Is Hepatocellular Disease The Same As Hepatocellular Carcinoma
liver cancerhepatocellular carcinomaHepatocellular carcinomachronic liver diseasescirrhosishepatitishepatitis
. Besides, what does hepatocellular disease mean?
Hepatocellular carcinoma: A cancer arising from the liver cells . Cirrhosis may be caused by viral hepatitis, primarily hepatitis B and C, alcohol abuse, hemochromatosis, certain autoimmune diseases of the liver, and other diseases that result in chronic inflammation of the liver.
Subsequently, question is, is hepatocellular carcinoma benign or malignant? A hemangioma is a non-cancerous tumor that consists of an overgrowth of blood vessels. Another benign tumor that can occur in the liver is focal nodular hyperplasia. A liver hemangioma and focal nodular hyperplasia are the two most common tumors of the liver.
Similarly, you may ask, is hepatocellular disease always cancer?
Liver cancer is cancer that begins in the cells of your liver. The most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma, which begins in the main type of liver cell . Other types of liver cancer, such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, are much less common.
Is hepatocellular carcinoma a fast growing cancer?
Liver Cancer: Hepatocellular CarcinomaHepatocellular cancers occur in two forms: As an isolated, growing tumor that only spreads late in the disease. As small cancer nodules that are spread throughout the liver. This more common pattern is often seen in people with cirrhosis of theliver.
What Are Symptoms Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
There are many conditions with the same symptoms as hepatocellular carcinoma. Having one or more of these symptoms doesnt mean you have hepatocellular carcinoma. But talk to your healthcare provider if you have these symptoms. Theyll identify and treat the condition that caused your symptoms. Potential hepatocellular symptoms include:
- Youre losing weight without trying.
- You feel very full after a small meal, or you dont have much appetite.
- Youre nauseous and vomiting.
- You notice a fullness or knot under your ribs on your right side. This might indicate your liver is enlarged.
- You notice fullness under your ribs on your left side. This might be a sign your spleen is enlarged.
- You have stomach pain or pain near your right shoulder blade.
- Your stomach feels swollen, as if its filling up with fluid.
- Your skin itches.
- Your eyes and skin are turning sallow or yellow. This might be a sign you have jaundice.
What Is Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form of liver cancer. It is a serious illness that can be life-threatening. If it diagnosed early, hepatocellular carcinoma can be treated with surgery to remove the cancerous tumor or with a liver transplant. Other treatments can shrink the tumor or slow its growth and relieve your symptoms. Hepatocellular carcinoma is linked to cirrhosis of the liver and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease . People who have cirrhosis or NAFLD should be regularly checked for signs of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Read Also: Well-differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
How Does Hepatocellular Carcinoma Affect My Body
Over time, hepatocellular carcinoma can cause liver failure. Before that happens, however, hepatocellular carcinoma can keep your liver from managing your bodys vital functions. Among other things, your liver:
- Keeps track of your bodys nutrients, converting them into substances your body can use, storing and delivering them to your cells as needed.
- Gathers toxic substances, making sure they are harmless or released from your body.
- Supports healthy blood flow, producing substances that help your blood to clot and removing bacteria that cause infection.
Box 1 Experimental Animal Models Of Hcc
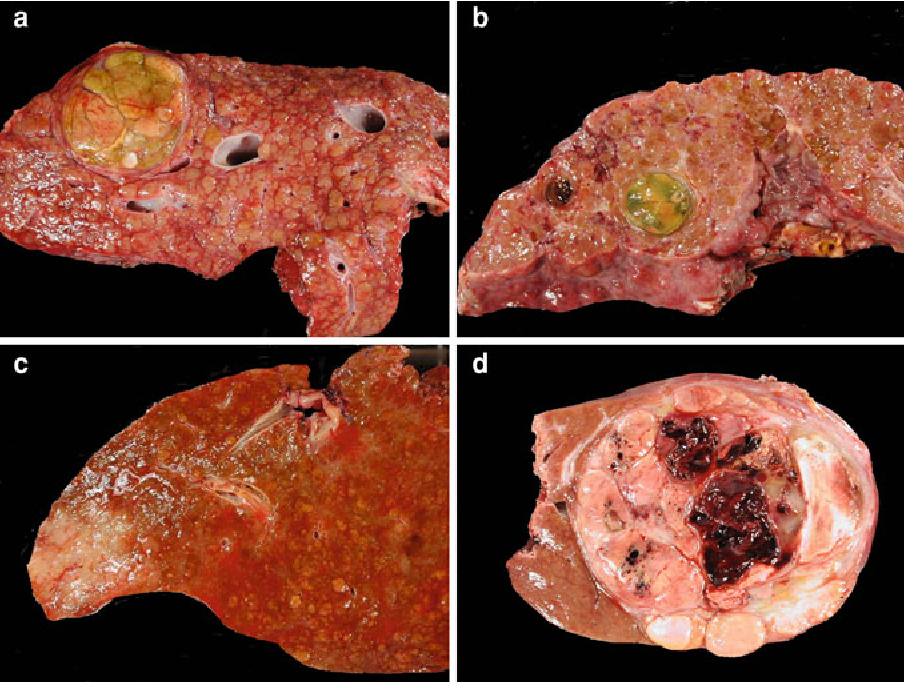
The establishment of experimental models that truly replicate the human disease is crucial for an improved understanding of the pathogenesis and to test novel therapeutic strategies. Animal models of hepatocellular carcinoma , consistent with the mouse tumour models proposed by The National Cancer Institute are categorized as explained below.
The ideal animal model should reproduce the natural history, pathophysiology and biochemistry of human HCC according to distinct aetiologies. Several hepatitis C virus-related HCC and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related HCC models have been produced to decipher the molecular pathogenesis of this disease, the advantages and disadvantages of which are reviewed elsewhere.
Also Check: Skin Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
Risk Factors For Hcc In Nash
Emerging evidence has established multiple independent risk factors for the development of HCC including obesity, diabetes, and iron deposition . These factors also increase the risk for the development of NASH, a probable precursor to CC. It is well established that HCC develops in the presence of chronic liver disease, typically associated with cirrhosis from HBV, HCV, and/or alcoholic liver disease. Cirrhosis is the most important single risk factor for HCC and is present in about 80% of patients with HCC, regardless of underlying liver disease. As noted previously, NASH likely accounts for a large proportion of the idiopathic cirrhosis that makes up 6.9%-50% of underlying liver disease in patients with HCC in developed countries. This conclusion is further supported by evidence of linking common risk factors for NASH with risk factors for HCC.
| Age |
| Iron deposition |
Selective Internal Radiation Therapy Also Known As Radioembolisation
Selective internal radiation therapy is a way of giving radiotherapy treatment for cancer in the liver that cant be removed with surgery. Its a type of internal radiotherapy, and is sometimes called radioembolisation. It involves using tiny spheres or beads, made from either glass or resin , which contain a radioactive substance called yttrrium-90. The tiny beads are put down a thin tube into the main blood vessel that supplies blood to your liver . Each bead is smaller than the width of a human hair. They enable the drugs to be delivered directly to the liver tumours. These spheres cluster around the small blood vessels surrounding the tumour, where they then release radiation and destroy the cancer cells.
In England and Wales NICE has recommended selective internal radiation therapy as an option for some people with advanced liver cancer.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 1
Cryptogenic Cirrhosis And Nash
NASH has been proposed as a probable cause of idiopathic or cryptic cirrhosis even though most of the histologic hallmarks of NASH are not present in CC.- Patients with CC have a prevalence of diabetes and obesity similar to that of patients with NASH, and a significantly higher prevalence than in patients with cirrhosis from viral and autoimmune disease. Patients with CC also have a significantly higher prevalence of diabetes and obesity than age and sex matched patients with cirrhosis of well-defined etiology. The histologic findings of NASH, fatty deposition, and necroinflammation may disappear when the disease progresses to cirrhosis.- These findings make a definitive diagnosis of NASH difficult when patients present with advanced disease, although the significant association between diabetes, obesity, and CC is very convincing. In addition, patients who undergo liver transplantation for CC frequently develop NAFLD and NASH after transplant. One study demonstrated that 25% of patients developed NAFLD and 16% showed histological evidence of NASH within 26 months of transplant. A large proportion of CC, therefore, likely represents end-stage NASH.
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
Its very hard to hear you have a life-threatening illness like hepatocellular carcinoma. It is completely normal to feel overwhelmed, anxious and even afraid. Give yourself and your loved ones some time to work through your initial emotions. Share your feelings with your healthcare provider. Theyll have suggestions to help you cope with your cancer diagnosis. Heres some steps you can take:
- Keep track of your questions and concerns about your condition and your treatment. Asking questions helps you understand what to expect and what you can do to help yourself.
- Cancer is stressful. You might find activities such as meditation, relaxation exercises or deep breathing help to ease your stress.
- Your treatments might affect your appetite. Try to eat a healthy diet, and talk to a nutritionist if youre having trouble eating.
- Get plenty of rest.
- Cancer can be lonely. Sometimes its hard talking to loved ones about your condition. Your healthcare provider can direct you to support groups and programs where you can share your thoughts and feelings with people who understand what youre going through.
Recommended Reading: Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
How Is Liver Cancer Diagnosed
Your GP will take your medical history and ask about your symptoms. They will also do a detailed clinical examination and take some blood samples. They might arrange for you to have an abdominal ultrasound scan.
If this first round of blood tests and any ultrasound results suggest cancer, you will be sent to see a specialist doctor who may take more blood tests and arrange for special imaging tests of your liver to examine it more closely. You may have a biopsy if doctors cant make a diagnosis after these tests.
Diabetes Mellitus And Hcc
Large population-based cohort studies from Sweden, Denmark, and Greece demonstrate a 1.86-fold to 4-fold increase in risk of HCC among patients with diabetes , which is closely associated with obesity and NAFLD.- More recently, a case-control study in the United States showed that diabetes was associated with an increased risk for HCC, but only in patients with concomitant HCV-related, HBV-related, or alcohol-related cirrhosis. In a larger longitudinal study, the same group compared 173,643 diabetic patients with 650,620 nondiabetic controls over 10-15 years. The incidence of HCC increased more than two-fold among diabetic patients with higher increase among those with longer duration of follow-up. The risk of HCC with diabetes remained elevated even after excluding patients who were subsequently diagnosed with HCV, HBV, alcohol use, and/or fatty liver disease at any time during the follow-up. The risk for HCC was attributable to diabetes, and could not be explained by the presence of underlying liver disease or other risk factors. Diabetes is clearly established as an independent risk factor for HCC.
Figure 3
Relative risk of HCC in diabetes mellitus.
Don’t Miss: Skin Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic
How Is Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated
There are several ways to treat hepatocellular carcinoma. Your healthcare providers will develop a treatment plan that takes into account your overall health, whether your liver is working well and your tumors size.
Beyond that, theyll talk to you about treatment goals, options and potential side effects. They want you to have a complete picture of your situation so you can feel confident about your decisions. Once theyve shared information, theyll ask about your personal preferences. Your final treatment plan will reflect your providers recommendations and your preferences.
Liver Cancer Risk Factors
A risk factor is anything that increases your chance of getting a disease, such as cancer. Different cancers have different risk factors. Some risk factors, like smoking, can be changed. Others, like a person’s age or family history, can’t be changed.
But having a risk factor, or even several risk factors, does not mean that you will get the disease. And some people who get the disease may have few or no known risk factors.
You May Like: Life Expectancy Metastatic Melanoma
Prognosis Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Most people with hepatocellular carcinoma do not live for more than a few years because the cancer is detected at a late stage. Screening and early detection result in a better prognosis. If the cancer is small and has not spread and liver transplantation Liver Transplantation Liver transplantation is the surgical removal of a healthy liver or sometimes a part of a liver from a living person and then its transfer into a person whose liver no longer functions. (See… read more can be done, the person can often live a number of years.
Symptoms Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Usually, the first symptoms are abdominal pain, weight loss, and a large mass that can be felt in the upper right part of the abdomen. People who have had cirrhosis Cirrhosis of the Liver Cirrhosis is the widespread distortion of the liver’s internal structure that occurs when a large amount of normal liver tissue is permanently replaced with nonfunctioning scar tissue. The… read more for a long time may unexpectedly become much more ill. A fever may occur. Occasionally, the first symptoms are sudden abdominal pain and shock caused by rupture or bleeding of the cancer.
Recommended Reading: Large Cell Cancers
Pathophysiology Of Hcc In Nash
The majority of basic and clinical evidence regarding the pathogenesis of HCC arise in the setting of chronic viral hepatitis. It is clear that cirrhosis is linked to the development of HCC regardless of the underlying etiology of liver disease. The exact mechanism behind the development of HCC in NASH remains unclear, although the pathophysiologic mechanisms behind the development of NASH related to insulin resistance and the subsequent inflammatory cascade likely contribute to the carcinogenic potential of NASH .
Figure 4
Proposed pathogenesis of HCC in NASH.
Hepatocarcinogenesis in NASH may also be partially mediated by increased release of inflammatory and inhibitory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and NF-κB., – Evidence suggests a complex molecular interplay related to these inflammatory cytokines that leads to hepatocyte death, compensatory proliferation, and ultimately carcinogenesis. NF-κB regulates immune and inflammatory responses and is activated in many tumors, inhibiting apoptosis. A recent study by Luedde et al. demonstrated that inhibition of NF-κB in mouse livers induced steatohepatitis and ultimately HCC by sensitizing hepatocytes to spontaneous apoptosis. This chronic cycle of injury, cell death, and regeneration through compensatory cellular proliferation likely contributes to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
What Causes Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Cirrhosis of the liver is the most common cause of hepatocellular carcinoma. Increasingly, healthcare providers are seeing hepatocellular carcinoma cases in people who have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease . There are other medical conditions and activities that increase your risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Kidney function .
You May Like: Stage 3 Melanoma Survival Rate
Diagnosis Screening And Prevention
Given that most cases of HCC occur in an identifiable patient population, that is, in those with chronic hepatitis B or cirrhosis, many patients are diagnosed through surveillance,. Nevertheless, given the under-implementation of screening in some clinical practices, a proportion of patients with HCC might present incidentally with a liver mass, identified on cross-sectional imaging performed for other reasons or owing to symptomatic advanced-stage HCC after developing abdominal pain, weight loss or worsening of liver dysfunction. Such incidental diagnosis has been estimated to occur in 50% of cases globally, particularly in developing jurisdictions.
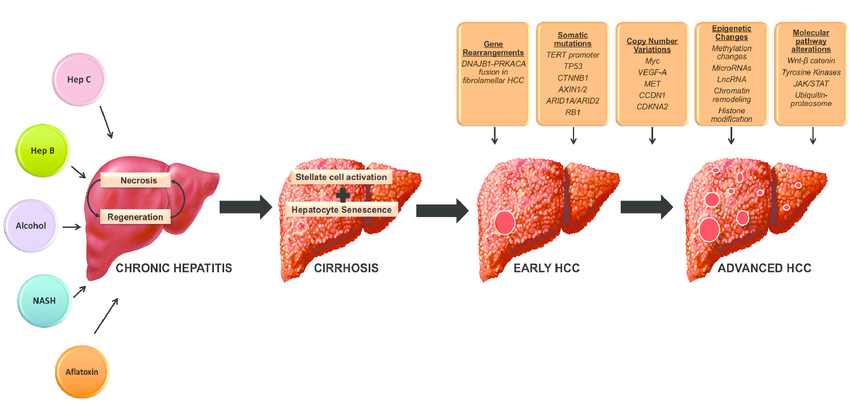
Cancer Driver Gene Mutations In Hcc
High throughput next-generation sequencing has enabled the identification of cancer driver genes with oncogenic functions or tumour suppressive functions that are recurrently altered in HCC. Telomerase activation via TERT promoter mutations, viral insertions, chromosome translocation or gene amplification are the most frequent driver gene alterations, observed in ~80% of HCC,. Studies have demonstrated the activation of the Wnt-catenin signalling pathway in 3050% of the cases, caused by mutations in CTNNB1 , AXIN1 or APC inactivation,. Other frequent mutations or genetic alterations are found in TP53, RB1, CCNA2, CCNE1, PTEN, ARID1A, ARID2, RPS6KA3 or NFE2L2, all of which alter cell cycle control. Additionally, variants in genes involved in epigenetic regulation, oxidative stress, and the AKTmTOR and MAPK pathways have been implicated in HCC . Furthermore, recurrent focal chromosome amplifications in CCND1, FGF19, VEGFA, MYC or MET leading to over-expression result in the activation of various oncogenic signalling pathways, including of receptor tyrosine kinases. Although cancer driver gene mutations accumulate randomly, specific genes are related to precise molecular HCC subclasses, defined by transcriptomic profiles and histological phenotypes,, . Overall, only ~2025% of patients with HCC have at least one potential actionable mutation as per current standards,,.
Fig. 2: Molecular and immune classification of HCC.
Viral infection-associated molecular alterations
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
As the name suggests, AFLD is attributed to excessive alcohol consumption that causes hepatic injury by the build-up of fats, inflammation, and scarring leading to HCC, which could be fatal . Globally, the prevalence of AFLD is increasing and has become a significant contributor to the liver disease burden accounting for 30% of HCC related deaths . The safe levels of drinking as defined in the dietary guidelines in the United States is two drinks for men and one drink for women per day as one alcoholic drink accounts for about 14 g of alcohol . By contrast, excessive alcohol consumption is considered to cause AFLD . The threshold level of alcohol intake causing hepatotoxic effect varies and it depends on a variety of factors such as gender, ethnicity, and genetics .
How Can I Reduce The Risk Ill Develop Hepatocellular Carcinoma
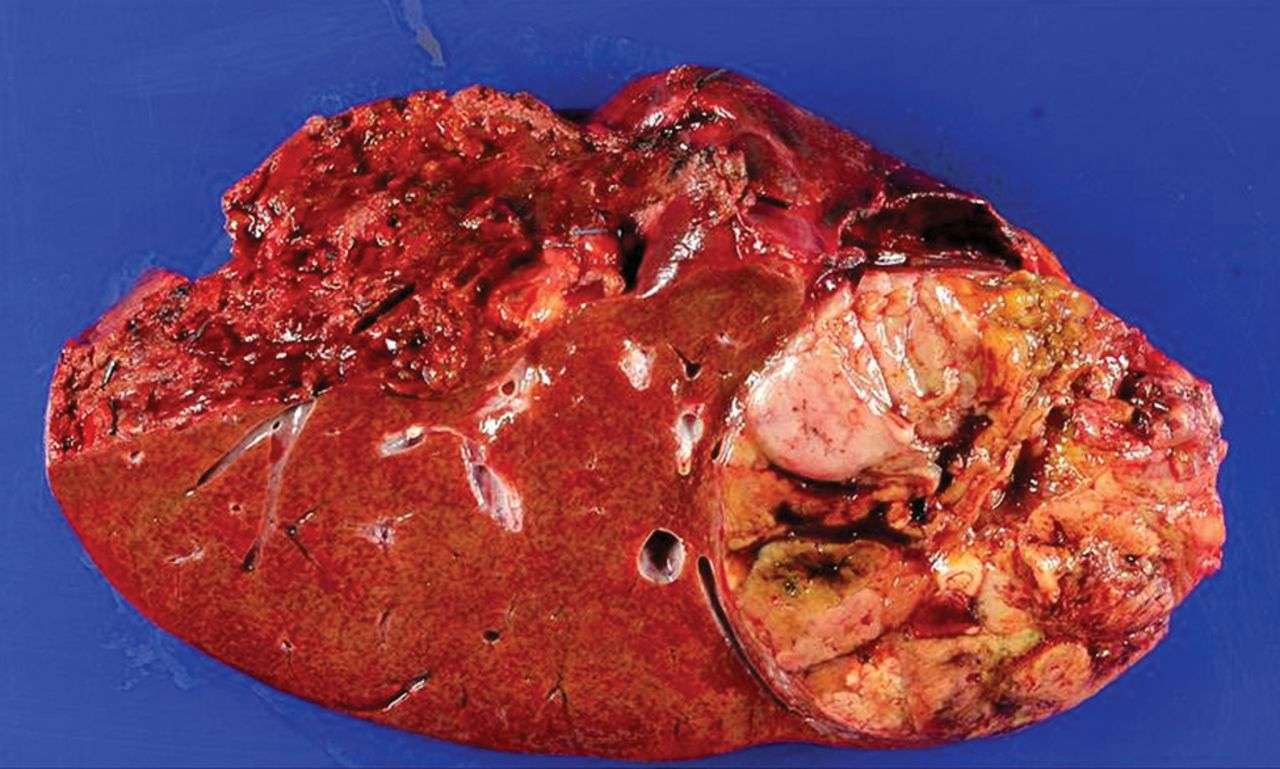
Fortunately, there are several ways you can reduce your risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma:
- Get your hepatitis B vaccination. There isnt a vaccine for hepatitis C.
- Talk to your healthcare provider if you think you might have hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
- Cut back on the amount of alcohol you drink.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
Don’t Miss: Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rate
How Fibrosis Develops
When someone has liver disease, their liver enters into a very dangerous cycle. Persistent inflammation, or hepatitis, sends nonstop signals to repair cells to continue depositing collagen. The extra collagen stiffens around the tissue like it is supposed to in the healthy liver but, instead of a signal being released to stop the inflammation and discard the extra collagen, the inflammation continues, and even more collagen is deposited, leading to more stiffening. This is how fibrosis develops.
When repetitive damage or long-lasting inflammation occurs, collagen and other proteins build-up between liver cells, forming scar tissue. Scar tissue can block or limit blood flow within the liver, starving and killing healthy liver cells, causing more scar tissue to form. Unlike healthy liver cells, scar tissue cannot function or repair itself. As fibrosis advances it can impact the livers ability to function, limit its ability repair itself and restrict blood flow. Over time, the scars in the liver will continue to build and replace healthy tissue. Gradually, the scars snake out farther, covering more of the healthy liver and grow together, or bridge, creating or bands of scar tissue. Fibrosis also restricts blood flow. When doctors want to determine how severe the scarring is, they examine the impact on the portal blood flow. The portal vein brings all the blood from the intestines to the liver to be processed.
Cirrhosis