How To Protect Yourself From Melanoma
Fortunately, most melanomas are diagnosed in early, localized stages, says Dr. González, and most patients treated for melanoma make a full recovery. But we do have patients that have ignored that funny looking mole for way too long, and its not uncommon to see cases that have metastasized to other organs, she adds.
Melanoma tends to a very aggressive form of cancer, and it can progress quickly from one stage to another. Says Dr. González: As soon as you see something unusual you should get it checked out, and as soon as you get a diagnosis, you need to be on top of the appropriate treatment.
Risk factors for melanoma include ultraviolet light exposure , having fair skin and light hair, and having a close relative whos also had melanoma. But monitoring skin for abnormal growths and changes is important for everyone, whether or not they are predisposed to skin cancer.
Going to see your board-certified dermatologist yearly and doing regular skin exams may not seem that important, Dr. González says, “but these are the things that could save your life.”
Signs Of Melanoma Include A Change In The Way A Mole Or Pigmented Area Looks
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by melanoma or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- A mole that:
- changes in size, shape, or color.
- has irregular edges or borders.
- is more than one color.
- is asymmetrical .
- itches.
- oozes, bleeds, or is ulcerated .
For pictures and descriptions of common moles and melanoma, see Common Moles, Dysplastic Nevi, and Risk of Melanoma.
Stage : Melanoma In Situ
The earliest stage of melanoma is stage 0, also known as melanoma in situ or carcinoma in situ. In situ is a Latin phrase that means in position, and this diagnosis means that the cancer cells are present only in the epidermisthe bodys most superficial layer of skinand nowhere else.
This diagnosis has a very good prognosis, Noelani González, MD, an instructor of dermatology at the Mount Sinai Icahn School of Medicine in New York City, tells Health. People with localized melanomas who are treated quickly have a 5-year survival rate of 97%meaning they are, on average, about 97% as likely to still be alive in five years as people who dont have these cancers.
Treatment for this stage cancer involves a wide excision surgery, where the affected skin is cut away and the wound is stitched and bandaged. The skin will be removed with margins, explains Dr. González. That means that some normal skin will also be removed around the edges to make sure there arent any cancer cells left over.
The removed skin is then looked at under a microscope to ensure that all of the cancer was removed with clean margins, says Dr. González. Because stage 0 cancer has not spread to any other tissues or organs, no further treatment is required.
RELATED: This Woman Had to Wait 4 Months to Get a Mole Checked Outand It Turned Out She Had Skin Cancer
You May Like: Melanoma Stage 4 Treatments
Patients May Want To Think About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today’s standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
The Following Stages Are Used For Melanoma:
Stage 0
Stage I
- Stage IA: The tumor is not more than 1millimeter thick, with or without ulceration.
- Stage IB: The tumor is more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Enlarge Stage I melanoma. In stage IA, the tumor is not more than 1 millimeter thick, with or without ulceration . In stage IB, the tumor is more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body.
Stage II
- Stage IIA: The tumor is either:
- more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, with ulceration or
- more than 2 but not more than 4 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Enlarge Stage IIA melanoma. The tumor is more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, with ulceration OR it is more than 2 but not more than 4 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body.
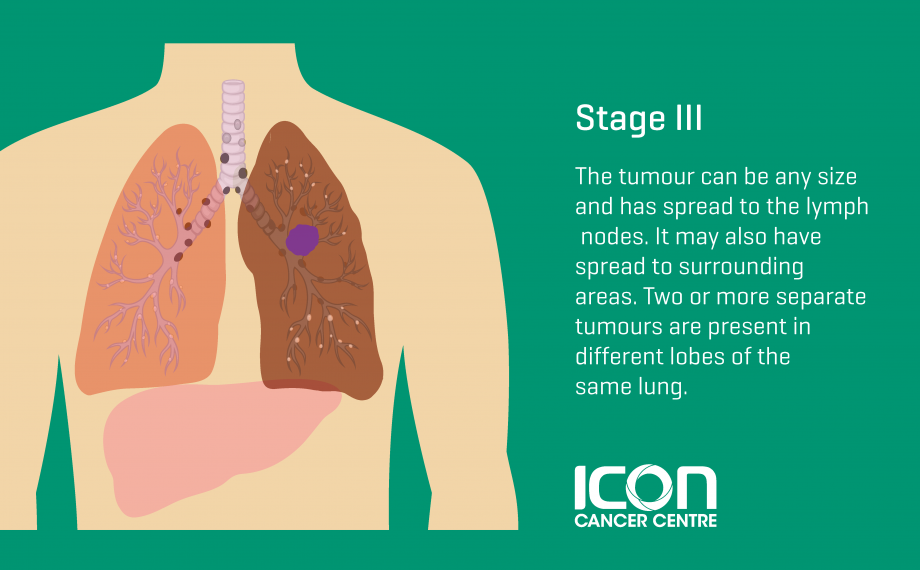
Stage III
Stage III is divided into stages IIIA, IIIB, IIIC, and IIID.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if melanoma spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually melanoma cells. The disease is metastatic melanoma, not lung cancer.
What Are The Signs Of Melanoma
Knowing how to spot melanoma is important because early melanomas are highly treatable. Melanoma can appear as moles, scaly patches, open sores or raised bumps.
Use the American Academy of Dermatology’s “ABCDE” memory device to learn the warning signs that a spot on your skin may be melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half does not match the other half.
- Border: The edges are not smooth.
- Color: The color is mottled and uneven, with shades of brown, black, gray, red or white.
- Diameter: The spot is greater than the tip of a pencil eraser .
- Evolving: The spot is new or changing in size, shape or color.
Some melanomas don’t fit the ABCDE rule, so tell your doctor about any sores that won’t go away, unusual bumps or rashes or changes in your skin or in any existing moles.
Another tool to recognize melanoma is the ugly duckling sign. If one of your moles looks different from the others, its the ugly duckling and should be seen by a dermatologist.
Don’t Miss: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Scalp Prognosis
There Are Different Types Of Treatment For Patients With Melanoma
Different types of treatment are available for patients withmelanoma. Some treatments arestandard , and some are being tested inclinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Staging For Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma usually do not spread to other parts of the body. On rare occasions, a persons lymph node may be removed to find out if the cancer has spread, which is called metastasis. Lymph nodes are bean-shaped organs that help fight infection. The doctor may recommend other tests to determine the extent of the disease, including blood tests, chest x-rays, and imaging scans of the lymph nodes and nerves, liver, bones, and brain, but this is uncommon.
Read Also: Brain Melanoma Treatment
I’ve Been Diagnosed With Melanomawhat Happens Next
Doctors use the TNM system developed by the American Joint Committee on Cancer to begin the staging process. Its a classification based on three key factors:
T stands for the extent of the original tumor, its thickness or how deep it has grown and whether it has ulcerated.
What Is Breslow depth?
Breslow depth is a measurement from the surface of the skin to the deepest component of the melanoma.
Tumor thickness: Known as Breslow thickness or Breslow depth, this is a significant factor in predicting how far a melanoma has advanced. In general, a thinner Breslow depth indicates a smaller chance that the tumor has spread and a better outlook for treatment success. The thicker the melanoma measures, the greater its chance of spreading.
Tumor ulceration: Ulceration is a breakdown of the skin on top of the melanoma. Melanomas with ulceration are more serious because they have a greater risk of spreading, so they are staged higher than tumors without ulceration.
N indicates whether or not the cancer has already spread to nearby lymph nodes. The N category also includes in-transit tumors that have spread beyond the primary tumor toward the local lymph nodes but have not yet reached the lymph nodes.
M represents spread or metastasis to distant lymph nodes or skin sites and organs such as the lungs or brain.
After TNM categories are identified, the overall stage number is assigned. A lower stage number means less progression of the disease.
Risk Of Getting Melanoma
Melanoma is more than 20 times more common in whites than in African Americans. Overall, the lifetime risk of getting melanoma is about 2.6% for whites, 0.1% for Blacks, and 0.6% for Hispanics. The risk for each person can be affected by a number of different factors, which are described in Risk Factors for Melanoma Skin Cancer.
Melanoma is more common in men overall, but before age 50 the rates are higher in women than in men.
The risk of melanoma increases as people age. The average age of people when it is diagnosed is 65. But melanoma is not uncommon even among those younger than 30. In fact, its one of the most common cancers in young adults .
Recommended Reading: What Is Braf Testing In Melanoma
What Are The Melanoma Stages And What Do They Mean
Early melanomas
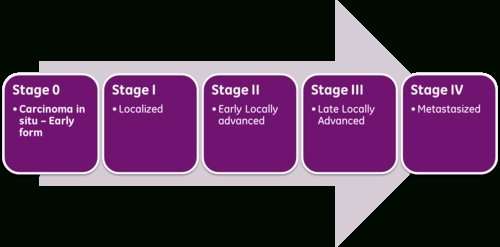
Stage 0 and I are localized, meaning they have not spread.
- Stage 0: Melanoma is localized in the outermost layer of skin and has not advanced deeper. This noninvasive stage is also called melanoma in situ.
- Stage I: The cancer is smaller than 1 mm in Breslow depth, and may or may not be ulcerated. It is localized but invasive, meaning that it has penetrated beneath the top layer into the next layer of skin. Invasive tumors considered stage IA are classified as early and thin if they are not ulcerated and measure less than 0.8 mm.
Find out about treatment options for early melanomas.
Intermediate or high-risk melanomas
Localized but larger tumors may have other traits such as ulceration that put them at high risk of spreading.
- Stage II: Intermediate, high-risk melanomas are tumors deeper than 1 mm that may or may not be ulcerated. Although they are not yet known to have advanced beyond the primary tumor, the risk of spreading is high, and physicians may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to verify whether melanoma cells have spread to the local lymph nodes. Thicker melanomas, greater than 4.0 mm, have a very high risk of spreading, and any ulceration can move the disease into a higher subcategory of stage II. Because of that risk, the doctor may recommend more aggressive treatment.
Learn more about sentinel lymph node biopsy and melanoma treatment options.
Advanced melanomas
The Stage Of Melanoma Depends On The Thickness Of The Tumor Whether Cancer Has Spread To Lymph Nodes Or Other Parts Of The Body And Other Factors
To find out the stage of melanoma, the tumor is completely removed and nearby lymph nodes are checked for signs of cancer. The stage of the cancer is used to determine which treatment is best. Check with your doctor to find out which stage of cancer you have.
The stage of melanoma depends on the following:
- The thickness of the tumor. The thickness of the tumor is measured from the surface of the skin to the deepest part of the tumor.
- Whether there are:
- Satellite tumors: Small groups of tumor cells that have spread within 2 centimeters of the primary tumor.
- Microsatellite tumors: Small groups of tumor cells that have spread to an area right beside or below the primary tumor.
- In-transit metastases: Tumors that have spread to lymph vessels in the skin more than 2 centimeters away from the primary tumor, but not to the lymph nodes.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival
What Tests Are Used To Stage Melanoma
There are several tests your doctor can use to stage your melanoma. Your doctor may use these tests:
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Patients with melanomas deeper than 0.8 mm, those who have ulceration under the microscope in tumors of any size or other less common concerning features under the microscope, may need a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes to determine if the melanoma has spread. Patients diagnosed via a sentinel lymph node biopsy have higher survival rates than those diagnosed with melanoma in lymph nodes via physical exam.
- Computed Tomography scan: A CT scan can show if melanoma is in your internal organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan: An MRI scan is used to check for melanoma tumors in the brain or spinal cord.
- Positron Emission Tomography scan: A PET scan can check for melanoma in lymph nodes and other parts of your body distant from the original melanoma skin spot.
- Blood work: Blood tests may be used to measure lactate dehydrogenase before treatment. Other tests include blood chemistry levels and blood cell counts.
Stage I And Stage Ii Melanomas
Making a melanoma diagnosis means gathering as much information about your skin cancer as possible. One key step is determining the cancers stage, which is a measure of the amount and severity of cancer in the body. Staging helps your doctor understand how best to treat the cancer, and is used when discussing survival rates.
Following stage 0 , the degrees of melanoma range from stage I through stage IV, with higher numbers indicating further spreading of the cancer throughout the body.
There are three factors commonly used to determine melanoma staging, and theyre represented by the TNM system. The first factor is the severity of the primary tumor , which includes how thick the tumor is and whether the skin covering it has broken. The second factor is whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes . The third factor is whether the cancer has spread, or metastasized , to lymph nodes farther away in the body or other organs.
You May Like: What Are The Forms Of Skin Cancer
Diagnosis And Staging What It Means For You
How is melanoma diagnosed?
To diagnose melanoma, a dermatologist biopsies the suspicious tissue and sends it to a lab, where a dermatopathologist determines whether cancer cells are present.
After the disease is diagnosed and the type of melanoma is identified, the next step is for your medical team to identify the stage of the disease. This may require additional tests including imaging such as PET scans, CT scans, MRIs and blood tests.
The stage of melanoma is determined by several factors, including how much the cancer has grown, whether the disease has spread and other considerations. Melanoma staging is complex, but crucial. Knowing the stage helps doctors decide how to best treat your disease and predict your chances of recovery.
There Are Different Types Of Cancer That Start In The Skin
There are two main forms of skin cancer: melanoma and nonmelanoma.
Melanoma is a rare form of skin cancer. It is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body than other types of skin cancer. When melanoma starts in the skin, it is called cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma may also occur in mucous membranes . This PDQ summary is about cutaneous melanoma and melanoma that affects the mucous membranes.
The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. They are nonmelanoma skin cancers. Nonmelanoma skin cancers rarely spread to other parts of the body.
Also Check: Osteomyoma
How Common Is Melanoma
Melanoma accounts for only about 1% of all skin cancers, but causes the great majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Its one of the most common cancers in young people under 30, especially in young women.
Melanoma incidence has dramatically increased over the past 30 years. Its widely accepted that increasing levels of ultraviolet exposure are one of the main reasons for this rapid rise in the number of melanoma cases.