Skin Cancer : A Significant And An Increasing Health Problem Worldwide
Arjun RamakrishnanMorgan State UniversitySkin CancerApril 28, 2016Health Education 103.001AbstractSkin cancer is becoming a significant and an increasing health problem worldwide. The main cause of this type of cancer is due to the damage done by the Ultraviolet radiation from sun. There are many other causes and behaviors which contribute towards skin cancer. Protecting the skin from sun by wearing appropriate clothing, a sunscreen with appropriate sun protection factor
Recurrent Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas are the most common type of skin cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. These cancers develop within the basal cell layer of the skin, in the lowest part of the epidermis.
Patients who have had basal cell carcinoma once have an increased risk of developing a recurrent;basal cell cancer. Basal cell cancers may recur in the same location that the original cancer was found or elsewhere in the body. As many as 50 percent of cancer patients are estimated to experience basal cell carcinoma recurrence within five years of the first diagnosis.
Basal cell carcinomas typically grow slowly, and it is rare for them to metastasize or spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. But early detection and treatment are important.
After completing treatment for basal cell carcinoma, it is important to perform regular self-examinations of the skin to look for new symptoms, such as unusual growths or changes in the size, shape or color of an existing spot. Skin cancers typically develop in areas of the body that are exposed to the sun, but they may also develop in areas with no sun exposure. Tell your oncologist or dermatologist about any new symptoms or suspicious changes you may have noticed.
- Have a history of eczema or dry skin
- Have been exposed to high doses of UV light;
- Had original carcinomas several layers deep in the skin
- Had original carcinomas larger than 2 centimeters
What Is The Staging For Skin Cancer
There is no specific staging system for basal cell carcinoma. If the tumor is wider than 2 cm , it is probably a more serious tumor. Basal cell carcinomas of the ears, nose, and eyelid may also be of more concern, regardless of the size.
There is a staging system for squamous cell carcinoma. Large tumors that are thicker than 2 mm, invade the nerve structures of the skin, occur on the ear, and have certain worrisome characteristics under the microscope are of more concern. If the tumor metastasizes to a site at some distance from the primary tumor, the cancer is likely to be a dangerous tumor.
Also Check: How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Removed From The Nose
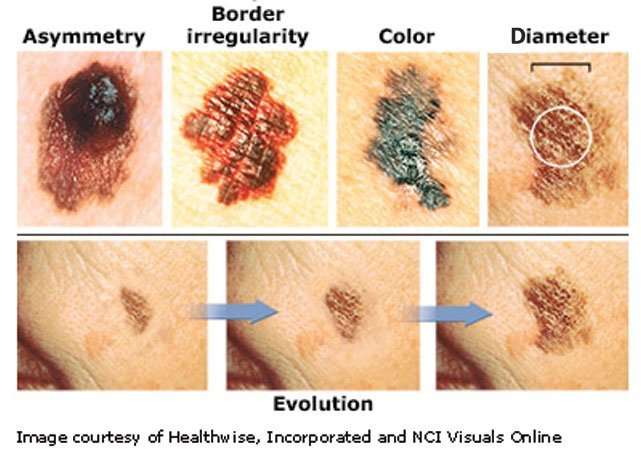
The A B C D Es Of Detecting Melanoma
According to the Skin Care Foundation, identifying melanoma early can be as easy as A, B, C, D, E. Beyond anything new, unusual, or changing, keep an eye out for the following signs:
- Asymmetry. Most melanomas are asymmetrical meaning if you drew a line through the middle of a lesion, the two halves would not match. Melanoma lesions are not round or oval like a normal mole.
- Border. The borders of a melanoma lesion are typically uneven edges. Normal moles have smooth, even borders.
- Color. Lesions that show more than one color are something to be concerned about. Regular, non-cancerous moles tend to be just a single shade of brown while melanoma lesions can be multiple shades of tan, brown or black.
- Diameter or Dark. Lesions that grow in diameter are cause for concern, as well as lesions that are darker than others.
- Evolving. Changes in size, shape, elevation or color of a spot, as well as bleeding, itching or crusting, can indicate presence of melanoma.
What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops when melanocytes start to grow out of control.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer, and can then spread to other areas of the body. To learn more about cancer and how it starts and spreads, see What Is Cancer?
Melanoma is much less common than some other types of skin cancers. But melanoma is more dangerous because its much more likely to spread to other parts of the body if not caught and treated early.
Read Also: How Does Skin Cancer Feel
Three Forms Of Melanoma
Melanoma is one of the rare diseases of the integumentary system; it is also the deadliest. It is a form of skin cancer and is held responsible for most skin-cancer related deaths. The three major forms of melanoma are: cutaneous melanoma, ocular melanoma, and mucosal melanoma. More and more cases of melanoma have been occurring throughout the years. In the early 2000s over 160,000 new cases of this deadly disease popped up. It is ranked the sixth most common cancer in both genders. While it does
What Are Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers are the most common types of skin cancer. They start in the top layer of skin , and are often related to sun exposure.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer cells. To learn more about cancer and how it starts and spreads, see What Is Cancer?
Read Also: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
For More Information About Skin Cancer
National Cancer Institute, Cancer Information Service Toll-free: 4-CANCER 422-6237TTY : 332-8615
Skin Cancer Foundation
Media file 1: Skin cancer. Malignant melanoma.
Media file 2: Skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma.
Media file 3: Skin cancer. Superficial spreading melanoma, left breast. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 4: Skin cancer. Melanoma on the sole of the foot. Diagnostic punch biopsy site located at the top. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 5: Skin cancer. Melanoma, right lower cheek. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Continued
Media file 6: Skin cancer. Large sun-induced squamous cell carcinoma on the forehead and temple. Image courtesy of Dr. Glenn Goldman.
What It Looks Like
Squamous cell cancer involves the runaway growth of keratinocytes, cells in the outermost layer of skin, which produce the protein keratin. Squamous means scaly; in 60%80% of cases, the lesions emerge on or near scaly patches called actinic keratoses that develop from sun-damaged skin.
To continue reading this article, you must log in.
- Research health conditions
- Prepare for a doctor’s visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
Don’t Miss: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
Benign Tumors That Start In Melanocytes
A mole is a benign skin tumor that develops from melanocytes. Almost everyone has some moles. Nearly all moles are harmless, but having some types can raise your risk of melanoma. See Risk Factors for Melanoma Skin Cancer for more information about moles.
A Spitz nevus is a kind of mole that sometimes looks like melanoma. Its more common in children and teens, but it can also be seen in adults. These tumors are typically benign and dont spread. But sometimes doctors have trouble telling Spitz nevi from true melanomas, even when looking at them under a microscope. Therefore, they are often removed, just to be safe.
What Are The Treatments For Skin Cancer
Most skin cancers are detected and cured before they spread. Melanoma that has spread to other organs presents the greatest treatment challenge.
Standard treatments for localized basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are safe and effective and cause few side effects. Small tumors can be surgically excised, removed with skin scraping and electric current cauterization, frozen with liquid nitrogen, or killed with low-dose radiation.
In rare cases where basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma has begun to spread beyond the local skin site, the primary tumors are first removed surgically. Then patients may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy in the form of interferon, and rarely, chemotherapy. However, responses to this therapy are infrequent and short-lived. Rare patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma respond well to a combination of retinoic acid and interferon . Retinoic acid may inhibit cancer recurrence in patients who have had tumors removed, but there is a lack of evidence to support either of these treatments. Vismodegib may be used to treat the rare cases of locally advanced, or metastatic, basal cell carcinoma and has been shown to shrink these tumors. Sonidegib can be used to treat patients with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma who are not candidates for surgery or radiation. It may also be used if the skin cancer returns after surgery or radiation.
Continued
You May Like: What Is Soft Tissue Carcinoma
What Happens If Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare but aggressive and potentially fatal form of skin cancer. It typically affects people above the age of 50 and those who have weakened immune systems. In most cases, Merkel cell carcinoma begins as a skin-toned growth that may bleed easily. The bumps or nodules may also have blue, purple, or red coloring. Because the Merkle cells are near nerve endings, this form of cancer has numerous health risks, and if left untreated, Merkle cell cancer may spread to the brain, lungs, or bones, becoming fatal.
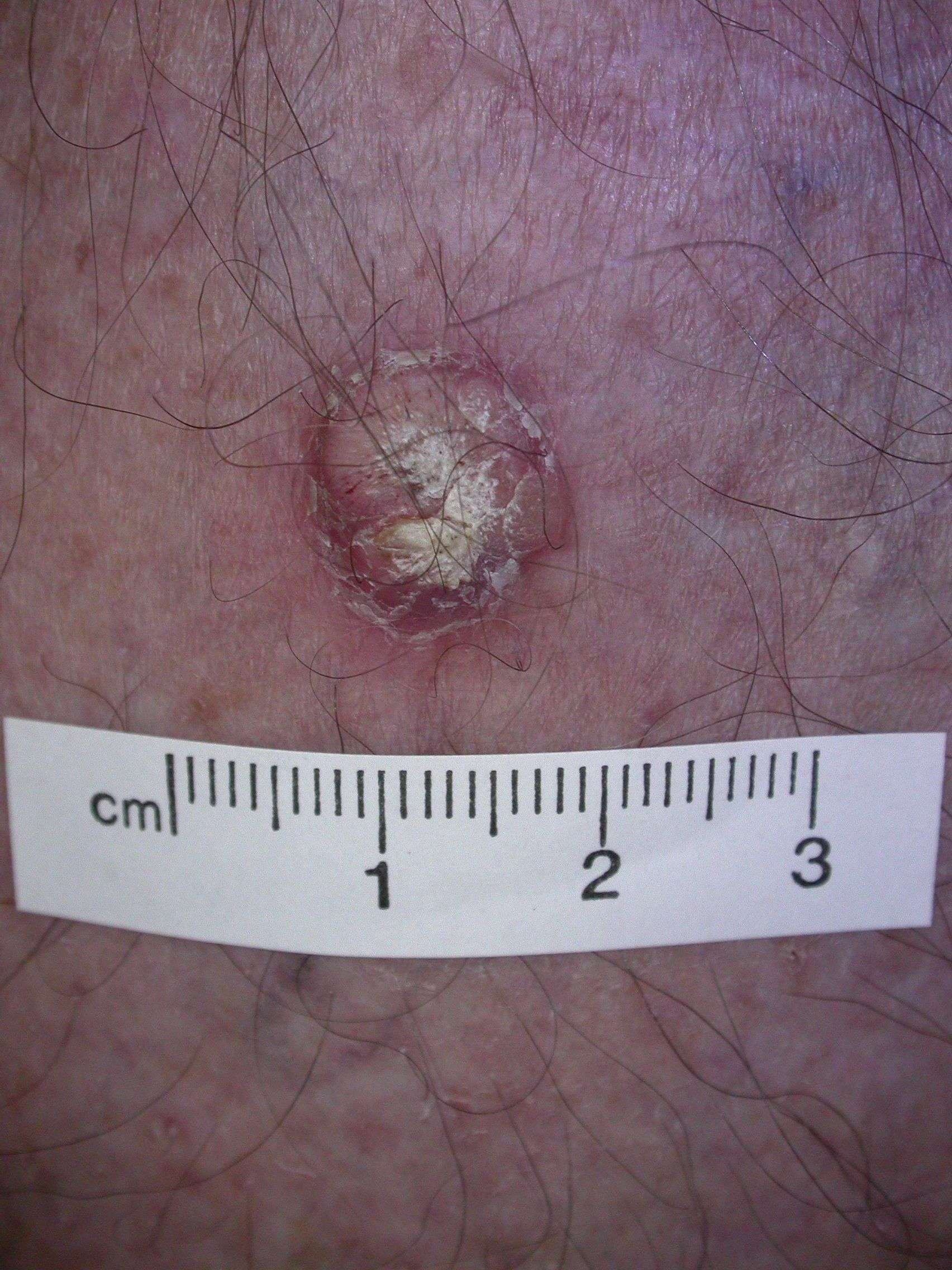
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage squamous cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is assigned to one of the five squamous cell carcinoma stages, which are labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of squamous cell cancer are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage;1 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high risk features.
Stage 3;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Main Cause Of Skin Cancer
Can You Prevent Skin Cancer
According to Dr. Dorsey, Skin cancer is an extremely serious condition, but with proactive care, most cases can be avoided altogether. In fact, taking a few small steps to limit sun damage and conducting regular skin self-exams is all you need to do to keep your skin healthy. Because sun exposure is the main underlying cause of skin cancer, sun protection is essential to prevent this condition. Patients need to apply sunscreen every day and reapply at least every two hours during prolonged sun exposure. Whenever possible, limit or avoid time spent outdoors during peak sun hours between 10 am and 4 pm. If patients need to be outdoors during these times, its important to wear protective coverings, seek shade, and reapply sunscreen frequently.
In addition to daily sun protection steps, patients also need to perform self-exams at least every month. Early detection is key to providing effective skin cancer treatment, so regular self-exams are an essential part of keeping people healthy. Your Board Certified Dermatologist can walk you through a self-exam when you visit the office, but the basic process involves carefully examining your skin, from the top of your head to the bottoms of your feet , and noting any spots, lesions, bumps, discoloration, or other skin changes or irregularities. When you know where marks are on your skin, youll be more likely to notice if they are growing or changing in ways that are concerning or that indicate skin cancer.
Visit Us Dermatology Partners
If youve been diagnosed with skin cancer or are concerned about a lesion that may be cancerous, contact U.S. Dermatology Partners to schedule an appointment right away. You can complete our online scheduling request any time, and one of our team members will be in touch to finalize your appointment details. We care deeply about you and the health of your skin!
Find a location near me
Sign Up for Our Newsletter!
Get the latest updates on news, specials and skin care information.
You May Like: What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
Three Most Common Skin Cancers
It is estimated that one in seven people in the United States will develop some form of skin cancer during their lifetime. Although anyone can get skin cancer, people who burn easily and are fair-skinned are at higher risk. Researchers believe that one serious sunburn can increase the risk of skin cancer by as much as 50%. A yearly skin exam by a doctor is the best way to detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable. If you have a new growth or any change in your skin, be sure to see your doctor to have it examined. Remember, protecting yourself from the sun is the best way to prevent all forms of skin cancer.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatment
Squamous cell carcinoma can usually be treated with minor surgery that can be done in a doctors office or hospital clinic. Depending on the size and location of the SCC, your doctor may choose different techniques to remove it.
For small skin cancers:
- Curettage and electrodessication : removing the top layer of the skin cancer then using an electronic needle to kill cancer cells
- Laser therapy: an intense light destroys the growth
- : a photosensitizing solution applied to your skin then activated with a light or daylight, or sometimes with intense pulsed light
- Cryosurgery: freezing of the spot using liquid nitrogen
For larger skin cancers:
- Excision: cutting out the cancer spot and some healthy skin around it, then stitching up the wound
- Mohs surgery: excision and then inspecting the excised skin using a microscope; this requires stitching up the wound
Medical Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of skin cancer treatment for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more information, see Surgery.People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the use of a small beam of radiation targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy can cause irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It can also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, topical chemotherapy creams have been FDA approved for the treatment of certain low-risk nonmelanoma skin cancers. Patients with advanced or many basal cell carcinomas are sometimes prescribed oral pills to block the growth of these cancers. Side effects include muscle spasms, hair loss, taste changes, weight loss and fatigue.
In advanced cases of melanoma, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work better than existing therapies.
How Often Does Scc Spread
Studies suggest that around 1.4% of people with SCC will experience metastasis.
As with BCC, the five-year survival rate is highhovering around 99%in the absence of metastasis. With metastasis, the three-year survival is roughly 29% in women and 46% in men.
What Is The Deadliest Form Of Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most deadly skin cancer, affecting over 100,000 people in the United States each year and killing over 7,000. When diagnosed in the early stages, melanoma has a five-year survival rate of 83%. But, if the cancer spreads to regional lymph nodes or distant organs, the five-year survival drops to 68% and 30% respectively.
What Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is a serious but common skin condition that causes skin cells to replicate in irregular ways or damages the structure of the cells themselves. While there are many different causes of skin cancer, exposure to the suns ultraviolet rays is the most common underlying cause of all forms of skin cancer. When damaged skin cells multiply, they form tumors. These growths can be either benign or malignant. Benign tumors are typically considered noncancerous or precancerous. Malignant tumors are more likely to impact surrounding cells or metastasize, which means they may spread to other parts of the body.
There are many different types of skin precancers and cancers. Skin precancers include actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi . The four most common skin cancers are basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, melanoma skin cancers, and merkel cell skin cancers. Most skin cancers are either basal or squamous cell carcinomas. While melanomas and merkel cell skin cancers make up a small percentage of cases, they cause the greatest number of skin cancer-related deaths each year as these types are more likely to metastasize.
Signs of skin cancer can be more easily remembered by the mnemonic ABCDEF.; This was developed initially for melanoma detection, but it can be applied to most skin cancers:
A asymmetry the shape isnt uniform throughout
D diameter is the spot greater than the size of a pencil eraser?; Is the diameter growing?