What We Do Know
UV exposure creates a double threat for MCC
Not only does UV exposure cause damage that increases your skin cancer risk it also suppresses your immune system, reducing its ability to repair damage and fight skin cancers and other diseases. No matter the source of UV radiation, there is a clear and dangerous correlation between exposure and MCC.
Immunosuppression and MCC are strongly linked.
If your immune system is persistently weakened or suppressed, you are about 15 times more likely to develop MCC than people with healthy immune systems. However, more than 90 percent of MCC cases arise in people with no known immune problems. Immunosuppression can be caused by:
- Diseases such as HIV and certain cancers including chronic lymphocytic leukemia and lymphomas.
- Immunosuppressant medications used for transplant recipients and for autoimmune diseases including lupus, psoriasis, Crohns disease and rheumatoid arthritis.
Immunosuppressed MCC patients often develop the disease at a far younger age about half of MCCs in these patients occur before age 50.
If your immune system is suppressed, talk to your doctors about your chances of developing MCC, and be sure to protect yourself against other risk factors, especially UV exposure.
A history of skin cancer is also highly associated with Merkel cell carcinoma. If youve had melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma or Bowens disease skin cancers frequently caused by UV exposure you are more likely to develop MCC.
Warning Signs Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The Skin Cancer Foundation offers this AEIOU guide to help spot Merkel cell carcinoma:
- “A” stands forasymptomatic. The lump isnt painful or tender.
- “E” stands forexpanding. The lesion expands very quickly.
- “I” stands forimmunocompromised. You are more at risk for Merkel cell carcinoma if you have a weak immune system.
- “O” stands forolder. You have a higher risk if youre older.
- “U” stands forUV-exposed. The lumps usually show up on areas of the skin that have been exposed to ultraviolet light.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is A Rare Aggressive Skin Cancer
Sometimes referred to as a neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, MCC arises from uncontrolled growth of cells in the skin that share some characteristics with normal Merkel cells in the skin. MCC primarily occurs on sun-exposed skin such as the head/neck and arms, but it can occur anywhere on the body, including sun-protected areas. MCC usually develops as a painless, firm bump that can be red-purple or skin-colored. Patients frequently point out a new MCC to their doctor because a bump is growing rapidly and/or does not look like anything the patient has ever had before.
Learn more about Merkel cells, MCC, its symptoms and appearances, and when a bump may be serious enough to see a specialist.
Jump to:
Read Also: What Does Stage 2 Melanoma Look Like
What Is A Merkel Cell
Merkel cells are located deep in the top layer of skin. Merkel cells are connected to nerves, signaling touch sensation as touch receptors. MCC was named after Merkel cells due to the similar microscopic features however, recent research suggests that it is unlikely that MCC originates directly from normal Merkel cells.
Normal Merkel cells in the skin: In this illustration of a cross-section of the skin, normal Merkel cells are shown in red and connect to nerves shown in yellow. The structures drawn include the epidermis , dermis , and deeper adipose layer containing the fatty tissue. Arteries are depicted in red and veins are blue. Figure copyright by Paul Nghiem & Quade Medical Group.
Clinical Photos Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
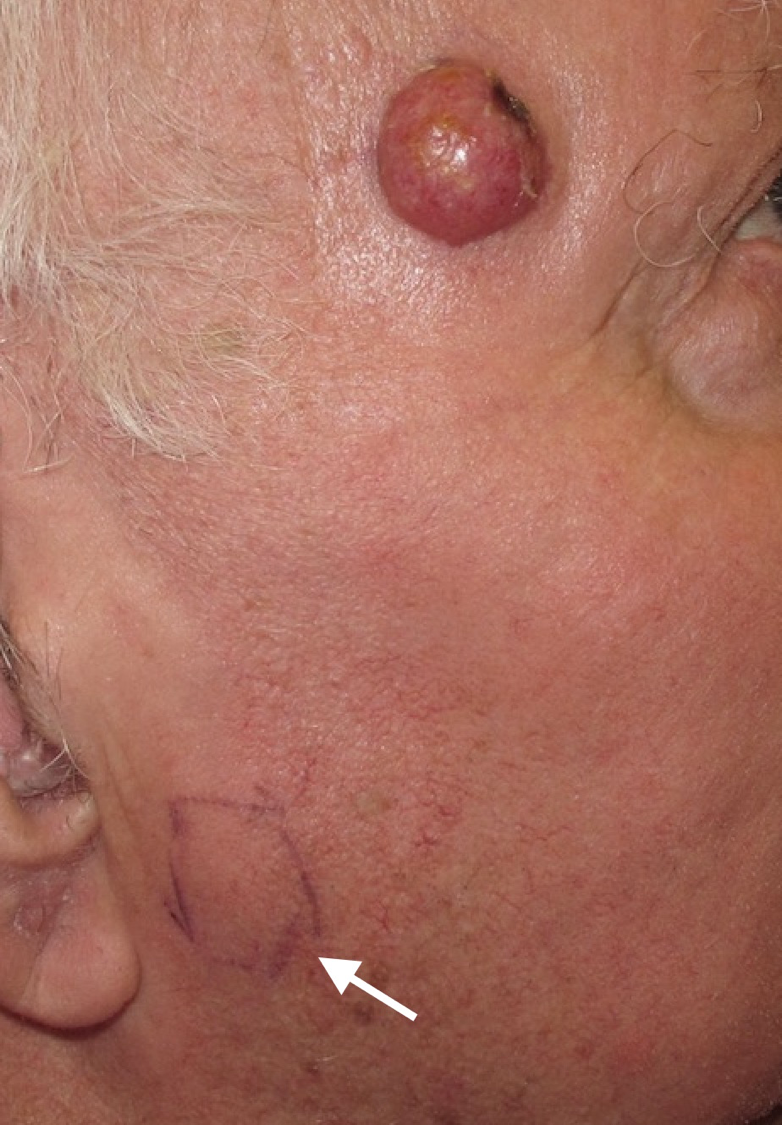
For more examples of MCC tumors, visit the Clinical Photos page.
A Closer Look
A study2 of 195 Merkel cell carcinoma patients was carried out to determine the features that doctors or patients typically find associated with this cancer. AEIOU summarizes the features that are usually associated with MCC. 89% of MCC tumors have three or more of these five features:A: Asymptomatic88% of MCCs are not tender.E: Expanding rapidly63% of MCCs have grown significantly within the past 3 monthsI: Immunosuppression*MCC patients are 16-times more likely to be immunosuppressed*O: Older than 5090% of MCC patients are over age 50 & MCC risk keeps increasing with ageU: UV exposed fair skin81% of MCCs arise on sun-exposed skin and 98% of MCCs arise in people whose skin tone is light* The relationship between immune suppression & MCC is tricky to understand. While only 8% of MCC patients have severe, long-term immune suppression , this is a 16-fold over-representation compared to the general population. Such long-term immunosuppressed patients have a higher risk of developing MCC and of later having their MCC recur.
Read Also: Is Skin Cancer Always Raised
What Are The Clinical Features Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma usually presents as a rapidly enlarging, solitary, irregular red nodule. It is often similar in appearance to other more common skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma but grows much more quickly.
Merkel cell cancers spread through the lymphatic system and multiple metastases can develop around the main tumour . Merkel cell carcinoma may also spread to lymph nodes in the neck, axillae and groin. This is more likely in thicker tumours. Most recurrences occur within the first two years after diagnosis.
Merkel cell carcinoma
What Causes Merkel Cell Cancer
Experts arent exactly sure what causes Merkel cell cancer. But it occurs when Merkel cells in the body change and grow out of control. These abnormal cells may grow to form a lump or mass called a tumor. If the tumor is cancerous, it can grow into nearby areas. It can even spread to other parts of the body .
You May Like: How Do You Say Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Is Merkel Cellcarcinoma Of The Skin
Merkel cell carcinoma of the skin is a rare form of skin cancer. It may be very aggressive and often metastasises to other parts of the body. It has also been called Toker tumour, cutaneousneuroendocrine carcinoma, trabecular cell carcinoma, and primary small-cell carcinoma of the skin.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Sun Exposure And Having A Weak Immune System Can Affect The Risk Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk. Risk factors for Merkel cell carcinoma include the following:
- Being exposed to a lot of natural sunlight.
- Having an immune system weakened by disease, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia or HIVinfection.
- Taking drugs that make the immune system less active, such as after an organ transplant.
- Having a history of other types of cancer.
- Being older than 50 years, male, or White.
Don’t Miss: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
Risk Factors + Warning Signs = Aeiou
Since MCCs can progress rapidly and become more difficult to treat, its crucial to understand your risks and warning signs. This AEIOU summary combines key points from both to help you with early detection.
- A: ASYMPTOMATIC lesion, not painful or tender
- E: Lesion is EXPANDING rapidly
- I: You are IMMUNOsuppressed
- O: You are OLDER than 50
- U: The lesion appears on UV-exposed skin
In a study of 195 patients, 89 percent of MCC patients presented with three or more of the AEIOU characteristics.
Left photo: Merkel cell carcinoma, local recurrence, forehead
Right photo: Merkel cell carcinoma, primary tumor, lower arm
Please note: Since not all Merkel cell carcinomas have the same appearance, these photos serve as a general reference for what MCC can look like. If you see anything NEW, CHANGING or UNUSUAL on your skin, go get checked by a dermatologist.
Treatment Options By Stage
While various considerations help determine the best approach to treatment, the stage of MCC is often the most important factor.Below, learn about the stages and the recommended treatments.
MCC without obvious spread
After having an SLNB to check whether the cancer has spread, most people undergo a wide local excision. This procedure removes the cancerous cells from the skin.
If MCC is on the face or other sensitive areas, a person may instead undergo Mohs micrographic surgery, which helps preserve more healthy skin.
Some people may also, or alternately, undergo radiation therapy, especially targeting the surrounding lymph nodes.
MCC with spread
This can be very difficult to cure. A person may need:
- surgery to remove affected cells
- radiation therapy
- immunotherapy drugs, such as pembrolizumab or avelumab
Recurring MCC
When MCC comes back, doctors often recommend a combination of:
- surgery to remove more of the affected tissue, possibly with surrounding lymph nodes
- radiation therapy
- chemotherapy
- immunotherapy drugs, such as Keytruda or Bavencio
Recurring MCC can be very difficult to treat, especially if it comes back in different areas. If this happens, doctors tend to focus on reducing symptoms, not curing the disease.
Some people also try complementary therapies for MCC, including:
- naturopathic medicine
Also Check: What Does Hepatocellular Carcinoma Mean
How Does An Mcc Differ In Appearance From A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Unlike a squamous cell carcinomasquamous cell carcinomaSquamous cell carcinoma is a cancer that begins in squamous cells, which are thin, flat cells. Squamous cells are located in the middle layers of the epidermis, the lining of portions of the respiratory and digestive tracts, and the lining of some organs. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma affects about 100,000 Americans and has a mortality of roughly 2%., MCCs are rarely scaly and are rarely ulcerated unless a biopsy has just been carried out.
Stages Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
After receiving a cancer diagnosis, your doctor will run tests to find out if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body. This is referred to as staging. Staging is important for determining what types of treatment are needed.
In general, a higher number stage means the further a cancer has spread. There are five main stages in MCC :
- stage 0: the cancer is only in the epidermis and hasnt spread to the lymph nodes
- stage 1: the cancer is less than 2 centimeters across and hasnt grown into the lymph nodes
- stage 2: the cancer is more than 2 cm across and hasnt spread to the lymph nodes
- stage 3: the cancer has grown into lymph nodes as well as nearby tissues
- stage 4: the cancer has spread to nearby tissues, the lymph nodes, and distant sites, such as the lungs, bones, or brain
The main symptom of Merkel cell carcinoma is the appearance of a single lump or nodule on the skin. The lump is typically:
- red or violet in color
- firm to the touch
- fast-growing
- painless
The nodule can form anywhere on the body, but most often appears on areas regularly exposed to sunlight, such as the:
- face
- neck
- arms
If the cancer spreads to the lymph nodes, the nodes may grow large enough to be seen as lumps under the skin.
Merkel cell carcinoma can look like many other types of skin cancer at first, so a definitive diagnosis usually isnt made until after a biopsy. Other types of skin cancers often present with:
Don’t Miss: How Deadly Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
One Location For Coordinated Merkel Cell Carcinoma Care
Patients with Merkel cell carcinoma often require a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Because of this, a team approach which can coordinate all care is the best way to manage these complicated cases.
At Brigham and Womens Hospital , our surgical oncologists are among the worlds leading surgical specialists treating complex and advanced-stage Merkel cell carcinoma. They are the surgical team at the Center for Cutaneous Oncology at the Dana-Farber/Brigham and Womens Cancer Center. Working together as one singularly-focused team, we help Merkel cell carcinoma patients get better faster with improved outcomes and fewer post-operative problems. From diagnosis to treatment, our multidisciplinary team of surgical oncologists, dermatologists, pathologists, medical oncologists, plastic and reconstructive surgeons and radiation oncologists work collaboratively with patients and families.
- The dermatopathologists at Dana-Farber/Brigham and Womens Cancer Center are among the best in the world with special expertise in diagnosing rare cases. This is extremely important as the patients treatment plan is guided by the diagnosis. For the ten percent of cases that are not routine, this is especially relevant.
- The BWH plastic and reconstructive surgeons are pioneers in ground-breaking procedures. The size and experience of our group allow us to tailor specific, individual care to each patient.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare, aggressive type of skin cancer.
Merkel cell carcinoma gets its name because these skin cancer cells resemble Merkel cells, which are located in the top layer of skin. Merkel cells are most concentrated in the fingertips, lips, and face, but MCC cells are most likely to develop on the head, neck, and other areas that have received the most sun exposure.
Below, learn about the causes of MCC, its symptoms, and how to prevent it. We also describe the diagnosis and treatment options.
Carcinoma is a type of cancer that develops in the skin or tissues covering or lining internal organs. Cancer occurs when cells begin to randomly divide and grow out of control. This cellular growth eventually forms a mass called a cancerous tumor.
MCC is one type of skin cancer, and its cells resemble Merkel cells. These are located close to the skins nerve endings and help provide a sense of light touch. They also relay information from the skin to the brain about details such as pressure and texture.
Merkel cells share traits with nerve and hormone-producing cells. As a result, they are classed as neuroendocrine cells, and MCC, in turn, is sometimes called neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin. Another name for MCC is trabecular carcinoma.
MCC is very rare. In 2018, around 2,000 people in the United States received the diagnosis. However, its prevalence seems to be growing.
Read Also: How Can Skin Cancer Kill You
How Is Merkel Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed
Your doctor diagnoses MCC with a physical examination and skin biopsy.
Because MCC often resembles other types of skin cancer, doctors perform skin biopsies to make a positive diagnosis. During a skin biopsy, your doctor removes a small portion of tissue from a lump and sends it to a laboratory for further examination.
Your doctor may also recommend a lymph node biopsy to determine whether MCC has spread to other tissues. A lymph node biopsy takes a small sample of tissue from lymph nodes near suspected MCC to test in a laboratory. Lymph nodes, which are found in clusters throughout the body, are part of the immune system and help to stop infections.
Imaging tests can also help doctors clarify if MCC has spread. These imaging tests may include:
- Computed tomography scans, which use X-rays to create detailed pictures of your body
- Magnetic resonance imaging scans, which use radio waves and magnets to create internal body pictures
- Positron emission tomography scans, which use a small amount of radioactive material to identify cancer cells anywhere in the body
We Were One Of The First And Are Still One Of The Few Multidisciplinary Programs In The Country Created Solely To Treat Patients With Merkel Cell Carcinoma Call Us At 734
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare and potentially aggressive form of skin cancer. Though the cancer can grow and spread rapidly, it is highly treatable and curable if caught in the early stages.
Merkel cell carcinoma is best managed with the collaboration of multiple surgical and medical specialties offered in the program’s Cutaneous Oncology Program. Our physicians offer experience and expertise in treating this disease at all stages.
You May Like: What Is Malignant Skin Cancer
Coping With Merkel Cell Cancer
Many people feel worried, depressed, and stressed when dealing with cancer. Getting treatment for cancer can be tough on your mind and body. Keep talking with your healthcare team about any problems or concerns you have. Work together to ease the effect of cancer and its symptoms on your daily life.
To help ease your stress:
- Talk with your family or friends.
- Ask your healthcare team or social worker for help.
- Speak with a counselor.
- Talk with a spiritual advisor, such as a minister or rabbi.
- Ask your healthcare team about medicines for depression or anxiety.
- Keep socially active.
- Join a cancer support group.
Cancer treatment is also hard on the body. To help yourself stay healthier, try to:
- Eat a healthy diet, with a focus on high-protein foods.
- Drink plenty of water, fruit juices, and other liquids.
- Keep physically active.
- Rest as much as needed.
- Talk with your healthcare team about ways to manage treatment side effects.
- Take your medicines as directed by your team.
What Are The Causes Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
While the exact causes of Merkel cell carcinoma are still not clear, certain possible risk factors have been identified. It is believed that infection with Merkel cell polyomavirus and long-term sun exposure may be responsible for triggering this illness. Other risk factors that can trigger or cause Merkel cell carcinoma also include aging. People older than 50 years of age and those with weak immunity are greater risk. Psoriasis patients treated with psoralen, people with light skin color, men, and excessive and prolonged exposure to UV rays, sunlight and tanning beds face greater risk and can be some of the causes of Merkel cell carcinoma.
Merkel cell carcinoma spreads rapidly, both locally and also to distant regions of the body. Nearly 66% of people diagnosed with this illness have local cancer, 27% have cancer involving the lymph node and 7% have metastasis disease. Early diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma is vital for proper treatment and better prognosis.
Don’t Miss: Are There Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma