Curettage and electrodesiccation: cancer is removed by scraping it with a long, thin instrument with a sharp looped edge on one end and the area is treated with an electric needle to destroy any remaining cancer cells
- Mohs surgery : removes one layer of skin at a time, samples are checked for cancer, and the process is repeated until there are no cancer cells in the skin sample. Process can be slow but can leave more tissue intact.
- Lymph node surgery
- Lymph node dissection: many nodes are removed;
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma