Preventing Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma prevention is the same as prevention methods for all skin cancers, with the goal of protecting skin from harmful UV rays.
The number one thing people can do is to practice good sun protection and sun avoidance, meaning wear sunscreen and protect the skin from getting sun damage, says Stevenson. Its also important to get skin checks regularly for early detection.
Stevenson says if someone is prone to skin cancers for example, has very fair skin, sunburns as a child, or a history of skin cancer in the family its better to go out in the late afternoon or early morning when the sun isnt as strong, or stay primarily in the shade.
Anyone spending time in the sun, regardless of complexion, should practice sun protective behaviors, including wearing sunscreen.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a sunscreen with a minimum sun protection factor of 15, and UVA and UVB broad spectrum protection. It also advises people to stay in the shade as much as possible and wear protective clothing including brimmed hats and sunglasses. Stevenson suggests looking for a SPF over 30.
Lebwohl says the SPF number directly correlates with the amount of protection it gives you. He says to divide the amount of time in the sun by the SPF number. For example, if someone is in the sun for 60 minutes, and wearing SPF 30, its as if they were exposed to two minutes of damaging rays rather than the full 60 minutes.
Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Sun exposure and other risk factors
Sun exposure is the major known environmental factor associated with the development of skin cancer of all types; however, different patterns of sun exposure are associated with each major type of skin cancer. Unlike basal cell carcinoma , SCC is associated with chronic exposure, rather than intermittent intense exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Occupational exposure is the characteristic pattern of sun exposure linked with SCC. Other agents and factors associated with SCC risk include tanning beds, arsenic, therapeutic radiation , chronic skin ulceration, and immunosuppression.
Characteristics of the skin
Like melanoma and BCC, SCC occurs more frequently in individuals with lighter skin than in those with darker skin. A case-control study of 415 cases and 415 controls showed similar findings; relative to Fitzpatrick type I skin, individuals with increasingly darker skin had decreased risks of skin cancer . The same study found that blue eyes and blond/red hair were also associated with increased risks of SCC, with crude ORs of 1.7 for blue eyes, 1.5 for blond hair, and 2.2 for red hair.
Immunosuppression
Personal history of BCC, SCC, and melanoma skin cancers
Family history of squamous cell carcinoma or associated premalignant lesions
The Risks The Causes What You Can Do
Basal cell carcinoma is caused by damage and subsequent DNA changes to the basal cells in the outermost layer of skin. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun and indoor tanning is the major cause of BCCs and most skin cancers.
Understanding what causes BCC and the factors that increase your risk of getting it can help you prevent the disease or detect it in its earliest stages, when its easiest to treat.
These factors increase your BCC risk:
Recommended Reading: What Is The Deadliest Type Of Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome
In this rare congenital condition, people develop many basal cell cancers over their lifetime. People with this syndrome may also have abnormalities of the jaw , eyes, and nervous tissue.
Most of the time this condition is inherited from a parent. In families with this syndrome, those affected often start to develop basal cell cancers as children or teens. Exposure to UV rays can increase the number of tumors these people get.
Risk Factors Of Basal Cell Carcinoma

Having a;risk factor;does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Some risk factors are out of your control, such as your complexion or family history. However, some risk factors, such as exposure to ultraviolet light, are factors you can control. People who think they may be at risk should discuss this with their doctor.
Recommended Reading: How Bad Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
What Are The Treatments For Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is treated by removing it. The choice of treatment depends on many things, including patient health and age, the location of the tumor, and the extent and type of the cancer. Treatment may occur in many ways:
- Scratching off with a curette, an instrument that may end in a ring or a spoon, and then burning with a special electric needle. This method is called electrodessication and curettage.
- Surgical removal
- Mohs surgery: This is a specialized technique. The doctor first removes the visible cancer and then begins cutting around the edges. The tissues are examined during the surgery until no more cancer cells are found in tissues around the wound. If necessary, a skin graft or flap might be applied to help the wound heal.
- Excisional surgery: The growth and a bit of surrounding skin is removed with a scalpel.
If the BCC has advanced locally or spread to another location, which is very rare for BCC, the FDA has approved two medicines: vismodegib and sonidegib . These drugs are of a class called hedgehog inhibitors.
Who Gets Basal Cell Carcinoma
Risk factors for BCC include:
- Age and sex: BCCs are particularly prevalent in elderly males. However, they also affect females and younger adults
- Repeated prior episodes of sunburn
- Fair skin, blue eyes and blond or red hairnote; BCC can also affect darker skin types
- Previous cutaneous injury, thermal burn, disease
- Inherited syndromes: BCC is a particular problem for families with basal cell naevus syndrome , Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome, Rombo syndrome, Oley syndrome and xeroderma pigmentosum
- Other risk factors include ionising radiation, exposure to arsenic, and immune suppression due to disease or medicines
You May Like: Can Cancer Cause Skin Rash
Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Malignant
Is basal cell carcinoma malignant?
Is basal cell carcinoma considered cancer?;Basal cell carcinoma is most common type of skin cancer. About 8 out of 10 skin cancers are basal cell carcinomas . These cancers start in the basal cell layer, which is the lower part of the epidermis.
What is basal cell carcinoma the most common malignant tumor of?;Basal cell carcinomas are the most common type of skin cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. These cancers develop within the basal cell layer of the skin, in the lowest part of the epidermis. Patients who have had basal cell carcinoma once have an increased risk of developing a recurrent basal cell cancer.
Is basal cell carcinoma an aggressive cancer?;Occasionally, however, BCC behaves aggressively with deep invasion, recurrence, and potential regional and distant metastasis. Several factors, including tumor size, duration, histology, and perineural spread, have been postulated as markers of the aggressive BCC phenotype.
Staging For Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin Depends On Where The Cancer Formed
Staging for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the eyelid is different from staging for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma found on other areas of the head or neck. There is no staging system for basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma that is not found on the head or neck.
Surgery to remove the primary tumor and abnormal lymph nodes is done so that tissue samples can be studied under a microscope. This is called pathologic staging and the findings are used for staging as described below. If staging is done before surgery to remove the tumor, it is called clinical staging. The clinical stage may be different from the pathologic stage.
Recommended Reading: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
You May Like: How Dangerous Is Skin Cancer On The Face
What Happens If Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
While basal cell carcinoma is a slow-growing type of cancer, you should not leave it untreated. In doing so, the basal cells can become quite large and cause disfigurement. Even scarier, it can spread to other parts of your body and cause death. Basal cell carcinoma has a high cure rate and theres no reason not to seek immediate treatment that will take care of the cancerous cells.
At Moffitt Cancer Center, we can provide you with additional information about basal cell carcinoma risk factors. No referral is necessary; make an appointment by calling ;or complete a new patient registration form.
- BROWSE
Epidemiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
| ; | Cite this page |
Whiteman, D,;Adele Green,;Catherine Olsen, Cancer Council Australia Keratinocyte Cancers Guideline Working Party. Guidelines:Keratinocyte carcinoma/Epidemiology BCC . In: Clinical practice guidelines for keratinocyte cancer. Sydney: Cancer Council Australia. . Available from: .
Recommended Reading: What Is Non Small Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatment
Squamous cell carcinomas detected at an early stage and removed promptly are almost always curable and cause minimal damage. However, left untreated, they may grow to the point of being very difficult to treat.
A small percentage may even metastasize to distant tissues and organs. Your doctor can help you determine if a particular SCC is at increased risk for metastasis and may need treatment beyond simple excision.
Fortunately, there are several effective ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma. The choice of treatment is based on the type, size, location, and depth of penetration of the tumor, as well as the patients age and general health. Squamous cell carcinoma treatment can almost always be performed on an outpatient basis.
Medicines To Lower Risk
Some people at increased risk for skin cancer, such as people with certain inherited conditions or a weakened immune system, might be helped by medicines that could lower their risk . Doctors are studying many different drugs that might lower risk, although these are not commonly used at this time. For more information, see Whats New in Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Research?;
Read Also: What Does Advanced Skin Cancer Look Like
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Basal cell cancers usually present as an abnormal growth on the skin. The growth may have the appearance of a wart, crusty spot, reddish patch, mole, nodule or bump, or a sore that does not heal. It may or may not bleed and can sometimes be painful. These are usually slow-growing tumors that begin as small spots on sun-exposed areas of the face. Because they can have such a range of appearances, any new persistent skin lesion should be evaluated.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery Specialists
Our head and neck surgeons and speech language pathologists take a proactive approach to cancer treatment. Meet the Johns Hopkins specialists who will work closely with you during your journey.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Symptoms
This disease is characterized by the growth of the skin in the form of lumps containing blood vessels in it. The lump is painless, bleeds easily, and is pink, brown, or black. Symptoms of basal cell carcinoma usually appear in areas of the body that are often exposed to the sun, such as the face, eyelids, neck, and hands. In rare cases, basal cell carcinoma can also occur in areas of the body that are not exposed to the sun, such as the breast.
The appearance of lumps may vary by person, including:
- Flat, scaly and reddish rash.
- Lesions are like scratch wounds, white in color, soft, without clear edges of the wound.
Also Check: How To Remove Skin Cancer Yourself
How To Treat Basal Cell Carcinoma
Once we make a clinical diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma, we can choose from several treatments. For superficial tumors, treatment with a special cream or freezing with liquid nitrogen may be sufficient. If the tumor has spread deeper, surgical excision is justified, of course, by histological examination and, in the case of a larger lesion, by a plastic solution. If the patients condition, the location and size of the tumor do not allow surgical removal, well-tolerated radiotherapy may be effective. explains dr. Schmidt Emese, dermatologist at the Birthmark Center, clinical oncologist. As basal cell carcinoma is prone to local recurrence, oncodermatological care after diagnosis and regular monitoring of the patient, initially every 3 and then every 6 months, is recommended.
It is not just high-factor sunscreens that are associated with the prevention of skin tumors, It is important to draw attention to the daily use of UV-filtered clothing, to avoid tanning beds and increased UV exposure, and to completely heal the basal cell carcinoma detected and treated in time during regular mole screenings.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2;basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage;3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones;or other organs in the body.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Chances Of Getting Skin Cancer
How Is Basal Cell Cancer Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Basal cell cancers are staged by size and extent of growth. These cancers rarely metastasize to lymph nodes or other organs, but they can grow quite large and invade small nerves and local structures.
Biopsy can help determine if the basal cell cancer is a low-risk tumor or a high-risk tumor that requires more aggressive treatment. Low-risk tumors are often nodular and do not have nerve involvement. High-risk tumors in the head and neck are those that involve the central face, nose and eye area, as well as those tumors that are greater than or equal to 10 millimeters on the cheeks, scalp and neck; tumors that are recurrent or arising from previously radiated tissue; and tumors arising in patients who are immunosuppressed. An aggressive growth pattern on the pathology evaluation and perineural invasion are also features of high-risk basal cell cancers.
Watchful Waiting: An Option For Some With Basal Cell Carcinoma
Limited life expectancy, slow BCC growth key factors to option. Watchful waiting appeared to be an appropriate approach for patients with basal cell carcinoma if they had a limited life expectancy or low-risk BCCs, an observational, real-world cohort study suggested. In a cohort of 89 patients, watchful waiting…
Also Check: Is Renal Cell Carcinoma Hereditary
Diagnosing Basal Cell Carcinoma
The most common way dermatologists diagnose basal cell carcinoma is with a full body skin check.
Stevenson says during the diagnosis process dermatologists are looking for papules with skin cancer characteristics. Sometimes dermatologists will use a tool called a dermatoscope, which uses a polarized light to look for other signs of skin cancer. With their training, dermatologists should be able to tell patients if the lesion is benign or something that should be removed because of a skin cancer concern.
RELATED: Do You Need to Wear Sunscreen Indoors?
How Can You Prevent Basal Cell Carcinoma
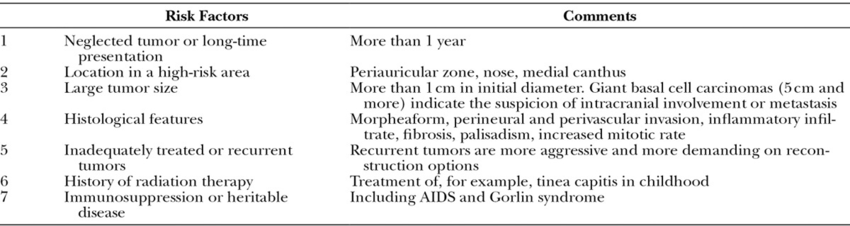
Being safe in the sun is the best way to prevent BCC and other skin cancers. Here are some tips:
- Avoid being in the sun from 10 am to 4 pm.
- Avoid tanning beds.
- Use a broad spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher each day. If you will be outside for longer periods of time, use a broad spectrum sunscreen that is water-resistant and has an SPF of 30 or higher. Put the sunscreen on 30 minutes before going outside. Put sunscreen on again every two hours, or more frequently if you have been swimming or sweating a lot.
- Use protective clothing that has built-in sun protection, which is measured in UPF. Also, use broad-brimmed hats and sunglasses.
- Do your own skin self-exam about once per month and see a dermatologist about one time per year for a professional skin exam.
- Have any skin changes examined as soon as possible by a healthcare provider.
Also Check: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
Uv Exposure From The Sun
The lesions commonly arise in areas of the body that are excessively exposed to ultraviolet rays from the sun, such as the head and neck. Occasional extended, intense sun exposure that leads to sunburn and cumulative sun exposure over your lifetime are the main causes of skin damage that can lead to basal cell carcinoma.
If your occupation requires long hours outdoors or if you spend your leisure time in the sun, your risk increases even more.