How To Spot An Scc
SCC of the skin can develop anywhere on the body but is most often found on exposed areas exposed to ultraviolet radiation like the face, lips, ears, scalp, shoulders, neck, back of the hands and forearms. SCCs can develop in scars, skin sores and other areas of skin injury. The skin around them typically shows signs of sun damage such as wrinkling, pigment changes and loss of elasticity.
SCCs can appear as thick, rough, scaly patches that may crust or bleed. They can also resemble warts, or open sores that dont completely heal. Sometimes SCCs show up as growths that are raised at the edges with a lower area in the center that may bleed or itch.
What Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like On Skin
Basal cell carcinoma has several different appearances. It can look like a: sore that doesnt heal after seven to 10 days. red patch that may itch, hurt, crust, or bleed easily. shiny bump that can be pink, red, or white if you have light skin. If you have darker skin, it can look tan, black, or brown.
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed
Diagnosis of cutaneous SCC is based on clinical features. The diagnosis and histological subtype are confirmed pathologically by diagnostic biopsy or following excision. See;squamous cell carcinoma pathology.
Patients with high-risk SCC may also undergo staging investigations to determine whether it has spread to lymph nodes or elsewhere. These may include:
- Imaging using ultrasound scan, X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans
- Lymph node or other tissue biopsies
Recommended Reading: What Can Happen If Skin Cancer Is Left Untreated
What Is Cutaneoussquamous Cell Carcinoma
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is a common type of keratinocytecancer, or non-melanomaskin cancer. It is derived from cells within the epidermis that make keratin the horny protein that makes up skin, hair and nails.
Cutaneous SCC is an invasive disease, referring to cancer cells that have grown beyond the epidermis. SCC can sometimes metastasise;and may prove fatal.
Intraepidermal carcinoma and mucosal SCC are considered elsewhere.
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
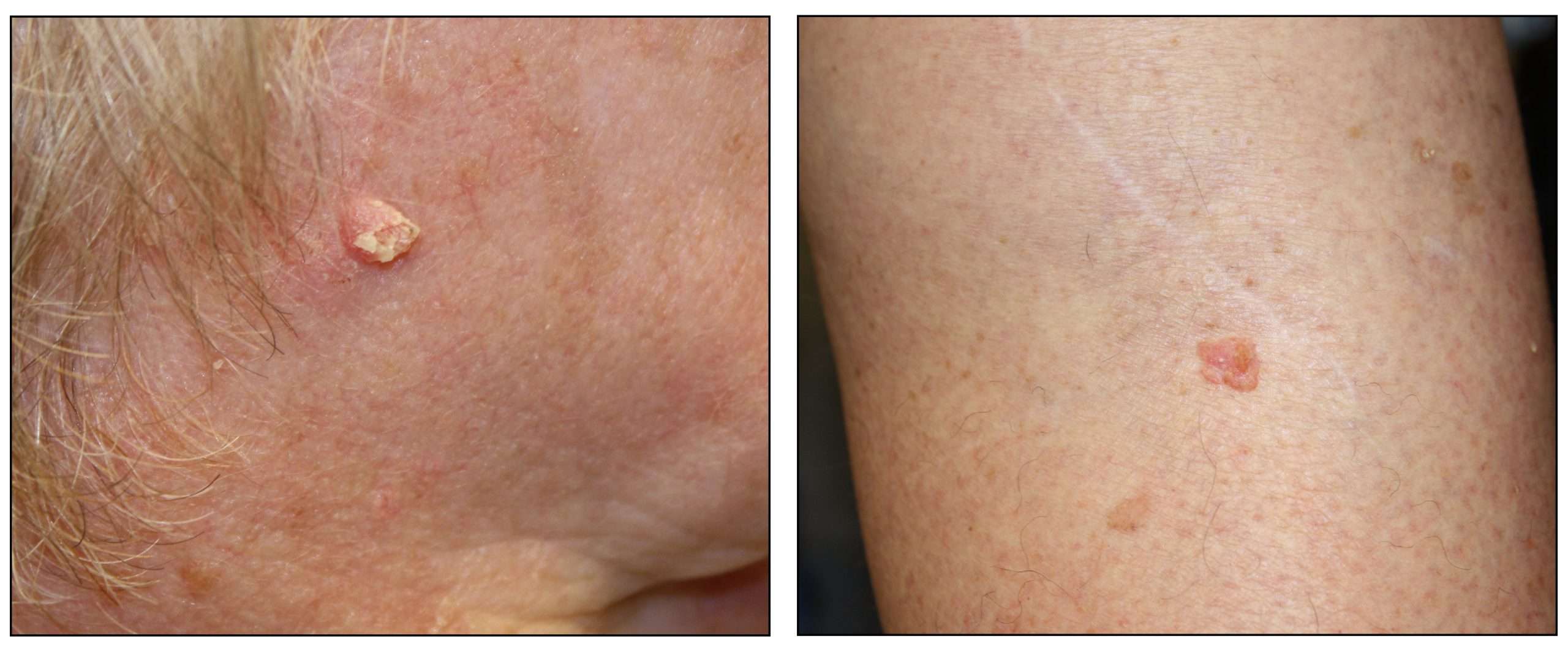
The first sign of an SCC is usually a thickened, red, scaly spot thatdoesnt heal. You are most likely to find an SCC on the back of your hands,forearms, legs, scalp, ears or lips. If its on your lips, it can look like asmall ulcer or patch of scaly skin that doesnt go away.
An SCC may also look like:
- a crusted sore
- a sore or rough patch inside your mouth
- a red, raised sore around your anus or genitals
An SCC will probably grow quickly over several weeks or months.
Also Check: What Is High Grade Papillary Urothelial Carcinoma
How Is Cancer On The Scalp Treated
Potential treatments for skin cancer on your scalp include:
- Surgery. Your doctor will remove the cancerous growth and some of the skin around it, to make sure that they removed all the cancer cells. This is usually the first treatment for melanoma. After surgery, you may also need reconstructive surgery, such as a skin graft.
- Mohs surgery. This type of surgery is used for large, recurring, or hard-to-treat skin cancer. Its used to save as much skin as possible. In Mohs surgery, your doctor will remove the growth layer by layer, examining each one under a microscope, until there are no cancer cells left.
- Radiation. This may be used as a first treatment or after surgery, to kill remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy. If your skin cancer is only on the top layer of skin, you might be able to use a chemotherapy lotion to treat it. If your cancer has spread, you might need traditional chemotherapy.
- Freezing. Used for cancer that doesnt go deep into your skin.
- . Youll take medications that will make cancer cells sensitive to light. Then your doctor will use lasers to kill the cells.
The outlook for skin cancer on your scalp depends on the specific type of skin cancer:
How To Spot A Bcc: Five Warning Signs
Check for BCCs where your skin is most exposed to the sun, especially the face, ears, neck, scalp, chest, shoulders and back, but remember that they can occur anywhere on the body. Frequently, two or more of these warning signs are visible in a BCC tumor.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these images serve as a general reference to what basal cell carcinoma looks like.
An open sore that does not heal
A reddish patch or irritated area
A small pink growth;with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
A shiny bump or nodule
A scar-like area;that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
Also Check: How To Get Tested For Melanoma
What Does Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Look Like
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
When Should You See A Dermatologist
If your skin exhibits any of the symptoms outlined above, its best not to wait it out and see what happens. As with all skin cancers, erring on the side of caution is the way to go. Your dermatologist will be able to identify whether a lesion is cancerous, precancerous, or benign.
Squamous cell carcinoma may move slowly, but it can spread and prove deadly. Reaching out to your New England dermatologist will give you the peace of mind that you need when your skin shows signs of cancer.
Also Check: Can Renal Cell Carcinoma Be Benign
What Is The Treatment For Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cutaneous SCC is nearly always treated surgically. Most cases are excised with a 310 mm margin of normal tissue around a visible tumour. A flap or skin graft may be needed to repair the defect.
Other methods of removal include:
- Shave, curettage, and electrocautery for low-risk tumours on trunk and limbs
- Aggressive cryotherapy for very small, thin, low-risk tumours
- Mohs micrographic surgery for large facial lesions with indistinct margins or recurrent tumours
- Radiotherapy for an inoperable tumour, patients unsuitable for surgery, or as adjuvant
What Kind Of Carcinoma Does A Dog Have
Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Dogs. Follow On: Squamous cell carcinoma in dogs may be referred to as malignant tumors, and is frequently diagnosed as carcinoma of the skin. Skin squamous cell carcinoma and subungual squamous cell carcinoma are the two forms that are known to occur in dogs.
Also Check: How Aggressive Is Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Types Of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Distinct clinical types of invasive cutaneous SCC include:
- Cutaneous horn the horn is due to excessive production of keratin
- Keratoacanthoma a rapidly growing keratinising nodule that may resolve without treatment
- Carcinoma cuniculatum , a slow-growing, warty tumour on the sole of the foot
- – a cutaneous SCC that has developed in a scar or chronic ulcer
- Multiple eruptive SCC/KA-like lesions arising in syndromes, such as multiple self-healing squamous epitheliomas of Ferguson-Smith and Grzybowski syndrome
The pathologist may classify a tumour as well differentiated, moderately well differentiated, poorly differentiated or anaplastic cutaneous SCC. There are other variants.
Subtypes of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
How Do People Find Bcc On Their Skin
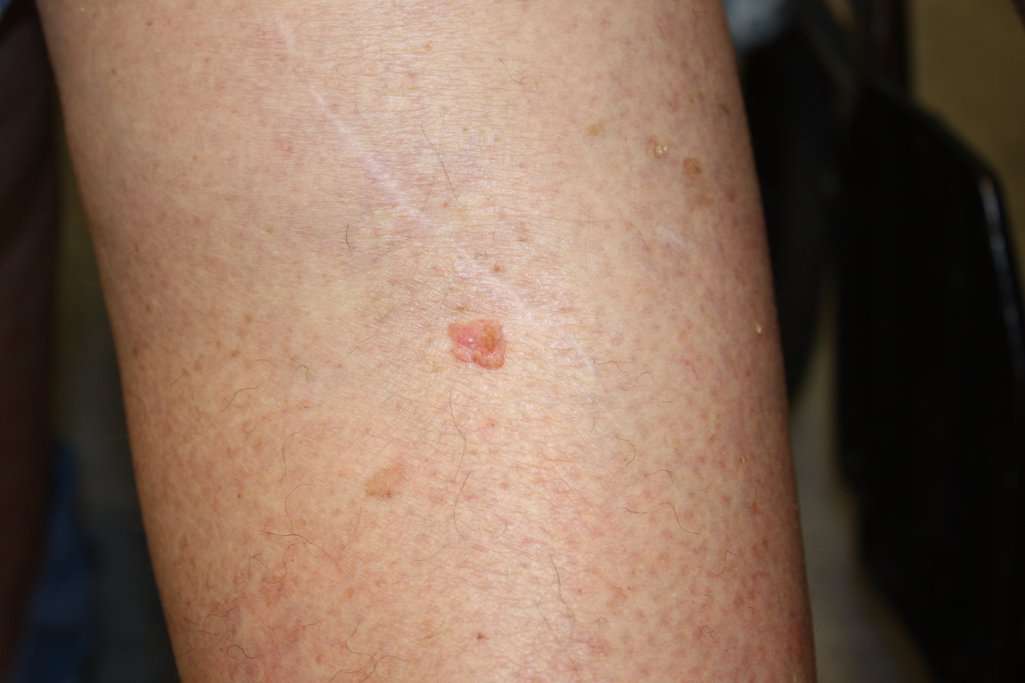
Many people find it when they notice a spot, lump, or scaly patch on their skin that is growing or feels different from the rest of their skin. If you notice any spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist. These doctors have the most training and experience in diagnosing skin cancer.
To find skin cancer early, dermatologists recommend that everyone check their own skin with a skin self-exam. This is especially important for people who have a higher risk of developing BCC. Youll find out what can increase your risk of getting this skin cancer at, Basal cell carcinoma: Who gets and causes.
Images used with permission of:
-
The American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
-
J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:303-17.
Dont Miss: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
Also Check: How Fast Does Renal Cell Carcinoma Grow
Scc Is Mainly Caused By Cumulative Uv Exposure Over The Course Of A Lifetime
If youve had a basal cell carcinoma you may be more likely to develop a squamous cell skin carcinoma, as is anyone with an inherited, highly UV-sensitive condition such as xeroderma pigmentosum.
Chronic infections, skin inflammation, HIV and other immune deficiency diseases, chemotherapy, anti-rejection drugs used in organ transplantation, and excessive sun exposure can all lead to a risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Occasionally, squamous cell carcinomas arise spontaneously on what appears to be normal, healthy skin. Some researchers believe the tendency to develop these cancers can be inherited.
SCCs may occur on all areas of the body including the mucous membranes and genitals, but are most common in areas frequently exposed to the sun:
- Ears
- Previous BCC or SCC
- Chronic inflammatory skin conditions or chronic infections
But anyone with a history of substantial sun exposure is at increased risk. Those whose occupations require long hours outside or who spend their leisure time in the sun are also at risk.
When Is A Mole A Problem
A mole is a benign growth of melanocytes, cells that gives skin its color. Although very few moles become cancer, abnormal or atypical moles can develop into melanoma over time. “Normal” moles can appear flat or raised or may begin flat and become raised over time. The surface is typically smooth. Moles that may have changed into skin cancer are often irregularly shaped, contain many colors, and are larger than the size of a pencil eraser. Most moles develop in youth or young adulthood. It’s unusual to acquire a mole in the adult years.
You May Like: What Type Of Skin Cancer Is Deadly
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated
It is usually possible to completely remove an SCC. The best type oftreatment for you will depend on the size of the SCC and where it is.
Usually, the doctor will remove an SCC using simple skin surgery. Theywill then look at the area under a microscope to check all the cancer has beenremoved. If it has spread, you might need radiotherapy afterwards.
Other ways of removing the SCC are:
- scraping it off then sealing the base of the wound with an electric needle or liquid nitrogen
- using a laser to burn the SCC away
- freezing it off
- Applying creams, liquids or lotions directly onto the SCC. Sometimes the doctor will shine a light on the area to make the medicine work
After treatment, you will need follow-up appointments with your doctor. You will be at greater risk of developing another skin cancer, so its more important than ever to protect your skin from the sun.
Tumour Staging For Cutaneous Scc
TX: Th Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0: No evidence of a primary tumour
Tis: Carcinoma in situ
T1: Tumour 2cm without high-risk features
T2: Tumour 2cm; or;;Tumour 2 cm with high-risk features
T3: Tumour with the invasion of maxilla, mandible, orbit or temporal bone
T4: Tumour with the invasion of axial or appendicular skeleton or perineural invasion of skull base
Also Check: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
What Are The Clinical Features Of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cutaneous SCCs present as enlarging scaly or crusted lumps. They usually arise within pre-existing actinic keratosis or intraepidermal carcinoma.
- They grow over weeks to months
- They may ulcerate
- They are often tender or painful
- Located on sun-exposed sites, particularly the face, lips, ears, hands, forearms and lower legs
- Size varies from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Cured
The majority of SCC tumors are found early and treated while they are still small. Treatment at an early stage can usually remove SCC.2
SCC is more likely than BCC to invade deeper layers of skin and spread to other parts of the body.2 This is uncommon. However, about 5% to 10% of SCC tumors are considered aggressive.2,4 It is more difficult to treat aggressive SCC. By one estimate, between 3,900 and 8,800 white individuals died from SCC in 2012.1 In the Midwest and southern United States, SCC may cause as many deaths as melanoma.1
Your dermatologist may recommend regular follow up for several years after treating any SCC. Most of the cases that return do so with 2 years of initial treatment.5
Read Also: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
What Is The Treatment For Advanced Or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Locally advanced primary, recurrent or metastatic SCC requires multidisciplinary consultation. Often a combination of treatments is used.
- Experimental targeted therapy using epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors
Many thousands of New Zealanders are treated for cutaneous SCC each year, and more than 100 die from their disease.
What Is The Outlook For Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
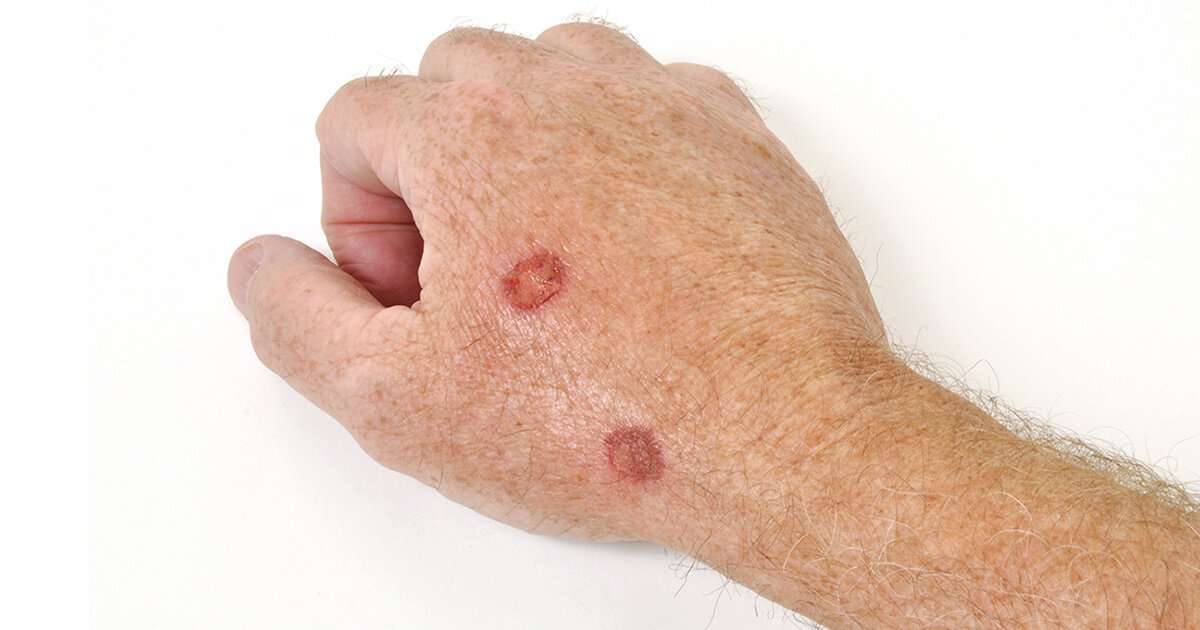
Most SCCs are cured by treatment. A cure is most likely if treatment is undertaken when the lesion is small. The risk of recurrence or disease-associated death is greater for tumours that are > 20 mm in diameter and/or > 2 mm in thickness at the time of surgical excision.
About 50% of people at high risk of SCC develop a second one within 5 years of the first. They are also at increased risk of other skin cancers, especially melanoma. Regular self-skin examinations and long-term annual skin checks by an experienced health professional are recommended.
Also Check: How Bad Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
How To Tell If A Lump Might Be Cancerous
They contain synovial fluid, which lubricates tendons and joints. If yours isnt causing discomfort, it can often be ignored and may disappear. Ganglia that limit movement or cause numbness, however, should be drained or removed. Theres no easy way to tell if a lump is cancerous from the outside, but there are some red flags, Dr. Shivadas says.
Squamous cell carcinomas may appear as flat reddish or brownish patches in the skin, often with a rough, scaly, or crusted surface. They tend to grow slowly and usually occur on sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and backs of the hands.
My Appointment With A Plastic Surgeon
Unfortunately, when they started showing up, I had a really terrible health insurance policy so I was unable to get them treated. Once I got better insurance and had built up some vacation time at work so I could be off for recovery, I made an appointment with my plastic surgeon.
As I was showing him the areas, he commented wryly that I must have been saving them up for him. In all, there were 22 areas he determined needed to be removed. He had a printout of a body map and marked each area for removal on the paper, which he would bring with him the day of surgery.
Also Check: How To Remove Skin Cancer On Face
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma occurs when a tumor makes its way into the dermis via thin strands between collagen fibers. This aggressive type of skin cancer is harder to diagnose and treat because of its location. Typically, infiltrative basal cell carcinoma appears as scar tissue or thickening of the skin and requires a biopsy to properly diagnose.
To remove this type of basal cell carcinoma, a specific form of surgery, called Mohs, is used. During a Mohs surgery, also called Mohs micrographic surgery, thin layers of skin are removed until there is no cancer tissue left.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Superficial basal cell carcinoma, also known as in situ basal-cell carcinoma, tends to occur on the shoulders or the upper part of the torso, but it can also be found on the legs and arms.;This type of cancer isnt generally invasive because it has a slow rate of growth and is fairly easy to spot and diagnose. It appears reddish or pinkish in color and may crust over or ooze. Superficial basal cell carcinoma accounts for roughly 15%-26% of all basal cell carcinoma cases.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ, also known as Bowens disease, is a precancerous condition that appears as a red or brownish patch or plaque on the skin that grows slowly over time. The patches are often found on the legs and lower parts of the body, as well as the head and neck. In rare cases, it has been found on the hands and feet, in the genital area, and in the area around the anus.
Bowens disease is uncommon: only 15 out of every 100,000 people will develop this condition every year. The condition typically affects the Caucasian population, but women are more likely to develop Bowens disease than men. The majority of cases are in adults over 60. As with other skin cancers, Bowens disease can develop after long-term exposure to the sun. It can also develop following radiotherapy treatment. Other causes include immune suppression, skin injury, inflammatory skin conditions, and a human papillomavirus infection.
Bowens disease is generally treatable and doesnt develop into squamous cell carcinoma. Up to 16% of cases develop into cancer.
You May Like: What Is The Worst Skin Cancer To Have