S Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma On The Skin
The following pictures show many of the ways that SCC can appear on the skin.
Rough-feeling, reddish patch
This is an early sign of squamous cell carcinoma.
Round growth with raised borders
This squamous cell carcinoma developed from a pre-cancerous growth called an actinic keratosis.
A sore that won’t heal or heals and returns
On the skin or lips, squamous cell carcinoma can look like a sore.
Age spot
This can be a sign of squamous cell carcinoma, which is why you want a board-certified dermatologist to examine your skin before you treat any age spot.
Raised, round growth
This is a common sign of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
Animal’s horn
When squamous cell carcinoma looks like this, it tends to grow quickly.
Because this common skin cancer can begin on any part of the body that has squamous cells, it can also develop inside the mouth, on the genitals, inside the anus, or in the tissue beneath a fingernail or toenail.
In these areas, this skin cancer may look like a:
-
Sore or rough patch
-
Raised, reddish patch
-
Wart-like sore
-
Brown or black line beneath a nail
Sore inside your mouth
This squamous cell carcinoma started inside the mouth and grew to cover a larger area.
Dark streak beneath a nail
Squamous cell carcinoma can look like a brown or black line beneath a nail, as shown here.
When it develops around the nail, it can look like a wart that just wont go away. If youve had a wart around a fingernail for years, its time for a dermatologist to examine it.
Scc Is Mainly Caused By Cumulative Uv Exposure Over The Course Of A Lifetime
If youve had a basal cell carcinoma you may be more likely to develop a squamous cell skin carcinoma, as is anyone with an inherited, highly UV-sensitive condition such as xeroderma pigmentosum.
Chronic infections, skin inflammation, HIV and other immune deficiency diseases, chemotherapy, anti-rejection drugs used in organ transplantation, and excessive sun exposure can all lead to a risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Occasionally, squamous cell carcinomas arise spontaneously on what appears to be normal, healthy skin. Some researchers believe the tendency to develop these cancers can be inherited.
SCCs may occur on all areas of the body including the mucous membranes and genitals, but are most common in areas frequently exposed to the sun:
- Ears
- Previous BCC or SCC
- Chronic inflammatory skin conditions or chronic infections
But anyone with a history of substantial sun exposure is at increased risk. Those whose occupations require long hours outside or who spend their leisure time in the sun are also at risk.
What Is Intermediate Squamous Cells
What is intermediate squamous cells? Intermediate Squamous CellsThe cell is found in the stratum spongiosum layer of the squamous epithelium. The intermediate cells cytoplasm is thin, transparent, and typically stains basophilic. The centrally placed nucleus is 35 µm. The nucleus is vesicular with fine evenly dispersed granular chromatin.
Do squamous cells mean cancer?;Squamous cells are found in many places in your body, and squamous cell carcinoma can occur anywhere squamous cells are found. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin refers to cancer that forms in the squamous cells found in the skin.
Are squamous cells normal in Pap smear?;Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance is the most common abnormal finding in a Pap test. It may be a sign of infection with certain types of human papillomavirus or other types of infection, such as a yeast infection.
What does squamous cells mean?;Squamous cells are thin, flat cells that look like fish scales, and are found in the tissue that forms the surface of the skin, the lining of the hollow organs of the body, and the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
Don’t Miss: How Does Immunotherapy Work For Melanoma
Who Is Most At Risk Of Developing A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
You are at highest risk of developing a squamous cell carcinoma if you:
- are older
- have pale skin and burn easily
- have spent a lot of time outdoors for work or leisure
- have a history of sunburns, sunbathing or using sun beds;
- live in;a sunny climate
- have previously had a squamous cell carcinoma or other type of skin cancer
- have a condition or take medications that affect your immune system .
Ask Your Doctor For A Survivorship Care Plan

Talk with your doctor about developing a survivorship care plan for you. This plan might include:
- A suggested schedule for follow-up exams and tests
- A schedule for other tests you might need in the future, such as early detection tests for other types of cancer, or tests to look for long-term health effects from your cancer or its treatment
- A list of possible late- or long-term side effects from your treatment, including what to watch for and when you should contact your doctor
- Diet and physical activity suggestions
Recommended Reading: How To Remove Skin Cancer On Face
Sudden Bleeding And Scabbing
Two days before surgery, I looked in the mirror in the morning and I noticed dried blood on my face. I had a few places on my face that had been bleeding and scabbing which my doctor was going to remove, but this was on the tip of my nose. And the day before, I had nothing on the tip of my nose. While this was bothersome, I planned on mentioning it to my doctor on the day of surgery.
Are You Wondering About Recurrence
The first question to keep in mind when discussing the potential for skin cancer recurrence is what type of skin cancer developed initially. There is sufficient data to suggest that patients who have been diagnosed with any type of skin cancer have a higher risk for another. For example, there is a ten-fold chance that Basal Cell Carcinoma or Squamous Cell Carcinoma may recur in the tissue surrounding an initial lesion during the two-year period following initial treatment. Patients diagnosed with melanoma have an increased risk of developing all other types of skin cancer. This is why routine follow-up is vital to lifelong health.
You May Like: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
How Do People Find Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cancer On Their Skin
Many people find it when they notice a spot, round lump, or scaly patch on their skin that is growing or feels different from the rest of their skin. If you notice such a spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist. These doctors have the most training and experience in diagnosing skin cancer.
To find skin cancer early, dermatologists recommend that everyone check their own skin with a skin self-exam. This is especially important for people who have a higher risk of developing SCC.
Youll find out what can increase your risk of getting this skin cancer at, Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Who gets and causes.
Images
-
Images 1,2,4,7,9: The American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides
-
Image 3: JAAD Case Reports 2018;4:455-7.
What Are The Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is classified into the following stages, which are partly based on how far the cancer has spread throughout the body:
- Stage 0 Squamous cell carcinoma develops in the squamous cells, which are located in the epidermis . During Stage 0, the cancer hasnt spread beyond the epidermis.
- Stage 1 When squamous cell carcinoma progresses to Stage 1, it means that the cancer has spread deeper into the skin, but not into any lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 2 A Stage 2 classification means that, in addition to progressing deeper into the skin, the cancer also displays at least one high-risk feature. This might include metastasizing to the lower skin layers or the nerves. However, at this stage, the cancer still hasnt spread to lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 3 Once squamous cell carcinoma reaches Stage 3, the cancer has spread into lymph nodes but not any other tissues or organs.
- Stage 4 This is the final stage of squamous cell carcinoma, where the cancer has spread to at least one distant organ, whether that be the brain, the lungs or a separate area of skin.
If you think you might have squamous cell carcinoma, its important to seek prompt medical attention to minimize the risk of cancer spread. The specialists in Moffitt Cancer Centers Cutaneous Oncology Program can provide you with the comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services you need. Call or complete our new patient registration form online to request an appointment.
- BROWSE
Recommended Reading: Is Melanoma The Worst Cancer
How Can I Prevent Squamous Cell Carcinoma From Coming Back
Most squamous cell carcinomas can be treated and cured. However, it is possible for these types of cancers to recur or for new skin cancers to appear.;
Do the following to reduce the risk of new cancers occurring:
- Keep all follow-up appointments with your GP or skin specialist.
- Regularly check all your skin .;If you see anything that is growing, bleeding or in any way changing, go and see your doctor straight away. See;skin checks.
- Protect your skin from the sun and avoid indoor tanning. This is essential to prevent further damage, which will increase your risk of getting another skin cancer.
Worried About Your Check Up
Many people find their check ups quite worrying. A;hospital appointment can bring all the worry about your cancer back, if youre feeling well and getting on with life
Remember that the risk of BCC;spreading to other parts of the body is extremely low. BCC;can come back in the skin close to where they started, but they hardly ever spread elsewhere.
A squamous cell skin cancer has a higher risk of spreading than a BCC. But this is still unusual.
You might;find it helpful to talk to someone close about how youre feeling. Its quite common for people to have;counselling;after their cancer treatment.
Don’t Miss: What Doctor Treats Skin Cancer
Key Points On Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Tests That Examine The Tissues Of The Neck Respiratory Tract And Upper Part Of The Digestive Tract Are Used To Detect And Diagnose Metastatic Squamous Neck Cancer And The Primary Tumor
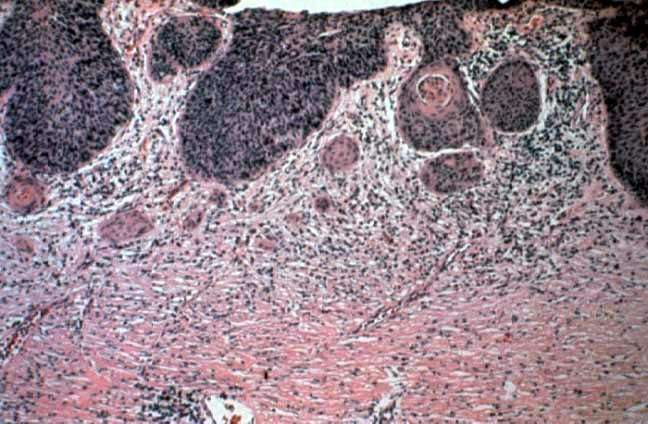
Tests will include checking for a primary tumor in the organs and tissues of the respiratory tract , the upper part of the digestive tract , and the genitourinary system.
The following procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and health history: An exam of the body, especially the head and neck, to check general signs of health. This includes checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patients health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist or tested in the laboratory to check for signs of cancer.
Three types of biopsy may be done:
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: The removal of tissue or fluid using a thin needle.
- Core needle biopsy: The removal of tissue using a wide needle.
- Excisional biopsy: The removal of an entire lump of tissue.
The following procedures are used to remove samples of cells or tissue:
One or more of the following laboratory tests may be done to study the tissue samples:
Also Check: Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatable
If The Cancer Comes Back
If your cancer does come back at some point, your treatment options will depend on where the cancer is and what treatments youve had before. If the cancer comes back just on the skin, options might include surgery, radiation therapy, or other types of local treatments. If the cancer comes back in another part of the body, other treatments such as targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or chemotherapy might be needed. For more general information on dealing with a recurrence, see our Recurrence section.
What Should I Do If I Think I Have A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
If you notice a change to or growth on your skin, make an appointment to see your doctor straight away. Your doctor will assess the size, location and look of the growth. They will also ask you how long you have had it and whether it bleeds or itches.;
If your doctor thinks the growth may be cancer, they may take a small sample of tissue . The tissue sample will be sent to a laboratory and examined under a microscope. Your doctor will let you know whether the sample shows any cancer cells or not, and will recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.;
You May Like: What Is Merkel Cell Skin Cancer
The Answer To The Question If Skin Cancer Can Come And Go Is Rather Tricky
Skin cancer coming and going would refer to malignant cells being there one day and then withering away shortly after without any treatment.
And then returning again in the same spot. This has not been shown to occur with the deadliest form of skin cancer, melanoma.
It has also not been shown to occur with another type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma there are no cases confirming that this particular cancer was literally coming and going without treatment.
The same can be said for the most common cancer in the world, a skin growth known as basal cell carcinoma.
Howeverthe concept of a skin cancer coming and going appearing and disappearing spontaneously without treatment might be applicable to precancerous lesions.
Your immune system will help destroy some early stages of skin cancer like actinic keratosis, says Janet Prystowsky, MD, board certified dermatologist in New York, NY, with 30+ years experience.
Dr. Prystowsky adds, The growth may recur, however. The process may repeat itself.
Metastatic Squamous Neck Cancer With Occult Primary Is A Disease In Which Squamous Cell Cancer Spreads To Lymph Nodes In The Neck And It Is Not Known Where The Cancer First Formed In The Body
Squamous cells are thin, flat cells found in tissues that form the surface of the skin and the lining of body cavities such as the mouth, hollow organs such as the uterus and blood vessels, and the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Some organs with squamous cells are the esophagus, lungs, kidneys, and uterus. Cancer can begin in squamous cells anywhere in the body and metastasize through the blood or lymph system to other parts of the body.
When squamous cell cancer spreads to lymph nodes in the neck or around thecollarbone, it is called metastatic squamous neck cancer. The doctor will try to find the primary tumor , because treatment for metastatic cancer is the same as treatment for the primary tumor. For example, when lung cancer spreads to the neck, the cancer cells in the neck are lung cancer cells and they are treated the same as the cancer in the lung. Sometimes doctors cannot find where in the body the cancer first began to grow. When tests cannot find a primary tumor, it is called anoccult primary tumor. In many cases, the primary tumor is never found.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
Data From The Largest 5
New findings from the largest-to-date 5-year follow-up of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma patients suggest that nearly all recurrences happen within 2 years of primary tumor excision, with perineural invasion standing out as the strongest prognostic indicator of local recurrence and nodal metastasis.1
Take Note
- 96% of squamous cell carcinoma recurrences occurred within 2 years after cutaneous tumor excision.
- Size of primary tumor, anatomical location of primary tumor, and depth of margin from clearance were not significantly associated with recurrence.
- Perineural invasion emerged as a strong predictor of both local recurrence and lymph node metastasis.
The 2018 study, published in the Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, retrospectively analyzed 5-year outcomes from 598 cutaneous SCC excision patients from 4 centers across the United Kingdom. Total recurrence rate, including local recurrence and nodal metastasis, time to recurrence, and risk factors associated with recurrence were investigated.
New findings and their implications
While a higher proportion of recurrence did occur in patients with the narrowest deep margin from clearance , this did not reach statistical significance. 1
Take-home messages
References
- 4. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology for Squamous Cell Skin Cancer V.2.2018. National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2018. Accessed June 20, 2018.
Treatment Options For Recurrent Bcc
A recurrent skin tumor is treated the same way as a high-risk primary tumor.3 Mohs surgery is the preferred option. Wide excision or radiation therapy are alternatives.
Your doctor may recommend adjuvant therapy with radiation therapy or targeted therapy. Adjuvant therapy is an additional cancer treatment that is given after the primary treatment. Adjuvant therapy can help lower the risk that the cancer comes back.
If the cancer recurs in the lymph nodes or distant organs, treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy. The targeted therapies approved for advanced BCC are:
Recommended Reading: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis