Exams And Tests For Skin Cancer
If you think a mole or other skin lesion has turned into skin cancer, your primary care provider will probably refer you to a dermatologist. The dermatologist will examine any moles in question and, in many cases, the entire skin surface. Any lesions that are difficult to identify, or are thought to be skin cancer, may then be checked. Tests for skin cancer may include:
- The doctor may use a handheld device called a dermatoscope to scan the lesion. Another handheld device, MelaFind, scans the lesion then a computer program evaluates images of the lesion to indicate if it’s cancerous.
- A sample of skin will be taken so that the suspicious area of skin can be examined under a microscope.
- A biopsy is;done in the dermatologist’s office.
If a biopsy shows that you have malignant melanoma, you may undergo further testing to determine the extent of spread of the disease, if any. This may involve blood tests, a chest X-ray, and other tests as needed. This is only needed if the melanoma is of a certain size.
Continued
Surgery For Skin Cancer
Small skin cancer lesions may be removed through a variety of techniques, including simple excision , electrodesiccation and curettage , and cryosurgery .
Larger tumors, lesions in high-risk locations, recurrent tumors, and lesions in cosmetically sensitive areas are removed by a technique called Mohs micrographic surgery. For this technique, the surgeon carefully removes tissue, layer by layer, until cancer-free tissue is reached.
Malignant melanoma is treated more aggressively than just surgical removal. To ensure the complete removal of this dangerous malignancy, 1-2;cm of normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor is also removed. Depending on the thickness of the melanoma, neighboring lymph nodes may also be removed and tested for cancer. The sentinel lymph node biopsy method uses a mildly radioactive substance to identify which lymph nodes are most likely to be affected.
Continued
Pathogenesis And Risk Factors
BCC develop from a complex interaction between environmental factors and individual phenotype and genotype . The main risk factors for BCC include UV exposure, male sex, light skin type , advanced age , long-term immunosuppression, a positive family or individual history, as well as genodermatoses such as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum .
UV radiation is the most important external risk factor, with intermittent high exposure during childhood and adolescence as well as tanning beds the most dangerous features . It has also been shown that outdoor workers with high occupational UV exposure have a significantly higher risk of BCC than people with low or moderate occupational UV exposure . Based on these data, it has been proposed that BCC be classified as an occupational disease in Germany. Less frequent external risk factors include chronic exposure to arsenic, as well as ionizing radiation . Basal cell carcinomas may also develop in scars or chronic ulcers . The significance of immunosuppression can be deducted from the fact that BCC risk in organ transplant recipients is six times higher than in the normal population . A meta-analysis showed that about one-third of patients who had one BCC will develop another .
You May Like: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Can Basal Cell Carcinomas Be Cured
Yes, BCCs can be cured in almost every case, although treatment can be more complicated if the BCC has been neglected for a long time, or if it occurs in an awkward place, such as close to the eye or on the nose or ear.
BCCs rarely spread to other parts of the body. Therefore, although it is a type of skin cancer it is almost never a danger to life.
What You Can Do
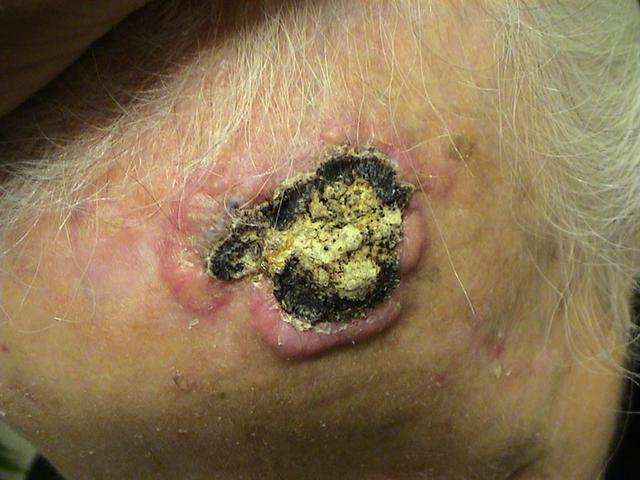
If youve already had a BCC, you have an increased chance of developing another, especially in the same sun-damaged area or nearby.
A BCC can recur even when it has been carefully removed the first time, because some cancer cells may remain undetectable after surgery and others can form roots that extend beyond whats visible. BCCs on the nose, ears and lips are more likely to recur, usually within the first two years after surgery.
Heres what you can do to detect a recurrence and safeguard yourself against further skin damage that can lead to cancer:
Reviewed by:
Read Also: How Do You Know If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has Spread
Dna Mismatch Repair Proteins
DNA mismatch repair proteins are a group of proteins that physiologically stimulate G2 cell cycle checkpoint arrest and apoptosis. Failure of MMR proteins to detect induced DNA damage results in the survival of mutating cells. MMR protein levels have been found to be higher in nonmelanoma skin cancers than in normal skin, and there is also some evidence of MMR dysregulation.
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Deadliest Type Of Skin Cancer
Skin_condition_infomation Mohs Micrographic Surgery
This surgical procedure is used to treat more complex BCCs such as those;present at difficult anatomical sites or recurrent BCCs. The procedure involves excision of the affected skin and examination of the skin removed under the microscope straight away to see if all of the BCC has been removed. If any residual BCC is left at the edge of the excision further skin is excised from that area and examined under the microscope and this process is continued until all of the BCC is removed. The site is then often closed with a skin graft. This is a time consuming process and is only undertaken when simple surgery may not be suitable.
Basal Cell Skin Cancer
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. About 75 out of every 100;non melanoma skin cancers are BCCs. They develop from basal cells and these are found in the deepest part of the outer layer of the skin .
They develop mostly in areas of skin exposed to the sun, including parts of the face such as the nose, forehead and cheeks. Also, on your back or lower legs.
They are;most often diagnosed in people who are middle aged or older.
Doctors might also call;a basal cell cancer;a rodent ulcer.
There are;a number of different types of BCC.;Each type can look and behave differently. They;include:
- nodular basal cell skin cancer
- superficial basal cell skin cancer
- morphoeic basal cell skin cancer – also known as sclerosing or infiltrating basal cell skin cancer
- pigmented basal cell skin cancer
Nodular basal cell cancer is the most common subtype.
It’s very rare for basal cell skin cancer to spread to another part of the body to form a;secondary cancer. It’s possible to have more than one basal cell cancer at any one time and having had one does increase your risk of getting another.
You May Like: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
Taking Care Of Yourself
After you’ve been treated for basal cell carcinoma, you’ll need to take some steps to lower your chance of getting cancer again.
Check your skin. Keep an eye out for new growths. Some signs of cancer include areas of skin that are growing, changing, or bleeding. Check your skin regularly with a hand-held mirror and a full-length mirror so that you can get a good view of all parts of your body.
Avoid too much sun. Stay out of sunlight between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m., when the sun’s UVB burning rays are strongest.
Use sunscreen. The suns UVA rays are present all day long — thats why you need daily sunscreen. Make sure you apply sunscreen with at least a;6% zinc oxide and a sun;protection factor of 30 to all parts of the skin that aren’t covered up with clothes every day. You also need to reapply it every 60 to 80 minutes when outside.
Dress right. Wear a broad-brimmed hat and cover up as much as possible, such as long-sleeved shirts and long pants.
Continued
Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment
There are several ways to treat, remove, and destroy basal cell skin cancers. The best option for each patient depends on factors such as tumor size and location, age, general health, and preferences.
Treatment options include one or a combination of these methods:
- Surgery
- Cryotherapy
- Medication to shrink or slow tumor growth
Surgery is the most common treatment, and micrographic surgery is considered to be the gold standard. In that category, Mohs surgery, which allows surgeons to closely examine the margins the area surrounding the tumor to make sure no cancer cells have encroached in those areas has the highest cure rate of all therapies and is especially effective for high-risk basal cell carcinomas.
With Mohs micrographic surgery, the dermatologist is both the surgeon and the pathologist, says Rossi, explaining Mohs surgery. Youre actually examining all the margins and looking at it in real time, whereas in a traditional excision, the surgeon removes the tissue and sends it to a pathologist and they examine only a portion of the margin.
Mohs surgery is often used for large tumors, tumors where the edges are not well-defined, tumors in sensitive locations such as on the head or face, hands, or genital area, and for tumors that have come back after other treatments.
Read Also: Can Melanoma Be Treated Successfully
Medical Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of skin cancer treatment for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more information, see Surgery.People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the use of a small beam of radiation targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy can cause irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It can also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, topical chemotherapy creams have been FDA approved for the treatment of certain low-risk nonmelanoma skin cancers. Patients with advanced or many basal cell carcinomas are sometimes prescribed oral pills to block the growth of these cancers. Side effects include muscle spasms, hair loss, taste changes, weight loss and fatigue.
In advanced cases of melanoma, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work better than existing therapies.
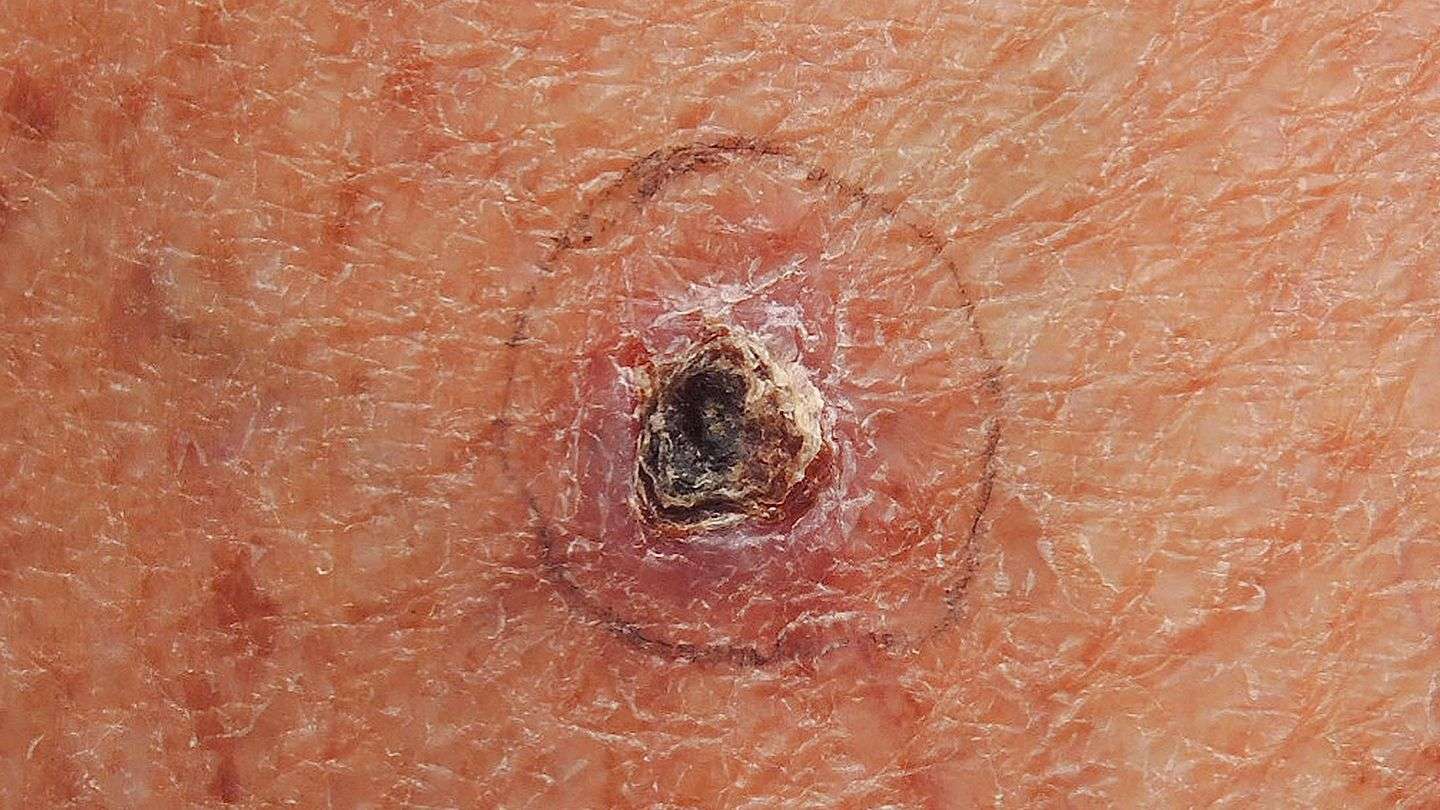
Skin Cancer Types: Basal Cell Carcinoma Overview
All content solely developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology gratefully acknowledges the support from Sanofi Genzyme and Regeneron.
Basal cell carcinoma
What is basal cell carcinoma?The most common type of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma can show up on the skin in many ways.
Is it contagious? No;
Recommended Reading: What Is The Main Cause Of Skin Cancer
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if skin cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually skin cancer cells. The disease is metastatic skin cancer, not lung cancer.
Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
Mohs micrographically controlled surgery involves examining carefully marked excised tissue under the microscope, layer by layer, to ensure complete excision.
- Very high cure rates achieved by trained Mohs surgeons
- Used in high-risk areas of the face around eyes, lips and nose
- Suitable for ill-defined, morphoeic, infiltrative and recurrent subtypes
- Large defects are repaired by flap or skin graft
You May Like: What Is Melanoma In The Brain
Surgical Lymph Node Biopsy
If an FNA doesn’t find cancer in a lymph node but the doctor still suspects the cancer has spread there, the lymph node may be removed by surgery and examined. If the lymph node is just under the skin, this can often be done in a doctors office or outpatient surgical center using local anesthesia. This will leave a small scar.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage squamous cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is assigned to one of the five squamous cell carcinoma stages, which are labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of squamous cell cancer are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage;1 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high risk features.
Stage 3;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Read Also: Can Skin Cancer Be Cured With Cream
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Because basal cell carcinoma seems to be related to ultraviolet exposure, a number of measures are recommended to limit exposure.
-
Sun avoidance: Seeking shade, minimizing outdoor activities between 10 AM and 4 PM , and avoiding sunbathing and the use of tanning beds
-
Use of protective clothing: Long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats
-
Use of sunscreen: At least sun protection factor 30 with broad-spectrum UVA/UVB protection, used as directed ; should not be used to prolong sun exposure
Prognosis For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas rarely metastasize but may invade healthy tissues. Rarely, patients die because the carcinoma invades or impinges on underlying vital structures or orifices .
Almost 25% of patients with a history of basal cell carcinoma develop a new basal cell cancer within 5 years of the original carcinoma. Consequently, patients with a history of basal cell carcinoma should be seen annually for a skin examination.
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Malignant
Is basal cell carcinoma malignant?
Is basal cell carcinoma considered cancer?;Basal cell carcinoma is most common type of skin cancer. About 8 out of 10 skin cancers are basal cell carcinomas . These cancers start in the basal cell layer, which is the lower part of the epidermis.
What is basal cell carcinoma the most common malignant tumor of?;Basal cell carcinomas are the most common type of skin cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. These cancers develop within the basal cell layer of the skin, in the lowest part of the epidermis. Patients who have had basal cell carcinoma once have an increased risk of developing a recurrent basal cell cancer.
Is basal cell carcinoma an aggressive cancer?;Occasionally, however, BCC behaves aggressively with deep invasion, recurrence, and potential regional and distant metastasis. Several factors, including tumor size, duration, histology, and perineural spread, have been postulated as markers of the aggressive BCC phenotype.
How Serious Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
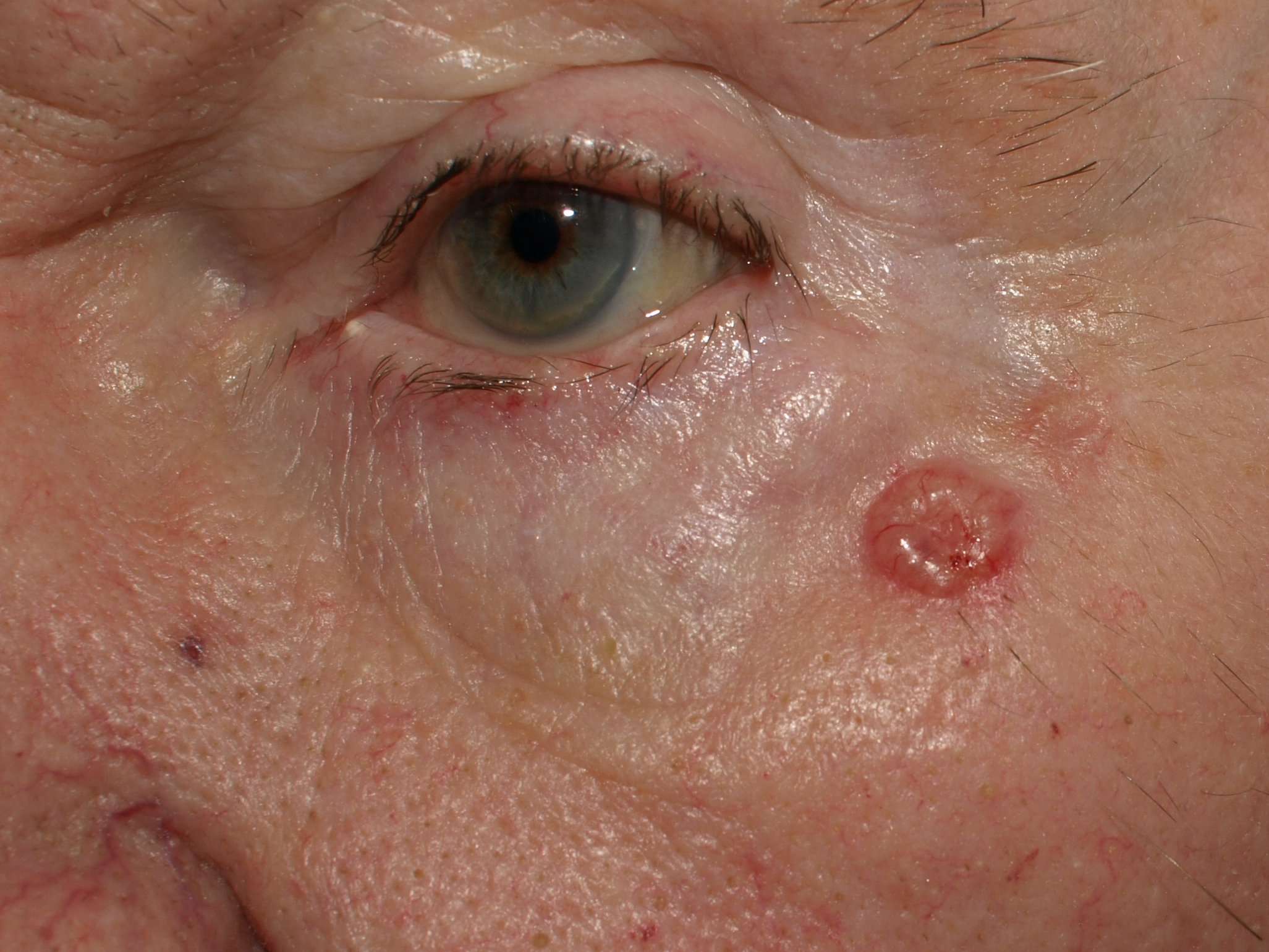
Basal cell skin cancer, also called basal cell carcinoma, is usually very curable, but it can cause disfigurement and complications if it’s not treated. In the majority of cases, basal cell carcinoma is very treatable.
It is unusual for basal cell carcinoma to cause death. Approximately 2,000 people in the U.S. die each year from basal and squamous skin cancers. In most cases, people who die from these types of skin cancer tend to be older, immunosuppressed, or have been diagnosed at a very late stage.;
Read Also: What Is The Leading Cause Of Skin Cancer