Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
Mohs micrographically controlled surgery involves examining carefully marked excised tissue under the microscope, layer by layer, to ensure complete excision.
- Very high cure rates achieved by trained Mohs surgeons
- Used in high-risk areas of the face around eyes, lips and nose
- Suitable for ill-defined, morphoeic, infiltrative and recurrent subtypes
- Large defects are repaired by flap or skin graft
What Is Spongiosis Of Esophagus
Background:The histological diagnosis of GERD is not based on a single feature in esophageal biopsies. However, the presence of eosinophils is considered a sensitive marker for GERD. A morphological finding that can also be seen in GERD is spongiosis, which is the presence of edema between squamous cells.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Causes And Prevention
Several causes for basal cell carcinoma have been identified. BCC can, however, arise without any of these. They start with a single cell that becomes abnormal due to damage to its DNA. These cells then multiply, and as abnormal cells build-up, the skin lesion becomes visible.4
Basal cell carcinoma risk factors include: 5
- Ultraviolet lightUV light from sunshine and commercial tanning beds can both cause damage to cells mentioned, ultimately resulting in abnormal skin lesions. More sun exposure from warm climates, excess suntanning and excess use of tanning beds all make BCC more likely. Severe sunburn can also be a factor.
- Fair skinFair skin is a risk factor as there is less protection for the deeper skin layers from melanin.
- AgeAs detailed, BCC starts with damage to cells and as we get more damage over time, increasing age is a significant factor.
- Medical treatmentRadiotherapy for other medical conditions and immunosuppressants drugs can increase the risks of basal carcinoma and must be taken into account when assessing skin lesions.
For more details of risks factors, see this article.
Basal cell carcinoma prevention
Avoiding or minimising these risk factors is the mainstay of basal cell carcinoma prevention. The most important preventable factor is sun exposure.
Don’t Miss: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like On Your Skin
Rarer Types Of Non Melanoma Skin Cancer
There are other less common types of skin cancer. These include:
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- T cell lymphoma of the skin
- Sebaceous gland cancer
These are all treated differently from basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is very rare. Treatment is with surgery or radiotherapy, or both. This usually works well, but sometimes the cancer can come back in the same place. And sometimes it spreads to nearby lymph nodes.
Sebaceous gland cancer
Sebaceous gland cancer is another rare type of skin cancer affecting the glands that produce the skin’s natural oils. Treatment is usually surgery for this type of cancer.
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Kaposis sarcoma is a rare condition. It’s often associated with HIV but also occurs in people who don’t have HIV. It’s a cancer that starts in the cells that form the lining of lymph nodes and the lining of blood vessels in the skin. Treatment is surgery or radiotherapy, and sometimes chemotherapy.
T cell lymphoma of the skin
T cell lymphoma of the skin can also be called primary cutaneous lymphoma. It’s a type of non Hodgkin lymphoma. There are a number of different types of treatment for this type of cancer.
Risk Factors For Basal Cell Carcinoma
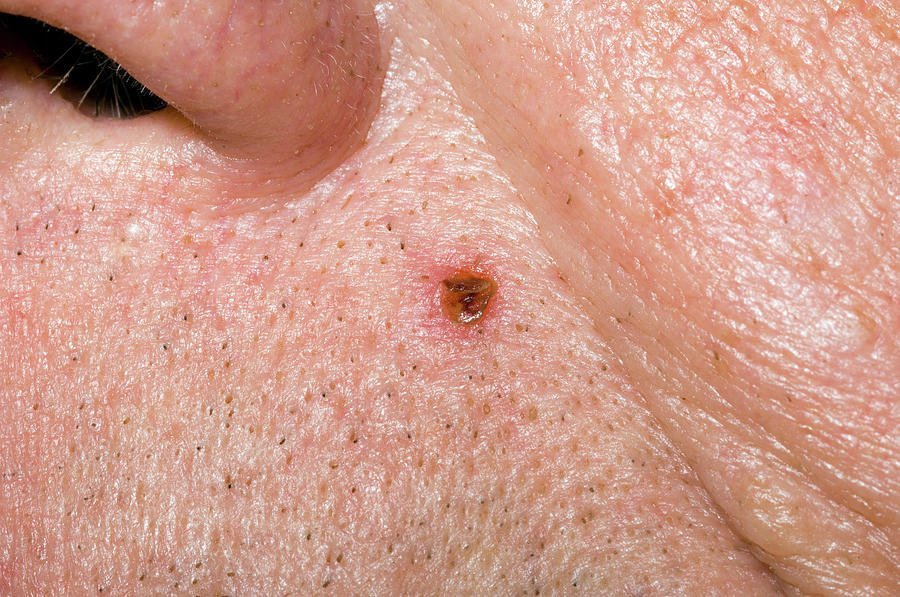
Anyone with a history of sun exposure can develop basal cell carcinoma. The disease is rarely seen in children, but occasionally a teenager is affected.
Men with BCC have outnumbered women with the disease, but more women are getting BCCs than in the past.
Workers in occupations that require long hours outside and people who spend a lot of time in the sun are particularly susceptible.
People who are at highest risk have fair skin, blond or red hair, and blue, green, or grey eyes.
Also Check: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
How To Spot A Bcc: Five Warning Signs
Check for BCCs where your skin is most exposed to the sun, especially the face, ears, neck, scalp, chest, shoulders and back, but remember that they can occur anywhere on the body. Frequently, two or more of these warning signs are visible in a BCC tumor.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these images serve as a general reference to what basal cell carcinoma looks like.
An open sore that does not heal
A reddish patch or irritated area
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
A shiny bump or nodule
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The two most common kinds of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are sometimes called nonmelanoma skin cancer. These cancers are carcinomas that begin in the cells that cover or line an organ.
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States and is the most common of all cancers. Typically, it is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but does so more often than basal cell carcinoma. It is important that skin cancers are found and treated early because they can invade and destroy nearby tissue. Organ transplant recipients have a 65-fold higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma than others. UCSF Medical Center offers a High Risk Skin Cancer Clinic for those at high risk for non-melanoma skin cancers, such as transplant recipients.
Recommended Reading: What To Do When You Get Skin Cancer
What Is The Prognosis Of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- In general, the prognosis of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is excellent, if it is detected and treated early.
- Stage of tumor: With this lower-stage tumor, the prognosis is usually excellent with appropriate therapy
- The surgical resectability of the tumor
- Overall health of the individual: Individuals with overall excellent health have better prognosis compared to those with poor health
- Age of the individual: Older individuals generally have poorer prognosis than younger individuals
- Whether the tumor is occurring for the first time, or is a recurrent tumor. Recurring tumors have a poorer prognosis compared to tumors that do not recur
Also Check: How To Say Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma Symptoms
An irritated patch of skin that wont heal, as was the case with Lebwohls colleague, isnt the only indication of basal cell carcinoma.
Anthony M. Rossi, MD, a dermatologic surgeon at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City who specializes in Mohs micrographic surgery and skin cancer treatment, says one of the most common scenarios is when people say they thought they had a pimple, but it wouldnt heal or go away.
Warning signs for basal cell carcinoma include something thats red, crusted, scaly, not healing, bleeding, or even a new shiny pearl papule says Dr. Rossi.
Basal cell carcinoma can also appear atypically it can be flat with a whitish discoloration or appear as a bump on the skin thats pink or brown, says Rossi. There are multiple subtypes of BCC, which, characteristically, have different degrees of pigmentation and can be broad ranging in appearance.
This type of skin cancer rarely causes pain as it develops. Because it can look like a scab and appear to heal repeatedly without growing, people can go for months or even years thinking the skin abnormality is just a sore or wound. If you notice a spot that won’t heal or constantly bleeds you should see a dermatologist, says Lebwohl.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment For Melanoma Skin Cancer
What Are The Treatments For Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is treated by removing it. The choice of treatment depends on many things, including patient health and age, the location of the tumor, and the extent and type of the cancer. Treatment may occur in many ways:
- Scratching off with a curette, an instrument that may end in a ring or a spoon, and then burning with a special electric needle. This method is called electrodessication and curettage.
- Surgical removal
- Mohs surgery: This is a specialized technique. The doctor first removes the visible cancer and then begins cutting around the edges. The tissues are examined during the surgery until no more cancer cells are found in tissues around the wound. If necessary, a skin graft or flap might be applied to help the wound heal.
- Excisional surgery: The growth and a bit of surrounding skin is removed with a scalpel.
If the BCC has advanced locally or spread to another location, which is very rare for BCC, the FDA has approved two medicines: vismodegib and sonidegib . These drugs are of a class called hedgehog inhibitors.
Radiation And Immunologic Origins
Radiation has proven to be tumorigenic by two mechanisms. The first entails the initiations of prolonged cellular proliferation, thereby increasing the likelihood of transcription errors that can lead to cellular transformation. The second mechanism is direct damage of DNA replication, leading to cellular mutation that may activate proto-oncogenes or deactivate tumor suppressor genes.
Immunologically, the mechanism by which prolonged ultraviolet radiation exposure leads to the development of BCC includes suppression of the cutaneous immune system and immunologic unresponsiveness to cutaneous tumors. This local effect includes a decrease in Langerhans cells, dendritic epidermal T cells, and Thy1+ cells. Furthermore, systemic proliferation of suppressor T cells and the release of immunosuppressive factors are believed to be pathogenic to the development of BCC.
You May Like: How Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Start
What Should I Do If I Think I Have A Basal Cell Carcinoma
If you notice a change to or growth on your skin, make an appointment to see your doctor straight away. Your doctor will assess the size, location and look of the growth. They will also ask you how long you have had it, whether it bleeds or itches, etc.
If your doctor thinks the growth may be cancer, they may take a small sample of tissue . The tissue sample will be sent to a laboratory and examined under a microscope. Your doctor will let you know whether the sample showed any cancer cells, and will recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.
Recommended Reading: How Quickly Can Melanoma Metastasis
Basal Cell Carcinoma Symptoms:
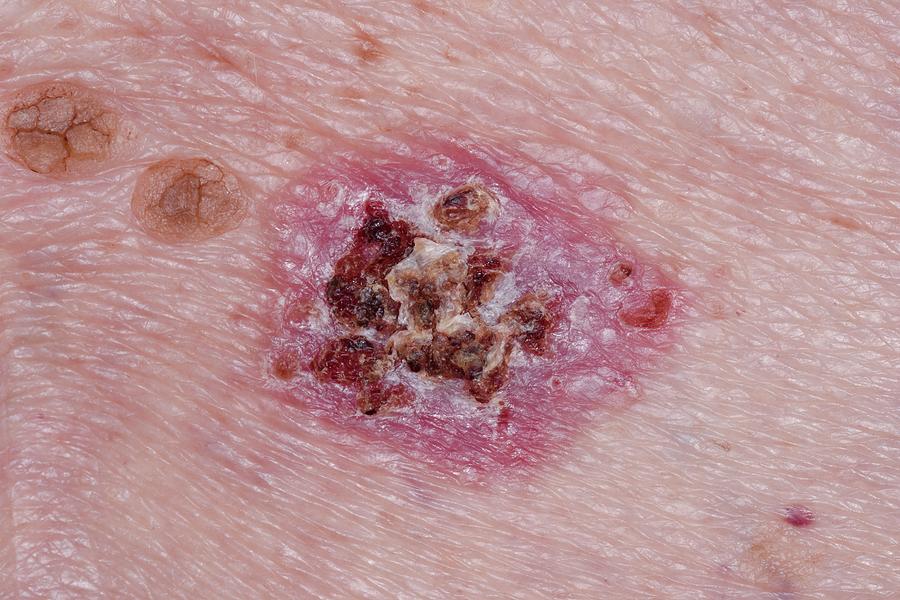
The basal cell carcinoma may display only a slightly different appearance of the skin normal and most common on the face, neck and other parts that are very exposed to the sun. It looks like a lump that:
- It has a pearly appearance, as if it were covered with wax
- It can be white, light pink, beige or brown
- Bleeds easily
- It looks like a wound that does not heal
- It may form crust and leak some liquid.
As a general rule, any new sign on the skin or change in a spot that already existed should be a warning sign for a dermatologist. It is important to seek medical attention whenever you notice a new injury.
Or when an old injury has some kind of modification. There is a didactic rule for patients, called ABCD, which aims to recognize a cancer of skin in its early stages:
Don’t Miss: What Is The Difference Between Age Spots And Skin Cancer
What Does Morpheaform Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like
One of the defining features of morpheaform BCC is its shape. These tumors tend to be less regular and do not have well-defined edges. They often have long strands that extend off the main tumor node. This means the tumors can grow into other layers of the skin, or nearby muscles or other structures. The irregular shape of these tumors can make them difficult to treat.2
What Is Advanced Bcc
An estimated 1% of all BCC cases will progress to advanced BCC and either invade the surrounding tissue or spread to other parts of the body . This may result in debilitating effects, severe deformities and even death.
Advanced BCCs are often open lesions that may bleed, become infected, and produce unpleasant odours.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Melanoma
Pearls And Other Issues
The best treatment of basal cell carcinoma of any type is prevention with adequate protection from ultraviolet light exposure. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor 30 or greater, reapplied every two hours while outdoors. Daily sunscreen should be encouraged to all patients, especially those who spend increased time outside. Many daily facial moisturizers and foundational makeup have SPF sun protection these cosmeceuticals should not replace regular sunscreen application when outside, but rather they should be viewed as an additional layer of protection. Other sun-protective measures include wearing a hat that shades the ears and neck and sunglasses. Tanning bed use should be strongly discouraged, as it greatly increases the risk for all types of skin cancer.
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Read Also: How Do Doctors Test For Skin Cancer
How Can Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Be Prevented
Currently, Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is a malignant skin cancer that has no preventive measures. However, the following factors may help reduce the risk for the condition:
- Avoid or minimize sun exposure
- Limit the use of tanning beds and tanning parlors
- Smoking cessation
- If it is caused by certain underlying disorders, then treating the underlying disorder may help in the treatment and early cure of BCC of skin
Regular medical screening at periodic intervals with blood tests, scans, and physical examinations, are mandatory, due to its metastasizing potential and high possibility of recurrence. Often several years of active vigilance is necessary
General Principles In Outer Nose Repair
Most of nasal skin is of the sebaceous type. Whenever possible, scar lines should be placed along relaxed skin tension lines. Aesthetic units of the nose need consideration although tumours do not respect their borders. Aging affects the nose anatomy. Characteristic symptoms are frown lines , transverse crease on the nasal root, drooping of tip of nose, and deepened nasolabial folds. Skin diseases of elderly, like rosacea and rhinophyma can interfere with surgical techniques.
The skin covering the bony parts is highly movable, while the skin over cartilage parts is thicker, tighter and bound to the cartilage. Healing by second ary intention of convex surfaces like the nose tip should be avoided since healing often is delayed and may lead to uneven scars.
You May Like: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated
BCCs can almost always be successfully treated. Treatment will depend on the type, size and location of the BCC, and on your age and health.
If the BCC was removed during the biopsy, you may not need any further treatment. Surgery is the most common treatment for a BCC. It involves cutting out the skin spot and nearby normal-looking tissue. A pathologist will check the tissue around the skin spot to make sure the cancer has been removed. If cancer cells remain, you may need more surgery.
Other treatment options include:
- freezing the spot with liquid nitrogen to kill the cancer cells
- scraping off the spot, then using low-level electric current to seal the wound and kill cancer cells
- immunotherapy creams, liquids and lotions, to treat superficial BCCs