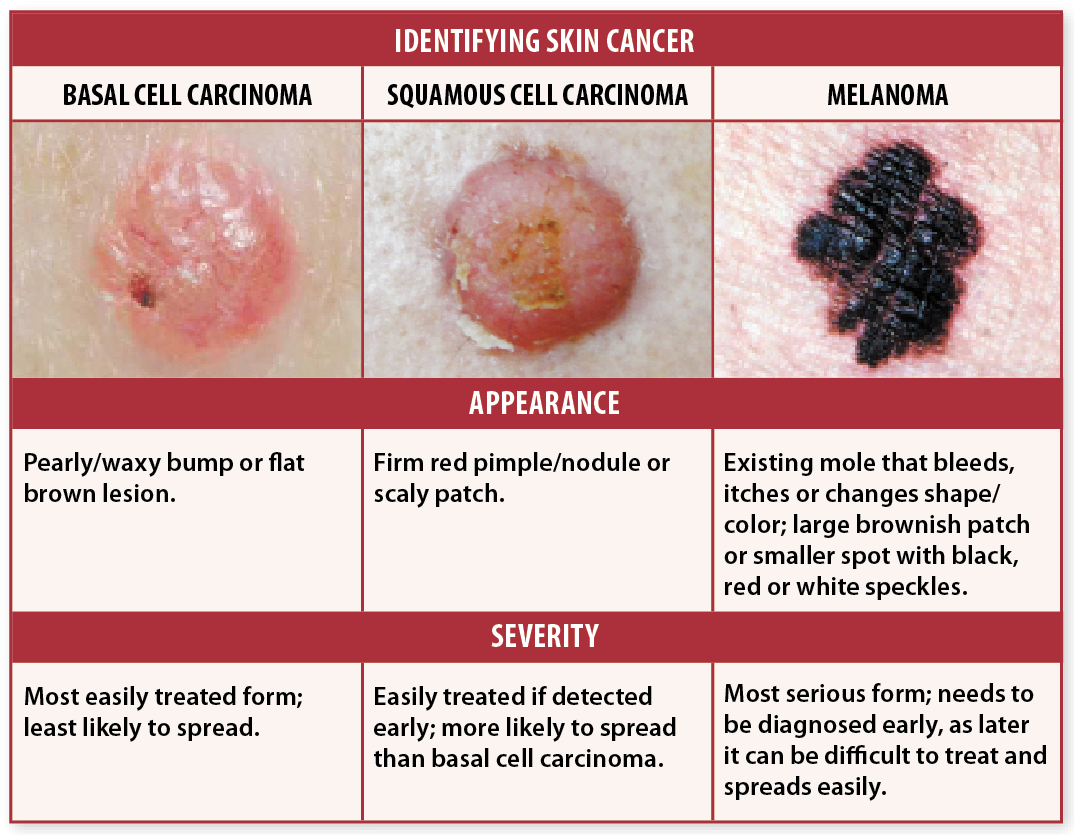
How The Government Of Canada Protects You
The Public Health Agency of Canada monitors cancer in Canada. PHAC identifies trends and risk factors for cancer, develops programs to reduce cancer risks, and researches to evaluate risks from the environment and human behaviours. Health Canada also promotes public awareness about sun safety and the harmful effects of UV rays.
Putative Genes For Basal Cell Carcinoma
BRCA1-associated protein 1
Pathogenic variants in the BAP1 gene are associated with an increased risk of a variety of cancers, including cutaneous melanoma and uveal melanoma. Although the BCC penetrance in individuals with pathogenic variants in BAP1 is not known, there are several BAP1 families that report diagnoses of BCC. In one study, pathogenic variant carriers from four families reported diagnoses of BCC. Tumor evaluation of BAP1 showed loss of BAP1 protein expression by immunohistochemistry in BCCs of two germline BAP1 pathogenic variant carriers but not in 53 sporadic BCCs. A second report noted that four individuals from families with BAP1 germline pathogenic variants were diagnosed with a total of 19 BCCs. Complete loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was observed in 17 of 19 BCCs from these individuals but none of 22 control BCC specimens. Loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was also reported in a series of 7 BCCs from individuals with loss of function BAP1 variants, but only in 1 of 31 sporadic BCCs.
Exposure To Certain Chemicals
Being exposed to large amounts of arsenic increases the risk of developing skin cancer. Arsenic is an element found naturally in well water in some areas. Its also used in making some pesticides and in some other industries.
Workers exposed to coal tar, paraffin, and certain types of petroleum products may also have an increased risk of skin cancer.
Recommended Reading: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
A Dangerous Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that begins in cells known as melanocytes. While it is less common than basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma , melanoma is more dangerous because of its ability to spread to other organs more rapidly if it is not treated at an early stage.
Learn more about melanoma types, risk factors, causes, warning signs and treatment.
Melanoma Fact
Only 20-30% of melanomas are found in existing moles.
While 70-80% arise on normal-looking skin.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are several stages of basal cell carcinoma. They start with stage 0, which means cancer has not spread to the deeper layers of skin and is only present in the upper layer. Then the stages progress in the following order:
- Stage 1: The tumor is smaller than one inch wide.
- Stage 2: The tumor is larger than one inch wide.
- Stage 3: Cancer has spread into facial bones and to one lymph node.
- Stage 4: Cancer has spread to one or more lymph nodes and might have spread to bones and organs.
Also Check: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a cancer that grows on parts of your skin that get a lot of sun. It’s natural to feel worried when your doctor tells you that you have it, but keep in mind that it’s the least risky type of skin cancer. As long as you catch it early, you can be cured.
This cancer is unlikely to spread from your skin to other parts of your body, but it can move nearby into bone or other tissue under your skin. Several treatments can keep that from happening and get rid of the cancer.
The tumors start off as small shiny bumps, usually on your nose or other parts of your face. But you can get them on any part of your body, including your trunk, legs, and arms. If you’ve got fair skin, you’re more likely to get this skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma usually grows very slowly and often doesn’t show up for many years after intense or long-term exposure to the sun. You can get it at a younger age if you’re exposed to a lot of sun or use tanning beds.
Diagnosing Basal Cell Carcinoma
To diagnose basal cell carcinoma your dermatologist will ask about your symptoms, risk factors, family history and other skin conditions and might also look at the suspect area with a dermatoscope a lighted magnifying lens.
If it looks suspicious, your doctor might remove it and send it to a lab. For basal cell carcinoma, its likely that the whole tumor will be removed as part of this skin biopsy.
You May Like: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Causes Of Skin Cancer
One of the main causes of skin cancer is being exposed to UV rays. UV rays are invisible, and are produced by the sun, and tanning equipment.
UV rays cause skin cancer by creating changes in the cells of your skin. In some cases, the UV rays cause direct damage to your cells. Tans and sunburns, for example, are both signs that UV rays have damaged your skin. In other cases, UV rays cause skin cancer indirectly, by weakening the immune system.
Many studies on skin cancer show that people who have suffered many severe sunburns in childhood are at greater risk of developing skin cancer. Family history, some chemical exposures, and immune dysfunction conditions can also create a greater risk of developing skin cancer.
What Causes Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
While many risk factors for basal and squamous cell skin cancers have been found, its not always clear exactly how these factors might cause cancer.
Most basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are caused by repeated and unprotected skin exposure to ultraviolet rays from sunlight, as well as from man-made sources such as tanning beds.
UV rays can damage the DNA inside skin cells. DNA is the chemical in each of our cells that makes up our genes, which control how our cells function. We usually look like our parents because they are the source of our DNA. But DNA affects more than just how we look.
Some genes help control when our cells grow, divide into new cells, and die:
- Genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes.
- Genes that keep cell growth in check by slowing down cell division or causing cells to die at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
Cancers can be caused by DNA changes that keep oncogenes turned on, or that turn off tumor suppressor genes. These types of gene changes can lead to cells growing out of control.
Researchers dont yet know all of the DNA changes that result in basal or squamous cell skin cancer, but they have found that in many skin cancers the cells have changes in tumor suppressor genes.
These are not the only gene changes that play a role in the development of skin cancer. There are many others as well.
Recommended Reading: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Almost all BCCs develop on parts of the body frequently exposed to the sun. Tumors can develop on the face, ears, shoulders, neck, scalp, and arms. In very rare cases, tumors develop on areas not often exposed to sunlight.
BCCs are typically painless. The only symptom is the growth or change in the appearance of the skin. There are different types of BCC. Each has a different appearance:
Skin cancers, including BCC, are primarily caused by long-term sun or ultraviolet light exposure. These cancers can also be caused by intense occasional exposure often resulting in sunburn.
In rarer cases, other factors can cause BCC. These include:
- exposure to radiation
How Do People Find Bcc On Their Skin
Many people find it when they notice a spot, lump, or scaly patch on their skin that is growing or feels different from the rest of their skin. If you notice any spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist. These doctors have the most training and experience in diagnosing skin cancer.
To find skin cancer early, dermatologists recommend that everyone check their own skin with a skin self-exam. This is especially important for people who have a higher risk of developing BCC. Youll find out what can increase your risk of getting this skin cancer at, Basal cell carcinoma: Who gets and causes.
Images used with permission of:
-
The American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
-
J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 80:303-17.
You May Like: Does Insurance Cover Skin Cancer Screening
Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Sun exposure and other risk factors
Sun exposure is the major known environmental factor associated with the development of skin cancer of all types however, different patterns of sun exposure are associated with each major type of skin cancer. Unlike basal cell carcinoma , SCC is associated with chronic exposure, rather than intermittent intense exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Occupational exposure is the characteristic pattern of sun exposure linked with SCC. Other agents and factors associated with SCC risk include tanning beds, arsenic, therapeutic radiation , chronic skin ulceration, and immunosuppression.
Characteristics of the skin
Like melanoma and BCC, SCC occurs more frequently in individuals with lighter skin than in those with darker skin. A case-control study of 415 cases and 415 controls showed similar findings relative to Fitzpatrick type I skin, individuals with increasingly darker skin had decreased risks of skin cancer . The same study found that blue eyes and blond/red hair were also associated with increased risks of SCC, with crude ORs of 1.7 for blue eyes, 1.5 for blond hair, and 2.2 for red hair.
Immunosuppression
Personal history of BCC, SCC, and melanoma skin cancers
Family history of squamous cell carcinoma or associated premalignant lesions
Basal Cell Carcinoma: The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma, which is also called basal cell skin cancer, is the most common form of skin cancer, accounting for about 80 percent of all cases.
Rates of basal cell carcinoma have been increasing. Experts believe this is due to more sun exposure, longer lives, and better skin cancer detection methods.
This type of cancer begins in the skins basal cells, which are found in the outermost layer, the epidermis. They usually develop on areas that are exposed to the sun, like the face, head, and neck.
Basal cell carcinomas may look like:
- A flesh-colored, round growth
- A pinkish patch of skin
- A bleeding or scabbing sore that heals and then comes back
They typically grow slowly and dont spread to other areas of the body. But, if these cancers arent treated, they can expand deeper and penetrate into nerves and bones.
Though its rare, basal cell carcinoma can be life-threatening. Experts believe that about 2,000 people in the United States die each year from basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma.
Some risk factors that increase your chances of having a basal cell carcinoma include:
- Being exposed to the sun or indoor tanning
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Being over age 50
- Having chronic infections, skin inflammation, or a weakened immune system
- Being exposed to industrial compounds, radiation, coal tar, or arsenic
- Having an inherited disorder, such as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum
Also Check: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
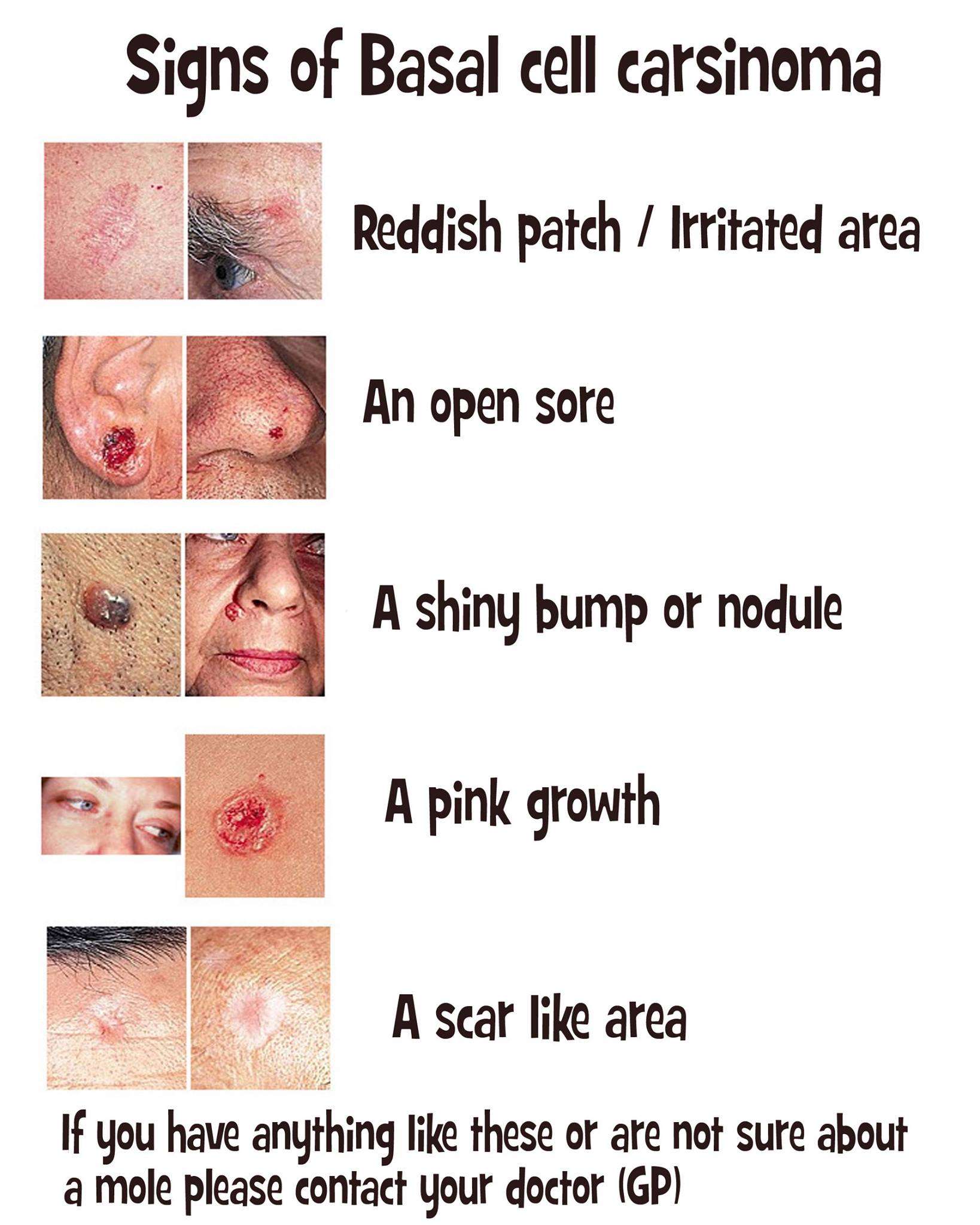
How To Spot A Bcc: Five Warning Signs
Check for BCCs where your skin is most exposed to the sun, especially the face, ears, neck, scalp, chest, shoulders and back, but remember that they can occur anywhere on the body. Frequently, two or more of these warning signs are visible in a BCC tumor.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these images serve as a general reference to what basal cell carcinoma looks like.
An open sore that does not heal
A reddish patch or irritated area
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
A shiny bump or nodule
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
Where Does Bcc Develop
As the above pictures show, this skin cancer tends to develop on skin that has had lots of sun exposure, such as the face or ears. Its also common on the bald scalp and hands. Other common areas for BCC include, the shoulders, back, arms, and legs.
While rare, BCC can also form on parts of the body that get little or no sun exposure, such as the genitals.
Recommended Reading: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Are The Risk Factors For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma are all skin cancers caused by exposure to damaging ultraviolet raysfrom natural and artificial sunlight. There’s also a genetic condition called basal cell nevus or Gorlin syndrome, which can cause people to develop hundreds of basal cell skin cancers, but it’s extremely rare, says Dr. Christensen.
People at the highest risk for basal cell carcinoma tend to have fair or light-colored skin, a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Fair-skinned people have a 50 percent risk of developing basal skin cancer at some point in their lives, Dr. Christensen says. The cancer is the result of cumulative damage of years spent in the sun, and may take 20 years to manifest.
Although it’s often more common in older people, it can occur in younger adults, too.
Basal cell carcinoma spreads very slowly and very rarely will metastasize, Dr. Christensen says. But if it’s not treated, basal cell carcinoma can continue to grow deeper under the skin and cause significant destruction to surrounding tissues. It can even become fatal. For example, an untreated basal cell carcinoma on the face can grow into the bones and, over time, directly into the brain, Dr. Christensen says.
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Basal cell cancers usually present as an abnormal growth on the skin. The growth may have the appearance of a wart, crusty spot, reddish patch, mole, nodule or bump, or a sore that does not heal. It may or may not bleed and can sometimes be painful. These are usually slow-growing tumors that begin as small spots on sun-exposed areas of the face. Because they can have such a range of appearances, any new persistent skin lesion should be evaluated.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery Specialists
Our head and neck surgeons and speech language pathologists take a proactive approach to cancer treatment. Meet the Johns Hopkins specialists who will work closely with you during your journey.
You May Like: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Metastasis
Syndromes And Genes Associated With A Predisposition For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Major genes have been defined elsewhere in this summary as genes that are necessary and sufficient for disease, with important pathogenic variants of the gene as causal. The disorders resulting from single-gene pathogenic variants within families lead to a very high risk of disease and are relatively rare. The influence of the environment on the development of disease in individuals with these single-gene disorders is often very difficult to determine because of the rarity of the genetic variant.
Identification of a strong environmental risk factorchronic exposure to UV radiationmakes it difficult to apply genetic causation for SCC of the skin. Although the risk of UV exposure is well known, quantifying its attributable risk to cancer development has proven challenging. In addition, ascertainment of cases of SCC of the skin is not always straightforward. Many registries and other epidemiologic studies do not fully assess the incidence of SCC of the skin owing to: the common practice of treating lesions suspicious for SCC without a diagnostic biopsy, and the relatively low potential for metastasis. Moreover, NMSC is routinely excluded from the major cancer registries such as the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registry.
With these considerations in mind, the discussion below will address genes associated with disorders that have an increased incidence of skin cancer.
Xeroderma pigmentosum
Multiple self-healing squamous epitheliomata
Oculocutaneous albinism
Basal Cell Carcinoma Pictures Types And Symptoms
Basal skin cancer accounts for eighty percent of all skin cancers. As with all types of cancer, early detection is vital. Early stage basal cell carcinoma is usually easily treatable, often with minor surgery under local anaesthetic. In this article we consider the main basal cell cancer symptoms along with pictures of basal cell carcinoma types.
Recommended Reading: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
In addition to basal cell carcinoma, this autosomal dominant disorder can result in the early formation of multiple odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies. Various tumors such as medulloblastomas, meningioma, fetal rhabdomyoma, and ameloblastoma also can occur.
Odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies may be seen. Mutations in the hedgehog signaling pathway, particularly the patched gene, are causative.
Go to Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome to see more complete information on this topic.