What About Other Treatments I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Treating Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage IV melanomas have already spread to distant lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
Metastases in internal organs are sometimes removed, depending on how many there are, where they are, and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab are typically the first drugs tried, especially in people whose cancer cells do not have BRAF gene changes. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Ipilimumab , a different type of checkpoint inhibitor, is not typically used by itself as the first treatment, although it might be combined with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. This slightly increase the chances that the tumor will shrink, although itâs also more likely to result in serious side effects, which needs to be considered carefully. People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects..
Itâs important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.
What If I Have Metastatic Melanoma Symptoms
Whether you have a suspicious mole or are experiencing some symptoms of advanced-stage melanoma, it is important to consult with a physician to receive an accurate diagnosis, as many other conditions can cause similar symptoms. At Moffitt Cancer Center, we provide a comprehensive range of screening, diagnostic, treatment and supportive care services for patients with melanoma and other types of cancer. Within our Cutaneous Oncology Program, our multispecialty team includes surgeons, dermatologists, medical oncologists and other experts who work together as a tumor board to ensure our patients receive the best possible treatment and care.
If you would like to schedule an appointment at Moffitt to discuss your metastatic melanoma symptoms, call or fill out a new patient registration form online. We do not require a referral to schedule an appointment.
- BROWSE
You May Like: How Bad Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
How Often Should You Follow Up With Your Doctor
After your treatment, your doctor will recommend a regular follow-up schedule to monitor your cancer. Theyll be checking to make sure the cancer hasnt come back or new cancerous lesions havent appeared. The types of follow-up include:
A yearly skin check: Skin checks are an important aspect of detecting melanoma in its earliest, most treatable stages. You should also conduct a skin check on yourself once per month. Look everywhere from the bottoms of your feet to behind your neck.
Imaging tests every three months to a year: Imaging studies, such as an X-ray, CT scan, or brain MRI, look for cancer recurrence.
Physical exam as needed: A physical exam to assess your overall health is important when you have had melanoma. For the first two years, youll want to get an exam every three to six months. Then for the next three years, the appointments can be every three months to a year. After the fifth year, the exams can be as needed. Do a monthly self-examination of your lymph nodes to check your progress.
Your doctor may recommend a different schedule based on your overall health.
Dont Miss: How Bad Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Whats The Outlook For Stage 4 Melanoma
Once the cancer spreads, locating and treating the cancerous cells becomes more and more difficult. You and your doctor can develop a plan that balances your needs. The treatment should make you comfortable, but it should also seek to remove or slow cancer growth. The expected rate for deaths related to melanoma is 10,130 people per year. The outlook for stage 4 melanoma depends on how the cancer has spread. Its usually better if the cancer has only spread to distant parts of the skin and lymph nodes instead of other organs.
Read Also: How Often Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Spread
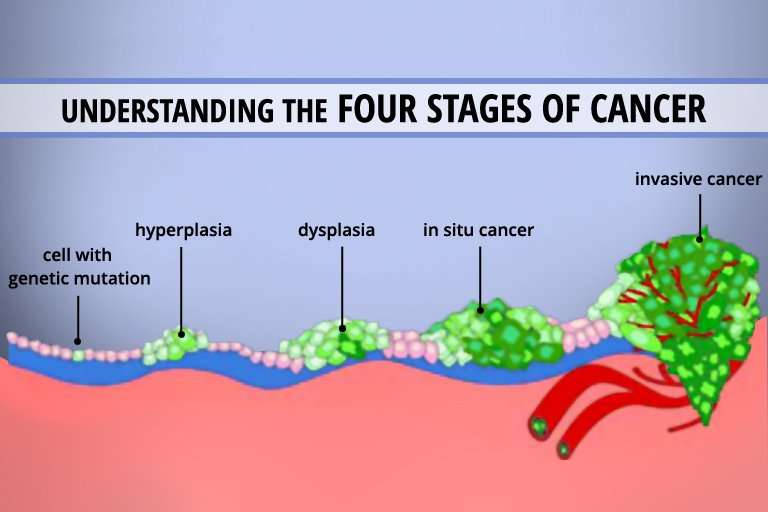
Stage : Melanoma In Situ
The earliest stage of melanoma is stage 0, also known as melanoma in situ or carcinoma in situ. In situ is a Latin phrase that means in position, and this diagnosis means that the cancer cells are present only in the epidermisthe bodys most superficial layer of skinand nowhere else.
This diagnosis has a very good prognosis, Noelani González, MD, an instructor of dermatology at the Mount Sinai Icahn School of Medicine in New York City, tells Health. People with localized melanomas who are treated quickly have a 5-year survival rate of 97%meaning they are, on average, about 97% as likely to still be alive in five years as people who dont have these cancers.
Treatment for this stage cancer involves a wide excision surgery, where the affected skin is cut away and the wound is stitched and bandaged. The skin will be removed with margins, explains Dr. González. That means that some normal skin will also be removed around the edges to make sure there arent any cancer cells left over.
The removed skin is then looked at under a microscope to ensure that all of the cancer was removed with clean margins, says Dr. González. Because stage 0 cancer has not spread to any other tissues or organs, no further treatment is required.
RELATED: This Woman Had to Wait 4 Months to Get a Mole Checked Outand It Turned Out She Had Skin Cancer
Mitotic Rate Of Your Melanoma
The staging system has been recently updated. It no longer includes the mitotic rate to work out your stage. But your doctor may still use it to work out how likely your cancer. is to spread.
Mitotic rate means the number of cells that are dividing in a certain amount of melanoma tissue. Higher mitotic rate may mean that the melanoma is at greater risk the spreading because more cells are dividing more.
You May Like: What Is High Grade Papillary Urothelial Carcinoma
How Is Melanoma Staged
Melanoma stages are assigned using the TNM system.
The stage of the disease indicates how much the cancer has progressed by taking into account the size of the tumor, whether its spread to lymph nodes, and whether its spread to other parts of the body.
A doctor can identify a possible melanoma during a physical exam and confirm the diagnosis with a biopsy, where the tissue is removed to determine if its cancerous.
But more sophisticated technology, such as PET scans and sentinel lymph node biopsies, are necessary to determine the cancers stage or how far its progressed.
There are five stages of melanoma. The first stage is called stage 0, or melanoma in situ. The last stage is called stage 4. Survival rates decrease with later stages of melanoma.
Its important to note that survival rates for each stage are just estimates. Each person with melanoma is different, and your outlook can vary based on a number of different factors.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
What Is A Cancer Grade
A cancers grade describes how abnormal the cancer cells and tissue look under a microscope when compared to healthy cells. Cancer cells that look and organize most like healthy cells and tissue are low grade tumors. Doctors describe these cancers as being well differentiated. Lower grade cancers are typically less aggressive and have a better prognosis.
The more abnormal the cells look and organize themselves, the higher the cancers grade. Cancer cells with a high grades tend to be more aggressive. They are called poorly differentiated or undifferentiated.
Some cancers have their own system for grading tumors. Many others use a standard 1-4 grading scale.
- Grade 1: Tumor cells and tissue looks most like healthy cells and tissue. These are called well-differentiated tumors and are considered low grade.
- Grade 2: The cells and tissue are somewhat abnormal and are called moderately differentiated. These are intermediate grade tumors.
- Grade 3: Cancer cells and tissue look very abnormal. These cancers are considered poorly differentiated, since they no longer have an architectural structure or pattern. Grade 3 tumors are considered high grade.
- Grade 4: These undifferentiated cancers have the most abnormal looking cells. These are the highest grade and typically grow and spread faster than lower grade tumors.
You May Like: Can I Die From Skin Cancer
What Are Some Of The Cancer Type
Breast and prostate cancers are the most common types of cancer that have their own grading systems.
Breast cancer. Doctors most often use the Nottingham grading system for breast cancer . This system grades breast tumors based on the following features:
- Tubule formation: how much of the tumor tissue has normal breast duct structures
- Nuclear grade: an evaluation of the size and shape of the nucleus in the tumor cells
- Mitotic rate: how many dividing cells are present, which is a measure of how fast the tumor cells are growing and dividing
Each of the categories gets a score between 1 and 3 a score of 1 means the cells and tumor tissue look the most like normal cells and tissue, and a score of 3 means the cells and tissue look the most abnormal. The scores for the three categories are then added, yielding a total score of 3 to 9. Three grades are possible:
- Total score = 35: G1
- Total score = 67: G2
- Total score = 89: G3
- Gleason X: Gleason score cannot be determined
- Gleason 26: The tumor tissue is well differentiated
- Gleason 7: The tumor tissue is moderately differentiated
- Gleason 810: The tumor tissue is poorly differentiated or undifferentiated
Systemic Adjuvant Treatment Of Stage Iii Melanoma
Systemic therapy is any treatment directed at destroying cancer cells throughout the body. Many patients with stage III melanoma are at high risk for disease recurrence because undetectable cancer cells referred to as micrometastases have already broken away from the primary cancer and traveled through the lymph and blood system to other locations in the body. The delivery of systemic cancer treatment following surgery is referred to as adjuvant therapy.
Adjuvant treatment of stage III melanoma with newer precision cancer medicines and immunotherapy drugs is the standard of care because they delay the time to cancer recurrence and prolong survival.
Don’t Miss: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
How To Protect Yourself From Melanoma
Fortunately, most melanomas are diagnosed in early, localized stages, says Dr. González, and most patients treated for melanoma make a full recovery. But we do have patients that have ignored that funny looking mole for way too long, and its not uncommon to see cases that have metastasized to other organs, she adds.
Melanoma tends to a very aggressive form of cancer, and it can progress quickly from one stage to another. Says Dr. González: As soon as you see something unusual you should get it checked out, and as soon as you get a diagnosis, you need to be on top of the appropriate treatment.
Risk factors for melanoma include ultraviolet light exposure , having fair skin and light hair, and having a close relative whos also had melanoma. But monitoring skin for abnormal growths and changes is important for everyone, whether or not they are predisposed to skin cancer.
Going to see your board-certified dermatologist yearly and doing regular skin exams may not seem that important, Dr. González says, “but these are the things that could save your life.”
What To Ask Your Doctor About Stage Iv Melanoma
When your doctor tells you that you have Stage IV melanoma, it can be frightening and overwhelming. But it is important to use the time with all of your doctors to learn as much about your cancer as you can. Your doctors will provide you important information about your diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment options.
It is often helpful to bring a friend or family member with you to your doctor appointments. This person can lend moral support, ask questions, and take notes.
The following questions are those you may want to ask your doctors. Some of the questions are for your medical oncologist, some are for your surgical oncologist, and some for your dermatologist. Remember, it is ALWAYS okay to ask your doctor to repeat or clarify something s/he has said so that you can better understand it. You may find it helpful to print out these questions and bring them with you to your next appointment.
Recommended Reading: What Color Is Skin Cancer Ribbon
Unusual Moles Exposure To Sunlight And Health History Can Affect The Risk Of Melanoma
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesnât mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for melanoma include the following:
- Having a fair complexion, which includes the following:
- Fair skin that freckles and burns easily, does not tan, or tans poorly.
- Blue or green or other light-colored eyes.
- Red or blond hair.
Being White or having a fair complexion increases the risk of melanoma, but anyone can have melanoma, including people with dark skin.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information on risk factors for melanoma:
Read Also: How Quickly Does Renal Cell Carcinoma Grow
How Fast Does Melanoma Spread
Melanoma is a deadly form of skin cancer because of its ability to metastasize to local lymph nodes and other organs. It is estimated that melanoma kills, on average, over 10,000 people in the United States every year.
The first sign of flat melanoma is usually a new spot or an existing mole or freckle that changes in appearance. Some changes can include:
- A spot that has grown in size
- A spot where the edges are looking irregular versus smooth and even
- A spot that has a range of colors such as brown, black, blue, red, white or light gray.
- A spot that has become itchy or is bleeding
According to Dr. Andrew Duncanson, board-certified dermatologist at Forefront Dermatology, It is important to know that melanoma can appear on areas of the skin not normally exposed to the sun such as under the arm, chest, and buttocks. It can also appear in areas that you are not able to see easily on your own including the ears, scalp, back of legs, and bottom of feet. I always recommend to my patients to look for the ugly duckling spot the new spot that doesnt look like any others. Additionally, ask a family member to look over the hard to see areas monthly, while also getting an annual skin cancer exam by a board-certified dermatologist to detect skin cancer early.
Read Also: Is Melanoma The Same As Skin Cancer
The Braf Gene Mutation And Melanoma
Roughly half of all documented melanoma cases present with mutations in the BRAF gene. The melanoma cells that have these changes create a BRAF protein, which aids them in their growth. If a person with the BRAF gene mutation has melanoma, knowing about the mutation is of great benefit for treatment because healthcare providers can use targeted therapy to inhibit the BRAF gene mutation from aiding in the growth of the cancer.
If a diagnosis of melanoma is already established, the healthcare provider will look at two factors to determine how advanced a stage 4 melanoma has become: the location of the distant tumors and an elevated level of serum lactate dehydrogenase , which is an enzyme responsible for turning sugar into energy. The higher the LDH level in body fluids, the more damage the cancer has done.
Treating Stage 4 Melanoma
If melanoma comes back or spreads to other organs itâs called stage 4 melanoma.
In the past, cure from stage 4 melanoma was very rare but new treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted treatments, show encouraging results.
Treatment for stage 4 melanoma is given in the hope that it can slow the cancerâs growth, reduce symptoms, and extend life expectancy.
You may be offered surgery to remove other melanomas that have grown away from the original site. You may also be able to have other treatments to help with your symptoms, such as radiotherapy and medicine.
If you have advanced melanoma, you may decide not to have treatment if itâs unlikely to significantly extend your life expectancy, or if you do not have symptoms that cause pain or discomfort.
Itâs entirely your decision and your treatment team will respect it. If you decide not to receive treatment, pain relief and nursing care will be made available when you need it. This is called palliative care.
Donât Miss: How To Identify Skin Cancer
Also Check: How Does Skin Cancer Feel