Continue Learning About Kidney Cancer
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
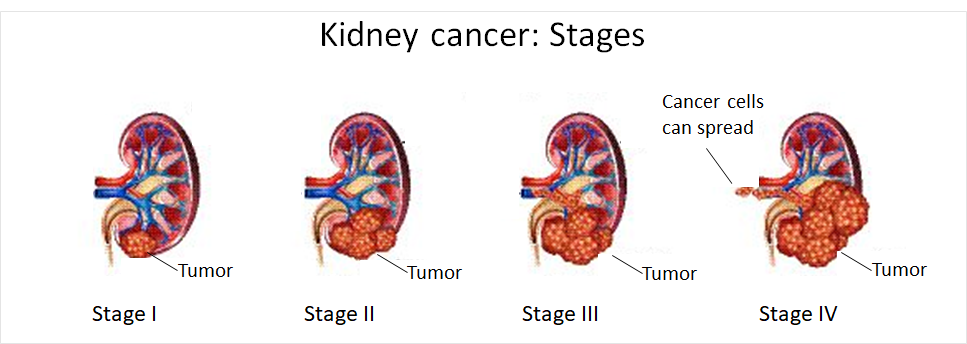
Treatment Of Stage Ii Renal Cell Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- Surgery , before or after radiation therapy.
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms in patients who cannot have surgery.
- Arterial embolization as palliative therapy.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Renal Cell Carcinoma: Diagnosis And Management
RICHARD E. GRAY, DO, and GABRIEL T. HARRIS, MD, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, Maryland
Am Fam Physician.;2019;Feb;1;99:179-184.
Kidney cancer is one of the 10 most common cancers in the United States with 90% being attributed to renal cell carcinoma. Men, especially black men, are more likely to be affected than women. Renal masses, either cystic or solid, are best detected with contrast-enhanced, triple-phase computed tomography. Renal tumors are often detected incidentally during a computed tomography scan of the abdomen or chest that was ordered for unrelated symptoms. Hematuria serves as a warning sign that necessitates further evaluation and imaging leading to a diagnosis and treatment plan. Treatment options include active surveillance, ablation, nephron-sparing tumor excision, nephrectomy, and systemic treatment. Predictors of a poor prognosis include poor functional status and metastasis. In recent years new therapies have improved the prognosis for patients with metastatic disease. The family physician should be aware of risk factors and lifestyle and dietary modifications that may reduce risk.
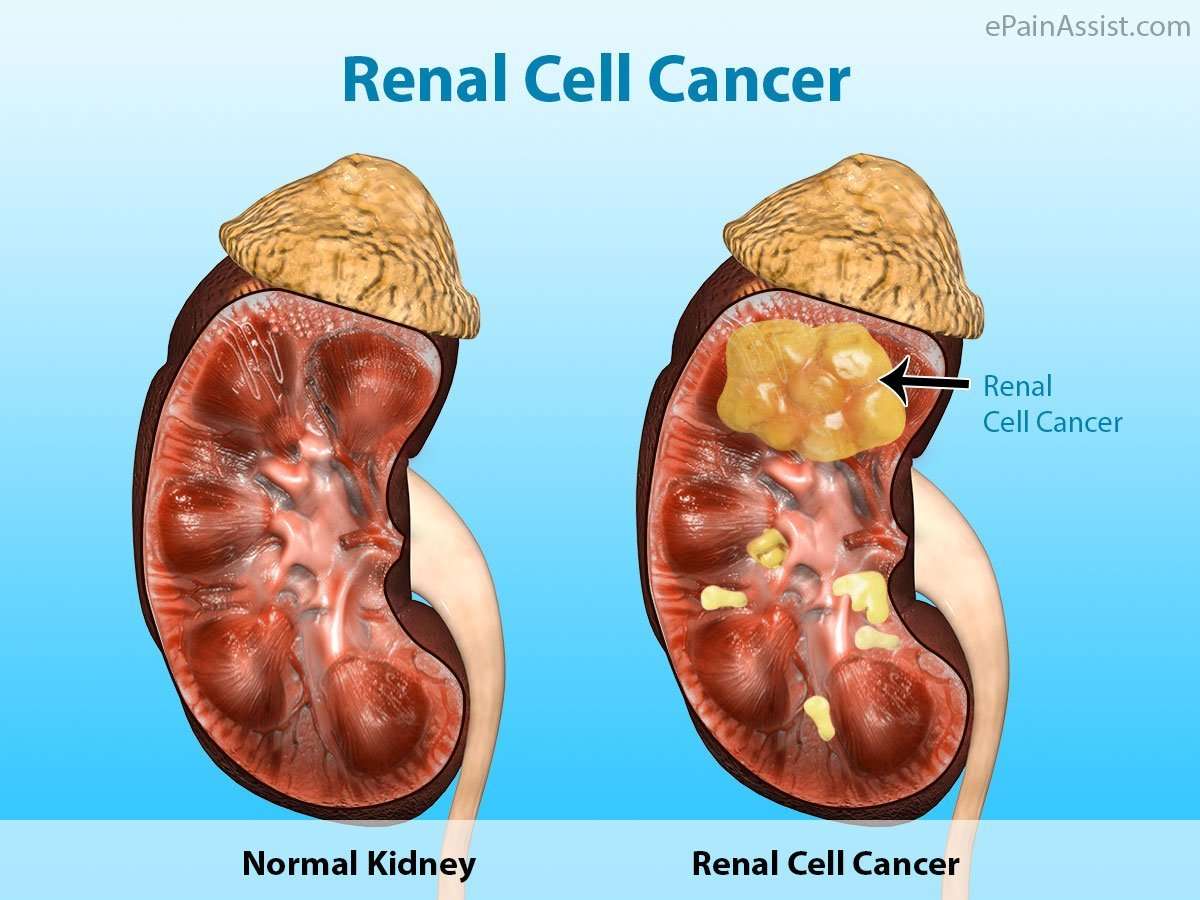
Renal cell carcinoma is classified in three major histological subtypes: clear cell , papillary , and chromophobe .4 Disease-specific survival is worst with clear cell renal cell carcinoma as it tends to be discovered at a more advanced stage.5
Also Check: Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Fatal
Symptoms And Signs Of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Symptoms usually do not appear until late, when the tumor may already be large and metastatic. Gross or microscopic hematuria is the most common manifestation, followed by flank pain, fever of unknown origin , and a palpable mass. Sometimes hypertension results from segmental ischemia or pedicle compression. Paraneoplastic syndromes occur in 20% of patients. Polycythemia can result from increased erythropoietin activity. However, anemia may also occur. Hypercalcemia is common and may require treatment. Thrombocytosis, cachexia, or secondary amyloidosis may develop.
Diagnosis Of Renal Cell Carcinoma
-
CT with contrast or MRI
Most often, a renal mass is detected incidentally during abdominal imaging done for other reasons. Otherwise, diagnosis is suggested by clinical findings and confirmed by abdominal CT before and after injection of a radiocontrast agent or by MRI. A renal mass that is enhanced by radiocontrast strongly suggests renal cell carcinoma . CT and MRI also provide information about local extension and nodal and venous involvement. MRI provides further information about extension into the renal vein and vena cava and has replaced inferior vena cavography. Ultrasonography and intravenous urography may show a mass but provide less information about the characteristics of the mass and extent of disease than do CT or MRI.
Often, nonmalignant and malignant masses can be distinguished radiographically, but sometimes surgery is needed for confirmation. Needle biopsy does not have sufficient sensitivity when findings are equivocal; it is recommended only when there is an infiltrative pattern instead of a discrete mass, when the renal mass may be a metastasis from another known cancer, or sometimes to confirm a diagnosis before chemotherapy for metastases.
A chest x-ray and liver tests are essential. If chest x-ray is abnormal, chest CT is done. If alkaline phosphatase is elevated, bone scanning is needed. Serum electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen , creatinine, and calcium are measured. BUN and creatinine are unaffected unless both kidneys are diseased.
Read Also: How Bad Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Renal Cell Carcinoma Symptoms Causes Treatment
Last Updated On By surekha
Renal cell cancer or renal cell carcinoma is a major type of cancer that develops in kidneys. This cancerous tumor is really challenging for the medical experts because it is associated with at least 4 types of hereditary syndrome. Often this will not show any symptom until the cancer cells have metastasized to distant organs of the body. About 3 persons in every 10 people diagnosed with renal cell cancer will have the presence of cancerous cells in the liver and lungs. Renal cell cancer can develop both due to hereditary and non-hereditary conditions. Treatment options available are surgery, immunotherapy and radiation therapy.
Symptoms :
It is very difficult to diagnose renal cell cancer since in most of the cases it will not show any signs. Only 10% of the affected patients will show significant symptoms like loss of weight, fever, high blood pressure and flank pain. Some people may develop malaise and night sweats. It would cause significant weight loss without any effort.
Renal Cell Carcinoma Causes :
Renal cell cancer originates in the tissues of renal tubular epithelium. Abnormal cell division takes place resulting in cloning of genes causing tumors in the kidneys.
Four major types of hereditary syndromes are related with renal cell cancer :
- Von Hippel Syndrome :
- Papillary Renal Carcinoma :
This is also a hereditary disorder inherited by birth.
- Birt Hogg Dube Syndrome :
- Renal Carcinoma :
Diagnosis :
Treatment :
- Immunotherapy :
- Surgery :
What Other Additional Laboratory Studies May Be Ordered
In patients with advanced or metastatic RCC, routine hematologic and biochemical studies are recommended. Hemoglobin levels, calcium and serum albumin, and serum LDH should be obtained to allow MSKCC classification of the untreated newly diagnosed RCC patient. There are no biomarkers or other specialized laboratory studies that are helpful during the initial evaluation. In the future, SNP analyses and tumor genetic studies may be helpful in this regard.
No sponsor or advertiser has participated in, approved or paid for the content provided by Decision Support in Medicine LLC. The Licensed Content is the property of and copyrighted by DSM.
Don’t Miss: Is Melanoma The Same As Skin Cancer
Prognostic Systems For Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Two similar prognostic systems are commonly used to calculate risk in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma . The;Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center /Motzer score includes the following criteria :
- Time from diagnosis to systemic treatment less than 1 year
- Hemoglobin concentration below the lower limit of normal
- Serum calcium concentration > 10 mg/dL
- Lactate dehydrogenase level more than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal
- Performance status less than 80%
The International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium risk model, validated and further developed by Heng et al, includes the following prognostic criteria :
- Time from diagnosis to systemic treatment less than 1 year
- Karnofsky performance status less than 80%
- Hemoglobin concentration below LLN
- Serum calcium above ULN
- Platelet count above the ULN
- Neutrophil count above the ULN
Both systems categorize patients into the following 3 risk groups:
- Favorable risk – Median survival 20 months ; 2-year overall survival 75%
- Intermediate risk – Median survival 10 months; 2y OS 53%
- Poor/high risk group – Median survival 4 months; 2y OS 7%
Review of an external validation cohort of 4657 patients treated for kidney cancer in clinical trials from 2003 to 2013 also demonstrated longer overall survival in obese patients, with median overall survivals of 23.4 months versus 14.5 months for those with low BMI.
Tcga’s Study Of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
What is kidney cancer?
The most common type of kidney cancer is called renal cell carcinoma. This cancer forms in the cells lining the small tubules in the;kidney;that filter waste from the blood and make urine. An estimated 58,240 Americans were expected to have been diagnosed with kidney cancer and an estimated 13,040 to have died of this cancer in 2010.1;Most people with kidney cancer are usually over 55 years of age and this cancer is more common in men. When detected early, most cases of kidney cancer can be treated effectively. However,;survival rates;are low when the cancer has spread from the kidney to other parts of the body.;View additional information on kidney cancer.
TCGA analyzed two common subtypes of;renal cell carcinoma: clear cell and papillary. The identification of these subtypes of kidney cancer is based on how the cancer cells look under a;microscope. Approximately 92% of cases are clear cell carcinoma.2
What have TCGA researchers learned about clear cell renal cell carcinoma?
- Molecular alterations in kidney clear cell carcinoma modulate cell signaling:
- Clear cell carcinoma tumors contained frequent alterations in;VHL;and its interaction partners, genes involved in cellular oxygen sensing.
- Genes of the PIK/AKT pathway were highly mutated, suggesting that tumors may respond to specific inhibitors of this pathway.
- SETD2;was frequently mutated, leading;to global hypomethylation and vast changes in gene expression.
Read Also: How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Removed From The Nose
Treatment Of Stage Iii Renal Cell Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- Surgery . Blood vessels of the kidney and some lymph nodes may also be removed.
- Arterial embolization followed by surgery .
- Arterial embolization as palliative therapy.
- Surgery as palliative therapy.
- Radiation therapy before or after surgery .
- A clinical trial of biologic therapy following surgery.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Adjuvant And Neoadjuvant Therapy
Adjuvant therapy, which refers to therapy given after a primary surgery, has not been found to be beneficial in renal cell cancer. Conversely, neoadjuvant therapy is administered before the intended primary or main treatment. In some cases neoadjuvant therapy has been shown to decrease the size and stage of the RCC to then allow it to be surgically removed. This is a new form of treatment and the effectiveness of this approach is still being assessed in clinical trials.
Also Check: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Regulation Of Oncogenic Autophagy
In clear cell renal cell carcinoma , oncogenic autophagy dependent on microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 alpha and beta is stimulated by activity of the transient receptor potential melastatin 3 channel through multiple complementary mechanisms. The VHL tumor suppressor represses this oncogenic autophagy in a coordinated manner through the activity of miR-204, which is expressed from intron 6 of the gene encoding TRPM3. TRPM3 represents an actionable target for ccRCC treatment.
Rcc In End Stage Renal Disease Patients

The benefit of early detection of RCC in ESRD would be that the RCC would be less likely metastatic and hence ultimately fatal. ESRD patients are not routinely scanned for RCC unless there are other issues. Transplantation also carries an increased risk for kidney cancer ; this is estimated to be 15-fold over the first three years following transplantation, and this risk increases with extent of exposure to immunosuppressive agents . The prevalence of RCC in native kidneys after transplantation is around 5% overall but 19% in ACKD patients or 54% in patients with complex cysts . The life expectancy of a transplant recipient has improved and cancer may soon be the leading cause of death late after transplantation. A marker of aggressiveness of RCC developing after transplantation could also aid in establishing priority for transplantation.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If I Have Skin Cancer
Chemotherapy Immunologic Therapy Targeted Therapy
There are several medications approved for treatment of renal cell carcinoma:
- Chemotherapy destroys actively growing cells
- Immune therapy uses a process that triggers your immune system to destroy tumor cells
- Targeted therapy is a type of therapy that specifically destroys the tumor cells
All of these medications are powerful, and they may produce serious side effects during your treatment and recovery.
Treatment Of Stage I Renal Cell Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- Arterial embolization as palliative therapy.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: What Does Early Squamous Skin Cancer Look Like
What Are The Types Of Kidney Cancer
The information in this document refers to renal cell carcinoma the most common form of kidney cancer. However, there are different types of kidney cancer, including:
- Renal cell carcinoma : This is the most common form of kidney cancer in adults and accounts for 85% of all kidney cancers. Renal cell carcinoma usually develops as a single tumor in one kidney, but it can affect both kidneys. Renal cell carcinoma begins in the cells that line the small tubes that are part of the nephrons within the kidneys. .
- Transitional cell carcinoma: Transitional cell carcinoma accounts for 6% to 7% of all kidney cancers. This cancer usually begins in the area where the ureter connects to the main part of the kidney. This area is called the renal pelvis. Transitional cell carcinoma also can occur in the ureters or bladder.
- Renal sarcoma: This is the least common form of kidney cancer, accounting for only 1% of kidney cancer cases. It begins in the connective tissues of the kidneys and, if not treated, can spread to nearby organs and bones.
- Wilms’ tumor: This is the most common type of kidney cancer in children. It accounts for about 5% of kidney cancers.
Tumor Behavior And Prognostic Molecular Markers
The stage of the tumor, grade within stage, the histological cell type as well as clinical indications are used for prognosis of RCC. Identification of the molecular alterations that contribute to the variation in tumor behavior and clinical outcome within organ-confined, locally advanced, or metatstatic RCC is needed for improved management of RCC. Molecular markers can be incorporated into nomograms for counseling of patients and for patient stratification in clinical trials . The majority of studies have examined prognostic markers, e.g. carbonic anhydrase IX , almost exclusively by immunohistochemistry usually in the context of advanced RCC. Other markers investigated include p53, p21, Hif-1 and Survivin reviewed by Lam et al 2008 . Some global array studies have examined expression signatures of progression but in small numbers of organ-confined RCC and as part of a wider analysis . Even so, genes previously implicated in the progression of RCC were identified e.g. elevated expression of the Caveolin-1 gene previously implicated as an immunohistochemical marker for poor disease-free survival in non-metatstatic RCC .
Also Check: What Is The Main Cause Of Skin Cancer
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
Other Types Of Non Clear Cell Kidney Cancer
- Transitional cell carcinoma : They are also known as urothelial carcinomas. TCCs do not start in the kidney but in the transitional cells in the lining of the renal pelvis. This cancer can look like other types of urothelial cancer such as bladder cancer. However, people with TCC will often have the same symptoms as people with kidney cancer, like blood in the urine and back pain. TCC is rare and can be aggressive.
- Wilms tumor : This tumor almost always occurs in children and is very rare in adults. About 90% of kidney cancers in children are Wilms tumors.
- Renal sarcoma: This is a rare type of kidney cancer that begins in the blood vessels or connective tissue of the kidney.
Dont Miss: What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
How Common Is Kidney Cancer
The American Cancer Societys most recent estimates for kidney cancer in the United States for 2021 are:
- About 76,080 new cases of kidney cancer will be diagnosed.
- About 13,780 people will die from this disease
These numbers include all types of kidney and renal pelvis cancers.
Most people with kidney cancer are older. The average age of people when they are diagnosed is 64 with most people being diagnosed between ages 65 and 74. Kidney cancer is very uncommon in people younger than age 45.
Kidney cancer is about twice as common in men than in women and it is more common in African Americans and American Indian /Alaska Natives.
Also Check: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
You May Like: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
How Is Kidney Cancer Diagnosed
If you have symptoms, your doctor will perform a complete medical history and physical exam. The doctor also may order certain tests that can help in diagnosing and assessing cancer. These tests can include:
Most cancers are grouped by stage, a description of cancer that aids in planning treatment. The stage of a cancer is based on:
- The location and size of the tumor.
- The extent to which the lymph nodes are affected.
- The degree to which the cancer spread, if at all, to other tissue and organs.
The doctor uses information from various tests including CT, MRI, and biopsy to determine the stage of cancer.
Mind & Body Therapies
These combine mental focus, breathing, and body movements to help relax the body and mind. Some examples are:
- Meditation: Focused breathing or repetition of words or phrases to quiet the mind
- Biofeedback: Using simple machines, the patient learns how to affect certain body functions that are normally out of one’s awareness
- Hypnosis: A state of relaxed and focused attention in which a person concentrates on a certain feeling, idea, or suggestion to aid in healing
- Yoga: Systems of stretches and poses, with special attention given to breathing
- Tai Chi: Involves slow, gentle movements with a focus on the breath and concentration
- Imagery: Imagining scenes, pictures, or experiences to help the body heal
- Creative outlets: Interests such as art, music, or dance
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Subungual Melanoma Grow