Reducing Your Risk Of Lobular Carcinoma
You may be able to lower your risk of breast cancer by maintaining a healthy weight, getting regular exercise, and drinking alcohol in moderation. Unfortunately, you cant change most of the other risk factors. This means you can still develop breast cancer despite living a healthy lifestyle.
While it can be hard to see ILC on mammograms, they are still the most effective tool for breast cancer screening. Screening recommendations vary depending on your risk level. Talk with your doctor about your risk and find out how screening guidelines apply to you.
Women at high risk of developing breast cancer may have options to help prevent the disease, including chemoprevention and mastectomy. Chemoprevention is medicine to block the effect of estrogen on breast cell growth. Surgery to remove the breasts in women at high risk for breast cancer can decrease the risk of breast cancer by about 97%. Your doctor and genetic will help you explore this option during genetic testing for breast cancer.
Morphological Features And Immunophenotype Of Ilc
Figure 1 Comparison of invasive lobular carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma of no special type. Haematoxylin and Eosin stained sections demonstrating the morphology of ILC and IDC of no special type. ILC showing diffuse infiltration of the stroma with a single file pattern, surrounding a normal breast duct in a concentric manner. IDC showing more cohesive tumor cells forming tubules with destructive infiltration of the mammary stroma. Comparison of E Cadherin expression in ILC and IDC of no special type. Complete absence of staining is seen in ILC. Strong and diffuse membranous expression is seen in IDC.
Figure 2 Classical morphology and immunophenotype of invasive lobular carcinoma. Haematoxylin and Eosin stained sections demonstrating the classical morphology of invasive lobular carcinoma . Single file pattern of invasion, highlighted with bracket High power view showing discohesive tumor cells. An intracytoplasmic vacuole is highlighted with the red arrow. Concentric pattern of infiltration around a normal breast duct, highlighted with asterisk . Classical immunophenotype of ILC. Strong and diffuse nuclear expression of oestrogen receptor and progesterone receptor. Absence of membranous E Cadherin expression.
Whats The Difference Between Stage 1 And 1a Breast Cancer
The breast cancer has been detected in the early stages and can be very effectively treated. Stage 1 can be divided into Stage 1A and Stage 1B. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and the lymph nodes with evidence of cancer. Stage 1A breast cancer means the following description applies:
Read Also: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Are Signs And Symptoms Of Lobular Breast Cancer How Does The Breast Tissue Feel
There may not be any obvious signs of lobular breast cancer at first. Unlike more common breast cancers, lobular breast cancer is less likely to form into a lump in the breast tissue or under the arm. Instead, you may feel a fullness, thickening or swelling in one area that feels different from the surrounding area. Nipple flattening or inversion can also be a sign of lobular breast cancer.
What To Expect From Your Doctor
Your doctor is likely to ask you a number of questions. Being ready to answer them may allow time later to cover other points you want to address. Your doctor may ask:
- When did you first begin experiencing symptoms?
- Have your symptoms been continuous or occasional?
- How severe are your symptoms?
- What, if anything, seems to improve your symptoms?
- What, if anything, appears to worsen your symptoms?
Don’t Miss: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
Treating Invasive Breast Cancer
Treatment of invasive breast cancer depends on how advanced the cancer is and other factors. Most women will have some type of surgery to remove the tumor. Depending on the type of breast cancer and how advanced it is, you might need other types of treatment as well, either before or after surgery, or sometimes both.
See Treating Breast Cancer for details on different types of treatment, as well as common treatment approaches based on the stage or other factors.
Our team is made up of doctors and oncology certified nurses with deep knowledge of cancer care as well as journalists, editors, and translators with extensive experience in medical writing.
Arpino G, Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast:tumor board characteristics and clinical outcome. Breast Cancer Research. 2004 6: 149.
Dillon DA, Guidi AJ, Schnitt SJ. Ch. 25: Pathology of invasive breast cancer. In: Harris JR, Lippman ME, Morrow M, Osborne CK, eds. Diseases of the Breast. 5th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott-Williams & Wilkins 2014.
Henry NL, Shah PD, Haider I, Freer PE, Jagsi R, Sabel MS. Chapter 88: Cancer of the Breast. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Doroshow JH, Kastan MB, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloffs Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Elsevier 2020.
Huober J, Gelber S, Goldhirsch A, et al. Prognosis of medullary breast cancer: analysis of 13 International Breast Cancer Study Group trials. Ann Oncol. 2012 23:28432851.
What Are The Treatment Options
ILC can be more difficult to diagnose than other forms of breast cancer because it spreads in a unique pattern that is not always noticeable in imaging tests. The good news is that its a relatively slow-growing cancer, which gives you time to form a treatment plan with your cancer team.
There are several treatment options that can help increase your chances of a full recovery.
Read Also: Soderstrom Skin Cancer Screening
What Is The Difference Between Invasive Lobular Carcinoma And Lobular Carcinoma In Situ
LCIS means the cancer is still contained in the milk glands and has not invaded any other area. ILC is cancer that began growing in the lobules and is invading the surrounding tissue. Cancer staging done by a physician, along with a physical exam and medical history can help identify the best treatment options.
Over 80% of the time, invasive lobular breast cancer is ER+ and HER2-. Sometimes invasive lobular breast cancer can be larger than it appears to be when reviewing a mammogram because of the way it grows. It can be commonly identified as a higher stage cancer.
Invasive lobular carcinoma is known for being a slow growing tumor, usually grade I or II. Slow growing, grade I tumors dont usually respond well to chemotherapy, so hormonal therapy is key for this type of cancer.
If it spreads to other organs, becoming Stage IV breast cancer, it typically goes to the colon, uterus, ovary, stomach, lung, bone, and other areas.
Determining The Extent Of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Once it’s determined that you have invasive lobular carcinoma, your doctor will determine if additional tests are needed to learn the extent of your cancer. Most women do not require additional tests other than breast imaging, physical exam and blood tests.
Using this information, your doctor assigns your cancer a Roman numeral that indicates its stage. Breast cancer stages range from 0 to IV, with 0 indicating cancer that is very small and noninvasive. Stage IV breast cancer, also called metastatic breast cancer, is cancer that has spread to other areas of the body.
Read Also: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Alternative Treatments For Hot Flashes
Hot flashes bouts of sudden, intense warmness that can leave you sweaty and uncomfortable can be a symptom of natural menopause or a side effect of hormone therapy for breast cancer.
Women with breast cancers that use hormones to grow may receive hormone therapy to block the interaction between hormones and cancer cells. Most invasive lobular carcinomas are hormone receptor positive.
Talk to your doctor if you experience hot flashes. If hot flashes are mild, they’re likely to subside over time. In most women, hot flashes eventually disappear. However, some women experience severe and bothersome hot flashes. Many conventional treatments are available for hot flashes, including medications.
If treatment for hot flashes won’t work as well as you’d like, it might help to add complementary and alternative treatments to make you feel better.
Options might include:
- Tai chi
- Yoga
While none of these alternative treatments is proved to help control hot flashes, some preliminary evidence shows that some breast cancer survivors find them helpful.
If you’re interested in trying alternative treatment for hot flashes, talk to your doctor about your options.
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rates
Survival rates for cancer are typically calculated in terms of how many people live at least 5 years after their diagnosis. The average 5-year survival rate for breast cancer is 90 percent, and the 10-year survival rate is 83 percent. This is an average of all stages and grades.
The stage of the cancer is important when considering survival rates. For instance, if the cancer is only in the breast, the 5-year rate of survival is 99 percent. If it has spread to the lymph nodes, the rate decreases to 85 percent.
Because there are many variables based on the type and spread of cancer, its best to talk with your doctor about what to expect.
Recommended Reading: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
Lobular Breast Cancer Comes Into The Research Spotlight
The first time Leigh Pate heard the term was when she got a phone call from her doctor following a series of diagnostic tests. The mammogram had been clean â like so many before it â but the ultrasound and biopsy told another story.
âAfter I hung up, I went to my computer and typed in âglobular breast cancer,ââ said Pate, a 51-year-old public policy consultant from Seattle of her diagnosis seven years ago. âGoogle had to correct me.â
Pate went through two surgeries, five months of chemotherapy, 33 courses of radiation and four years of tamoxifen, a daily pill that cuts off the fuel source for this very estrogen receptorâpositive disease. By the end of her treatment and recovery, she not only knew what lobular breast cancer was, she was determined to shine a spotlight on this idiosyncratic subtype.
âI started asking about lobular and realized they donât know enough,â she said. âItâs lumped together and treated just like regular ER+ breast cancer. But lobular presents differently, it behaves differently and it has different subtypes and variants.â
Patients like Pate arenât the only ones pushing for more lobular research.
President and executive director of Seattle Cancer Care Alliance and head of medical oncology at the University of Washington, Davidson was the powerhouse who built University of Pittsburghâs strong lobular research program before joining Fred Hutch.
Lobular, it would seem, is finally having its day.
Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Aggressive

invasive lobular carcinomainvasive lobular carcinomacancercancer
Over time, invasive lobular carcinoma can spread to the lymph nodes and possibly to other areas of the body. Although invasive lobular carcinoma can affect women at any age, it is more common as women grow older.
Subsequently, question is, is invasive lobular carcinoma curable? If treatment cures cancer, this means that it destroys all of the cancer cells, and the cancer will never return. Although this is the goal of treatment, it is not always possible. Often, cancer goes into remission. A person may have few or no clinical symptoms, but cancer cells still exist in the body.
Accordingly, does invasive lobular breast cancer spread?
Over time, invasive lobular breast cancer can also spread to the lymph nodes in the underarms, beneath the breast or inside the chest or to other areas in the body away from the breast.
What is the treatment for invasive lobular carcinoma?
The treatment options for invasive lobular carcinoma include localized approaches such as surgery and radiation therapy that treat the tumor and the surrounding areas, as well as systemic treatments such as chemotherapy and hormonal or targeted therapies that travel throughout the body to destroy cancer cells that may
Read Also: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Metastasis
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Stages
When diagnosing breast cancer, staging becomes an important thing. When we talk of staging, it is process used to find out how much the cancer has advanced or spread and where its located. The details on staging also help plan for the cancer treatment and come up with a prognosis.
Staging provides a way of ensuring that a cancer patient gets the best possible treatment. In a majority of cancers, staging is based on these three main factors:2
- The size of the tumor as well as its growth into the areas around it
- The spread of the cancer to lymph nodes close to it
- The spread of the cancer to other areas of the body distance areas from its original location
When the TNM are established, the stage can be assigned to the cancer. That said, here are the different stages of invasive lobular carcinoma:
How Is Lobular Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Your doctor will likely order a mammogram and ultrasound to look for abnormal breast tissue. A breast MRI scan is a more sensitive test for detecting breast cancer. Your doctor may order this test if you are at higher risk of breast cancer or if mammogram or ultrasound findings raise concerns that should be investigated further.
If abnormal breast tissue is seen on breast imaging, a small sample of tissue is taken from the area of concern using a needle and examined under a microscope. The results of the biopsy either confirm or rule out a diagnosis of breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Osteomyoma
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Diagnosis
Your doctor will start with a physical exam of your breasts and nearby lymph nodes. If they feel any problems like thickening, hardening, or swelling, you may have tests including:
- Mammogram. ILC can be hard to spot on a mammogram, which makes X-ray pictures of your breast, because the cancer cells tend to grow in a line rather than in a mass.
- Ultrasound. Sound waves create images of the inside of your breast. An ultrasound may be better at finding ILC than a mammogram.
- Biopsy. If they find a suspicious area, your doctor will order a biopsy to check the cells. Most biopsies use a needle to take out a sample of cells from the breast. In some cases, the doctor will remove a larger sample or the entire tumor.
- CT scan. This is a powerful X-ray that makes detailed pictures inside your body.
- PET scan. Along with a CT scan, this test can help find cancer in lymph nodes and other areas.
- MRI. This uses strong magnets and radio waves to make pictures of the breast and things inside your body.
- Bone scan. A radioactive material called a tracer is injected into your arm. It shows up on pictures to tell your doctor whether cancer may have traveled to your bones.
- The results of your exams will tell your doctor whether you have cancer and whether its spread so they can recommend the best treatment options.
What Are The Treatments For Stage 1 Ductal Breast Cancer
Treatments for Stage 1 Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer. For Stage I cancer patients, radiation is generally not needed if the entire breast is removed. Reconstruction techniques vary and can include implants or using a womans own tissues. The plastic and reconstructive surgeon will help a woman make the most appropriate choice for her.
Recommended Reading: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Of The Breast: The Increasing Importance Of This Special Subtype
1UQ Centre for Clinical Research, The University of Queensland, Herston, Brisbane, Australia
2QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute, Herston, Brisbane, Australia
1UQ Centre for Clinical Research, The University of Queensland, Herston, Brisbane, Australia
3Department of Histopathology, Sullivan Nicolaides Pathology, Bowen Hills, Brisbane, Australia
What Is New In The Phenotypic And Molecular Characteristics Of Lobular Carcinoma In Situ
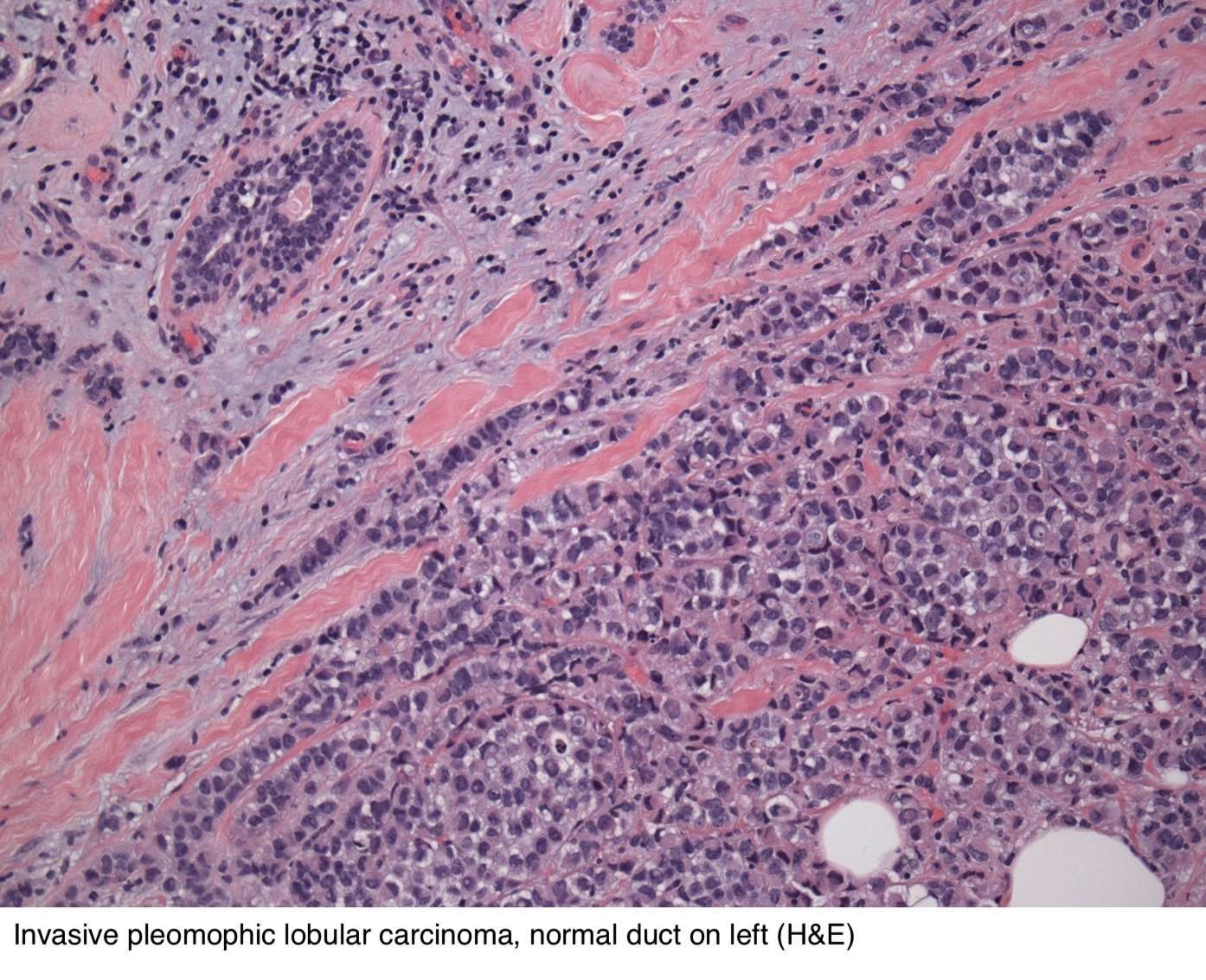
The WHO Classification recognises three variants of LCIS: classic , pleomorphic , and florid . The defining features of both PLCIS and FLCIS have recently been clarified: PLCIS is characterised by cells with enlarged nuclei or similar cytological features to those seen in high-grade ductal carcinoma in situ . FLCIS is characterised by confluent expansive growth, and there must be marked distension of involved acini with little intervening stroma or an expanded acinus or duct approximately 4050 cells in diameter . PLCIS is therefore characterised by its degree of cytological atypia, whereas FLCIS describes an architectural pattern with proliferation that is of classic type . Unlike CLCIS, PLCIS and FLCIS are more likely to have comedo-necrosis and calcifications and hence clinical and radiological presentations . CLCIS is invariably ER and PR positive, and HER2 negative FLCIS exhibits a similar phenotype, though may occasionally be HER2 positive, whilst PLCIS exhibits a more varied phenotype, with less frequent hormone receptor positivity, and an increased likelihood for HER2 overexpression, particularly in the apocrine-type of PLCIS as well as a higher proliferative index . The natural history of PLCIS and FLCIS is as yet not well understood, and as such, relative risk of progression to frank invasive disease remains unclear, and we await long-term outcome data .
Read Also: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Outlook For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Cancer affects everyone differently. Your outlook may depend on things like how early youre diagnosed and how well your body responds to treatment.
In general, about 90% of all women with breast cancer live at least 5 years after diagnosis. While there isnt much information about specific types of breast cancer, these survival rates are tracked by stage at diagnosis or how far the cancer has spread:
- Localized : 98.9% live at least 5 years.
- Regional : 85.7% live at least 5 years.
- Distant : 28.1% live at least 5 years.
Breastcancer.org: Lobular carcinoma in situ , Invasive lobular carcinoma, Bone Scans, LCIS and Breast Cancer Risk, Treatments for LCIS, Test for Diagnosing ILC, and Systemic Treatments for ILC: Chemotherapy, Hormonal Therapy, Targeted Therapies, Signs and Symptoms of ILC, Local Treatments for ILC: Surgery and Radiation Therapy.
Breast Cancer Network of Strength: Lobular carcinoma in situ and Infiltrating lobular carcinoma.
National Cancer Institute: Lobular carcinoma in situ, Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer.
American Cancer Society: What is breast cancer? and “Special Section: Breast Carcinoma in Situ,” Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer, Radiation for Breast Cancer.
College of American Pathologists: Lobular carcinoma in situ, “Invasive lobular carcinoma.
MedlinePlus: Tamoxifen.