When Is A Mole A Problem
If a new or existing mole begins to change shape, color, size, or becomes flaky, crusty, or begins to bleed, it’s time to make an appointment with your dermatologist to get it checked out. A mole can turn into melanoma on rare occasions. In early melanoma, the shape of a mole becomes asymmetrical and uneven.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
Nodular basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that is most often found on the head. This type of cancer starts in basal cells, which are tasked with making new skin cells to push the old ones toward the surface of the skin. Nodular basal cell carcinoma is responsible for 60%-80% of all basal cell carcinomas. In the United States, its estimated that 4.3 million cases of basal cell carcinoma are diagnosed every year, with 2.5 to 3.4 million of those cases being nodular basal cell carcinoma.
This type of cancer appears as a pearl-like papule that is round and surrounded by threadlike red lines on the skin made up of tiny blood vessels. The risk of developing nodular basal cell carcinoma can be increased by spending a lot of time out in the sun, living in high-altitude and sunny locations, and radiation therapy.
Other risk factors include:
- Prolonged exposure to arsenic
- Certain rare genetic disorders such as basal cell nevus syndrome
Although this type of cancer is common, it is highly treatable, and the five-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Why Should You Seek Out A Dermatologist
Seek a professional opinion to rule out melanoma. If you notice one or more melanoma symptoms, contact Schaumburg Dermatology to set up an appointment. If the pathology lab identifies a pimple or mole as cancerous, we will develop a treatment plan to isolate and remove the skin cancer. Give us a call today at 497-8679 to set up a consultation.
Copyright © 2021 – All Rights Reserved – Schaumburg DermatologyPowered by Launch Digital Marketing
Visitor policies continue to evolve at Schaumburg Dermatology to ensure a safe, trusted, and comfortable care environment for all patients, visitors, physicians, and staff.
To align with recent changes made by the CDC, Schaumburg Dermatology updated our patient/visitor policy.
Effective 08/03/20211, the following visitor policies are in effect.
Screen for illness, At the point of check-in, patients and companions will be screened for COVID-19 symptoms by answering the screening questions below:
All guests who do not comply with the masking policy may be asked to leave.
Dermoscopy Of Superficial Melanoma
Superficial melanomas usually have one or more of the following dermoscopic features:
- Blue-white veil
- Multiple colours, especially red and blue
- Broad network
- Negative network
- Irregular vascularity
The blue-white veil is described as an irregular structureless area of confluent blue pigment with a ground glass haze, as if the image were out of focus. It is due to hyperkeratinisation over dense epidermal pigment. Uniform blue-white structures may be observed over some blue naevi and haemangiomas but in melanoma they are focal, asymmetrical and irregular.
Scar-like depigmentation due to regression of melanoma results in irregular white areas that must be distinguished from the uniform peripheral loss of pigment seen in benign halo naevi. It arises in about 50% of melanomas.
Negative network, although a feature of melanoma, may also be found in some benign melanocytic lesions and seborrhoeickeratoses.
Some of the structural features may be subtle in early melanoma, as in several examples shown here. Melanoma may be recognised when there are only 2-3 colours in the lesion on dermoscopy . Deeper melanomas reveal more colours.
Dermoscopic features of melanoma
Not all facial melanoma have these characteristics. In the absence of network, there may be amelanotic areas and irregular blotches.
Facial SSM
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Renal Cell Carcinoma
How To Prevent Melanoma
Most skin cancers, including melanoma are preventable. The following protective measures can help prevent skin cancer:
- Avoiding the sun during the hottest part of the day, which is typically 11 AM to 4 PM.
- Applying sunscreen throughout the year. Sunscreens don’t usually filter out all harmful UV radiation, especially radiation that can lead to melanoma but they are essential in providing overall protection from the sun. A broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 should be used all year around and reapplied as required. Sunscreen is to be applied on all days including winter and cloudy days. It is advised to apply sunscreen over all exposed skin of the body and face, including the lips and ears. Special sunscreen is needed while swimming in the pools and beaches.
- Wearing protective clothing can provide protection against the sun and harmful UV radiation. Sunglasses are essential to protect the eyes and skin around the eyes, such as the eyelids, against UVB radiation.
- Avoid tanning beds because they emit UV rays that cause skin cancer.
- Consuming sun-sensitizing medications such as certain antibiotics or isotretinoin for acne can increase skin sensitivity to sun.
- Self examination of the skin regularly is important for diagnosis and treatment. Any new skin changes or changes in existing skin growths, patches or moles should be reported to a physician as soon as possible
What Is The Incidence Of Melanoma
It is the sixth most common cancer in the United States, and currently is the cancer with the most rapid rise in incidence in the United States. The lifetime risk in the year 2000 was 1 in 75 versus 1 in 150 in 1985. Over 59,000 new cases of melanoma are reported each year with more than 8000 deaths from the disease.
Also Check: What Does Merkel Cell Skin Cancer Look Like
Future Directions For Research
Results from our formative study can guide the development of quantitative measures to assess early detection of nodular and superficial spreading melanoma, which would allow for further quantification of rates of self-identified early features of melanoma. Our results could also guide future research to develop educational materials about the early detection of various types of melanoma, including the NM subtype, which appears to be more amenable to earlier detection by patients than previously claimed. Further validation of our findings may then warrant revision of existing criteria for earlier clinical recognition of the NM subtype.
Tools That Can Help You Find Melanoma On Your Skin
To help you find melanoma early, the American Academy of Dermatology developed the following:
Melanoma can look different on a childs skin. Taking this short quiz can help you hone your skills at finding childhood melanoma.
ImagesImages 1,3,4,5,6,7,8,10: Images used with permission of the American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
Image 2: Developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
Image 9: Used with permission of the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
ReferencesBarnhill RL, Mihm MC, et al. Malignant melanoma. In: Nouri K, et al. Skin Cancer. McGraw Hill Medical, China, 2008: 140-167.
Gloster HM Jr, Neal K. Skin cancer in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol 2006 55:741-60.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN guidelines for patients: Melanoma. 2018. Last accessed February 12, 2019.
Read Also: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like On Shoulder
What Are The Breslow And Clark Classifications Of Melanoma Invasion
Clark selected five levels of melanoma thickness in the skin:
-
Level I: intradermal melanoma that does not metastasize may be better termed atypical melanotic hyperplasia: a benign lesion.
-
2.01 to 4.0 mm
-
= 4.0 mm
Lesions < 1 mm include melanoma in situ and thin invasive tumors. The cure rate in the latter is over 95% with excision. Tumors of 1.0 to 4.0 mm are called intermediate but involve risk of metastasis. Lesions > 4.0 mm are high-risk lesions with a poor cure rate.
All melanomas should be checked by both methods because some tumors may show a low Breslow measurement with a deeper Clark level, indicating a great risk of recurrence and spread. Measurement of thickness is important, and the tumor should be measured from the total height of the lesion vertically at the point of maximal thickness. In addition, if ulceration is present, the measurement should be from the bottom of the ulcer crater down to the deepest margin of the lesion .
What Does Melanoma Look Like
Melanoma is a type of cancer that begins in melanocytes . Below are photos of melanoma that formed on the skin. Melanoma can also start in the eye, the intestines, or other areas of the body with pigmented tissues.
Often the first sign of melanoma is a change in the shape, color, size, or feel of an existing mole. However, melanoma may also appear as a new mole. People should tell their doctor if they notice any changes on the skin. The only way to diagnose melanoma is to remove tissue and check it for cancer cells.
Thinking of “ABCDE” can help you remember what to look for:
- Asymmetry: The shape of one half does not match the other half.
- Border that is irregular: The edges are often ragged, notched, or blurred in outline. The pigment may spread into the surrounding skin.
- Color that is uneven: Shades of black, brown, and tan may be present. Areas of white, gray, red, pink, or blue may also be seen.
- Diameter: There is a change in size, usually an increase. Melanomas can be tiny, but most are larger than the size of a pea .
- Evolving: The mole has changed over the past few weeks or months.
Melanomas can vary greatly in how they look. Many show all of the ABCDE features. However, some may show changes or abnormal areas in only one or two of the ABCDE features.
Also Check: What Is Basal Carcinoma Cancer
Prognosis For Melanoma On The Nail
Like other forms of melanoma, subungual melanoma can metastasize to other parts of the body if left untreated.3,4 Because it can be difficult to see and is often mistaken for a bruise or other nail problem, this condition often goes undetected. However, checking your nails and showing any changes to your healthcare provider can help reduce your chances of an undetected subungual melanoma.
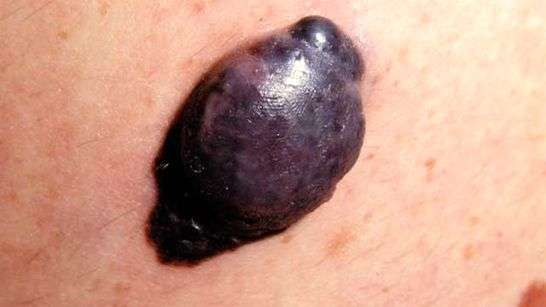
What Is Nodular Melanoma
Nodular melanoma is a type of skin cancer. Its a dangerous form of melanoma that grows quickly.
Only about 15% of all melanomas are nodular. But it causes nearly half of melanoma-related deaths. So you need to know the signs. If its found early on, doctors may be able to cure it.
What It looks like: A nodular melanoma can look like a mole, bug bite, or pimple. Often, it looks like a round black bump. But it can be other colors.
Where you get it: It can happen in any part of your body. But usually it appears on the parts of the body that get a lot of sun, such as your:
- Legs
- Arms
- Head
What to do: Dont try to pop it. The skin may break open, but theres no pus inside. Youll just cause a wound. If you have a new growth or spot on your skin that doesnt go away in 5 days, see your doctor.
You May Like: What Does Clear Cell Carcinoma Mean
Types Of Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma skin cancer can grow into and destroy nearby tissue. It can also spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma skin cancer is also called cutaneous melanoma and malignant melanoma of the skin.
There are 4 main types of melanoma skin cancer superficial spreading, nodular, lentigo maligna and acral lentiginous.
Melanoma Pictures: What To Look For
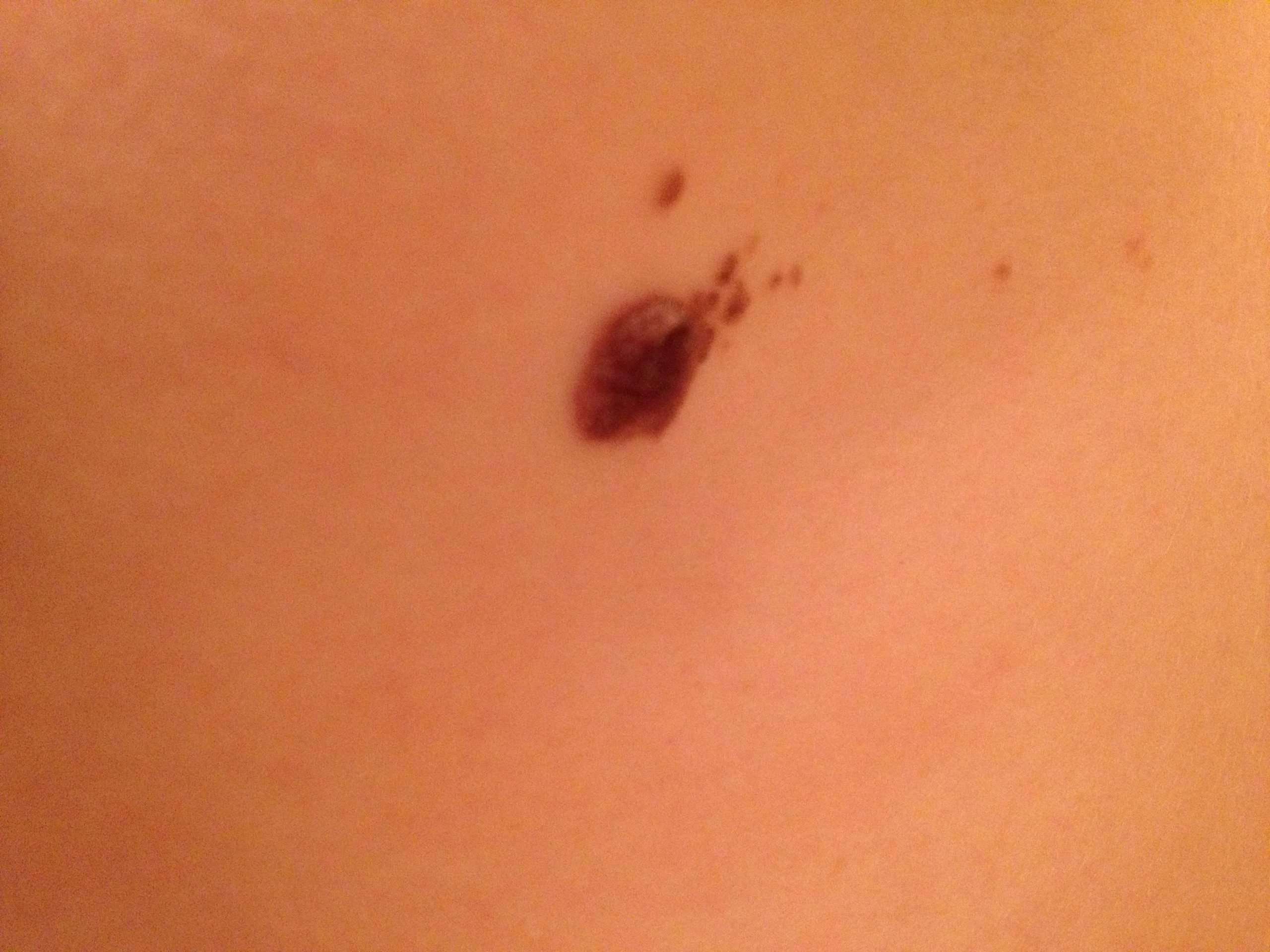
Malignant melanoma may differ from these melanoma images. Determining if a mole is cancerous is not easy.
Medically reviewed by Professor Chris Bunker *
The most important sign of potential melanoma is a change in the skins appearance, such as a change in an existing mole, or, more importantly, the appearance of a new spot. Normal moles dont typically turn into melanoma with 70% of melanomas arising in normal skin, not moles.
If you have a particular mole or mark on your skin that you are worried about, please seek your doctors opinion as soon as possible as melanoma of the skin can differ in appearance from the melanoma pictures presented here. Each melanoma is unique in appearance.
READ MORE ABOUT:
You May Like: How Is Metastatic Melanoma Diagnosed
What Do The Early Signs Of Melanoma Look Like
Melanoma in its early stages may presents as:
- A large brownish spot with darker speckles
- A mole that changes in color, size or texture or bleeds
- Large brownish patch or spot
- A small lesion with an irregular border with areas that appear red, pink, white, blue or blue-black
- Pain, itching or burning of the mole
Melanoma can develop anywhere on the body. It may arise from an existing mole that becomes cancerous or from normal skin. Melanoma tends to occur on the face or the trunk in men. In women, it tends to occur on the legs. Melanoma can also occur in areas not exposed to the sun. Melanoma can affect all skin tones but more common in lighter skin tones.
Risk Of Further Melanomas
Most people treated for early melanoma do not have further trouble with the disease. However, when there is a chance that the melanoma may have spread to other parts of your body, you will need regular check-ups. Your doctor will decide how often you will need check-ups everyone is different. They will become less frequent if you have no further problems. After treatment for melanoma it is important to limit exposure to the sun’s UV radiation. As biological family members usually share similar traits, your family members may also have an increased risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. They can reduce their risk by spending less time in the sun and using a combination of sun protection measures during sun protection times. It is important to monitor your skin regularly and if you notice any changes in your skin, or enlarged lymph glands near to where you had the cancer, see your specialist as soon as possible.
Don’t Miss: How Often Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Diagnostic Excision Of A Lesion Suspicious Of Nodular Melanoma
If the skin lesion is suspected to be a nodular melanoma, it should be urgently cut out . A small biopsy is best avoided, except in unusually large lesions. An incisional or punch biopsy could be misleading.
The pathological diagnosis of melanoma can be challenging. Nodular melanomas have little or no spread of malignant cells within the epidermis the melanoma cells are found within the dermis or subcutaneous fat. Extra tests using immunohistochemical stains may be necessary.
What Are The Risk Factors For Nodular Melanoma
Anyone who has skin that burns easily is more likely to get nodular melanoma. Moreover, it is also seen more often in men and in people who have already had another type of melanoma. If you are a person who has numerous moles, then there is a chance for nodular melanoma to grow in your body.
People with the following factors may also face an increased risk of having nodular melanoma:
- Previous history of having melanoma
- Having many moles
- Having one or more moles that do not look like normal moles in the body
- Fair skin
- The normal tissue around the melanoma
- Measure of how speedily the cells are increasing or growing
- Growth patterns and type of cells
- Inflammatory response
Recommended Reading: Is Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Curable
Other Primary Malignancies Of The Skin
FIGURE 24.
Kaposi’s sarcoma.
Sebaceous carcinoma has a nonspecific appearance similar to that of a squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, with nodularity, telangiectasias and hair loss .
Sebaceous carcinoma at the outer angle of the left eye.
FIGURE 25.
Sebaceous carcinoma at the outer angle of the left eye.
Malignant eccrine spiradenoma is a slowly growing, deeply invasive sclerotic plaque that occurs on the face of older women. It is often painful .
FIGURE 26.
Malignant eccrine spiradenoma.
Syringoid sweat duct carcinoma is a rare malignant condition that occurs on the face or scalp of elderly patients, causing local hair loss. The surface may be warty and secrete fluid .
Syringoid sweat duct carcinoma. Note the characteristic warty appearance.
FIGURE 27.
Syringoid sweat duct carcinoma. Note the characteristic warty appearance.
Paget’s disease of the nipple appears to be an unresponsive eczema of the areola but actually is a carcinoma in the ducts of the breast that grows outward to involve the skin.
Pigmented lesions that appear suspicious can be evaluated by using the ABCD rules: asymmetry, border irregularity, color variation and diameter 6 mm or greater.14,15 Two other suspicious signs are more rapid growth than other lesions and the presence of a narrow pink halo around the lesion.
FIGURE 28.
Dysplastic nevi cascade.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ, also known as Bowens disease, is a precancerous condition that appears as a red or brownish patch or plaque on the skin that grows slowly over time. The patches are often found on the legs and lower parts of the body, as well as the head and neck. In rare cases, it has been found on the hands and feet, in the genital area, and in the area around the anus.
Bowens disease is uncommon: only 15 out of every 100,000 people will develop this condition every year. The condition typically affects the Caucasian population, but women are more likely to develop Bowens disease than men. The majority of cases are in adults over 60. As with other skin cancers, Bowens disease can develop after long-term exposure to the sun. It can also develop following radiotherapy treatment. Other causes include immune suppression, skin injury, inflammatory skin conditions, and a human papillomavirus infection.
Bowens disease is generally treatable and doesnt develop into squamous cell carcinoma. Up to 16% of cases develop into cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Does Squamous Skin Cancer Look Like