What Do Stage 4 Tumors Look Like
A change to an existing mole or normal skin can be the first sign that the cancer has spread. But the physical symptoms of stage 4 melanoma arent the same for everyone. A doctor will diagnose stage 4 melanoma by looking at the primary tumor, the spread to nearby lymph nodes, and whether the tumor has spread to different organs. While your doctor wont base their diagnosis only on what your tumor looks like, part of their diagnosis involves looking at the primary tumor.
The Warning Signs Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancers — including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma — often start as changes to your skin. They can be new growths or precancerous lesions — changes that are not cancer but could become cancer over time. An estimated 40% to 50% of fair-skinned people who live to be 65 will develop at least one skin cancer. Learn to spot the early warning signs. Skin cancer can be cured if it’s found and treated early.
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
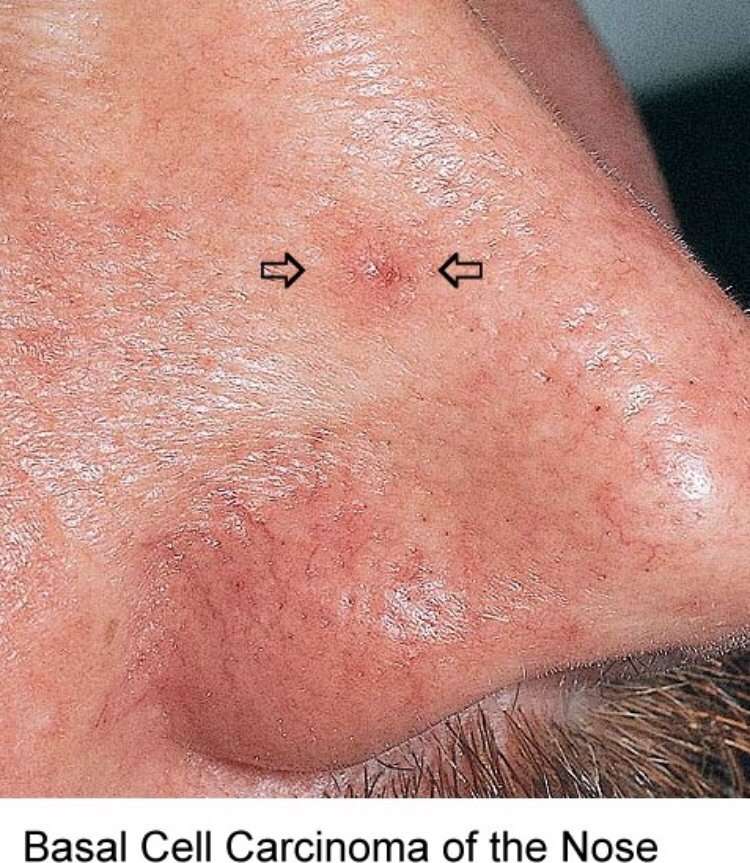
Basal cell carcinoma
-
BCC frequently develops in people who have fair skin. People who have skin of color also get this skin cancer.
-
BCCs often look like a flesh-colored round growth, pearl-like bump, or a pinkish patch of skin.
-
BCCs usually develop after years of frequent sun exposure or indoor tanning.
-
BCCs are common on the head, neck, and arms; however, they can form anywhere on the body, including the chest, abdomen, and legs.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment for BCC are important. BCC can grow deep. Allowed to grow, it can penetrate the nerves and bones, causing damage and disfigurement.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
-
People who have light skin are most likely to develop SCC. This skin cancer also develops in people who have darker skin.
-
SCC often looks like a red firm bump, scaly patch, or a sore that heals and then re-opens.
-
SCC tends to form on skin that gets frequent sun exposure, such as the rim of the ear, face, neck, arms, chest, and back.
-
SCC can grow deep into the skin, causing damage and disfigurement.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent SCC from growing deep and spreading to other areas of the body.
SCC can develop from a precancerous skin growth
-
People who get AKs usually have fair skin.
-
AKs usually form on the skin that gets lots of sun exposure, such as the head, neck, hands, and forearms.
-
Because an AK can turn into a type of skin cancer, treatment is important.
Melanoma
Read Also: What Is The Blue Light Treatment For Skin Cancer
Rarer Types Of Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, and Merkel cell cancer make up the vast majority of all skin cancer cases. However, there are several other rare types of skin cancer:
- Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma can affect the skin, blood, lymph nodes, and internal organs, and presents as a dry, itchy red rash
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans causes a tumor in the deep layers of the skin and starts out as a patch of firm skin that raises over time. The tumors have a high rate of recurring or returning once treated;
- Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer caused by an infection with human herpesvirus-8 . It causes abnormal tissue growth under the skin, and looks like red and purple lesions. Those with a compromised immune system, such as people who are HIV-positive, are more at risk
- Sebaceous carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually affects the skin on or around the eyelid. It presents as a small, round, painless tumor on the upper or lower eyelid
- Skin adnexal tumors are very rare tumors that grow in the sebaceous glands or hair follicles. They are often misdiagnosed as benign growth, and almost always require a pathologist to diagnose;
- Soft tissue sarcomas are cancerous growths that can develop in the deep layers of skin, as well as the bodys fat, muscle, nerves and blood vessels;
What You Need To Know
Merkel cell carcinoma is rare and dangerous but treatable, especially when found at an early stage. Be watchful for any new or changing lesions on your skin and look out for these warning signs.
If youve been treated for a previous MCC, pay close attention to the site and the surrounding region. Contact your medical team immediately if you see any suspicious changes.
How to spot a Merkel Cell Carcinoma
APPEARANCE;Painless shiny or pearly lesions or nodules
SIZE;Dimensions vary, but the average size at detection is 1.7 cm, about the diameter of a dime.
COLOR;Skin-colored, red, purple or bluish-red
LOCATION;Frequently on sun-exposed areas, often on the head and neck, particularly the eyelids.
While rare, Merkel cell carcinomas are often aggressive and can advance rapidly which is why early detection and removal are especially important. Memorial Sloan Kettering oncologist Sandra DAngelo, MD, shares some important warning signs you should never ignore.
Don’t Miss: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
There are 3 main types of skin cancer:
-
Basal cell carcinoma. The majority of skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma. Its a very treatable cancer. It starts in the basal cell layer of the skin and grows very slowly. The cancer usually appears as a small, shiny bump or nodule on the skin. It occurs mainly on areas exposed to the sun, such as the head, neck, arms, hands, and face. It more often occurs among people with light-colored eyes, hair, and skin.
-
Squamous cell carcinoma. This cancer is less common. It grows faster than basal cell carcinoma, but its also very treatable. Squamous cell carcinoma may appear as nodules or red, scaly patches of skin, and may be found on the face, ears, lips, and mouth. It can spread to other parts of the body, but this is rare. This type of skin cancer is most often found in people with light skin.
-
Melanoma. This type of skin cancer is a small portion of all skin cancers, but it causes the most deaths. It starts in the melanocyte cells that make pigment in the skin. It may begin as a mole that turns into cancer. This cancer may spread quickly. Melanoma most often appears on fair-skinned people, but is found in people of all skin types.
Four Main Types Of Skin Melanoma
There are four main types of skin melanoma.
Also Check: Is Skin Cancer Always Visible
What Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells in the skin. Left untreated, with certain types of skin cancer, these cells can spread to other organs and tissues, such as lymph nodes and bone. Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States, affecting 1 in 5 Americans during their lifetimes, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
Tests Or Procedures That Examine The Skin Are Used To Diagnose Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
The following procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and health history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patients health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- Skin exam: An exam of the skin for bumps or spots that look abnormal in color, size, shape, or texture.
- Skin biopsy: All or part of the abnormal-looking growth is cut from the skin and viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. There are four main types of skin biopsies:
- Shave biopsy: A sterile razor blade is used to shave-off the abnormal-looking growth.
- Punch biopsy: A special instrument called a punch or a trephine is used to remove a circle of tissue from the abnormal-looking growth. Enlarge Punch biopsy. A hollow, circular scalpel is used to cut into a lesion on the skin. The instrument is turned clockwise and counterclockwise to cut down about 4 millimeters to the layer of fatty tissue below the dermis. A small sample of tissue is removed to be checked under a microscope. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body.
- Incisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove part of a growth.
- Excisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove the entire growth.
Also Check: What Is The Most Effective Treatment For Melanoma
What Can I Do To Prevent Skin Cancer In My Child
The American Academy of Dermatology and the Skin Cancer Foundation advise you to:
-
Limit how much sun your child gets between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
-
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF 30 or higher that protects against both UVA and UVB rays. Put it on the skin of children older than 6 months of age who are exposed to the sun.
-
Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours, even on cloudy days. Reapply after swimming.
-
Use extra caution near water, snow, and sand. They reflect the damaging rays of the sun. This can increase the chance of sunburn.
-
Make sure your child wears clothing that covers the body and shades the face. Hats should provide shade for both the face, ears, and back of the neck. Wearing sunglasses will reduce the amount of rays reaching the eye and protect the lids of the eyes, as well as the lens.
-
Dont let your child use or be around sunlamps or tanning beds.
The American Academy of Pediatrics approves of the use of sunscreen on babies younger than 6 months old if adequate clothing and shade are not available. You should still try to keep your baby out of the sun. Dress the baby in lightweight clothing that covers most surface areas of skin. But you also may use a small amount of sunscreen on the babys face and back of the hands.
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers do not know why certain cells become cancerous. However, they have identified some risk factors for skin cancer.
The most important risk factor for melanoma is exposure to UV rays. These damage the skin cellsâ DNA, which controls how the cells grow, divide, and stay alive.
Most UV rays come from sunlight, but they also come from tanning beds.
Some other risk factors for skin cancer include:
- A lot of moles: A person with more than 100 moles is more likely to develop melanoma.
- Fair skin, light hair, and freckles: The risk of developing melanoma is higher among people with fair skin. Those who burn easily have an increased risk.
- Family history:Around 10% of people with the condition have a family history of it.
- Personal history: Melanoma is likelier to form in a person who has already had it. People who have had basal cell or squamous cell cancers also have an increased risk of developing melanoma.
The best way to reduce the risk of skin cancer is to limit oneâs exposure to UV rays. A person can do this by using sunscreen, seeking shade, and covering up when outdoors.
People should also avoid tanning beds and sunlamps to reduce their risk of skin cancer.
It can be easy to mistake benign growths for skin cancer.
The following skin conditions have similar symptoms to skin cancer:
Also Check: Is Melanoma The Same As Skin Cancer
Whats The Outlook For Stage 4 Melanoma
Once the cancer spreads, locating and treating the cancerous cells becomes more and more difficult. You and your doctor can develop a plan that balances your needs. The treatment should make you comfortable, but it should also seek to remove or slow cancer growth. The expected rate for deaths related to melanoma is 10,130 people per year. The outlook for stage 4 melanoma depends on how the cancer has spread. Its usually better if the cancer has only spread to distant parts of the skin and lymph nodes instead of other organs.
Tracking Changes To Your Skin With An App
Some people find it helpful to photograph areas of their skin such as the back or individual lesions to be able to better spot any future changes.
Over the past years, smartphone apps that can help consumers track moles and skin lesions for changes over time have become very popular and can be a very helpful tool for at-home skin checks.
This page does not replace a medical opinion and is for informational purposes only.
Please note, that some skin cancers may look different from these examples. See your doctor if you have any concerns about your skin.
It might also be a good idea to visit your doctor and have an open talk about your risk of skin cancer and seek for an advice on the early identification of skin changes.
* Prof. Bunker donates his fee for this review to the;British Skin Foundation;, a charity dedicated to fund research to help people with skin disease and skin cancer.
Make a difference. Share this article.
Recommended Reading: How To Detect Melanoma Early
How To Diagnose Skin Cancer
First, a doctor will examine a personâs skin and take their medical history. They will usually ask the person when the mark first appeared, if its appearance has changed, if it is ever painful or itchy, and if it bleeds.
The doctor will also ask about the personâs family history and any other risk factors, such as lifetime sun exposure.
They may also check the rest of the body for other atypical moles and spots. Finally, they may feel the lymph nodes to determine whether or not they are enlarged.
The doctor may then refer a person to a skin doctor, or dermatologist. They may examine the mark with a dermatoscope, which is a handheld magnifying device, and take a small sample of skin, or a biopsy, and send it to a laboratory to check for signs of cancer.
What Else Could This Skin Lesion Be
Other skin conditions may look like BCC. Nodular BCC without ulceration may look similar to:3
- Molluscum contagiosum, a viral infection that causes numerous small bumps.
- Sebaceous hyperplasia, a condition characterized by small yellow bumps.
- Intradermal melanocytic nevus, a nest of melanocytes in the dermis layer of skin.
- Fibrous papule, a firm bump that may develop on the nose.
- Other skin cancers
Ulcerated BCC may be confused with squamous cell carcinoma or keratoacantoma.
Conditions that look similar to superficial BCC include:3
Read Also: How Can You Detect Skin Cancer
Scc Is Mainly Caused By Cumulative Uv Exposure Over The Course Of A Lifetime
If youve had a basal cell carcinoma you may be more likely to develop a squamous cell skin carcinoma, as is anyone with an inherited, highly UV-sensitive condition such as xeroderma pigmentosum.
Chronic infections, skin inflammation, HIV and other immune deficiency diseases, chemotherapy, anti-rejection drugs used in organ transplantation, and excessive sun exposure can all lead to a risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Occasionally, squamous cell carcinomas arise spontaneously on what appears to be normal, healthy skin. Some researchers believe the tendency to develop these cancers can be inherited.
SCCs may occur on all areas of the body including the mucous membranes and genitals, but are most common in areas frequently exposed to the sun:
- Ears
- Previous BCC or SCC
- Chronic inflammatory skin conditions or chronic infections
But anyone with a history of substantial sun exposure is at increased risk. Those whose occupations require long hours outside or who spend their leisure time in the sun are also at risk.
How Do You Know If A Spot Is Skin Cancer
To learn more you can read this article on the signs of skin cancer or this article on melanoma symptoms, but dont forget to get any skin concern you may have checked out by your doctor.
You can also read our guide on how to check your skin regularly, if you want to learn more about how to form a skin checking routine for yourself.
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Spotting Other Types Of Skin Cancer
While “the big three” are the most common types of skin cancer, they’re not the only ones you should be aware of.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma
“After ‘the big three,’ the next skin cancer you think about is Merkel cell carcinoma,”Doris Day, a board-certified dermatologist in New York City and a spokesperson for the Skin Cancer Foundation, tells Allure. While it’s pretty uncommon about 40 times rarer than melanoma Day says it’s deadlier. Merkel cell carcinoma kills one in three patients , according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
This type of cancer is incredibly hard to spot, which explains why it’s so deadly. “Merkel cell can be tricky to diagnose because it doesn’t always present the same way; it can look like a cyst or just a little red bump, and it can occur anywhere on the body,” says Day. “This is one of the reasons why it’s super important to see a board-certified dermatologist for skin checks.”
Merkel cell carcinomas typically don’t occur in people under 50, but recent data suggests that could change. As we previously reported, rates of Merkel cell are estimated to be rising six times faster than other types of skin cancer something seriously concerning to dermatologists, given how aggressive this type of cancer can be. “If a Merkel cell is not treated, it’s certainly deadlier than a melanoma,” says McNeill.
Other Cancers
For these types of skin issues, a dermatologist would refer you to a specialist in treating that specific cancer.