What Are The Ten Most Common Cancers
The most common type of cancer women and men both can have is basal or squamous cell skin cancer. These tend not to be fatal, though some percentage of people with a basal or squamous cell cancer will at a later point develop melanomas. In considering how common a cancer is, the Centers for Disease Control leaves out the above two cancers.
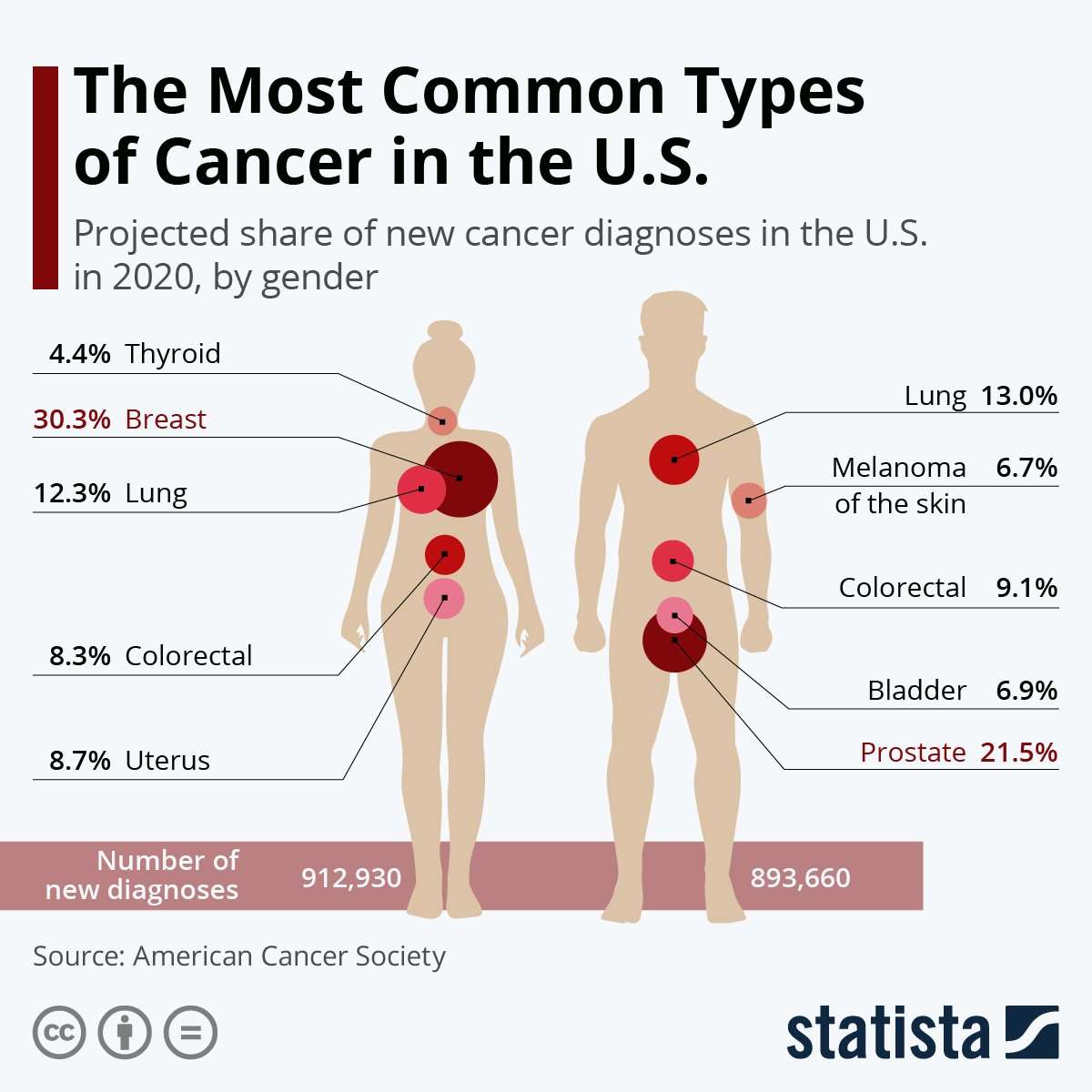
The CDC addresses common cancer by looking at incidence rates. There are separate lists for men and women, since women and men have separate body parts. For example, a woman doesn’t have a prostate and a man doesn’t have a uterus or cervix. Other statistics in determining common cancers include race and age, as well as region. These factors are of value when evaluating risk for cancer. Behavior must also be taken into account since certain high risk behaviors like alcoholism and smoking increase ones risk for certain forms of cancer, particularly cancer of the lungs and liver.
The statistics listed here are the total statistics for common cancers. This means that race, behavior and location are not taken into account. Gender is taken into account for the above-mentioned reasons. These statistics do not include basal or squamous cell cancer.
Skin Cancer: Types & Stages
Basal and squamous cell cancers
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers are by far the most common cancers of the skin. Both are found mainly on parts of the body exposed to the sun, such as the head and neck. These cancers are strongly related to a persons sun exposure.
Basal and squamous cell cancers are much less likely than melanomas to spread to other parts of the body and become life threatening. Still, its important to find and treat them early. If left alone, they can grow larger and invade nearby tissues and organs, causing scarring, deformity, or even loss of function in some parts of the body. Some of these cancers can spread if not treated, and in some cases they can even be fatal.
Melanomas
Melanomas are cancers that develop from melanocytes, the cells that make the brown pigment that gives skin its color. Melanocytes can also form benign growths called moles.
Melanomas can occur anywhere on the body, but are more likely to start in certain areas. The trunk is the most common place in men. In women, the legs are the most common site. The neck and face are other common places for melanoma to start.
Melanomas are not as common as basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers, but they can be far more serious. Like basal cell and squamous cell cancers, melanoma is almost always curable in its early stages. But if left alone, melanoma is much more likely to spread to other parts of the body, where it can be very hard to treat.
Other skin cancers
How To Identify Skin Cancer Vs Age Spots
Finding a strange spot on your body can be pretty scary. You dont know how long it will be there, if its dangerous, or what it even is. The best thing you can do when you find weird-looking spot on your body is to visit your dermatologist.
While youre waiting to see a doctor, you may want to better understand two common types of skin spots: skin cancer and age spots, also known as liver spots. Its easy to get the two confused, so lets take a closer look at them.
You May Like: Should I Be Worried About Basal Cell Carcinoma
Read Also: What Is Precancerous Skin Cancer
Melanomas That Could Be Mistaken For A Common Skin Problem
Melanoma that looks like a bruise
Melanoma can develop anywhere on the skin, including the bottom of the foot, where it can look like a bruise as shown here.
Melanoma that looks like a cyst
This reddish nodule looks a lot like a cyst, but testing proved that it was a melanoma.
Dark spot
In people of African descent, melanoma tends to develop on the palm, bottom of the foot, or under or around a nail.
Did you spot the asymmetry, uneven border, varied color, and diameter larger than that of a pencil eraser?
Dark line beneath a nail
Melanoma can develop under a fingernail or toenail, looking like a brown line as shown here.
While this line is thin, some are much thicker. The lines can also be much darker.
Read Also: What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
How Can I Help Prevent Sun Damage And Ultimately Skin Cancer
Nothing can completely undo sun damage, although the skin can sometimes repair itself. So, its never too late to begin protecting yourself from the sun. Your skin does change with age for example, you sweat less and your skin can take longer to heal, but you can delay these changes by limiting sun exposure.
Maintaining healthy skin
- Stop smoking: People who smoke tend to have more wrinkles than nonsmokers of the same age, complexion, and history of sun exposure. The reason for this difference is unclear. It may be because smoking interferes with normal blood flow in the skin.
- Apply sunscreen with a sun protection factor of 30 or greater 30 minutes before sun exposure and then every 2 to 3 hours thereafter. Reapply sooner if you get wet or perspire significantly.
- Select cosmetic products and contact lenses that offer UV protection.
- Wear sunglasses with total UV protection.
- Avoid direct sun exposure as much as possible during peak UV radiation hours between 10 am and 4 pm.
- Perform skin self-exams regularly to become familiar with existing growths and to notice any changes or new growths.
- Relieve dry skin using a humidifier at home, bathing with soap less often , and using a moisturizing lotion.
- Become a good role model and foster skin cancer prevention habits in your child. Eighty percent of a persons lifetime sun exposure is acquired before age 18.
Understanding UV index
11 or higher : Extreme
Also Check: How To Treat Melanoma Skin Cancer Naturally
The Risks The Causes What You Can Do
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is caused by DNA damage that leads to abnormal changes in the squamous cells in the outermost layer of skin.
Understanding what causes this damage and the factors that increase your risk of developing SCC can help you detect the disease early or prevent it from happening in the first place.
These factors increase your SCC risk:
- Unprotected exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
- Weakened immune system due to illness or certain immunosuppressive medications.
- History of skin cancer including basal cell carcinoma .
- Age over 50: Most SCCs appear in people over age 50.
- Fair skin: People with fair skin are at an increased risk for SCC.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop SCC.
- Sun-sensitive conditions including xeroderma pigmentosum.
- Chronic infections and skin inflammation from burns, scars and other conditions.
How To Spot An Scc
SCC of the skin can develop anywhere on the body but is most often found on exposed areas exposed to ultraviolet radiation like the face, lips, ears, scalp, shoulders, neck, back of the hands and forearms. SCCs can develop in scars, skin sores and other areas of skin injury. The skin around them typically shows signs of sun damage such as wrinkling, pigment changes and loss of elasticity.
SCCs can appear as thick, rough, scaly patches that may crust or bleed. They can also resemble warts, or open sores that dont completely heal. Sometimes SCCs show up as growths that are raised at the edges with a lower area in the center that may bleed or itch.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Tell If You Have Skin Cancer
It May Grow Slowly And It’s Typically Treatable
When malignant cancer cells form and grow within a person’s breast tissue, breast cancer occurs. Being armed with information is vital to begin the fight. The earlier the detection of prostate cancer, the better the patient’s chance of survival is. Not only does the stage tell you how serious the disease is, but it can help you and. Although the percentage of cases in men is much lower than in women, male breast cancer accounts for a por. But hearing the words can still be scary. A cancer diagnosis can leave you unable to comprehend anything else your doctor says, but it’s important to pay attention to what stage of cancer you have. Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer diagnosed in men. The pancreas is located behind the stomach, so having pancreatic cancer doesn’t involve a palpable mass that you can feel. Breast cancer is the second most common cancer found in women after skin cancer but that doesn’t mean men aren’t at risk as well. If breast cancer is diagnosed at an early enough stage, it’s treatable. A diagnosis of lung cancer naturally causes some overwhelming emotions, but you don’t have to let those emotions get the best of you. There are a number of different treatments doctors recommend.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The majority of skin cancers can be prevented. Besides the physician, the nurse and the pharmacist play a vital role in patient education. The patient must be told to avoid excessive sun exposure and use sunscreen when going out. Tanning beds should be avoided and one should wear protective clothing that covers the arms and upper body. Further, the patient must be told to avoid the sun between 10 am to 4 pm. Finally, all patients should be taught how to perform a skin examination and see a healthcare provider if there is any skin lesion that suddenly changes in its growth or shape. To date, there is no evidence that the use of herbs or other supplements can prevent skin cancer, and the patient should be told not to rely on these treatments.
Outcomes
Small squamous cell cancer lesions can be excised and are not fatal but they can add significant morbidity depending on their location. Most squamous cell cancers around the head and neck region require complex surgery, which even in the best of hands can lead to poor cosmesis. Further, the cost of management of these cancers is escalating each year, and the patient is often burdened with huge copayments. Advanced squamous cell cancers have a poor prognosis with a 5-year survival rate below 40%. With larger lesions, tumor recurrence is also a problem despite wide excision. Local recurrences have been reported in 10-18% of cases.
You May Like: What Is Renal Carcinoma Cancer
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Squamous cell skin cancer is mainly caused by cumulative ultraviolet exposure from the sun, according to Dr. Leffell.
Daily year-round exposure to the suns UV light and intense exposure in the summer months add to the damage that causes this type of cancer, he says. People at the highest risk for squamous cell skin cancer tend to have light or fair-colored skin blue, green or gray eyes a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Squamous cell cancers occur four times more frequently in men than in women.
Although squamous cell cancer can be more aggressive than basal cell cancer, the risk of this type of cancer spreading is lowas long as the cancer is treated early, Dr. Leffell says. He notes that the lesions must be treated with respect because they may grow rapidly and invade deeply. While it is more difficult to treat squamous cell cancer that has metastasized, up to half of cases can be cured.
In a small percentage of cases, squamous cell skin cancer can grow along the tiny nerves in the skin. In this very serious condition, the squamous cell cancer of the face or scalp can travel along the nerves and spread to the brain.
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
SCC is generally faster growing than basal cell cancers. About 20 out of every 100 skin cancers are SCCs. They begin in cells called keratinocytes, which are found in the epidermis.
Most SCCs develop on areas of skin exposed to the sun. These areas include parts of the head, neck, and on the back of your hands and forearms. They can also develop on scars, areas of skin that have been burnt in the past, or that have been ulcerated for a long time.
SCCs don’t often spread. If they do, it’s most often to the deeper layers of the skin. They can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other parts of the body, but this is unusual.
Recommended Reading: Does Melanoma Itch Or Hurt
What Kind Of Treatment Will I Need
There are many ways to treat melanoma. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
Most early stage melanomas can be treated with surgery alone. More advanced cancers need other treatments.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage of the cancer
- The results of lab tests on the cancer cells
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the melanoma or help in some way
- Your age
What Is Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer

Nonmelanoma skin cancers are the most common types of cancer. Theyre so common that doctors dont even report many of them to the cancer registries, which track cancer incidence and survival rates.
Research suggests that there are 5.4 million nonmelanoma skin cancers diagnosed every year in the United States. However, some patients are diagnosed and treated for multiple lesions simultaneously or repeatedly, so the number is more like 3.3 million.
Cancers occur when cells in the body start to grow out of control due to changes in their genetic material called mutations. These changes add up over time, so cancers grow more common as you age. This is especially true for skin cancers, which are mainly due to mutations caused by cumulative UV exposurethe longer you live, the more UV exposure you get.
The mutated cells may look and act differently than the cells around them, forming lesions or tumors. Cancer cells can break away from these tumors and spread to other parts of the body, though this is uncommon with nonmelanoma skin cancers.
While exposure to UV rays is an important risk factor for most people, there are several genetic mutations that can play a role in increasing your risk of developing nonmelanoma skin cancers.
Recommended Reading: What Race Is More Likely To Get Skin Cancer
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
Melanoma is a skin cancer that can show up on the skin in many ways. It can look like a:
-
Changing mole
-
Spot that looks like a new mole, freckle, or age spot, but it looks different from the others on your skin
-
Spot that has a jagged border, more than one color, and is growing
-
Dome-shaped growth that feels firm and may look like a sore, which may bleed
-
Dark-brown or black vertical line beneath a fingernail or toenail
-
Band of darker skin around a fingernail or toenail
-
Slowly growing patch of thick skin that looks like a scar
Early melanoma
This early melanoma could be mistaken for a mole, so its important to look carefully at the spots on your skin.
Scc Is Mainly Caused By Cumulative Uv Exposure Over The Course Of A Lifetime
If youve had a basal cell carcinoma you may be more likely to develop a squamous cell skin carcinoma, as is anyone with an inherited, highly UV-sensitive condition such as xeroderma pigmentosum.
Chronic infections, skin inflammation, HIV and other immune deficiency diseases, chemotherapy, anti-rejection drugs used in organ transplantation, and excessive sun exposure can all lead to a risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Occasionally, squamous cell carcinomas arise spontaneously on what appears to be normal, healthy skin. Some researchers believe the tendency to develop these cancers can be inherited.
SCCs may occur on all areas of the body including the mucous membranes and genitals, but are most common in areas frequently exposed to the sun:
- Ears
- Previous BCC or SCC
- Chronic inflammatory skin conditions or chronic infections
But anyone with a history of substantial sun exposure is at increased risk. Those whose occupations require long hours outside or who spend their leisure time in the sun are also at risk.
Don’t Miss: How To Prevent Melanoma Cancer
What Is Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is a common skin cancer that typically develops in chronic sun-exposed areas of your body. This type of skin cancer is usually not nearly as aggressive as melanoma and is uncontrolled growth of cells in the epidermis of your skin.
It can become disfiguring and sometimes deadly if allowed to grow. Squamous cell carcinomas are at least twice as frequent in men as in women. They rarely appear before age 50 and are most often seen in individuals in their 70s.
An estimated 700,000 cases of SCC are diagnosed each year in the United States, resulting in approximately 2,500 deaths.
The Stats Point To Greater Mortality Risk For Dark Skin
Its true that, in general, skin cancer is a greater risk for light-skinned individuals. A 2014 analysis by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showed that:
Among men, Caucasian men had the highest rate of getting melanoma of the skin, followed by American Indian/Alaska Native, Hispanic, Asian/Pacific Islander, and African-American men.
Among women, Caucasian women had the highest rate of getting melanoma of the skin, followed by Hispanic, American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian/Pacific Islander, and African-American women.
While the risk of skin cancer is lower for those with darker skin, the five-year survival rate for melanoma for African Americans is 73 percent, compared with 91 percent for Caucasians, according to the American Academy of Dermatology.
Many attribute this gap to lower awareness, and, as a result, later detection and skin cancer that is harder to treat. The Skin Cancer Foundation cites a study that found: Late-stage melanoma diagnoses are more prevalent among minority patients than Caucasian patients 52 percent of non-Hispanic dark-skinned patients and 26 percent of Hispanic patients receive an initial diagnosis of advanced stage melanoma, versus 16 percent of non-Hispanic light-skinned patients.
Latinos, Chinese, and Japanese Asians tend to develop basal cell carcinoma, the most common skin cancer. But the second most common, squamous cell carcinoma, is more frequent among African Americans and Asian Indians.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Skin Cancer From Drawing On Yourself