What Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma is an invasive cancer where abnormal cancer cells that began forming in the milk ducts have spread beyond the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body. It is also sometimes called infiltrative ductal carcinoma.
- IDC is the most common type of breast cancer, making up nearly 70- 80% of all breast cancer diagnoses.
- IDC is also the type of breast cancer that most commonly affects men.
Additional Grading Criteria: A Composite Total Of Tubular Nuclear And Mitotic Index Assesments
As a grade of low, intermediate or high is obtained through a composite sum by assigning a score based on the nuclear assessment, a mitotic index assessment, and a tubular assessment.
The nuclear assessment is based on the nuclear size within the invasive cells. They are described from small to medium to large in size, as well as by their uniformity in size and shape.
The tubular assessment refers to an approximate, quantitative account of the amount of cell groupings which remain in their normal tubular shape. The smaller the percentage of tubular structures in comparison to other shapes, the higher the score. Other structures to appear may include solid trabecula, vacuolated single cells, alveolar nests, and solid sheets of cells.
The mitotic index refers to evident patterns of cell division.Mitosis is a process by which a cell separates into two genetically identical daughter cells. . So, the mitotic index is assessment of the abundance of these pairs of daughter cells, measured in the count per square millimeter. Mitoses are only counted in the invasive area of the lesion .
| Histologic Grade | |
| 11-19 = 2 | >20 = 3. |
How Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast Treated
Treatment options available for individuals with Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast are dependent upon the following:
- Type of cancer
- The staging of the cancer
- Whether the cancer cells are sensitive to certain particular hormones, and
- Personal preferences
In general, breast cancer stages range from 0 to IV. 0 may indicate a small and non-invasive cancer, while IV indicates that the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. Briefly, as per US National Cancer Institute , breast cancer is staged as follows:
- Stage 0 : The abnormal cancer cells are confined to their site of origin
- Stage I: The tumor is 2 centimeters in diameter or less, and has not spread outside the breast
- Stage II: The tumor may be up to 5 centimeters in diameter and may have spread to lymph nodes. Another criteria is that the tumor may be larger than 5 centimeters in diameter, but has not spread to surrounding lymph nodes
- Stage III: The tumor may be more than 5 centimeters in diameter and may have spread to several axillary lymph nodes, or to the lymph nodes near the breastbone. The cancer may also have spread to the breast skin/chest wall, causing ulcer-like sores, or a swelling
- Stage IV: The tumor has spread outside the breast and to other organs, such as the bones, liver, lungs, or brain, regardless of its size
If breast cancer is diagnosed, staging helps determine whether it has spread and which treatment options are best for the patient.
Hormone therapy:
Also Check: How Serious Is Skin Cancer
Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Stage 2 breast cancer is divided into two groups:
- Stage 2A
- Stage 2B
Stage 2A can mean:
No cancer is seen in the breast but cancer is found in one to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is 2cm or smaller and cancer is found in one to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone.
The cancer in the breast is larger than 2cm but smaller than 5cm and no cancer is found in the lymph nodes under the arm.
Stage 2B can mean:
The cancer in the breast is larger than 2cm but smaller than 5cm. Cancer is found in one to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is larger than 5cm and no cancer is found in the lymph nodes under the arm.
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment
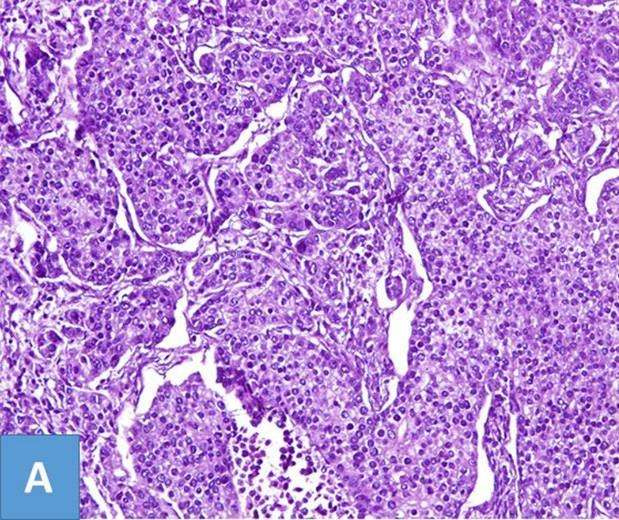
What is invasive ductal carcinoma?
About 268,600 women in the United States will be diagnosed with breast cancer in 2019. The most common form of breast cancer is called invasive ductal carcinoma . Its responsible for about 80 percent of all breast cancer diagnoses.
Carcinoma refers to a type of cancer that begins in the skin cells or the tissues lining your internal organs. Adenocarcinomas are more specific types of carcinomas that originate in the glandular tissue of the body.
Invasive ductal carcinoma, also known as infiltrating ductal carcinoma, gets its name because it begins in the milk-carrying ducts of the breast, and spreads to surrounding breast tissues. The two most common forms of invasive breast cancer are:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. Accounts for 80 percent of breast cancer diagnoses. This type begins in and spreads from the milk ducts.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Accounts for 10 percent of breast cancer diagnoses. This type begins in the milk-producing lobules.
While IDC can affect women at any age, its most frequently diagnosed in
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with IDC, rest assured that there are many different forms of treatment available.
The treatments for IDC fall into two main types:
Don’t Miss: Does Melanoma Metastasize To The Brain
What Does It Mean If My Report On Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Mentions Estrogen Receptor Or Progesterone Receptor
ER and PR are special tests that the pathologist does that are important in predicting response of the DCIS to hormone therapy . Testing for ER is done for most cases of DCIS, but testing for PR is not typically needed. Results for ER and PR are reported separately and can be reported in different ways:
- Negative, weakly positive, positive
- Percent positive with something saying whether the staining is weak, moderate, or strong
Ask your doctor how these results will affect your treatment.
Additional Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma:
There are four types of invasive ductal carcinoma that are less common:
- Medullary Ductal Carcinoma This type of cancer is rare and only three to five percent of breast cancers are diagnosed as medullary ductal carcinoma. The tumor usually shows up on a mammogram and it does not always feel like a lump; rather it can feel like a spongy change of breast tissue.
- Mucinous Ductal Carcinoma This occurs when cancer cells within the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma carries a better prognosis than more common types of IDCs.
- Papillary;Carcinoma ;This is a very good prognosis breast cancer that primarily occur in women over the age of 60.
- Tubular Ductal Carcinoma ;This is a rare diagnosis of IDC, making up only two percent of diagnoses of breast cancer. The name comes from how the cancer looks under the microscope; like hundreds of tiny tubes.; Tubular breast cancer has an excellent prognosis.
Show me more…
Read Also: What Is Merkel Cell Skin Cancer
Who Gets Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast is a very common type of breast cancer. Almost 70-80% of breast cancers are Ductal Carcinoma NOS types
- Middle-aged and older women past the age of 40 years are affected, though women over 65 years have the highest risk
- Although both women and men are capable of developing the condition, it is much more common in women
- All racial and ethnic groups are affected and no specific predilection is seen
- Developed countries show higher prevalence rate for breast cancer than developing countries; average of 80 cases per 100,000 populations, as against 18 cases per 100,000 populations seen in the developing countries. Thus, America, Europe, Australia have greater incidences than Asia and Africa
Cancer Cure And All Clear
Many people who have cancer want to know if theyre cured. You may hear words like cure and all clear in the media.
Cured means theres no chance of the breast cancer coming back. However, its not possible to be sure that breast cancer will never come back. Treatment for breast cancer will be successful for most people, and the risk of;recurrence;gets less as time goes on. Recurrence, unfortunately, can happen even many years after treatment, so no one can say with certainty that youre definitely cured.
All clear, or in remission which is another term you may have heard used, means theres no obvious sign of cancer at the moment.;
If your breast cancer has spread to other parts of your body this will affect your prognosis. Secondary breast cancer can be treated, sometimes for many years, but not cured. Find out more about secondary breast cancer.
In order to be as clear as possible, your treatment team is more likely to talk about your chances of survival over a period of time or the possibility of remaining free of breast cancer in the future.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Scientific Name For Skin Cancer
How Can Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast Be Prevented
The following measures may help in reducing the risk for Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast :
General lifestyle changes:
- Maintain a healthy weight and exercise regularly; physical activity can reduce risk, especially in post-menopausal women
- Implement and follow a well-balanced diet; a high intake of fiber via fresh fruits and vegetables can reduce the risk
- Drink alcohol in moderation; limit to one or two drinks a day
- Limit combination hormone therapy used to treat symptoms of menopause. It is advised that individuals be aware of the potential benefits and risks of hormone therapy
- Cancer screenings can help detect any breast cancer, at its earliest stages
- Learn to do âbreast self-examsâ, in order to help identify any unusual lumps, signs in the breasts
In women with a high risk for developing Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast , the physician may suggest the following:
- Preventative medications: The medications tamoxifen and raloxifene are estrogen-blocking drugs that can help prevent the onset of breast cancer in women at high risk. Both drugs have potential side effects; including being at a higher risk for blood clots
- Preventative mastectomy: Prophylactic mastectomy, a procedure to surgically remove healthy breasts, is another possible preventative option for women, at a high risk for breast cancer
Staging And Grading Of Breast Cancer
Knowing the stage and grade of the cancer helps your doctors plan the best treatment for you.
On this page
Your specialist doctor needs certain information about the cancer to advise you on the best treatment for you. This includes:
- the stage of the cancer
- the grade of the cancer
- whether the cancer has;receptors; for hormones or a protein called HER2.
This information comes from the results of all the tests you have had, including:
- the biopsy, when the tissue was examined
- other tests that were done on the cells.
Your specialist doctor and nurse will talk to you about this. They will explain how it helps you and your doctor decide on your treatment plan.
We understand that waiting to know the stage and grade of your cancer can be a worrying time. We’re here if you need someone to talk to. You can:
Recommended Reading: How To Know You Have Skin Cancer
Age At The Time Of Diagnosis Affects Breast Cancer Survival Rates
It has always been known that curiously, young women have a poorer prognosis than older ones
Indeed, one cohort study examined 4,453 women with breast cancer between 1961 and 1991 who were all treated at the same center.
This study found that both ends of the age spectrum fared less well. So, women under the age of 40 years at diagnosis and those over 80 years had a statistically poorer prognosis.
However, for younger women, this may be due to the fact that they often present with higher-grade tumors that tend to be more aggressive and less likely to be hormone receptor-positive. This means that breast cancer may not respond as well to treatment.
So, it is important to bear in mind other factors discussed in this post, such as stage, grade and hormone receptor status play an important role in prognosis.
What Is The Staging For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
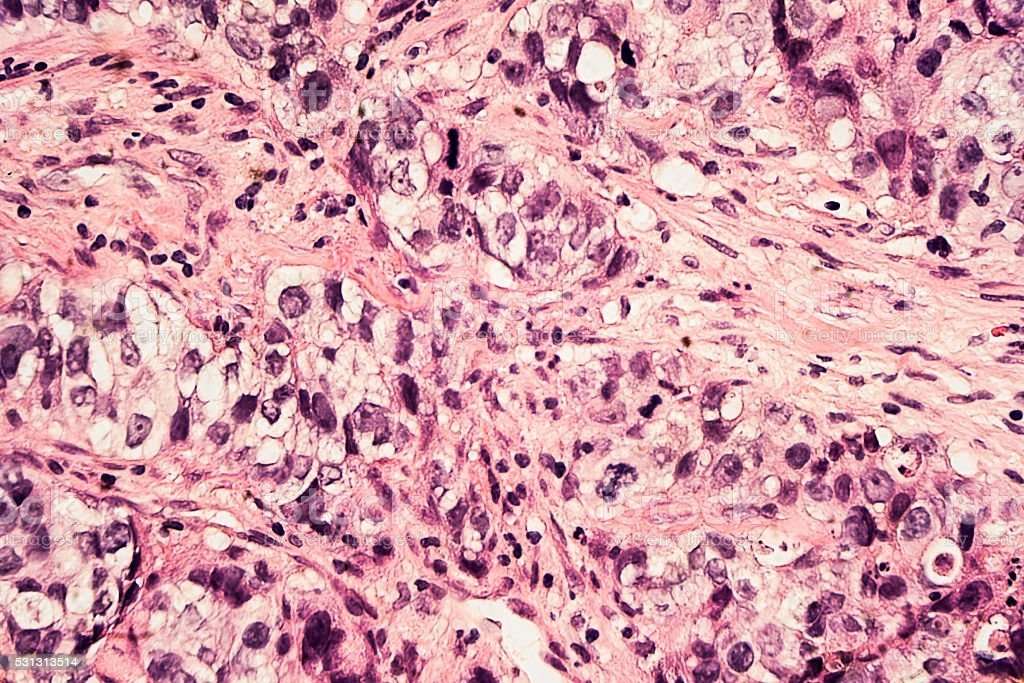
Staging refers to the extent of a cancer. A cancer is always referred to by the stage it was determined to be at diagnosis, even if it spreads.;
Stages of invasive ductal carcinoma include:
- Stage I: Breast tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters in diameter and the cancer has not spread beyond the breast
- Stage II: Breast tumor measures 2 to 4 centimeters in diameter or cancerous cells have spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area
- Stage III: Cancer is more extensive but it is confined to the breast, surrounding tissues, and lymph nodes
- Stage IV: Breast cancer has spread to lymph nodes beyond the underarm area or to distant sites, such as the lungs, liver, bones, or brain
Read Also: Is Melanoma Skin Cancer Hereditary
Breast Cancer Survival Rates Are Affected By Tumor Grade
Breast cancer grade refers to the size and shape of the malignant breast cancer cells. If the breast cancer cells look very different than normal breast tissue cells, and somewhat random in appearance, they are called poorly differentiated and described as high grade.
There are three main breast cancer grades and these are as follows:-
- Grade 1: The cancer cells are well differentiated and look the most like normal cells. These type of cancers tend to be slow-growing.
- Grade 2: These cancer cells are moderately differentiated. This means that the cells look less like normal cells and tend to grow faster.
- Grade 3: Poorly differentiated cells do not appear like normal cells at all and tend to be very fast growing. Hence, the affect on prognosis.
Microscopic Images of Ductal cell carcinoma in Situ Grades 1, 2 and 3
Higher grade breast cancers tend to have a poorer prognosis.
You will be able to find the Grade of your tumor on your pathology report.
How Does Staging Relate To Types Of Breast Cancer
In addition to cancer stage, doctors will determine the tumor grade and subtype.
Tumors are graded on a scale of 1 to 3, based on how abnormal the cells appear compared to normal cells. The higher the grade, the more aggressive the cancer, meaning that it tends to be growing quickly.
The subtype is important because treatment and outlook will vary depending on which subtype of breast cancer that you have. Subtypes include:
Don’t Miss: How To Remove Skin Cancer Yourself
What Does It Mean If My Carcinoma Has Tubular Mucinous Cribriform Or Micropapillary Features
These are different types of invasive ductal carcinoma;that can be identified under the microscope.
- Tubular, mucinous, and cribriform carcinomas are “special types” of well-differentiated cancers that often have a better prognosis than the more common type of invasive ductal carcinoma .
- Micropapillary carcinoma is a type of invasive breast carcinoma that often has a worse prognosis.
If your doctor knows that your tumor is made up of one of these special types of breast cancer, he or she may recommend different treatment.
Since some tumors are made up of more than one type, the entire tumor must be removed in order to know what types your tumor contains. A needle biopsy doesnt give enough information to guide treatment.
Diagnosing Invasive Breast Cancer
In many people the cancer is found during breast screening.
Its important that you see your GP if you have any symptoms. They may refer you to a specialist breast clinic. At the breast clinic the doctor or specialist nurse takes your medical history and examines your breasts. They also feel for any swollen lymph nodes under your arms and at the base of your neck.
You may have some or all of the following tests:
- a mammogram
- an ultrasound
- a biopsy a small sample of cells or tissue is taken from your breast and looked at under a microscope
Changes seen on the mammogram or ultrasound could;be due to cancer, so you may have a biopsy of the breast. You might also have an ultrasound of the lymph nodes under your arm. You may also have lymph node biopsies if they look abnormal.
You should get your results within 1 or 2 weeks at a follow up appointment.;
- drugs that help prevent or slow down bone thinning or bone damage
- a combination of these treatments
You may have surgery to your armpit called a sentinel lymph node biopsy. This means having about 3-5 lymph nodes removed. Sometimes surgeons have to remove more lymph nodes. Your doctor will let you know whether you need this.;
You might have chemotherapy or hormone therapy before surgery called neoadjuvant therapy. The aim is to shrink the cancer down. This means that some people may be able to;have breast conserving surgery, who might;have needed removal of the breast .;
Recommended Reading: Is Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Curable
What If A Carcinoma Is Infiltrating Or Invasive
These words are used to mean that the cancer is not a pre-cancer , but is a true cancer.
The normal breast is made of tiny tubes that end in a group of sacs . Cancer starts in the cells lining the ducts or lobules, when a normal cell becomes a carcinoma cell. As long as the carcinoma cells are still confined to the breast ducts or lobules, without breaking out and growing into surrounding tissue, it is considered in-situ carcinoma .
Once the carcinoma cells have grown and broken out of the ducts or lobules, it is called invasive or infiltrating carcinoma. In an invasive carcinoma, the tumor cells can spread to other parts of your body.