What Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Skin malignancies are the most common cancer in the United States, responsible for more than half of all new cancer cases. These can be broken down into melanoma and non-melanoma malignancies, which are squamous cell cancer and basal cell cancer. These skin malignancies are caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Squamous cell cancer is the second most common form of skin cancer. It is more aggressive and may require extensive surgery depending on location and nerve involvement. Radiation, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are used in advanced cases.
Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
A key factor used to identify a Squamous Cell Carcinomas is any ongoing change that persists beyond a few weeks in a lesion on the skin.
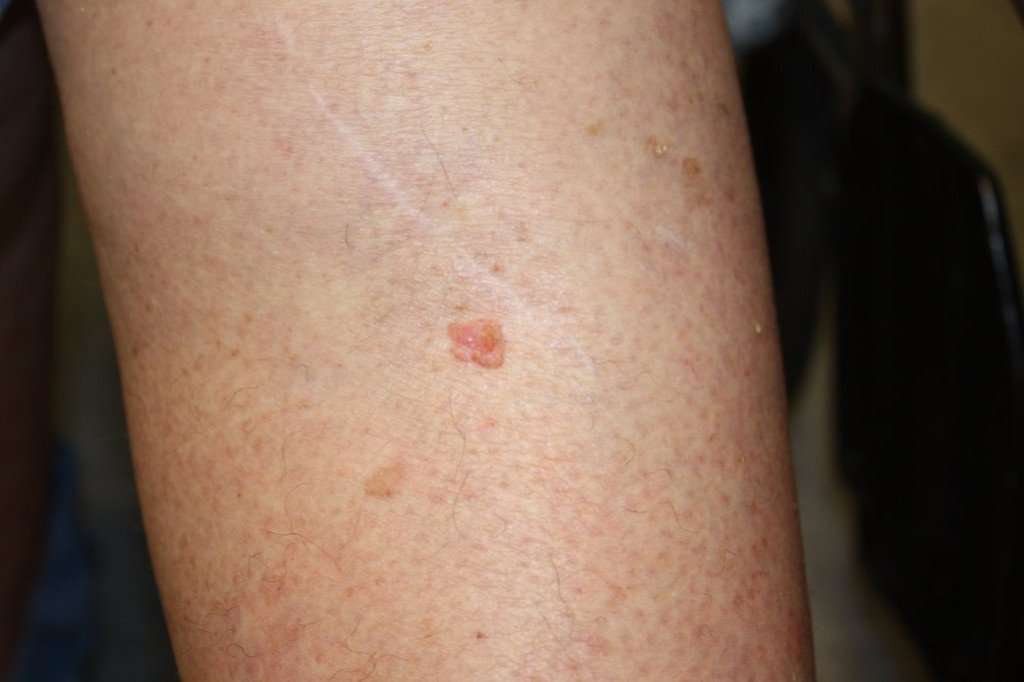
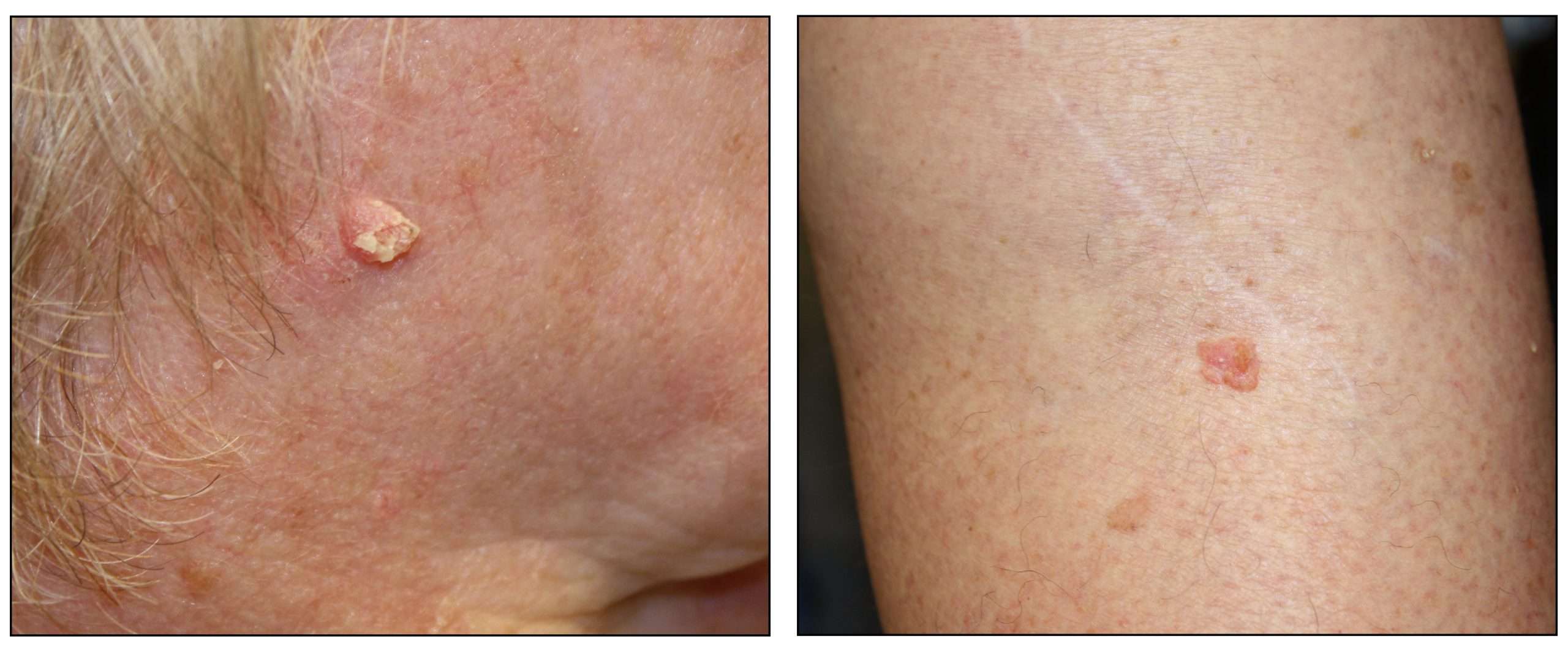
Squamous Cell Carcinomas typically appear as persistent, thick, rough, scaly patches that can bleed if bumped, scratched or scraped.
If you observe two or more of the signs below, you should consult the Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic immediately.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma can sometimes resemble non-cancerous skin conditions such as psoriasis or eczema.
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Hurt To The Touch
What Are The Different Types Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
People assume there is just a single type of squamous cell carcinoma, but there are actually several different types. Some are more likely to spread than others, but in general, most types share similar characteristics. The primary difference between the following types is related to the unique characteristics of the cancerous cells.
The primary types of squamous cell carcinoma are:
- Adenoid/pseudoglandular squamous cell carcinoma
- Small cell keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
- Spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma
- Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma
Don’t Miss: How Long Until Melanoma Spreads
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Causes
Exposure to ultraviolet rays, like the ones from the sun or a tanning bed, affects the cells in the middle and outer layers of your skin and can cause them to make too many cells and not die off as they should. This can lead to out-of-control growth of these cells, which can lead to squamous cell carcinoma.
Other things can contribute to this kind of overgrowth, too, like conditions that affect your immune system.
Where Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Spread
It’s important to know that basal cell carcinoma can spread to other surrounding tissue and can grow around nerves. I had two separate basal cells that grew around nerves: one in my forehead and one in my upper lip. Both of those surgeries required moving the nerve to remove the cancer, and I was left with permanent numbness in both areas because of that.
You May Like: How To Tell If Melanoma Has Spread
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer. Its usually found on areas of the body damaged by UV rays from the sun or tanning beds. Sun-exposed skin includes the head, neck, chest, upper back, ears, lips, arms, legs, and hands.
SCC is a fairly slow-growing skin cancer. Unlike other types of skin cancer, it can spread to the tissues, bones, and nearby lymph nodes, where it may become hard to treat. When caught early, its easy to treat.
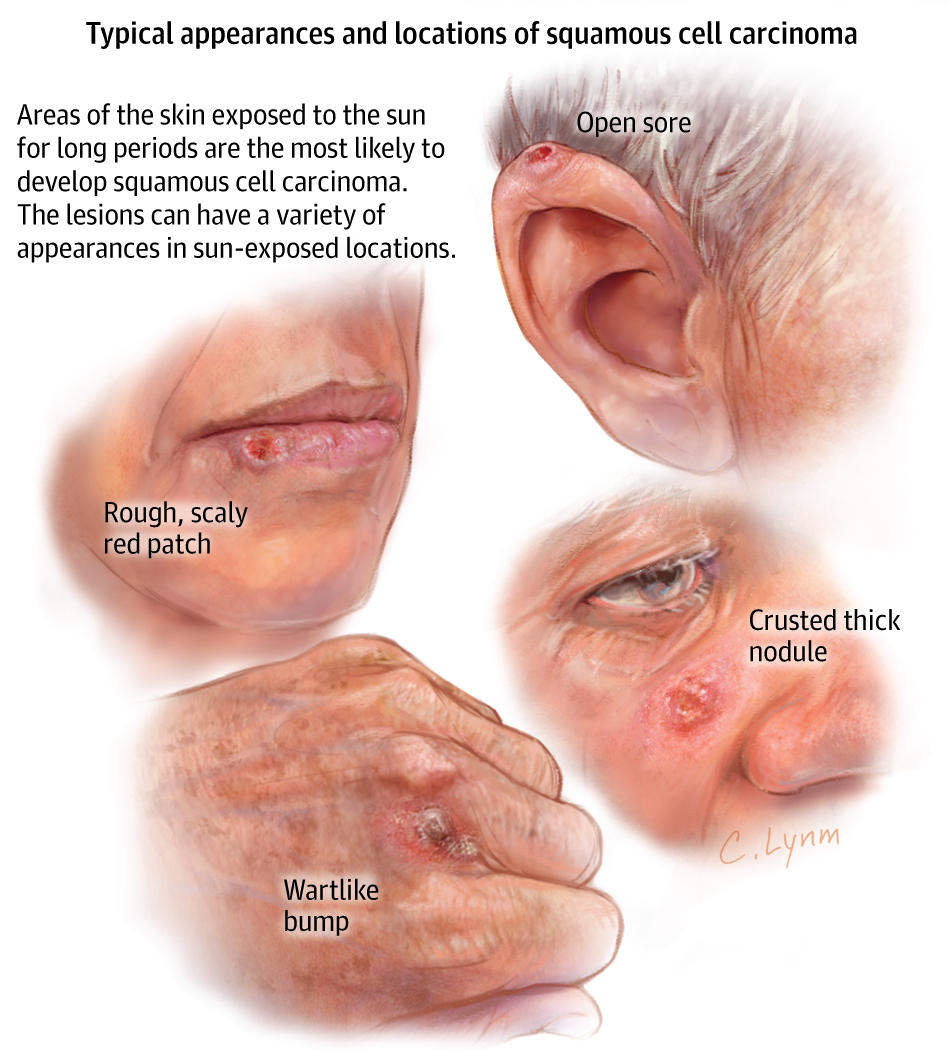
SCC can show up as:
- A dome-shaped bump that looks like a wart
- A red, scaly patch of skin thats rough and crusty and bleeds easily
- An open sore that doesnt heal completely
- A growth with raised edges and a lower area in the middle that might bleed or itch
Care For Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomas
We take a multidisciplinary approach to your medical care, which means that the expertise of other specialists can be coordinated easily and effectively, if needed.
Patients who come to our clinic receive a preoperative consultation to assess, coordinate, plan and prepare you for surgery. In most cases this can be done on the phone without scheduling a preoperative visit. All patients have their biopsy slides reviewed by one of our pathologists before receiving a treatment plan. If it’s determined Mohs surgery is your best option, you will be scheduled for the procedure at a later date.
Read Also: What Does Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mean
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Squamous cell cancers are usually raised growths, ranging from the size of a pea to the size of a chestnut. They may appear as scaly red patches, open sores or protruding growths with a dented center, or they may look like a wart. Most are found in areas of the body that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the ears, lips, face, balding scalp, neck, hands, arms, and legs. Less commonly, they may appear on mucous membranes and genitals. Regardless of what form the bumps take, they do not heal or go away on their own.
Untreated Squamous Cell Carcinomas
The incidence of Squamous Cell Carcinoma is rising and can be life-threatening.
While Squamous Cell Carcinomas seldom spread to vital organs, Squamous Cell Carcinomas respond well to early treatment. If untreated the consequences could include:
- Disfigurement
- Nerve, or muscle injury, or other injury to nearby structures like eyelids or nostrils
- Certain rare, aggressive forms can be lethal if not treated promptly.
The larger the tumour has grown, the more extensive any surgical treatment would be. This could result in scarring.
In 2016 it is estimated that there were 560 deaths in Australia from non-melanoma skin cancers. It is not possible to identify how many of these are Squamous Cell Carcinomas as this data is not separately recorded.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Melanoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
Certain things make you more likely to develop SCC:
- Older age
- Blue, green, or gray eyes
- Blonde or red hair
- Spend time outside, exposed to the sun’s UV Rays
- History of sunburns, precancerous spots on your skin, or skin cancer
- Tanning beds and bulbs
- Long-term exposure to chemicals such as arsenic in the water
- Bowens disease, HPV, HIV, or AIDS
Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist who specializes in skin conditions. They will:
- Ask about your medical history
- Ask about your history of severe sunburns or indoor tanning
- Ask if you have any pain or other symptoms
- Ask when the spot first appeared
- Give you a physical exam to check the size, shape, color, and texture of the spot
- Look for other spots on your body
- Feel your lymph nodes to make sure they arent bigger or harder than normal
If your doctor thinks a bump looks questionable, theyll remove a sample of the spot to send to a lab for testing.
Continued
What Patients And Caregivers Need To Know Abo
This the most important factor in determining treatment and probable outcome. What patients and caregivers need to know abo. There are different staging guidelines for basal and squamous cell cancer and melanoma. The aad’s coronavirus resource center will help you find information about how you can continue to care for your skin, hair, and nails. Some types of skin cancer are more dangerous than others, but if you have a spot. Being armed with information is vital to begin the fight. Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the united states by a pretty large margin, and it does not discriminate. A cancer diagnosis can leave you unable to comprehend anything else your doctor says, but it’s important to pay attention to what stage of cancer you have. The stage of a basal or squamous cell skin cancer is a description of how widespread the cancer is. Not only does the stage tell you how serious the disease is, but it can help you and. According to the american cancer society, just over 100,000 new cases of skin cancer are diagnosed in the united states each year. The aad’s coronavirus resource center will help you find information about how you can continue to care for your skin, hair, and nails. Cancer stages describe the size of the primary tumor and how far cancer has spread.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Basal Cell Carcinoma On The Nose
Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Most of squamous cell carcinomas can be cured if they are treated early. Once squamous cell carcinoma has spread beyond the skin, though, less than half of people live five years, even with aggressive treatment.
There are many ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma that has not spread. These include:
- cutting away the cancer and a small amount of healthy tissue around it. If a large area of skin is removed, a skin graft may be necessary.
- scraping away the cancer with a surgical tool. An electric probe is used to kill any cancerous cells left behind.
- freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen. This treatment is usually used only for very small tumors or for a patch of skin that looks abnormal but isn’t yet cancerous.
- destroying the tumor with radiation.
- shaving away the cancer, one thin layer at a time. Each layer is examined under the microscope as it is removed. This technique helps the doctor preserve as much healthy skin as possible.
- applying drugs directly to the skin or injecting them into the tumor
- using a narrow laser beam to destroy the cancer.
The treatment that is best for you depends on the size and location of the cancer, whether it has returned after previous treatment, your age, and your general health.
Once your treatment is finished, it’s important to have regular follow-up skin exams. Your doctor may want to see you every three months for the first year, for example, and then less often after that.
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Squamous cell skin cancers usually present as an abnormal growth on the skin or lip. The growth may have the appearance of a wart, crusty spot, ulcer, mole or a sore that does not heal. It may or may not bleed and can be painful. If you have a preexisting mole, any changes in the characteristics of this spot such as a raised or irregular border, irregular shape, change in color, increase in size, itching or bleeding are warning signs. Pain and nerve weakness are concerning for cancer that has spread. Sometimes a lump in the neck can be the only presenting sign of skin cancer that has spread to lymph nodes, particularly when there is a history of previous skin lesion removal.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
Delay In Diagnosis And Treatment Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Cristina Renzi1, Simona Mastroeni1, Thomas J. Mannooranparampil1, Francesca Passarelli2, Alessio Caggiati3, Clemente Potenza3 and Paolo Pasquini1
1Clinical Epidemiology Unit, 2Pathology Department, 3Department of Plastic Surgery, Istituto Dermopatico dellImmacolata , Rome, Italy
Advanced squamous cell carcinomas of the skin can cause significant tissue destruction and may metastasize. Understanding the determinants of patient delay could help prevent advanced presentation. The purpose of the present study was to examine patient- and healthcare-related factors associated with delay before the detection and treatment of SCC. A sample of 308 patients with SCC treated at a dermatological referral centre in Italy were interviewed. Clinical data were obtained from the medical records. The highest quartile patients reported > 9 months delay between noticing the lesion and the first medical visit . Multivariate analysis showed that SCC arising on pre-existing chronic lesions were associated with long patient delay . Controlling for confounders, the first physicians advice to remove the lesion immediately was associated with a shorter treatment delay . In conclusion, our work emphasizes the importance of seeing a doctor about any change in a pre-existing lesion, particularly in light of the fact that SCC on chronic lesions are at greater risk of metastasis and recurrence. Key words: skin cancer cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma delay.
Acta Derm Venereol 2010 90: 595601.
What Are The Types Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma develops when the flat cells in the toplayer of skin grow and divide in an uncontrolled way.
You can get an SCC wherever there are squamous cells which is in manydifferent parts of the body. However, typically they appear on parts of theskin that have been exposed to a lot of ultraviolet radiation from the sunor from tanning beds.
An early form of skin cancer, called Bowens disease, which looks like a red, scaly patch, can also develop into an SCC if nottreated.
An SCC can be quite an aggressive cancer if left untreated. If you evernotice a sore, scab or scaly patch of skin that doesnt heal within 2 months,see a doctor.
Also Check: What Does Early Squamous Skin Cancer Look Like
Don’t Miss: What Do Melanoma Spots Look Like
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
This is the second most common form of skin cancer, it occurs most commonly on the head and neck, and exposed arms. However, these are frequently seen on the front of the legs as well, or the shin area. This form of skin cancer grows more quickly, and though it can be confined to the top layer of skin, it frequently grows roots. Squamous cell carcinoma can be more aggressive and does have a potential to spread internally. This is more likely in cases where an individual is immunosuppressed, or the tumor is invading deeply in the second layer of skin, or tracking along nerves. These tumors need to be treated early as they are not only locally destructive, but can spread along nerves, into lymph nodes, and internally.
How Fast Does Oral Cancer Spread
About one half of people with oral cancer will live more than 5 years after they are diagnosed and treated.
If the cancer is found early, before it has spread to other tissues, the cure rate is nearly 90%.
More than half of oral cancers have spread when the cancer is detected.
Most have spread to the throat or neck.17 Oct 2017
Recommended Reading: What Are The Stages Of Malignant Melanoma
When Was My Husband Diagnosed With Squamous Cell Lung Cancer
My husband was also a Vietnam Vet his last tour of duty in Vietnam ended in 1969. In June 2001 he was diagnosed with Squamous Cell Lung Cancer. The doctors at the VA in Tampa Florida made the diagnosis. They asked him if he was a Vietnam Vet and he said yes he was and that he did 2 tours of duty in Vietnam.
Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Deadly
Skin cancer is by far the most common type of cancer and each year there are more new cases of skin cancer than the combined cases of breast, prostate, lung and colon cancer. This translates to one in five Americans developing skin cancer over their lifetime. Following basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, about 5.4 million basal and squamous cell skin cancers are diagnosed each year in America. Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for ~20% of these cases.
Who is at risk for squamous cell carcinoma?Skin cancer occurs at every age in persons of every ethnicity and gender. Risk for squamous cell carcinoma increases with the following factors:
- Ultraviolet light exposure from the sun and indoor tanning
- History of sunburns, especially during childhood
- Lighter skin color equating to increased sensitivity to ultraviolet light. Although less common overall in darker skin types, squamous cell carcinoma accounts for a larger proportion of skin cancers in this population.
- Incidence increases with age
- Male gender men are especially at risk after age 60, whereas women account for more skin cancers in those under age 40
- Personal or family history of skin cancer
- Human Papillomavirus Virus infection
Recommended Reading: How To Get Skin Cancer
Also Check: What Can Skin Cancer Do
How Aggressive Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is not often considered to be life threatening. This form of skin cancer that affects the squamous cells tends to create slow-growing tumors. Although squamous cell carcinoma is more likely to invade deeper layers of the skin and spread to other parts of the body than basal cell carcinoma, this is still uncommon.
Only about 5 to 10 percent of squamous cell carcinoma tumors are considered to be aggressive.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis
Occasionally a punch or shave biopsy may be required to confirm the diagnosis and to guide effective treatment.
This diagnostic process involves a Doctor taking a tissue sample for biopsy by removing a portion of the lesion with a biopsy punch or by scraping the lesion with a curette .Usually a biopsy is sufficient to establish the diagnosis of a Squamous Cell Carcinoma. In the rare case of suspected metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma, lymph nodes may be examined by the Doctor to see if the cancer has spread or by the use of imaging technologies like ultrasound, CT, or PET scanning.
Read Also: How To Reduce Risk Of Skin Cancer
How Is Squamous Cell Cancer Diagnosed
Your doctor will first perform a physical exam and inspect any abnormal areas for signs of SCC. Theyll also ask you about your medical history. If SCC is suspected, your doctor may decide to take a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
A biopsy usually involves removing a very small portion of the affected skin. The skin sample is then sent to a laboratory for testing.
In some cases, your doctor may need to remove a larger part or all of the abnormal growth for testing. Talk to your doctor about any potential scarring or biopsy concerns.
Treatment for SCC varies. Treatment is based on:
- the extent and severity of your cancer
- your age
- your overall health
- the location of the cancer
If SCC is caught early, the condition can usually be successfully treated. It becomes harder to cure once it has spread. Many treatments can be performed as in-office procedures.
Some doctors may also use photodynamic therapy, laser surgery, and topical medications to treat SCC. However, the Food and Drug Administration hasnt approved these methods for treating SCC:
Once SCC has been treated, its critical to attend all follow-up visits with your doctor. SCC can return, and its important to monitor your skin for any precancerous or cancerous areas at least once per month.