Clinical Staging And Pathologic Staging
To add to the complexity of staging, the cancer also may have a clinical stage and a pathologic stage.
Clinical staging takes place before surgery, based on blood tests, physical exams or imaging tests such as X-rays, a computed tomography scan, magnetic resonance imaging or positron emission tomography scans.
What doctors discover during surgery may provide more detailed information about the cancers size and spread. Often, some tissue from the surgery will be examined afterward to provide more clues. This process is known as pathologic staging, or surgical staging.
If surgery isnt possible, doctors will use the clinical stage when determining a treatment plan.
Survival Rates For Melanoma Skin Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
Donât Miss: Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Fatal
Diagnosis And Staging What It Means For You
How is melanoma diagnosed?
To diagnose melanoma, a dermatologist biopsies the suspicious tissue and sends it to a lab, where a dermatopathologist determines whether cancer cells are present.
After the disease is diagnosed and the type of melanoma is identified, the next step is for your medical team to identify the stage of the disease. This may require additional tests including imaging such as PET scans, CT scans, MRIs and blood tests.
The stage of melanoma is determined by several factors, including how much the cancer has grown, whether the disease has spread and other considerations. Melanoma staging is complex, but crucial. Knowing the stage helps doctors decide how to best treat your disease and predict your chances of recovery.
Don’t Miss: Well-differentiated
Melanoma Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In Melanocytes
The skin is the bodys largest organ. It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D. The skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells:
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun or artificial light, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
The number of new cases of melanoma has been increasing over the last 30 years. Melanoma is most common in adults, but it is sometimes found in children and adolescents.
Imaging Techniques And Laboratory Investigations In Staging Work
Since the prognosis for patients with melanoma is determined by histology of the primary tumour and by the presence and extent of metastatic disease, imaging studies using radiographic and nuclear medicine techniques are an important component of the evaluation of patients with both localised and advanced melanoma . However, the staging evaluations used at the time of initial diagnosis are often excessive. Few established guidelines for melanoma define the appropriate tests for the initial evaluation and subsequent follow-up.
Read Also: What Does Cancer Look Like Outside The Body
Treatment Of Stage I Melanoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage I melanoma may include the following:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and some of the normaltissue around it. Sometimes lymph node mapping and removal of lymph nodes is also done.
- A clinical trial of new ways to find cancercells in the lymph nodes.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Melanoma In The Area Between The Primary Melanoma And The Nearby Lymph Nodes
You usually have surgery to remove satellite or in-transit metastases. If youre not able to have surgery you might have one of the following:
- laser surgery using a carbon dioxide laser
- injecting treatment directly into the melanoma , for example talimogene laherparepvec
- chemotherapy combined with an electric current
- chemotherapy directly into the leg or arm where the melanoma is
- targeted cancer drugs
Also Check: What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Where Else Does Melanoma Spread To
When melanoma advances to stage 3, it means the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes or the skin around the primary tumor and lymph nodes. In stage 4, the cancer has moved to other areas far beyond the lymph nodes, like your internal organs. The most common places melanoma spreads to are the:
- lungs
- brain
- stomach, or abdomen
These growths will cause different symptoms, depending on which areas it has spread to. For example, you may feel breathless or constantly cough if the cancer has spread to your lungs. Or you may have a long-term headache that wont go away if it has spread to your brain. Sometimes the symptoms for stage 4 melanoma may not appear for many years after the original tumor was removed.
Talk to your doctor if youre feeling new pains and aches or symptoms. Theyll be able to help diagnose the cause and recommend treatment options.
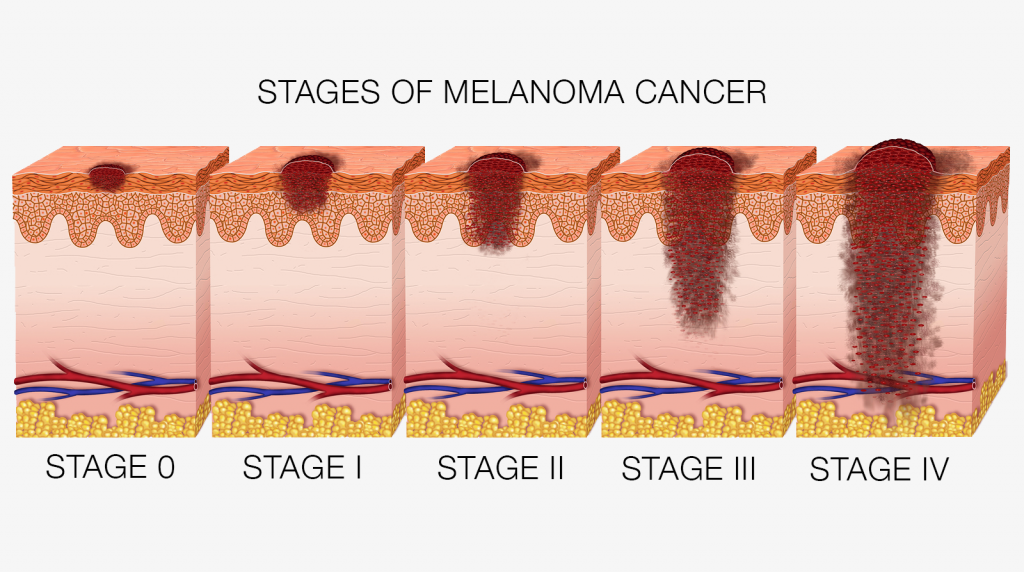
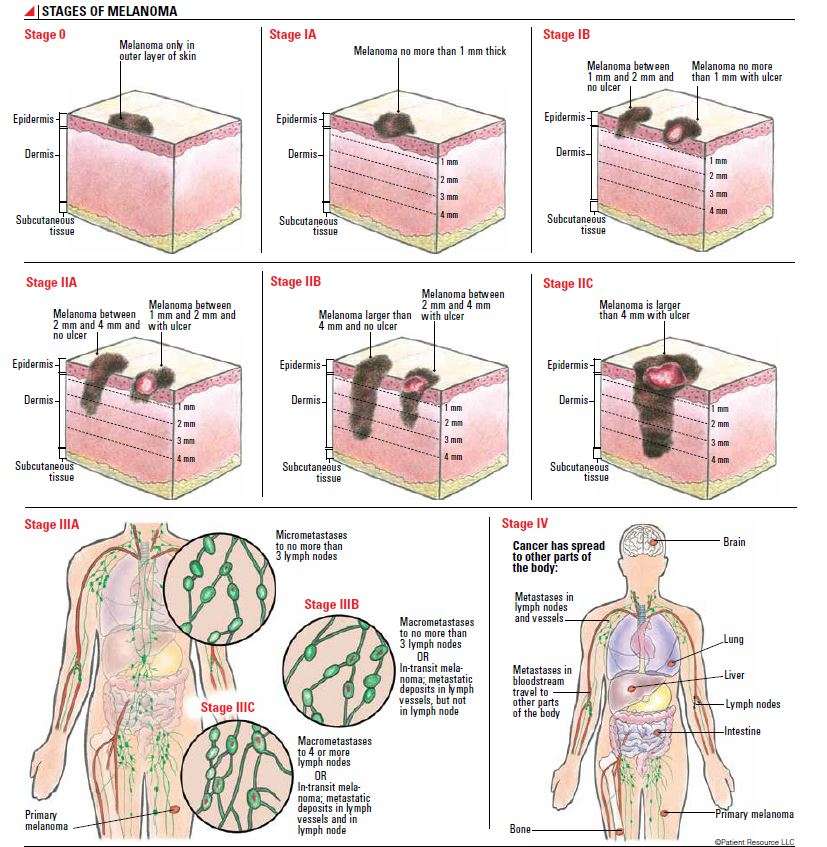
The Stage Of Melanoma Depends On The Thickness Of The Tumor Whether Cancer Has Spread To Lymph Nodes Or Other Parts Of The Body And Other Factors
To find out the stage of melanoma, the tumor is completely removed and nearby lymph nodes are checked for signs of cancer. The stage of the cancer is used to determine which treatment is best. Check with your doctor to find out which stage of cancer you have.
The stage of melanoma depends on the following:
- The thickness of the tumor. The thickness of the tumor is measured from the surface of the skin to the deepest part of the tumor.
- Whether there are:
- Satellite tumors: Small groups of tumor cells that have spread within 2 centimeters of the primary tumor.
- Microsatellite tumors: Small groups of tumor cells that have spread to an area right beside or below the primary tumor.
- In-transit metastases: Tumors that have spread to lymph vessels in the skin more than 2 centimeters away from the primary tumor, but not to the lymph nodes.
You May Like: Stage 3 Cancer Symptoms
Signs Of Melanoma Include A Change In The Way A Mole Or Pigmented Area Looks
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by melanoma or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- A mole that:
- changes in size, shape, or color.
- has irregular edges or borders.
- is more than one color.
- is asymmetrical .
- itches.
- oozes, bleeds, or is ulcerated .
For pictures and descriptions of common moles and melanoma, see Common Moles, Dysplastic Nevi, and Risk of Melanoma.
Relative Survival By Stage At Diagnosis
Introduction:
This measure comprises national data on relative survival by stage at diagnosis for melanoma of the skin .
Stage at diagnosis indicates the extent to which a cancer has spread at diagnosis. It is an important prognostic factor for cancer outcomes. It also provides contextual information for interpreting cancer outcomes, including survival, at a population level.1
Relative survival refers to the probability of being alive for a given amount of time after diagnosis, compared with survival of the general population. Observed survival refers to the overall proportion of people who are alive following a specified amount of time after diagnosis of cancer. In this report, survival refers to relative survival unless otherwise stated. Examining survival by stage at diagnosis provides insights into how survival outcomes differ depending on extent of cancer spread at diagnosis.
To provide a better understanding of cancer stage at diagnosis at the population-level, Business Rules were developed to collect national data on Registry-derived stage at diagnosis using data sources that are routinely accessible to all population-based cancer registries. RD-stage is defined for invasive tumours only. More information on the capture and distribution of RD-stage at diagnosis can be accessed through the following measures:
Read Also: What Does Different Types Of Skin Cancer Look Like
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
Central Nervous System Changes
Patients dying of stage IV melanoma may exhibit changes in their mentation.Their activity decreases and they may sleep quite a bit. The Hospice Foundation notes that patients may not respond to conversation or questions 2. Patients with brain metastasis from the melanoma may lapse into a coma, a deep state of unconsciousness from which they cannot be aroused. Hospice states that even though patients are in a coma they may still hear what is said and feel pain. One of the last senses to go before death is hearing. As patients near death, they may experience sensory changes and hallucinate or hear things that are not there.
- Patients dying of stage IV melanoma may exhibit changes in their mentation.
- As patients near death, they may experience sensory changes and hallucinate or hear things that are not there.
Recommended Reading: Chances Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreading
Is Stage 4 Melanoma A Death Sentence
Stage 4 melanoma used to be a death sentence. The disease doesnt respond to radiation or chemotherapy, and patients survived, on average, less than a year. But over the last decade, doctors are successfully using a new approach, one significantly different than the treatment options available for the last 150 years.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Treatments For Stage Ii Melanoma
As with stage I, stage II melanoma is typically treated with wide excision surgery, which cuts out the melanoma along with a margin of healthy surrounding skin. In the case of stage II melanoma, many doctors will recommend looking for cancer in nearby lymph nodes by performing a sentinel lymph node biopsy, which may necessitate further treatment if cancer cells are found.
What Are The Components Of Staging
The TNM system is the staging criterium usually implemented. It refers to three separate things that are considered that match the letters. Each letter receives a score. T stands for the size of the initial tumor and whether or now the infection has spread beyond the initial mass. If the location of cancerous cells remains in the primary location of initiation, then staging is lower. Its raised when the lump is enlarged and/ or its invaded neighboring tissues. Its rated as Tx, Tis, T0, T1, T2, T3, or T4.
N describes whether the closest lymph nodes were infected. They act as filters for the body and can become swollen in the presence of cancer. Its rated as Nx, N0, N1, N2, or N3.
Finally, M describes metastasis, whether cancer has traveled to other regions of the body. In the beginning it should be rather contained to the initial site of infection, however, it becomes dangerous when it spreads. It can spread to other nonvital organs like the intestines or esophagus. Vital organs such as the heart, brain, or liver often lead to a terminal conclusion. Its rating is M0 or M1.
This system was developed by Pierre Denoix between 1943 and 1952. Other parameters considered are the grade of cancer cells, the elevation of serum , completeness of operation, and modifier for the certainty of the information gathered.
You May Like: Scalp Melanoma Stages
General Survival Rate Information
Five-year and ten-year survival rates tell you what percent of people live at least five years and ten years, respectively, after the cancer is found.
Statistics on the survival rates for people with melanoma are based on annual data from past cases and over multi-year timeframes.
Because treatments for melanoma are more successful in early stages, it is informative to look at survival rates based on stage and stage subgroups rather than on the cancer as a whole.
It is important to remember that survival rates do not predict an individuals survival. Every person and every case are different, and many factors contribute to an individuals survival. Its also important to remember that new and successful treatments have emerged over the last few years, and survival rates have increased in Stage III and Stage IV melanoma.
Donât Miss: What Is The Deadliest Type Of Skin Cancer
Melanoma In The Lymph Nodes
If your lymph nodes feel normal but a sentinel lymph node biopsy shows that a small number of melanoma cells have spread there, you might have either:
- regular ultrasound scans to check your lymph nodes
- treatment with targeted cancer drugs or immunotherapy
You dont usually have surgery to remove the rest of the lymph nodes in this situation, except in specific circumstances. Your doctor will talk to you about this.
Some people may decide to have ultrasound surveillance of their lymph nodes instead of having a sentinel lymph node biopsy. In this case, you usually have regular ultrasound scans over 5 years. You may need a biopsy if there is a concern that melanoma is in your lymph nodes.
You May Like: Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy
Stage I And Stage Ii Melanomas
Making a melanoma diagnosis means gathering as much information about your skin cancer as possible. One key step is determining the cancers stage, which is a measure of the amount and severity of cancer in the body. Staging helps your doctor understand how best to treat the cancer, and is used when discussing survival rates.
Following stage 0 , the degrees of melanoma range from stage I through stage IV, with higher numbers indicating further spreading of the cancer throughout the body.
There are three factors commonly used to determine melanoma staging, and theyre represented by the TNM system. The first factor is the severity of the primary tumor , which includes how thick the tumor is and whether the skin covering it has broken. The second factor is whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes . The third factor is whether the cancer has spread, or metastasized , to lymph nodes farther away in the body or other organs.
I’ve Been Diagnosed With Melanomawhat Happens Next
Doctors use the TNM system developed by the American Joint Committee on Cancer to begin the staging process. Its a classification based on three key factors:
T stands for the extent of the original tumor, its thickness or how deep it has grown and whether it has ulcerated.
What Is Breslow depth?
Breslow depth is a measurement from the surface of the skin to the deepest component of the melanoma.
Tumor thickness: Known as Breslow thickness or Breslow depth, this is a significant factor in predicting how far a melanoma has advanced. In general, a thinner Breslow depth indicates a smaller chance that the tumor has spread and a better outlook for treatment success. The thicker the melanoma measures, the greater its chance of spreading.
Tumor ulceration: Ulceration is a breakdown of the skin on top of the melanoma. Melanomas with ulceration are more serious because they have a greater risk of spreading, so they are staged higher than tumors without ulceration.
N indicates whether or not the cancer has already spread to nearby lymph nodes. The N category also includes in-transit tumors that have spread beyond the primary tumor toward the local lymph nodes but have not yet reached the lymph nodes.
M represents spread or metastasis to distant lymph nodes or skin sites and organs such as the lungs or brain.
After TNM categories are identified, the overall stage number is assigned. A lower stage number means less progression of the disease.
Read Also: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
It Usually Starts With Suspicious Spot
Maybe you noticed a mole that stood out from the rest . Its edges were irregular, maybe it was asymmetrical in shape, unevenly pigmented, noticeably large , or rapidly changing . These are the spots that concern dermatologists. If you had one, your doc did a biopsy on your own ugly duckling. During this in-office procedure, your doctor either shaved off a layer of your mole, punched it out with a hole-punch-like tool, or removed it with surgical excision, along with a margin of healthy skin to check for wandering cancer cells.
You May Have A Genetic Mutation
Its very likely that your melanoma tumor will have a DNA mutation. These mutations turn off tumor-suppressor genes, allowing cancers to grow out of control, according to the American Cancer Society. Discovering which mutation you have through genetic profiling can help your doctor determine the best course of treatment. Research has shown that about 50% of melanomas contain the BRAF mutation, while others may contain MEK mutations or the less common C-KIT mutation. Most people will only have only one of these mutations.
Also Check: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest