Can A Squamous Cell Carcinoma Kill You
All skin cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body but this isn’t common. Most cases of SCC can be cured if they’re caught early. But if you don’t get treatment, it can spread beyond the skin.
Around 2% to 4% of SCCs will spread to lymph nodes, bones, or other tissue. SCCs in people of color are more often diagnosed at a later stage, when they may have had a chance to spread.
If it spreads somewhere like your lymph nodes, that means the cancer may be aggressive and more likely to spread. This is called metastatic disease and it can become life-threatening.
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Lung
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung is a type of lung cancer. It occurs when abnormal lung cells multiply out of control and form a tumor. Eventually, tumor cells can spread to other parts of the body including the
- lymph nodes around and between the lungs
- liver
- adrenal glands
- brain.
In general, there are two categories of lung cancer: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. The cancer cells in each type look different under the microscope. They are also treated differently. The prognosis for non-small cell lung cancer tends to be better than for small cell lung cancer non-small cell lung cancers are more likely to be contained in one area, making treatment more likely to be successful.
Squamous cell carcinoma is one type of non-small cell lung cancer. The others are
- adenocarcinoma
- large cell carcinoma.
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer. Squamous cell carcinoma is the second-most common type. It accounts for about 30% of all cases of non-small cell lung cancer.
Your risk of all types of lung cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma, increase if you
Most cases of squamous cell carcinoma start in the center of the lungs. These tumors may cause some symptoms, such as coughing up blood, at an earlier stage than tumors on the edges of the lungs, such as adenocarcinomas.
What Is The Best Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The best treatment for squamous cell carcinoma depends on several factors: the type of squamous cell carcinoma the location of the skin cancer your health and medical conditions. Your dermatologist can assess your skin cancer and come up with an individualized treatment to meet your goals and specific needs.
When appropriate, Mohs surgery is the treatment that offers the highest cure rate amongst all treatments. 99% of all squamous cell carcinomas can be cured with Mohs Surgery. Mohs surgery is a technique that preserves your normal skin, only removing the skin cancer, and thereby minimizing scaring and maximizing your cosmetic outcome. Mohs surgery is the most advanced treatment for squamous cell carcinoma.
When is it appropriate to treat a squamous cell carcinoma with Mohs Surgery?
Did you know:
- You can use your smartphone to take photos of your skin to document your moles, both how they look and their location. Then, if in the future you are concerned a spot changed, you can refer back to those high-quality photos.
Also Check: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
SCC signs and symptoms include skin changes like:
- A rough-feeling bump or growth which might then crust over and bleed.
- A growth that is higher than the skin but has a depression in the middle.
- A sore that will not heal, or a sore that heals and then comes back.
- A piece of skin that is flat, is scaly and red.
- A precancerous growth called actinic keratosis, which is a bump or lump that can feel dry, itchy, scaly, or be discolored.
- A precancerous skin lesion called actinic cheilitis, which happens mainly on the lower lip. The tissue becomes pale, dry, and cracked.
- A precancerous condition called leukoplakia, in which white spots develop in the mouth, on the tongue, gums, or cheeks
The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
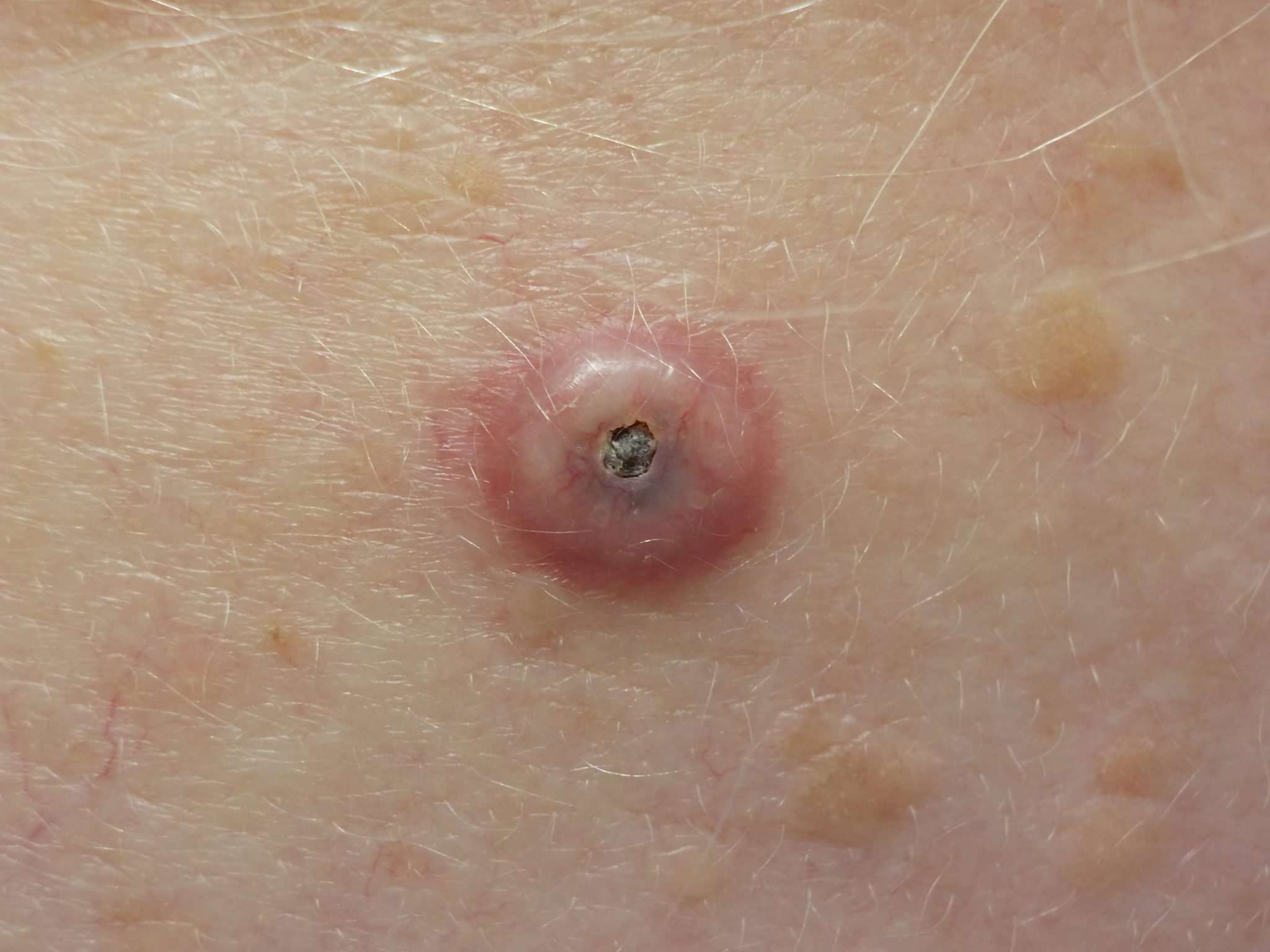
Squamous cell carcinoma usually first appears as a red, scaly plaque of skin or as a hard domed bump. Both varieties typically feel rough and crusty and can bleed when scraped. Growths may also be pink and dry and may itch or burn.
As mentioned above, the cancer usually forms on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, lips, arms, legs, and tops of the hands, but it can also more rarely appear on areas not exposed to the sun including the lower lip, genitals, in the lining of organs and the passages of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
Squamous cell carcinoma usually develops slowly but can spread to the lymph nodes and other organs if left untreated. If caught early though, it is highly treatable.
You May Like: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
The Risks The Causes What You Can Do
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is caused by DNA damage that leads to abnormal changes in the squamous cells in the outermost layer of skin.
Understanding what causes this damage and the factors that increase your risk of developing SCC can help you detect the disease early or prevent it from happening in the first place.
These factors increase your SCC risk:
- Unprotected exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
- Weakened immune system due to illness or certain immunosuppressive medications.
- History of skin cancer including basal cell carcinoma .
- Age over 50: Most SCCs appear in people over age 50.
- Fair skin: People with fair skin are at an increased risk for SCC.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop SCC.
- Sun-sensitive conditions including xeroderma pigmentosum.
- Chronic infections and skin inflammation from burns, scars and other conditions.
How Can I Prevent Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The best way to prevent squamous cell carcinoma is to limit sun exposure:
-
Stay out of the sunsit in the shade, try to avoid the sun between 10:00 am and 4:00 pm
-
Don’t sunbathe or use tanning beds
-
Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, and hats with broad brims
-
Use sunscreen thats at least 30 sun protection factor it’s important to use more sunscreen every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating
See a doctor if you see a change in a skin growth that doesn’t go away after a few weeks.
Recommended Reading: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Metastasis
References And Information Sources Used For The Article:
Wolff, K., & Johnson, R. A. . Fitzpatricks color atlas and synopsis of clinical dermatology. McGraw-Hill Medical.
Thiers, B. H. . Year Book of Dermatology 1988. Archives of Dermatology, 125, 1150.
Burns, T., & Breathnach, S. . Rooks Textbook of dermatology Vol 4. London: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1992.
Bolognia, J. L., Schaffer, J. V., Duncan, K. O., & Ko, C. J. . Dermatology Essentials E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
How Can I Prevent Scc
Reducing ultraviolet exposure will reduce the risk of getting an SCC.
Top sun safety tips
- Protect your skin with clothing, and dont forget to wear a hat that protects your face, neck and ears, and a pair of UV protective sunglasses.
- Spend time in the shade between 11am and 3pm when its sunny. Step out of the sun before your skin has a chance to redden or burn. Keep babies and young children out of direct sunlight.
- When choosing a sunscreen look for a high protection SPF to protect against UVB, and the UVA circle logo and/or 4 or 5 UVA stars to protect against UVA. Apply plenty of sunscreen 15 to 30 minutes before going out in the sun, and reapply every two hours and straight after swimming and towel-drying.
- Sunscreens should not be used as an alternative to clothing and shade, rather they offer additional protection. No sunscreen will provide 100% protection.
- It may be worth taking Vitamin D supplement tablets as strictly avoiding sunlight can reduce Vitamin D levels. You should consult your doctor about this.
Treatment of areas of scaly sun damage may reduce your risk of an SCC.
Read Also: Osteomyoma
Answer: Invasive Scc Diagnosis
First, I applaud you for noticing something that wasnt healing and going in to have it checked. Although invasive SCC sounds very scary, its usually quite treatable with a Mohs surgery in that location. You will be ok. Continue to check your skin often. Now that youve had one type of skin cancer, you are prone to more surfacing over time .This answer has been solicited without seeing this patient and cannot be held as true medical advice, but only opinion. Seek in-person treatment with a trained medical professional for appropriate care.
You May Like: Do You Need Chemo For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
How Is Squamous Cell Cancer Diagnosed
Your doctor will first perform a physical exam and inspect any abnormal areas for signs of SCC. Theyll also ask you about your medical history. If SCC is suspected, your doctor may decide to take a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
A biopsy usually involves removing a very small portion of the affected skin. The skin sample is then sent to a laboratory for testing.
In some cases, your doctor may need to remove a larger part or all of the abnormal growth for testing. Talk to your doctor about any potential scarring or biopsy concerns.
Treatment for SCC varies. Treatment is based on:
- the extent and severity of your cancer
- your age
- your overall health
- the location of the cancer
If SCC is caught early, the condition can usually be successfully treated. It becomes harder to cure once it has spread. Many treatments can be performed as in-office procedures.
Some doctors may also use photodynamic therapy, laser surgery, and topical medications to treat SCC. However, the Food and Drug Administration hasnt approved these methods for treating SCC:
Once SCC has been treated, its critical to attend all follow-up visits with your doctor. SCC can return, and its important to monitor your skin for any precancerous or cancerous areas at least once per month.
Read Also: Soderstrom Skin Cancer Screening
What Does A Squamous Cancer Look Like
Squamous cell carcinomas look like spots or bumps on the skin that are usually scaly or crusty. They might crack or bleed, and theyre often painful or tender. They do not go away on their own but instead grow over time. They also may look like a big ulcer that does not close up by itself.
SCCs often arise in areas of your body that are in the sun a lot, like the face, neck, and hands. Some are caused by the human papilloma virus , so they can develop in areas where the virus causes warts like the skin on the fingers, toes, genitals, and around the mouth.
Pro Tip
Many times patients think that the growth is a spider bite. Once we see the lesion it is easy for us to determine that it needs a biopsy to rule out skin cancer. Dr. Lauren Levy
SCCs can also show up in or next to places where you have a chronic wound, scarring , or skin inflammation .
How Does This Cancer Typically Progress

In the skin form of the disease, although spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs is possible, it is very uncommon. With SCC of the nose, spread may occur to the lymph nodes under the chin .
Dogs with multicentric SCC often develop new lesions in other sites after surgical removal of lesions.
The digit form of SCC is far more aggressive. It can spread to the local lymph nodes and beyond. For this reason, your veterinarian may recommend staging . Staging may include bloodwork, urinalysis, X-rays of the lungs, and possibly an abdominal ultrasound. If any lymph nodes appear to be affected , samples may be taken via FNA to determine if the tumor has spread into them.
Read Also: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Hi a family member has just been diagnosed with this can someone tell me how serious this is? Caused by over exposure to sun lump on the scalp.
Welcome to Cancer Chat, Hawk.
Im sorry youve not received a reply from anyone here yet.
Ive had a little look on the forum and found a similar conversation between another member and one of our cancer nurses, Jean. It might be of some help and reassurance: Skin cancer. It explains a little bit about the difference between basal cell skin cancer , and squamous cell skin cancer, the type of skin cancer that your family member has.
You May Like: How Is Skin Cancer Detected And Diagnosed
What Are The Types Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma develops when the flat cells in the toplayer of skin grow and divide in an uncontrolled way.
You can get an SCC wherever there are squamous cells which is in manydifferent parts of the body. However, typically they appear on parts of theskin that have been exposed to a lot of ultraviolet radiation from the sunor from tanning beds.
An early form of skin cancer, called Bowen’s disease, which looks like a red, scaly patch, can also develop into an SCC if nottreated.
An SCC can be quite an aggressive cancer if left untreated. If you evernotice a sore, scab or scaly patch of skin that doesnt heal within 2 months,see a doctor.
Don’t Miss: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Do Some People Have A Higher Risk Of Developing Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Cancer
Yes. The key risk factors for getting this skin cancer are listed below. A risk factor is anything that increases your risk of developing a disease.
While having one or more risk factors for SCC of the skin increases your risk of developing it, some people who get this skin cancer dont seem to have any risk factors. People of all colors get this skin cancer, including people of African, Asian, and Latin descent.
If you find a spot on the skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist to find out what it is. Youll find out how this skin cancer is diagnosed and treated at, Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Diagnosis and treatment.
1 American Academy of Dermatology. Indoor tanning fact sheet. Last accessed January 31, 2019.
2 Omland SH, Ahlstrom MG, et al. Risk of skin cancer in patients with HIV: A Danish nationwide cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018 79:689-95.
ImagesGetty Images
ReferencesAnadolu-Brasie R, Patel AR, et al., Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. In: Nouri K, et al. Skin Cancer. McGraw Hill Medical, China, 2008: 86-114.
Nadhan KS, Chung CL, et al. Risk factors for keratinocyte carcinoma skin cancer in nonwhite individuals: A retrospectiveaAnalysis. J Am Acad Dermatol , doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2019.01.038.
Omland SH, Ahlstrom MG, et al. Risk of skin cancer in patients with HIV: A Danish nationwide cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018 79:689-95.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prevention:
Disadvantages of the treatment theres a chance of scarring. There is it. There wasnt any mortality connected with second primary tumors. Its important that populations at probability particularly those who have fair skin residing in regions with high UV radiation exposure know of means to reduce the danger of the status. The growth of cancer cells within this area is comparatively slow. A couple of months before, a little growth appeared on the top side of my left forearm. There is typically an obvious growth on the epidermis or an ulcerated location.
Unfortunately, there is absolutely no control regarding how deep the tissue was destroyed. Modern-day treatment approaches are now increasingly complex, as sophisticated methods are developed to attempt to preserve vocal function. These cells are located in the top layer of the epidermis.
Squamous cell carcinoma is a disease that can easily be brought about by an individuals working atmosphere or living atmosphere. It may be a serious medical condition but it is very easy to avoid and prevent. This is a disease that can be easily caused by a persons living environment or working environment.
The sooner a skin cancer is identified, the simpler its to deal with. Cutting out the tumor, together with a little margin of normal skin, is frequently used to deal with squamous cell cancers.
Recommended Reading: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
What Should I Do If I Think I Have A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
If you notice a change to or growth on your skin, make an appointment to see your doctor straight away. Your doctor will assess the size, location and look of the growth. They will also ask you how long you have had it and whether it bleeds or itches.
If your doctor thinks the growth may be cancer, they may take a small sample of tissue . The tissue sample will be sent to a laboratory and examined under a microscope. Your doctor will let you know whether the sample shows any cancer cells or not, and will recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented Or Avoided
Most cases of squamous cell carcinoma can be prevented by avoiding exposure to UV rays.
- Avoid the sun, especially during peak hours of 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.
- Use sunscreen, even on cloudy days.
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat, protective clothing, and sunglasses when you go outside.
- Avoid places that reflect light, such as water, sand, or concrete.
- Dont try to get a tan, including using tanning beds or sunlamps.
If squamous cell carcinoma is caught early, it is usually easy to treat. Examine your skin once a month. See your family doctor right away if you find anything that looks suspicious.
Recommended Reading: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn