It May Not Be Your First Run
Many people with stage 4 melanoma have a history of primary melanoma, says Philip Friedlander, M.D., a medical oncologist specializing in melanoma at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City. Earlier-stage melanoma that was considered high risk may return at some point as stage 4, he says. In fact, 13.4% of those with a high-risk melanoma had a recurrence, research in JAMA Dermatology showed. Seventy percent of those recurred in a local area, while 29% had a recurrence somewhere else on their body.
Clinical Staging And Pathologic Staging
To add to the complexity of staging, the cancer also may have a clinical stage and a pathologic stage.
Clinical staging takes place before surgery, based on blood tests, physical exams or imaging tests such as X-rays, a computed tomography scan, magnetic resonance imaging ;or positron emission tomography scans.
What doctors discover during surgery may provide more detailed information about the cancers size and spread. Often, some tissue from the surgery will be examined afterward to provide more clues. This process is known as pathologic staging, or surgical staging.
If surgery isnt possible, doctors will use the clinical stage when determining a treatment plan.
The Following Stages Are Used For Melanoma:
Stage 0
Stage I
- Stage IA: The tumor is not more than 1millimeter thick, with or without ulceration.
- Stage IB: The tumor is more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Enlarge Stage I melanoma. In stage IA, the tumor is not more than 1 millimeter thick, with or without ulceration . In stage IB, the tumor is more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body.
Stage II
- Stage IIA: The tumor is either:
- more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, with ulceration; or
- more than 2 but not more than 4 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Enlarge Stage IIA melanoma. The tumor is more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, with ulceration ; OR it is more than 2 but not more than 4 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body.
Stage III
Stage III is divided into stages IIIA, IIIB, IIIC, and IIID.
You May Like: How Do You Know If You Have Basal Cell Carcinoma
Five Types Of Standard Treatment Are Used:
Surgery
Surgery to remove thetumor is the primary treatment of all stages of melanoma. A wide local excision is used to remove the melanoma and some of the normal tissue around it. Skin grafting may be done to cover the wound caused by surgery.
Sometimes, it is important to know whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. Lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy are done to check for cancer in the sentinel lymph node . It is the first lymph node the cancer is likely to spread to from the primary tumor. A radioactive substance and/or blue dye is injected near the tumor. The substance or dye flows through the lymphducts to the lymph nodes. The first lymph node to receive the substance or dye is removed. A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells. If cancer cells are found, more lymph nodes will be removed and tissue samples will be checked for signs of cancer. This is called a lymphadenectomy. Sometimes, a sentinel lymph node is found in more than one group of nodes.
After the doctor removes all the melanoma that can be seen at the time of the surgery, some patients may be given chemotherapy after surgery to kill any cancer cells that are left. Chemotherapy given after the surgery, to lower the risk that the cancer will come back, is called therapy.
Surgery to remove cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes, lung, gastrointestinal tract, bone, or brain may be done to improve the patients quality of life by controlling symptoms.
What Are The Melanoma Stages And What Do They Mean
Early melanomas
Stage 0 and I are localized, meaning they have not spread.
- Stage 0: Melanoma is localized in the outermost layer of skin and has not advanced deeper. This noninvasive stage is also called melanoma in situ.
- Stage I: The cancer is smaller than 1 mm in Breslow depth, and may or may not be ulcerated. It is localized but invasive, meaning that it has penetrated beneath the top layer into the next layer of skin. Invasive tumors considered stage IA are classified as early and thin if they are not ulcerated and measure less than 0.8 mm.
Find out about treatment options for early melanomas.
Intermediate or high-risk melanomas
Localized but larger tumors may have other traits such as ulceration that put them at high risk of spreading.
- Stage II: Intermediate, high-risk melanomas are tumors deeper than 1 mm that may or may not be ulcerated. Although they are not yet known to have advanced beyond the primary tumor, the risk of spreading is high, and physicians may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to verify whether melanoma cells have spread to the local lymph nodes. Thicker melanomas, greater than 4.0 mm, have a very high risk of spreading, and any ulceration can move the disease into a higher subcategory of stage II. Because of that risk, the doctor may recommend more aggressive treatment.
Learn more about;sentinel lymph node biopsy;and melanoma treatment options.
Advanced melanomas
Recommended Reading: What Does Skin Cancer On Your Lip Look Like
Drugs Can Target Your Type Of Tumor
If your melanoma tumor has one of the gene mutations we mentioned, your oncologist may start with a drug that targets specific proteins in the mutation. Depending on which mutation your melanoma tested positive for, your oral drug options include: BRAF inhibitors including Zelboraf , Tafinlar , and Braftovi ; MEK inhibitors such as Mekinist , Cotellic , and Mektovi ; and C-KIT inhibitors, which include Gleevac and Tasigna . Because BRAF and MEK mutations are closely associated, research has shown that combining the two types of drugs may yield better results.
What Is A Level
Melanoma levels is the depth of melanoma cell invasion in the skin. This is determined by histopathology study of the biopsy sample under the microscope by specialist pathologists. Obviously, the deeper through the skin a melanoma has invaded, the greater potential it has, of spreading. There are 5 levels of melanoma, reflecting how deep the melanoma has progressed through the anatomical layers of skin. This is always reported with Breslow thickness, which measures the physical depth of melanoma invasion in millimeters. The reason both the Level and Breslow Thickness are taken into account when considering the seriousness of the melanoma, is because in certain part of the body, the skin layers are thicker, e.g. the back. Thus even though the report may say that the melanoma is only Level II, but the thickness is 1.2mm. Some studies have shown that it is the Breslow Thickness that seem to have a better correspondence to the likelihood of spread, than the Level itself.;
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Age Spots And Skin Cancer
Clark S Level 4 Malignant Melanoma
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
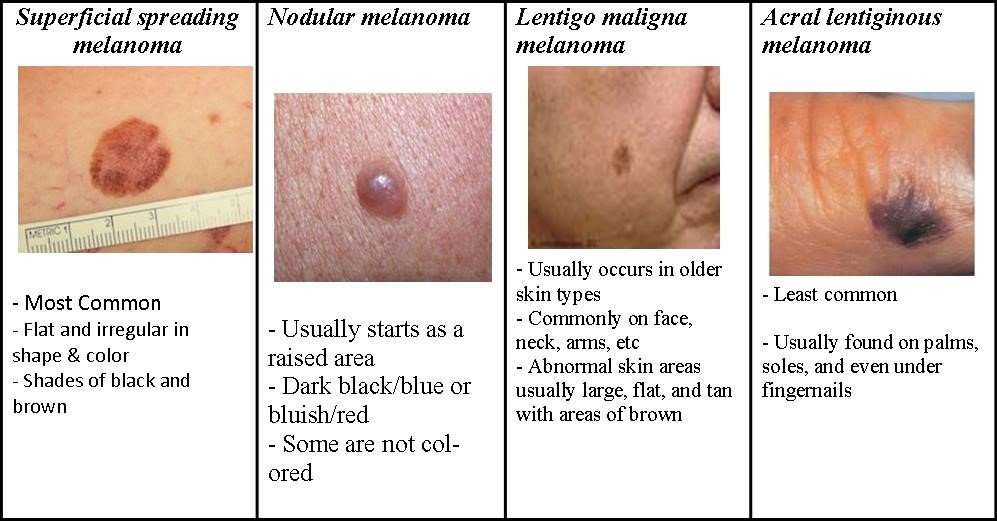
Signs Of Melanoma Include A Change In The Way A Mole Or Pigmented Area Looks
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by melanoma or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- A mole that:
- changes in size, shape, or color.
- has irregular edges or borders.
- is more than one color.
- is asymmetrical .
- itches.
- oozes, bleeds, or is ulcerated .
For pictures and descriptions of common moles and melanoma, see Common Moles, Dysplastic Nevi, and Risk of Melanoma.
Recommended Reading: Is Melanoma Skin Cancer Curable
Youll Have A Team On Your Side
Once your physician finds out where your stage 4 melanoma has spread, youll be referred to more doctors for treatment. If your tumors are operable, youll be referred to a surgical oncologist, who will perform the surgery. Youll also have a medical oncologist, who will determine your ideal type of treatment, or combination of treatments. Treatments for stage 4 melanoma include immunotherapy, targeted drugs, chemotherapy, and radiation.
Recognizing The Signs And Symptoms
The most noticeable sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole or birthmark. People should be aware of any pigmented areas on the skin that appear abnormal in color, shape, size, or texture.
People with stage 4 melanoma may also have ulcerated skin, which is skin with tiny breaks on the surface. These ulcerations can bleed.
Another sign is swollen or hard lymph nodes, which a doctor can confirm by carrying out a physical examination. Other tests include blood tests and imaging scans to confirm the presence of cancer and check how much it has spread.
Read Also: What Is Soft Tissue Carcinoma
How Fast Does Melanoma Spread
Melanoma is a deadly form of skin cancer because of its ability to metastasize to local lymph nodes and other organs.; It is estimated that melanoma kills, on average, over 10,000 people in the United States every year.
The first sign of flat melanoma is usually a new spot or an existing mole or freckle that changes in appearance. Some changes can include:
- A spot that has grown in size
- A spot where the edges are looking irregular versus smooth and even
- A spot that has a range of colors such as brown, black, blue, red, white or light gray.
- A spot that has become itchy or is bleeding
According to Dr. Andrew Duncanson, board-certified dermatologist at Forefront Dermatology, It is important to know that melanoma can appear on areas of the skin not normally exposed to the sun such as under the arm, chest, and buttocks. It can also appear in areas that you are not able to see easily on your own including the ears, scalp, back of legs, and bottom of feet. I always recommend to my patients to look for the ugly duckling spot the new spot that doesnt look like any others. Additionally, ask a family member to look over the hard to see areas monthly, while also getting an annual skin cancer exam by a board-certified dermatologist to detect skin cancer early.
Unusual Moles Exposure To Sunlight And Health History Can Affect The Risk Of Melanoma

Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for melanoma include the following:
- Having a fair complexion, which includes the following:
- Fair skin that freckles and burns easily, does not tan, or tans poorly.
- Blue or green or other light-colored eyes.
- Red or blond hair.
Being White or having a fair complexion increases the risk of melanoma, but anyone can have melanoma, including people with dark skin.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information on risk factors for melanoma:
Read Also: What Type Of Skin Cancer Is Deadly
Treatment Of Stage Iii Melanoma That Can Be Removed By Surgery
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage III melanoma that can be removed by surgery may include the following:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and some of the normal tissue around it. Skin grafting may be done to cover the wound caused by surgery. Sometimes lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy are done to check for cancer in the lymph nodes at the same time as the surgery to remove the tumor. If cancer is found in the sentinel lymph node, more lymph nodes may be removed.
- Surgery followed by immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors if there is a high risk that the cancer will come back.
- Surgery followed by targeted therapy with signal transduction inhibitors if there is a high risk that the cancer will come back.
- A clinical trial of immunotherapy with or without vaccine therapy.
- A clinical trial of surgery followed by therapies that target specific gene changes.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for melanoma skin cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread beyond the skin where it started.
- Regional: The cancer has spread beyond the skin where it started to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the lungs, liver, or skin on other parts of the body.
Recommended Reading: What Is Stage 4 Melanoma Cancer
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Melanoma Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at: . Accessed <MM/DD/YYYY>.
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
What Is The Stage
Melanoma staging is whether the melanoma has advanced beyond the skin. This is often determined by either physical examination of nearby lymph node groups or imaging studies such as CT scans, Ultrasounds, PET/CT or MRI. Stage I and II Melanoma are confined to the skin, with different depth. Stage III Melanoma means it has progressed beyond the original tumour as satellite lesions in the surrounding skin or travelled to a lymph node basin nearby. Stage IV Melanoma means the Melanoma has travelled to a distant site, usually an organ such as the lung, bones, liver or brain.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Feel When You Have Skin Cancer
Treatment Of Stage Ii Melanoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage II melanoma may include the following:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and some of the normal tissue around it. Sometimes lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy are done to check for cancer in the lymph nodes at the same time as the surgery to remove the tumor. If cancer is found in the sentinel lymph node, more lymph nodes may be removed.
- A clinical trial of new types of treatment to be used after surgery.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.