How They Are Diagnosed
Diagnosing a carcinoma can involve any of the following tests:
- Biopsy to remove a piece of tissue or a sample of cells from your body to determine whether the cells are cancerous and, if so, where the cancer originated
- Blood tests including a CBC , blood protein testing, tumor marker tests or circulating tumor cell tests
- Imaging tests including X-ray, CT scan, nuclear imaging, ultrasound, MRI, digital mammography, sentinel node mapping or virtual colonoscopy
To identify a sarcoma, a biopsy is done with samples taken from the primary tumor, lymph nodes and other potentially cancerous areas. The tissue sample then undergoes any of the following tests: immunohistochemistry, light and electron microscopy, cytogenetic analysis, FISH or flow cytometry to determine the presence and extent of the cancer.
Can Skin Cancer Go Away By Itself
Simply put, no. Keratoacanthoma, a rare type of skin cancer that appears as dome-shaped tumors on skin prone to sun exposure, can potentially shrink and go away on its own without treatment. However, this is rare, and many keratoacanthomas continue to grow and may potentially spread to various areas in the body.
How They Are Treated
Treatment options for both carcinoma and sarcoma can involve any of the following: surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, chemoradiation , targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
Factors that can affect treatment options include:
- type of cancer;
- size, grade, and stage of the tumor;
- rate at which the cancer cells are growing and dividing;
- location of tumor in the body;
- amount of tumor removed by surgery;
- patient’s age and general health;
- and status of the cancer initial occurrence or recurrence.
You May Like: How Serious Is Skin Cancer
How Long Can Skin Cancer Go Untreated
Melanoma can put a patients life at risk in as little as six weeks if left to grow untreated. When melanoma spreads to other areas of the body, it can become much more difficult to treat. A small melanoma tumor, if caught early on, can be treated with procedures like excision surgery or Mohs micrographic surgery.
In Situ Vs Invasive Breast Cancers
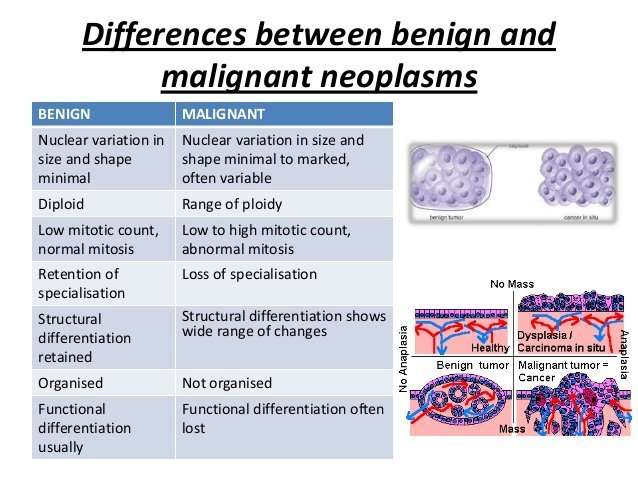
The type of breast cancer can also refer to whether the cancer has spread or not. In situ breast cancer is a cancer that starts in a milk duct and has not grown into the rest of the breast tissue. The term invasive breast cancer is used to describe any type of breast cancer that has spread into the surrounding breast tissue.
Invasive breast cancer has spread into surrounding breast tissue. The most common types are;;invasive ductal carcinoma;and;invasive lobular carcinoma.;Invasive ductal carcinoma makes up about 70-80% of all breast cancers.;
Also Check: Can Cancer Cause Skin Rash
Are Blood Cancers Solid Tumors
Blood cancers do not usually take the form of a solid tumor. In leukemia, usually a cancer of certain white blood cells, immature blood cells become cancerous and crowd out the healthy blood cells. Lymphoma begins in lymphocytes, another type of white blood cell, and tends to travel throughout the body and land in multiple places. Another blood cancer, multiple myeloma, involves the build-up of plasma cells, mature lymphocytes that produce antibodies, in the bone marrow.
Each blood cancer has its own staging system, which determines how much cancer is in the body and where its located. Solid tumors, by contrast, are commonly staged using the American Joint Committee on Cancers TNM system. Each type of cancer is staged based on factors such as how large the primary tumor is and whether it has spread to the lymph nodes and to other parts of the body.
What Is The Difference Between Carcinoma And Melanoma
Carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that does not usually spread to other areas of the body, while melanoma is a more destructive form of cancer that is likely to spread, according to WebMD. Carcinoma occurs more frequently in older patients, while melanoma more often develops in younger patients.
Carcinomas are identified as either basal cell or squamous cell. Basal cell carcinoma appears as a flat, pearly bump raised above the skin of the head, neck or shoulders. Squamous cell carcinoma shows up as a red, scaly bump on skin exposed to the sun. Usually, basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas do not require any treatment other than removal of the spot on the skin, and the cure rate is about 95 percent as of 2015, according to WebMD.
Melanoma is often identified through a skin lesion that turns from brown to black, as explained by WebMD. This type of skin cancer may also be identified through a change in the size, shape or height of a mole, or as the development of a new mole. Melanoma usually requires more aggressive treatment than carcinomas depending on the severity of the tumor. These treatments may include radiation, chemotherapy, surgery and immunotheraphy. The possibility of treating melanoma through the removal of tissue alone is better with thinner skin lesion.
Also Check: What Does Melanoma Look Like On The Leg
What Are The Similarities In Basal Cell Carcinoma Vs Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The majority of people who are diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma are fair skinned and have signs of sun damage. These signs include deep wrinkles, age spots, and patches of discolored skin. However, people of all skin tones can be diagnosed with skin cancer.
You are at a higher risk of being diagnosed with skin cancer if you:
- Regularly use a tanning bed
- Spend time in the sun without protecting your skin using sunscreen or clothing
- Are fair skinned, have light colored eyes, or are a natural red head or blonde
- A history of skin cancer
- Experienced blistering sunburns
What Is The Difference Between Ductal And Lobular Breast Cancer
Ductal carcinomacancerLobular carcinomain thebreastbreast
Invasive lobular cancer is a less common type of breast cancer than invasive ductal cancer. This cancer accounts for about 10% of all invasive breast cancer cases. Prognosis for infiltrating and invasive lobular breast carcinomas will naturally be influenced by tumor size, grade, stage and hormone receptor status..
Likewise, is lobular breast cancer aggressive? Depending on the aggressiveness of the cancer type, the cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. Lobular carcinoma cells tend to invade breast tissue by spreading out in a distinct way rather than forming a firm nodule.
In this regard, is lobular breast cancer curable?
Depending on the stage of breast cancer, the general 5-year survival rates for women are: Stage 0 or 1: nearly 100 percent. Stage 2: about 93 percent. Stage 3: around 72 percent.
What is the difference between invasive lobular carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Invasive means that the cancer has invaded or spread to the surrounding breast tissues. Lobular means that the cancer began in the milk-producing lobules, which empty out into the ducts that carry milk to the nipple.
Read Also: Is Renal Cell Carcinoma Hereditary
Undifferentiated Carcinoma With Osteoclast
This tumor is composed of two cell types. The cancerous cells are the big cells on the right of this image. The large osteoclast-like cells contain lots of nuclei and are the body’s non-tumorous cells reacting to the cancer.
Third Degree Relatives – First cousins, great-aunts and uncles
An inherited genetic variation in DNA that you are born with
Second Degree Relatives – Aunts, uncles, grandparents, nieces and nephews
First Degree relatives – Blood relatives in your immediate family: parents, children, and siblings
This is an experimental type of treatment. It is a medication made of killed or weakened cells, organisms or manufactured materials, which is used to boost the body’s immune system. Ideally, this will allow the body to fight and kill the cancer cells more effectively. Vaccines include whole killed cancer cells or specific proteins from the cancer.
Also known as a pancreatoduodenectomy, the Whipple procedure is the surgery typically performed to remove cancers of the head of the pancreas . It typically involves the surgical removal of the head of the pancreas, a portion of the duodenum and a portion of the bile ducts.
The part of the pancreas that bends backwards, hooking around two very important blood vessels, the superior mesenteric artery and vein. The word “uncinate” comes from the word uncus which means “hook.”
Unable to be surgically removed. This usually means that the cancer has spread beyond the areas that can be removed surgically.
What Are The Treatment Options For Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Before discussing your treatment options, your dermatologist will examine your skin carefully and ask about your overall health and symptoms. To verify a diagnosis of skin cancer, your dermatologist will perform a skin biopsy. This is when the area is numbed and some of the cells in question are removed. A biopsy will allow the dermatologist to closely inspect the skin cells and determine if and what type of skin cancer you may have. This will allow you and your dermatologist to create an individualized treatment plan.
Both basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma can be removed using one of three surgical methods.
- Excision is when the dermatologist removes the affected cells, as well as surrounding normal cells to ensure the removal of all cancerous cells.
- Mohs surgery, which is performed by our highly trained professionals in our Mohs Surgery Center, allows less tissue to be removed when removing cancerous cells.
- Curettage and electrodessication are the third surgical option. Curettage is used to scrape the cancerous cells from the top layer of skin and electrodessication uses heat to destroy the remaining cancerous cells.
Don’t Miss: How Many People Survive Skin Cancer
Remember: All Omas Arent Cancer
In cancers, including carcinoma and sarcoma, cells divide uncontrollably, invade nearby tissues and can eventually spread to distant sites.
It is important to know that benign masses may also end in oma, which means tumor, but these cells behave and are treated quite differently, says Dr. Shepard.
For example, cells in benign tumors such as adenomas, fibromas and angiomas will not invade nearby tissues or spread to other sites.
Thus, the tumors dont have the same negative consequences as a carcinoma or sarcoma.
What Are Benign And Malignant Tumors And Neoplasms
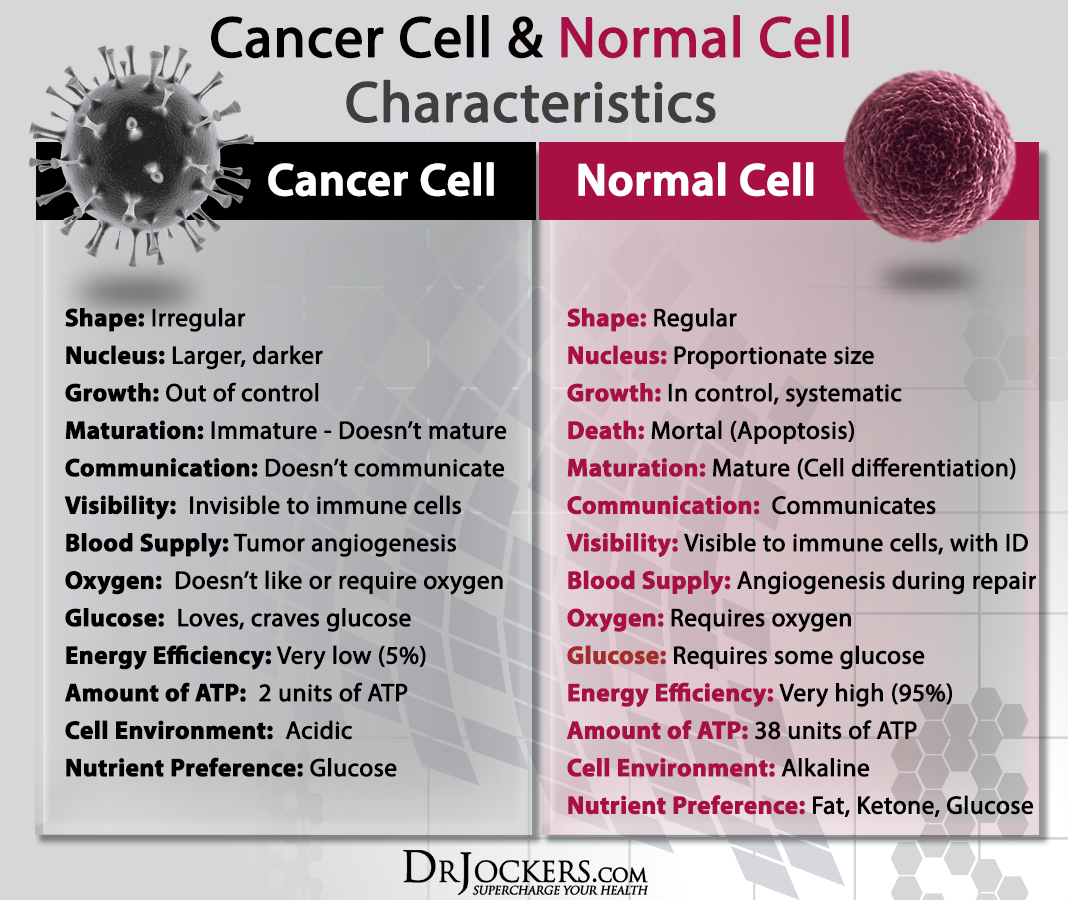
Both tumor and neoplasms can be benign or malignant, which means non-cancerous or cancerous. Benign tumors and neoplasms are not cancer, while malignant tumors and neoplasms are cancer. Benign tumors do not spread throughout the body and grow slowly. Malignant tumors can grow quickly and spread throughout the body, making early detection important. One of the first tests doctors will do when a tumor or neoplasm is detected, is determine if it is benign or malignant, in order to help determine the next treatment step and understand why the tumor or neoplasm is forming. If you suspect a change in your body or find a new growth or lump, contact your doctor for testing to ensure you receive treatment if needed.
Recommended Reading: How Quickly Can Melanoma Appear
Tissue Types And Subtypes Of Sarcomas
Unlike carcinomas, there are over 50 different subtypes of sarcomas. Examples of sarcoma based on tissue type include:
- Bone
- Fat : liposarcoma
- Cells surrounding nerves: neurofibrosarcomas, malignant Schwammomas
- Connective tissue in the brain: glioma, astrocytoma
- Digestive tract: gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- Primitive embryonic tissue: myxosarcoma
- Combination of cell types: undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma
The most common sarcomas in childhood are rhabdomyosarcomas. In adults, the most common sarcomas are soft tissue sarcomas, including undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma, liposarcomas, and leiomyosarcomas.
Types Of Breast Cancer
There are many types of breast cancer, and many different ways to describe them. Its easy to get confused over a breast cancer diagnosis.
The type of breast cancer is determined by the specific cells in the breast that are affected. Most breast cancers are carcinomas, which are tumors that start in the epithelial cells that line organs and tissues throughout the body. When carcinomas form in the breast, they are usually a more specific type;called adenocarcinoma, which starts in cells in the ducts or the lobules .
Also Check: Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Fatal
The Main Types Of Cancer
Our bodies are;made up of billions of cells. The;cells;are so small that we can only see them under a microscope.;
Cells group;together to make up the tissues and organs of our bodies. They are very similar. But vary in some ways because body organs do very different things. For example, nerves and muscles do different things, so the cells have different structures.
There are more than 200 types of cancer and we can classify cancers according to where they start in the body, such as breast cancer or lung cancer. ;
We can also group cancer according to the type of cell they start in. There are 5 main groups. These are:
- carcinoma; this cancer begins in the skin or in tissues that line or cover internal organs. There are different subtypes, including adenocarcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma;and transitional cell carcinoma
- sarcoma; this cancer begins in the;connective or supportive tissues such as;bone, cartilage, fat, muscle;or;blood vessels
- leukaemia; this is cancer of the white blood cells. It starts in the tissues that make blood cells such as the bone marrow.;;
- lymphoma and myeloma; these cancers begin in the cells of the immune system
- brain and spinal cord cancers; these are known as central nervous system cancers
What Are Treatment Options
The treatment is highly variable depending on the type and stage of a cancer as well as the overall health of the patient. The most common treatments are surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Other treatments include targeted/biological therapies, hematopoietic stem cell transplants, angiogenesis inhibitors, cryosurgery, and photodynamic therapy.
Every treatment has potential risks, benefits, and side effects. The patient and his or her care team, which may include an internist or other specialist, surgeon, oncologist, radiation oncologist, and others, will help determine the best and most appropriate course of treatment.
Is There a Cure for Cancer?
Despite enormous effort and funding, no one cure has been found yet to eliminate cancer. In 2016, the United States announced a $1 billion investment into creating such a cure, named the âNational Cancer Moonshotâ by President Barack Obama.
Until a cure can be found, prevention through a healthy lifestyle is the best way to stop cancer. Some ways to help protect yourself from cancer include eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, abstaining from tobacco, drinking only in moderation, exercising, avoiding sun damage, getting immunizations, and getting regular health screenings.
You May Like: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
How Are Solid Tumor And Blood Cancers Treated
For solid tumor cancers, treatment options can include therapies such as radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy, and/or surgery to remove the tumor. Surgery may also ease side effects caused by other therapies. Immunotherapy has had success treating some patients with lung, bladder, head and neck, and kidney cancer, as well as melanoma and lymphoma, and is currently being tested in a wide range of cancer types.
Much like treatment for solid tumors, treatment for blood cancers can include chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy. Stem cell transplants are also used to treat several types of blood cancers as well as certain noncancerous blood disorders such as aplastic anemia, immunodeficiency diseases and metabolic disorders. CAR T-cell therapy is a new form of immunotherapy that uses specially altered T lymphocytes to more specifically target cancer cells. To date, it has been approved to treat some forms of refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, as well as;pediatric relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia .
Every patient is different, and oncologists develop each patients treatment plan depending on a variety of factors, including the diseases progression, where the cancer is located, and the overall health of the patient.
The Differences Between Sarcoma And Carcinoma
Cancer interrupts the body’s natural process of replacing old and damaged cells, allowing damaged cells to survive and creating an excess of new cells when they are not needed, causing tumors. The tumor’s location or point-of-origin helps define a patient’s type of cancer. Cancers that originate in an organ or tissue are called primary cancers.
There are two types of primary cancers; carcinomas and sarcomas. When talking about carcinomas and sarcomas , it is important to know the similarities as well as differences that can affect a patient’s cancer journey.
You May Like: What Does Advanced Skin Cancer Look Like
What Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
It’s the most common type of kidney cancer. Although itâs a serious disease, finding and treating it early makes it more likely that youâll be cured. No matter when youâre diagnosed, you can do certain things to ease your symptoms and feel better during your treatment.
Most people who have renal cell carcinoma are older, usually between ages 50 and 70. It often starts as just one tumor in a kidney, but sometimes it begins as several tumors, or itâs found in both kidneys at once. You might also hear it called renal cell cancer.
Doctors have different ways to treat renal cell carcinoma, and scientists are testing new ones, too. Youâll want to learn as much about your disease as you can and work with your doctor so you can choose the best treatment.
What Is A Sarcoma

Sarcoma is a rare type of carcinoma which affects connective tissues in the body in places such as bones, muscles, tendons, cartilage, nerves, fat, and blood vessels. Accounting for more than 50 different types, Sarcoma can mainly be divided into soft tissue sarcoma and bone sarcoma or osteosarcoma.
Positive family history, Pagets disease, genetic disorders like neurofibromatosis, Gardner syndrome and retinoblastoma and radiation therapy for cancer are known to be the commonest etiological factors for Sarcoma.
Soft tissue sarcomas are often left undiagnosed since they can grow anywhere in the body. Patients will usually complain of a painless lump in the first place, and when it increases in size, it tends to press against nerves or muscles and result in difficulty in breathing and discomfort. This is mainly a clinical diagnosis.
Major signs and symptoms of Osteosarcoma include, on and off pain in the affected bone, often worsening at night accompanied by swelling, which may start about one week after the onset of pain and limping, in case of sarcomas in the leg. Children and young adults are at a higher risk of getting affected by this condition.
Methods of diagnosis are similar to those of cancer and specifically include a bone scan if osteosarcoma is suspected.
Radiation, chemotherapy, and surgery are indicated as treatment types which are based on the severity and type of sarcoma.
Optical Coherence Tomography image of a sarcoma
Read Also: What Is The Leading Cause Of Skin Cancer