How Does The Doctor Know I Have Skin Cancer
Basal and squamous skin cancer may look like:
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas that look a lot like a scar
- Raised reddish patches that might itch
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Small, pink or red, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas
- Pink growths or lumps with raised edges and a lower center
- Open sores that dont heal, or that heal and then come back
- Wart-like growths
Screening For Skin Cancer
Again, the best way to screen for skin cancer is knowing your own skin. If you are familiar with the freckles, moles, and other blemishes on your body, you are more likely to notice quickly if something seems unusual.
To help spot potentially dangerous abnormalities, doctors recommend doing regular self-exams of your skin at home. Ideally, these self-exams should happen once a month, and should involve an examination of all parts of your body. Use a hand-held mirror and ask friends or family for help so as to check your back, scalp, and other hard-to-see areas of skin. If you or someone else notices a change on your skin, set up a doctors appointment to get a professional opinion.
Read Also: What Is The Best Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What They Look Like
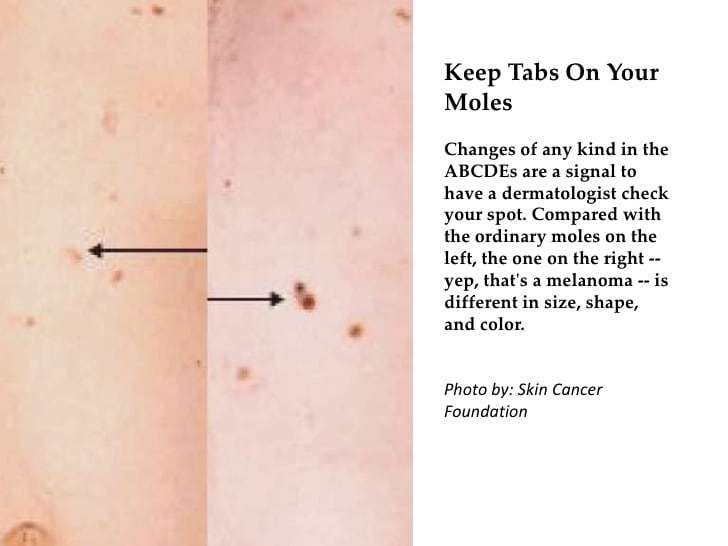
Melanomas in situ tend to be flat and asymmetric with irregular borders. They can be black, brown, tan, gray or even pink if the person has very fair skin. Areas that receive the greatest sun exposure, such as the scalp, face and neck, are more likely to develop melanoma in situ than the arms or legs. However, non-sun exposed areas, such as the buttocks, are also at risk. We dont always understand the causes of these melanomas, though heredity can play a role. To detect melanoma in situ as early as possible, it helps to monitor your own skin. Head-to-toe self-examinations are a good place to start, including the areas where the sun doesnt shine. When evaluating your skin, focus on the ABCDEs of melanoma detection. A stands for asymmetry B for irregular borders C for more than one color D for diameter greater than 6mm , or the size of a pencil eraser and E for evolving, meaning any lesion that is new or changing. View helpful photos showing the ABCDEs of melanoma.
Don’t Miss: What Is Triple Negative Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Treating Stage 1 To 2 Melanoma
Treating stage 1 melanoma involves surgery to remove the melanoma and a small area of skin around it. This is known as surgical excision.
Surgical excision is usually done using local anaesthetic, which means you’ll be awake, but the area around the melanoma will be numbed, so you will not feel pain. In some cases, general anaesthetic is used, which means you’ll be unconscious during the procedure.
If a surgical excision is likely to leave a significant scar, it may be done in combination with a skin graft. However, skin flaps are now more commonly used because the scars are usually less noticeable than those resulting from a skin graft.
Read more about flap surgery.
In most cases, once the melanoma has been removed there’s little possibility of it returning and no further treatment should be needed. Most people are monitored for 1 to 5 years and are then discharged with no further problems.
What Causes Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet light exposure, most commonly from sunlight, is overwhelmingly the most frequent cause of skin cancer.
Other important causes of skin cancer include the following:
- Use of tanning booths
- Immunosuppression – This means impairment of the immune system. The immune system protects the body from foreign entities, such as germs or substances that cause an allergic reaction. This suppression may occur as a consequence of some diseases or can be due to medications prescribed to combat conditions such as autoimmune diseases or prevent organ transplant rejection.
- Exposure to unusually high levels of X-rays
- Contact with certain chemicals-arsenic , hydrocarbons in tar, oils, and soot
The following people are at the greatest risk:
- People with fair skin, especially types that freckle, sunburn easily, or become painful in the sun
- People with light hair and blue or green eyes
- Those with certain genetic disorders that deplete skin pigment such as albinism, xeroderma pigmentosum
- People who have already been treated for skin cancer
- People with numerous moles, unusual moles, or large moles that were present at birth
- People with close family members who have developed skin cancer
- People who had at least one severe sunburn early in life
A basal cell carcinoma usually looks like a raised, smooth, pearly bump on the sun-exposed skin of the head, neck, or shoulders.
A squamous cell carcinoma is commonly a well-defined, red, scaling, thickened patch on sun-exposed skin.
Also Check: What Can Happen If Skin Cancer Is Left Untreated
Preparing For Your Appointment
If you have any concerns about the health of your skin, it is important to share them with your doctor. After making an appointment, there are steps you can take to prepare yourself and make the most of your time with your doctor.
Here are some things to consider and be prepared to discuss before visiting the clinic or hospital:
-
What symptoms are you experiencing ?
-
When did you first notice your symptoms?
-
Have there been any major changes or stressors in your life recently?
-
What medications and/or vitamins are you taking?
-
What questions do you have for your doctor?
Also Check: Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Slow Growing
What Is The Treatment For Skin Cancer
Treatment for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma is straightforward. Usually, surgical removal of the lesion is adequate. Malignant melanoma, however, may require several treatment methods, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy or immunotherapy or both. Because of the complexity of treatment decisions, people with malignant melanoma may benefit from the combined expertise of the dermatologist, a cancer surgeon, and a medical oncologist.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Recommended Reading: What Are Symptoms Of Melanoma That Has Spread
How Is Skin Cancer Treated
The treatment depends on the type and extent of skin cancer. Treatment options include
- Cryosurgery: Destroying small precancerous lesions and early-stage cancer by freezing with a liquid nitrogen gun.
- Excisional surgery: Surgical excision of the cancerous tissue along with a surrounding margin of healthy skin.
- Mohs surgery: This procedure is performed for large, invasive and recurring skin cancer. The lesion is surgically removed layer by layer, and each layer is analyzed under the microscope until no abnormal cells are found. This procedure prevents excessive removal of surrounding healthy skin.
- Curettage: After the majority of the cancerous growth is removed, the remaining layers of cancer cells are scraped away using a sharp device called a curet.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses external radiation beams to destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Anticancer drugs are used to kill cancer cells.
- : This treatment destroys skin cancer cells using a combination of laser light and medication that makes cancer cells sensitive to light and hence destroys them.
- Biological therapy: Biological therapy modulates the immune system to kill cancer cells.
Skin Cancer Treatment In Older Adults
According to Dr. Truong, Some of my older patients tell me they prefer to leave skin cancer untreated. Every patient has unique attributes and a different picture of overall health, therefore, the pros and cons of leaving cancer untreated must be thoroughly discussed to determine the most appropriate management. Most of the time, I will recommend treatment to avoid further complications in the future, however, in some cases, it is more appropriate to defer treatment. Each patient situation will be different, but at any age, a serious conversation with your dermatologist is necessary to determine whether or not skin cancer treatment is necessary for your specific situation.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Melanoma Skin Cancer Naturally
Skin Cancer Diagnosis & Treatment
On skin cancer diagnosis, Dr. Truong says, To the untrained eye, skin cancer can mimic the appearance of natural irregularities or other common skin conditions. The deadliest form of skin cancer, melanoma, may look like a mole, therefore, it is very important to note new growths or changing lesions, and to bring them to the attention of your dermatologist. A skin biopsy may be needed for a definitive diagnosis.
Once a patient receives a definitive skin cancer diagnosis, treatment planning begins. The treatment depends on the type of skin cancer, the size, location, and level of aggressiveness. The main methods of treatment include surgery, radiation, and light-based treatments.
Surgery is the most common and effective treatment for most skin cancers. Depending on the size, aggressiveness, and location of the skin cancer, a wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery may be recommended. Both surgeries are minimally invasive and usually done under local anesthesia. Mohs Micrographic Surgery is a specialized skin cancer surgery designed to remove skin cancers on sensitive areas such as the head and neck. The surgery removes skin cancer completely while preserving as much healthy skin as possible. The cancerous lesion is removed layer by layer, and the margins of each specimen are examined by your Mohs surgeon while you wait. Due to the on-site 100% margin evaluation, cure rates are superior and more healthy skin can be preserved, minimizing the scar.
What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
The main types of skin cancers are
Basal cell carcinoma usually occurs in sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face, lips or neck. Basal cell carcinoma may present as
- A pearly or waxy bump
- A flat, flesh or brownish scar-like lesion
- An ulcer that bleeds and has crusting
- An ulcer heals and recurs quickly
Squamous cell carcinoma usually arises in sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face, ears, hands or legs. People with darker skin tones may develop squamous cell carcinoma on areas that are not exposed to the sun. Squamous cell carcinoma presents as
- A firm, red nodule
Melanoma can develop anywhere on the body. It may arise from an existing mole that becomes cancerous or from normal skin cells. Melanoma tends to occur on the face or the trunk in men. In women, it tends to occur on the legs. Melanoma can occur on areas not exposed to the sun. Melanoma can affect people of all skin tones but it is more common in people who have lighter skin tones. Melanoma presents as
- A large brownish spot with darker speckles
- A mole that changes in color, size or feel or bleeds
- A large brownish patch or spot
- A small lesion with an irregular border with areas that appear red, pink, white, blue or blue-black
- Pain, itching or burning of the lesions
Rare types of skin cancers
Other rare types of skin cancer that may occur are
Don’t Miss: How To Get Skin Cancer
How Does Cancer Kill You
Abnormal growth of cells leads to cancer or malignancy. Cancer can arise from any type of calls and can affect any organ in the body. The most common cancers are breast cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer, skin cancer, lymphomas and prostate cancer. Signs and symptoms of cancer depend upon the type and site of cancer. Cancer can spread to other areas of body and some spreads more rapidly and aggressively than others.
The main forms of treatment are chemotherapy, radiation, surgery or a combination of them. Early detection and treatment can improve life expectancy but the scare of losing life stays. It can be fatal itself or can lead to life threatening complications.
Does Skin Cancer Kill You
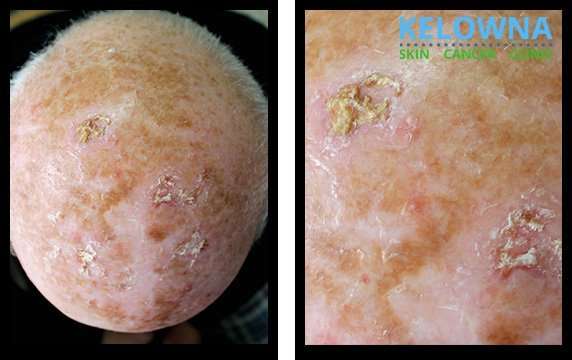
Malignant melanoma is a highly aggressive skin cancer that tends to spread to other parts of the body. All other types of skin cancers have the potential to be locally invasive and spread to other parts of the body. Nonmelanoma skin cancers are comparatively less aggressive. Self-examination of the skin for suspicious changes, changes in existing moles, persistent inflammation, ulcers, etc. can help detect skin cancer at its earliest stages. Early detection of skin cancer gives the patient the greatest chance of having successful skin cancer treatment.
You May Like: What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
A key factor used to identify a Squamous Cell Carcinomas is any ongoing change that persists beyond a few weeks in a lesion on the skin.
Squamous Cell Carcinomas typically appear as persistent, thick, rough, scaly patches that can bleed if bumped, scratched or scraped.
If you observe two or more of the signs below, you should consult the Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic immediately.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma can sometimes resemble non-cancerous skin conditions such as psoriasis or eczema.
Staging Basal Cell Carcinoma
In most cases, basal cell carcinoma does not require staging because it rarely spreads. Staging is only applicable if your cancer is very large or has spread. It determines how severe the cancer is and how to treat it.
The TNM system is used most often to stage cancer:
- Tumor: Takes into consideration tumor size and if it has infiltrated into other structures nearby, such as bone.
- Node: Describes cancer spread to the lymph nodes.
- Metastases: Identifies if cancer has spread to other distant body parts.
You May Like: How To Know Skin Cancer Symptoms
What Are The Types Of Testicular Cancer
Most testicular cancers are germ cell tumors. There are two main types of testicular cancer.
Seminomas grow and spread slowly. There are two subtypes
- Classical seminoma: This is the most common and usually happens in men ages 25 to 45.
- Spermatocytic seminoma: Commonly occurs in older men and usually does not spread.
Nonseminomas grow and spread more quickly. They usually consist of multiple types of cancer cells, including
- Embryonal carcinoma: Contains cells look like cells from embryos under microscopic examination.
- Yolk sac carcinoma: These cells look like the sac that surrounds the embryos and usually occurs in children.
- Choriocarcinoma: Usually rare and spreads to the rest of the body quickly.
- Teratoma: A rare tumor that contains other tissue and organs, including teeth and hair.
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Typically, basal cell carcinoma will begin asa new growth on the surface of the skin. These growths can vary greatlydepending on the individual. In some cases, the condition can create shiny redbumps. In others, open sores or red patches may form. In rare instances, thesegrowths can become itchy or start to bleed.
Another thing to consider when looking forwarning signs of BCC is that it occurs on the parts of the body that get themost sun. Usually, the face and head are prime targets, as are arms and legs.
Overall, if you notice any of these things onsun-exposed skin, it could be a sign of basal cell carcinoma:
- Sores that wont heal
- Reddish or irritated area of theskin
- Scar-like tissue
Also Check: What To Do To Prevent Skin Cancer
Also Check: Does Skin Cancer Cause Pain
Melanoma Incidence And Mortality
Melanoma of the skin is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer in in Australia . In 2016,14,485 new cases of melanoma were diagnosed in Australia, and in 2019, 1,415 people died.
Table 2 Australian incidence and mortality of melanoma
| Men | |
|---|---|
| 2.8 | 4.6 |
The rates were age-standardised to the Australian population as at 30 June 2001, and are expressed per 100,000 population
In Australia, the age-standardised incidence rate for melanoma increased by 100% between 1982 and 2016, from 26.7 cases per 100,000 persons to 53.5 cases per 100,000 persons,. However, how much of this increase is due to a real increase in the underlying disease, and how much is due to improved detection methods, is unknown. The incidence of melanoma of the skin rose at around 5.0% per year during the 1980s, moderating to 2.8% per year after that up until 2010. It is predicted that the initial rapid increase is partly attributable to individual behaviour and the use of solariums, resulting in increased exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation. The moderated trend seen after the 1980s is consistent with increased awareness of skin cancer and improved sun protective behaviours as a result of extensive skin cancer prevention programs dating back to the 1980s.
Economic Burden Of Skin Cancer
In addition to causing illness and death, skin cancer is costly to the nation. Skin cancer treatment is estimated to cost about $8.1 billion in the United States each year, $4.8 billion of which is for NMSC and $3.3 billion of which is for melanoma. Several new medications are available for skin cancer, which increases treatment options but could also lead to higher costs.-
Skin cancer also results in significant costs beyond those related to treatment. Annual costs associated with lost workdays and restricted-activity days are estimated at $76.8 million for NMSC and $29.4 million for melanoma., An individual in the United States dying from melanoma loses an average of 20.4 years of potential life, compared with an average of 16.6 years for all malignant cancers. Annual productivity losses associated with these lost years is estimated to cost an additional $4.5 billion .,
Read Also: What Does Advanced Skin Cancer Look Like
You May Like: Can You Die From Melanoma Cancer
What Is Melanoma
Cancer can start any place in the body. Melanoma is a kind of skin cancer that starts when skin cells called melanocytes grow out of control.
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body and grow there. When cancer cells do this, its called metastasis. To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones that started in the skin.
Cancer is always named based on the place where it starts. So when melanoma skin cancer spreads to any other organ, its still called melanoma.
The skin
Ask your doctor to use this picture to show you where your cancer is