Who Is At Risk For Merkel Cell Cancer
A risk factor is anything that may increase your chance of having a disease. The exact cause of someones cancer may not be known. But risk factors can make it more likely for a person to have cancer. Some risk factors may not be in your control. But others may be things you can change.
The risk factors for Merkel cell cancer are:
- Being exposed to a lot of ultraviolet rays from the sun or other sources such as tanning beds or PUVA treatments
- Not protecting your skin from the sun
- Having light-colored skin
- Having a weakened immune system, such as from HIV or an organ transplant
- Arsenic exposure
- Infrared light exposure, such as lasers or heat lamps
Researchers have found that Merkel cell cancer almost always shows infection with a virus known as Merkel cell polyomavirus . Doctors dont know much about MCV yet, or how it might be linked to cancer. Most people are infected with this virus at some point. But very few people develop this cancer.
After Merkel Cell Carcinoma Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment.
The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process:
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is A Very Rare Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Skin
Merkel cells are found in the top layer of the skin. These cells are very close to the nerve endings that receive the sensation of touch. Merkel cell carcinoma, also called neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin or trabecular cancer, is a very rare type of skin cancer that forms when Merkel cells grow out of control. Merkel cell carcinoma starts most often in areas of skin exposed to the sun, especially the head and neck, as well as the arms, legs, and trunk.
Merkel cell carcinoma tends to grow quickly and to metastasize at an early stage. It usually spreads first to nearby lymph nodes and then may spread to lymph nodes or skin in distant parts of the body, lungs, brain, bones, or other organs.
Merkel cell carcinoma is the second most common cause of skin cancer death after melanoma.
Recommended Reading: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Tests And Procedures That Examine The Skin Are Used To Diagnose Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The following tests and procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and health history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patients health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- Full-body skin exam: A doctor or nurse checks the skin for bumps or spots that look abnormal in color, size, shape, or texture. The size, shape, and texture of the lymph nodes will also be checked.
- Skin biopsy: The removal of skin cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer.
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Recommended Reading: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Surgical Treatments For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The first step in treating Merkel cell carcinoma is usually surgery to remove the tumor, assuming it has not spread beyond your lymph nodes. Your surgeon will remove the tumor and surrounding tissue and may perform a sentinel lymph node evaluation to assess if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. This can allow for accurate staging, which will then guide consideration for preventative treatments or inclusion into clinical trials.
Surgery usually leaves some type of scarring. The most common risk for surgeries is infection. Ask your doctor how to reduce your risk of infection after surgery and about any other possible side effects.
Key Points About Merkel Cell Cancer
- Merkel cell cancer is a rare type of skin cancer. It forms in the Merkel cells. These cells are found in the outer layer of the skin.
- Merkel cells are very close to nerve endings. They help the skin sense light touch.
- Being exposed to a lot of UV light can raise your risk for this cancer.
- Merkel cell cancer often looks like firm, shiny lumps on your skin that dont hurt. They may be red, pink, or blue.
- This cancer grows and spreads quickly.
- Treatment includes surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. One type of treatment or a combination of treatments may be used.
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
New Pathology Reporting Recommendations
The College of American Pathologists develops protocols to assist pathologists in reporting relevant pathologic information to clinicians. In 2010, they released recommendations for reporting MCC of the skin. The protocol consists of a checklist of required and suggested elements for the pathologic reporting of cutaneous MCC and not only includes elements found in the most recent AJCC staging system but also suggests reporting additional characteristics that may prove to be valuable. Thus, in addition to required elements of tumor site, size, margins, etc., suggested elements include tumor thickness, lymph-vascular invasion, mitotic index/mm2, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, tumor growth pattern and pathologic staging . Explanatory notes and diagrams are included to assist the pathologist and clinician in understanding and interpreting these characteristics. Clinicians should familiarize themselves with these recommendations and request them from pathologists reporting MCC.
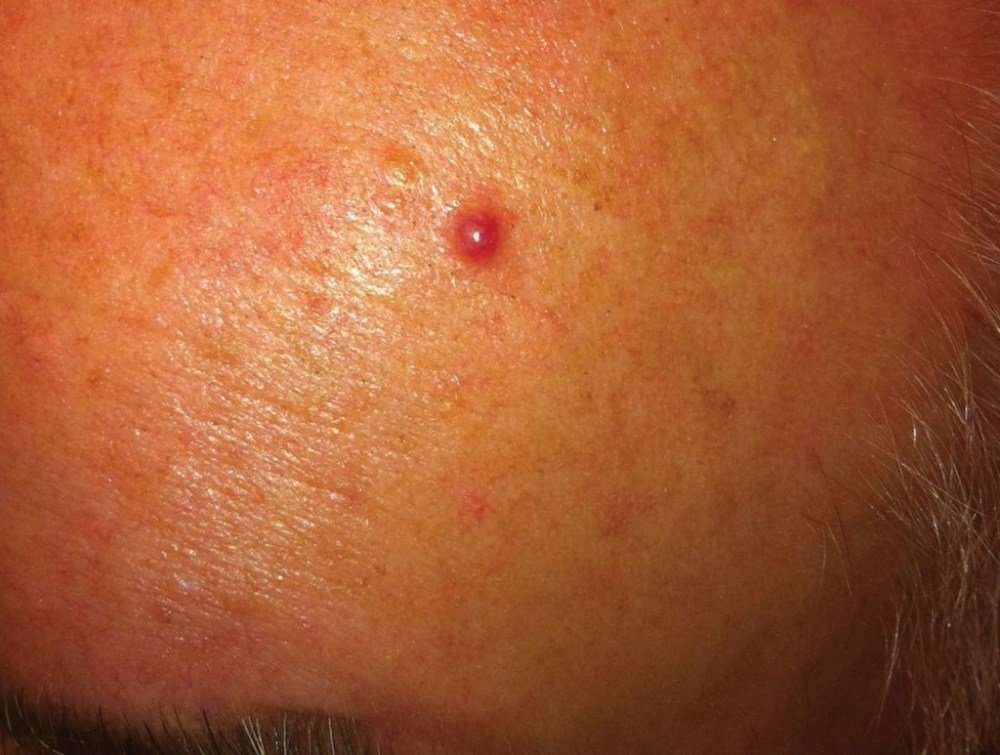
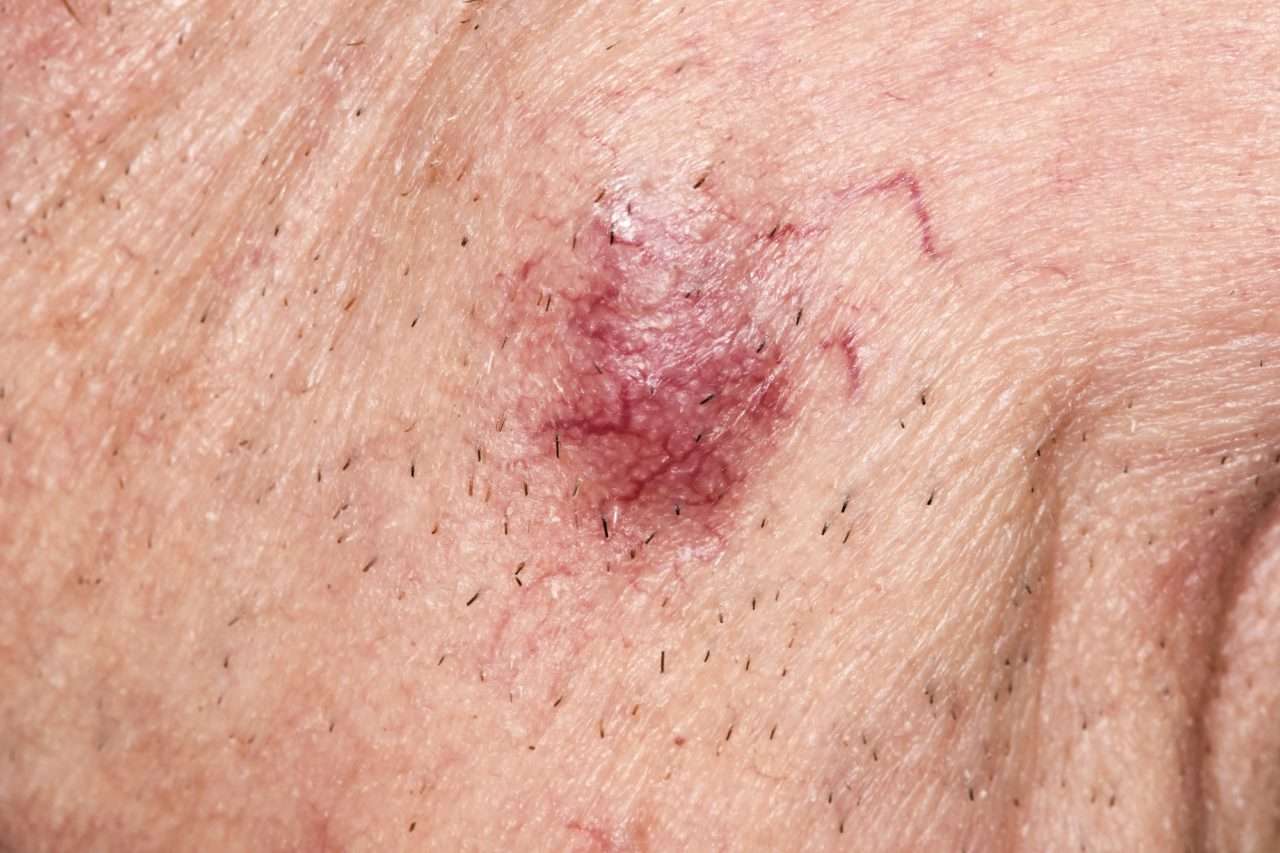
What Does Mcc Look Like
MCC tumors often, but not always, appear on sun-exposed areas of the body. The tumors are not nearly as distinctive as other skin cancers and can appear as a pearly pimple-like lump, sometimes skin-colored, red, purple or bluish-red, though they are rarely tender to the touch. The rapid speed at which they grow is what often causes patients and doctors to take notice.
A recurrence of Merkel cell carcinoma on the forehead.
Merkel cell carcinoma on the lower leg.
Please note: Since not all Merkel cell carcinomas have the same appearance, these photos serve as a general reference for what MCC can look like. If you see something new, changing or unusual on your skin, schedule an appointment with your doctor. Photos courtesy of Paul Nghiem, MD, PhD
Read Also: Basal Skin Cancer Survival Rates
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Merkel Cell Carcinoma Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
What Causes Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell polyomavirus has been detected in about 80% Merkel cell carcinomas tested. It is thought that the virus causes genemutations leading to Merkel cell carcinoma when immune function is defective. The virus-negative tumours are associated with high exposure to ultraviolet radiation, due to the occurrence of the tumour on sun-exposed skin.
Immunosuppression is an important factor for the development of Merkel cell carcinomas.
Merkel cell carcinoma was previously believed to arise from Merkel cells, which are pressure receptors in the skin. A recent investigation is pointing to their origin being early B-cells based on cellularmorphology, the expression of early B-cell markers and clonalimmunoglobulin chain rearrangement.
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
Chemotherapy Treatments For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Chemotherapy refers to drugs that kill quickly dividing cells, including cancer cells.
However, adjuvant chemotherapy is not recommended in all patients.
Research so far has not shown a strong benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with Merkel cell carcinoma. Chemotherapy is generally recommended primarily for patients who have not responded to radiation and cannot receive immunotherapy.
Side effects include hair loss, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. The drugs can sometimes cause patients’ health to deteriorate more.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare, aggressive type of skin cancer.
Merkel cell carcinoma gets its name because these skin cancer cells resemble Merkel cells, which are located in the top layer of skin. Merkel cells are most concentrated in the fingertips, lips, and face, but MCC cells are most likely to develop on the head, neck, and other areas that have received the most sun exposure.
Below, learn about the causes of MCC, its symptoms, and how to prevent it. We also describe the diagnosis and treatment options.
Carcinoma is a type of cancer that develops in the skin or tissues covering or lining internal organs. Cancer occurs when cells begin to randomly divide and grow out of control. This cellular growth eventually forms a mass called a cancerous tumor.
MCC is one type of skin cancer, and its cells resemble Merkel cells. These are located close to the skins nerve endings and help provide a sense of light touch. They also relay information from the skin to the brain about details such as pressure and texture.
Merkel cells share traits with nerve and hormone-producing cells. As a result, they are classed as neuroendocrine cells, and MCC, in turn, is sometimes called neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin. Another name for MCC is trabecular carcinoma.
MCC is very rare. In 2018, around 2,000 people in the United States received the diagnosis. However, its prevalence seems to be growing.
Also Check: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Immunotherapy Treatments For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
If the cancer has spread, your doctor may recommend immunotherapy. Clinical trials suggest immunotherapy drugs may be more effective against Merkel cell carcinoma than chemotherapy.
Two FDA-approved immunotherapy drugs for Merkel cell carcinoma are avelumab and pembrolizumab. Side effects of immunotherapy drugs can include fatigue, inflammation, itchiness, skin reactions, high or low blood pressure, and flu-like symptoms.
Coping With Merkel Cell Cancer
Many people feel worried, depressed, and stressed when dealing with cancer. Getting treatment for cancer can be tough on your mind and body. Keep talking with your healthcare team about any problems or concerns you have. Work together to ease the effect of cancer and its symptoms on your daily life.
To help ease your stress:
- Talk with your family or friends.
- Ask your healthcare team or social worker for help.
- Speak with a counselor.
- Talk with a spiritual advisor, such as a minister or rabbi.
- Ask your healthcare team about medicines for depression or anxiety.
- Keep socially active.
- Join a cancer support group.
Cancer treatment is also hard on the body. To help yourself stay healthier, try to:
- Eat a healthy diet, with a focus on high-protein foods.
- Drink plenty of water, fruit juices, and other liquids.
- Keep physically active.
- Rest as much as needed.
- Talk with your healthcare team about ways to manage treatment side effects.
- Take your medicines as directed by your team.
Recommended Reading: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Stages Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
After receiving a cancer diagnosis, your doctor will run tests to find out if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body. This is referred to as staging. Staging is important for determining what types of treatment are needed.
In general, a higher number stage means the further a cancer has spread. There are five main stages in MCC :
- stage 0: the cancer is only in the epidermis and hasnt spread to the lymph nodes
- stage 1: the cancer is less than 2 centimeters across and hasnt grown into the lymph nodes
- stage 2: the cancer is more than 2 cm across and hasnt spread to the lymph nodes
- stage 3: the cancer has grown into lymph nodes as well as nearby tissues
- stage 4: the cancer has spread to nearby tissues, the lymph nodes, and distant sites, such as the lungs, bones, or brain
The main symptom of Merkel cell carcinoma is the appearance of a single lump or nodule on the skin. The lump is typically:
- red or violet in color
- firm to the touch
- fast-growing
- painless
The nodule can form anywhere on the body, but most often appears on areas regularly exposed to sunlight, such as the:
- face
- neck
- arms
If the cancer spreads to the lymph nodes, the nodes may grow large enough to be seen as lumps under the skin.
Merkel cell carcinoma can look like many other types of skin cancer at first, so a definitive diagnosis usually isnt made until after a biopsy. Other types of skin cancers often present with:
What Does Merkel Cell Carcinoma Look Like What Are The Symptoms
Merkel cell carcinoma is different from other skin cancers in that it does not have a common identifiable trait across all cases.
Merkel cell carcinoma tumors:
- are most often found on sun-exposed areas of skin, such as the face, neck, and arms but they can start anywhere on the body.
- usually appear as firm, shiny skin lumps that don’t hurt. The lumps may be red, pink, purple, or blue.
- tend to grow very quickly.
Between 10 20% of cases present without skin involvement and are found as a swelling of a lymph node.
You May Like: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Key Statistics For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Skin cancer is by far the most common type of cancer in the United States. Merkel cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer, but it’s not common. About 2,000 cases of MCC are diagnosed in the United States each year.
But the number of people diagnosed with MCC each year has been rising quickly over the past few decades. Some of this is probably because lab tests to diagnose these cancers have become more accurate. But the rise in MCC might also be caused by increases in risk factors. For instance, people are living longer, and more people are living with weakened immune systems.
More than 4 out of 5 Americans diagnosed with MCC are older than age 70. And men are nearly 2-times more likely to have it compared with women.
MCC is much more common in white people than in people of other races. More than 9 out of 10 cases of MCC in the United States are diagnosed in whites.
What Causes Merkel Cell Cancer
Experts arent exactly sure what causes Merkel cell cancer. But it occurs when Merkel cells in the body change and grow out of control. These abnormal cells may grow to form a lump or mass called a tumor. If the tumor is cancerous, it can grow into nearby areas. It can even spread to other parts of the body .
Don’t Miss: Does Insurance Cover Skin Cancer Screening
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor If I Have Merkel Cell Carcinoma
If your doctor diagnoses MCC, you may have many questions about your condition. These may include:
- How can I know whether the cancer has spread?
- Which treatments will be most beneficial for me?
- Is there a chance my cancer could come back after treatment?
- How can I protect my skin to lessen my chances of developing cancer again?
Make sure you contact your doctor if you notice any changes in your skin that worry you.
Does Merkel Cell Carcinoma Hurt
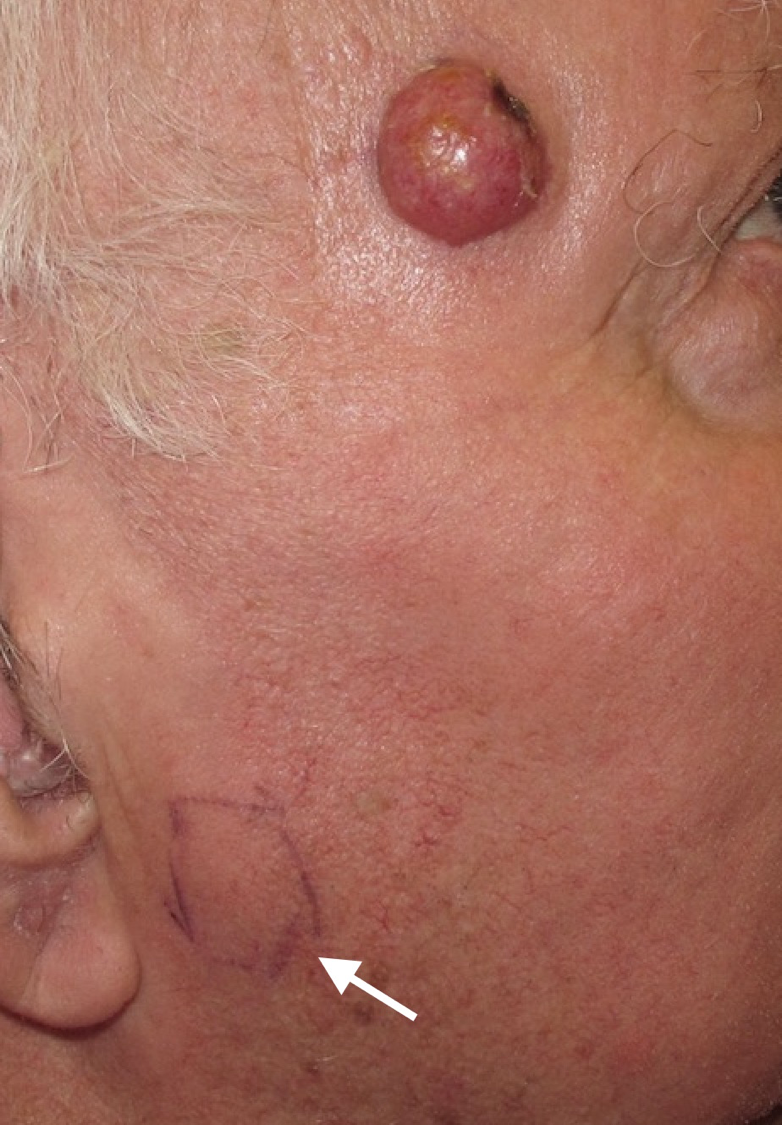
While MCC is often painless, it can feel sore and tender. Some people say the growth itches.
Many people who develop MCC are otherwise healthy. If you have certain risk factors, you have a greater risk of getting this skin cancer.
Youll find out what increases the risk of developing MCC at, Merkel cell carcinoma: Causes.
1 Haley CT, Mui UN, et al. Human Oncoviruses: Mucocutaneous Manifestations, Pathogenesis, Therapeutics, and Prevention . J Am Acad Dermatol. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.09.062. .
2 Coggshall K, Tello TL, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma: An update and review Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and staging. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018 78:433-42.
ImagesImages used with permission of Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology:
Image 1: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001 45:309-12.Image 3: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 73:968-75.Image 4: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012 66:923-7.Image 5: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010 62:463-8. Image 6: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008 58:375-81.Image 7: IbidImage 8: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 78:433-42.Image 9: J Am Acad Dermatol.2012 66:923-7.Image 2: Used with permission of the American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
ReferencesCoggshall K, Tello TL, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma: An update and review Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and staging. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 78:433-42.
Tello, TL. Coggshall K, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma: An update and review Current and future therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 78:445-54.
Also Check: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis