Dont Leave Basal Cell Carcinoma Untreated
Now that you know what happens if you leave basal cell carcinoma untreated, its time to take action on your skin cancer diagnosis. To learn more about how IG-SRT works, contact our skin cancer specialist team at 855-222-6858. We can answer your questions and help you understand whether IG-SRT is right for you.
Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer impacts the lives of 4 million Americans each year. GentleCure is committed to raising awareness of IG-SRT and is a trademark owned by SkinCure Oncology, LLC.
The information on this website is provided without any representations or warranties. You should not rely on this website as an alternative to medical advice from your doctor or healthcare provider. The information on this site, as well as any information provided by the skin cancer information specialists on our educational hotline, is intended to help you make a better-informed treatment decision in conjunction with trained and licensed medical professionals.
Answer: Risk Of Not Treating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma is a locally destructive type of skin cancer that is notorious for recurrence when not adequately treated. It can become quite disfiguring if left untreated, especially when located in cosmetically sensitive areas such as the nose. Typically this type of skin biopsy is performed for diagnosis and is not adequate treatment for a skin cancer. Biopsies sample a portion of the lesion, leaving some behind. This type of “sampling” biopsy is not intended to remove the entire lesion. It is not advisable to leave a known skin cancer untreated as it will likely grow and become more of a problem to remove in the future. Mohs micrographic surgery allows for 100% margin control and is tissue-sparing, which means it offers the highest cure rate while preserving as much normal tissue as possible.
What Happens If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Like basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma is relatively common, slow-growing, and at low risk to metastasize in most cases. This form of skin cancer is also likely to develop on the areas of the body that are exposed to sunlight like the face, hands, neck, shoulders, and lower legs, especially for people who have a history of sunburns. Unlike the smooth appearance of basal cell carcinoma lesions, squamous cell carcinoma tumors often appear as rough, thickened, scaly patches of skin. The growths may appear wart-like or like a donut shape. Squamous cell carcinoma lesions may form sores and bleed often or develop into a large, thick, and firm mass. Squamous cell carcinoma typically impacts people over the age of 50. While the condition does spread slowly, the risk that squamous cell carcinoma will spread to other parts of the body is higher than that of basal cell carcinoma. Additionally, these have the potential to arise suddenly and grow rapidly in some cases.
Also Check: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
How Do They Cut Out Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment
What Causes Skin Cancer
The main cause of skin cancer is overexposure to sunlight, especially when it results in sunburn and blistering. Ultraviolet rays from the sun can damage the skin and, over time, lead to skin cancer. The UV light damages DNA in the skin and causes it to grow abnormally. Exposure to certain chemicals such as tar and coal can cause skin cancer for those with jobs that require them to frequently be in contact with these chemicals. Those with a weakened immune system also have an increased risk for skin cancer.
You May Like: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
What Is A Basal Cell
One of three main types of cells in the top layer of the skin, basal cells shed as new ones form. BCC most often occurs when DNA damage from exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or indoor tanning triggers changes in basal cells in the outermost layer of skin , resulting in uncontrolled growth.
Leaving Squamous Cell Carcinoma Untreated
The third type of skin cancer we have to be cautious of in Australia is squamous cell carcinoma. This is potentially life threatening and is most dangerous when found on the face, lips, ears or neck. As it grows, there is the chance it may spread to the lymph nodes and internal organs, and while it isnt as fast growing as melanoma, it still requires treatment.
You may notice squamous cell carcinoma in the top layer of your skin and it will likely be red and scaly. Surgery is often used for removal, but if it has progressed significantly some reconstruction to the face may be needed. This is the second most common form of skin cancer, and can be quite painful to touch.
All skin cancer has the potential to be fatal, and regular checks and any necessary treatment is recommended. Melanoma is by far the most serious form of skin cancer, and if suspected you should seek an urgent skin check. Please contact My Skin Centre to book your appointment in the Perth region.
Also Check: Osteomyoma
What Happens If Precancers Go Untreated
As the name suggests, precancers are damaged skin cells that arent considered cancerous, but if they are left untreated, these lesions are at high risk to become skin cancer. There are two main types of precancerous skin conditions: actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi. Actinic keratosis looks like a rough, scaly patch of the skin that is usually red or brown. This condition may develop into squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Nevi are moles, and dysplastic nevi is a term that means a mole is abnormal. Dysplastic nevi may develop into melanoma without proper treatment. While precancerous skin cancers are not malignant on their own, the potential to develop into life-threatening forms of this condition means they need to be evaluated regularly.
Can Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Go Away On Its Own
They may go away on their own and come back. You should call your doctor if you notice a change in the color, texture, or appearance of your skin or if you have a sore that does not heal or bleeds. Your doctor can diagnose squamous cell carcinoma by examining the growth and performing a biopsy of the suspected area.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Do I Need To Know
- AKs are evidence of sustained sun damage. Having them raises your lifetime risk for skin cancer. Since having one AK means that its likely you have already developed more, this may translate into an especially elevated risk for developing an SCC.
- An untreated SCC can become invasive and even life-threatening.
Can Skin Cancer Be Prevented
In most cases, skin cancer can be prevented. The best way to protect yourself is to avoid too much sunlight and sunburns. Ultraviolet rays from the sun damage the skin, and over time lead to skin cancer.
Here are ways to protect yourself from skin cancer:
- Seek shade. Don’t spend long periods of time in direct sunlight.
- Wear hats with wide brims to protect your face and ears.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants to protect your arms and legs.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher that protect against burning and tanning rays. Apply the sunscreen 30 minutes before you go outside.
- Wear sunglasses to protect your eyes.
- Use a lip balm with sunscreen.
- Avoid the sun between 10:00 a.m. and 4:00 p.m.
- Show any changing mole to your healthcare provider.
Recommended Reading: Soderstrom Skin Cancer Screening
What Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like
Basal cell carcinomalookbasal cell carcinomalikelooks like
People Also Asked, what is a basal cell carcinoma pictures?
Basal cell carcinoma often occurs on the face and neck, where the skin is exposed to sunlight. These tumors are locally invasive and tend to burrow in but not metastasize to distant locations.
Also know, how serious is basal cell skin cancer? The Most Common Skin Cancer BCCs arise from abnormal, uncontrolled growth of basal cells. Because BCCs grow slowly, most are curable and cause minimal damage when caught and treated early. Understanding BCC causes, risk factors and warning signs can help you detect them early, when they are easiest to treat and cure.
Contents
Neglected Basal Cell Carcinomas In The 21st Century

Erika Varga
1Department of Dermatology and Allergology, Albert Szent-Györgyi Clinical Center, University of Szeged, Korányi fasor 6, 6720 Szeged, Hungary
2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Albert Szent-Györgyi Clinical Center, University of Szeged, Kálvária sgt. 57, 6725 Szeged, Hungary
Abstract
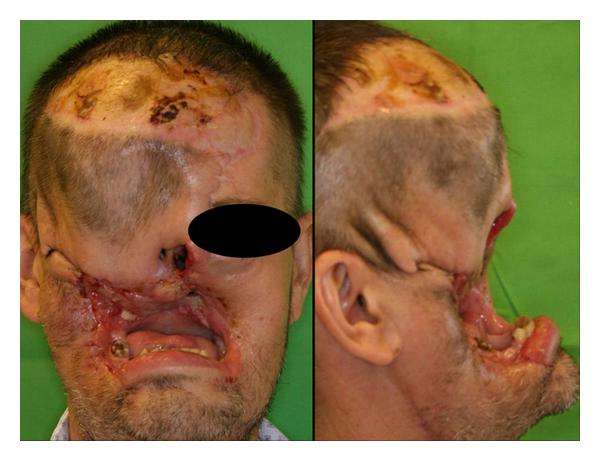
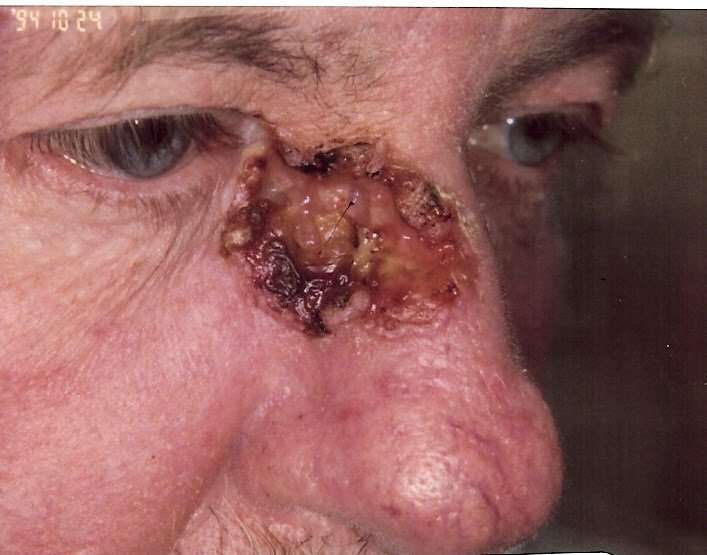
Although tumors on the surface of the skin are considered to be easily recognizable, neglected advanced skin neoplasms are encountered even in the 21st century. There can be numerous causes of the delay in the diagnosis: fear of the diagnosis and the treatment, becoming accustomed to a slowly growing tumor, old age, a low social milieu, and an inadequate hygienic culture are among the factors leading some people not to seek medical advice. The treatment of such advanced neoplasms is usually challenging. The therapy of neglected cases demands an individual multidisciplinary approach and teamwork. Basal cell carcinoma , the most common cutaneous tumor, usually develops in the elderly, grows slowly, and has an extremely low metastatic potential these factors are suggesting that BCCs might well be the ideal candidates for neglected tumors. Five neglected advanced cases of BCC were diagnosed in our dermatological institute between 2000 and 2009. The clinical characteristics and treatment modalities of these neoplasms are discussed, together with the possible causes of the neglect.
1. Introduction
2. Case Reports
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
References
Read Also: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Treatment Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
-
Removal of the tumor
Doctors may remove the cancer in the office by scraping and burning it with an electric needle or by cutting it out. Doctors may destroy the cancer by using extreme cold .
Certain chemotherapy drugs may be applied to the skin. Photodynamic therapy , in which chemicals and a laser are applied to the skin, also may be used. Occasionally, radiation therapy is used.
A technique called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery may be required for some basal cell carcinomas that are large or regrow or occur in certain areas, such as around the nose and eyes.
People whose cancer has spread to nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body and who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy may be given the drug vismodegib or sonidegib taken by mouth.
What Happens If Melanoma Is Left Untreated
Even though this form of skin cancer impacts a relatively low percentage of patients, melanoma skin cancers make up the majority of skin cancer deaths. Melanoma lesions often look like moles, freckles, or sunspots, and they may even develop within an existing mark on your body. Unlike other forms of skin cancer that are slow to progress and unlikely to spread to other areas, melanoma advances quickly and can form or spread anywhere on the body. In order to diagnose melanoma in the earliest stages, patients need to remember the ABCDEFs of melanoma, as discussed above.
You May Like: Basal Skin Cancer Survival Rates
Untreated Basal Cell Carcinoma
Any irregular marks or sores that refuse to heal should be checked by your dermatologist for a specific diagnostic and treatment plan. Non-melanoma skin cancer has a high success rate for treatment, but only when caught within a reasonable time frame.
While rare, untreated basal cell carcinoma can spread to other parts of the body, affecting surrounding tissues. The cancerous area can become quite large and in some cases cause disfigurement, especially when on the face. Small bumps can grow into massive protrusions that destroy healthy tissues and create permanent damage.
In extreme cases, untreated basal cell carcinoma can be fatal, so it is crucial to seek treatment as early as possible.
What Happens If I Dont Have A Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated
As mentioned above, basal cell carcinomas are almost never fatal, but they can be highly disfiguring if left to grow unimpeded. These lesions will grow wider and will penetrate more deeply into the skin, damaging underlying tissue and eventually bone. Removing these growths once they have become so established will involve removing much more surrounding tissue and possibly bone, which can be quite challenging if the growth is on an area such as the face.
Another thing about leaving a basal cell carcinoma untreated is that by doing so you are increasing the odds it will return even if it is removed at this point. Now youll have extra future costs of excision or another removal, along with more tissue loss.
None of this should happen. When basal cell carcinoma is diagnosed early on, removing the lesion is usually quite simple and the success rate is very high. If addressed early, its unlikely another basal cell carcinoma will return to that location, as well.
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
What Does Bcc Look Like
BCCs can look like open sores, red patches, pink growths, shiny bumps, scars or growths with slightly elevated, rolled edges and/or a central indentation. At times, BCCs may ooze, crust, itch or bleed. The lesions commonly arise in sun-exposed areas of the body. In patients with darker skin, about half of BCCs are pigmented .
Its important to note that BCCs can look quite different from one person to another. For more images and information on BCC signs, symptoms and early detection strategies, visit our BCC Warning Signs page.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these photos serve as a general reference to what they can look like. If you see something new, changing or unusual on your skin, schedule an appointment with your dermatologist.
An open sore that does not heal
A shiny bump or nodule
A reddish patch or irritated area
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
Signs Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC generally starts out in the upper layer of your skin. Thatâs called your epidermis. Hereâs what it may look like:
- A bloody or oozing sore that doesnât go away
- A rough patch of skin, usually in a sun-exposed area
- A reddish area that may hurt or itch
- A shiny bump thatâs clear, reddish, or white
- A flat white, yellow, or âwaxyâ area that looks like a scar
- A colored mole-like bump
BCC tends to grow slower than other kind of cancer, but thatâs not always the case. And if itâs advanced BCC, it can spread much deeper into your tissue. Call your doctor if you see any of these changes in your skin. Ask them about genetic conditions and other risk factors that can raise your chances of advanced BCC.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
What Causes Basal Cell Carcinoma
Currently, about 8 in 10 diagnosed skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma. Because basal cell cancer grows slowly, most are curable and cause minimal damage when caught and treated early.
Understanding basal cell carcinoma causes, risk factors and warning signs can help you prevent the disease or detect it early, when it is easiest to treat.
Exposure to UV rays from the sun and indoor tanning is the major cause of basal cell carcinoma and most skin cancers. About 90% of non-melanoma skin cancers are associated with UV radiation.
Symptoms
Taking Care Of Yourself
After you’ve been treated for basal cell carcinoma, you’ll need to take some steps to lower your chance of getting cancer again.
Check your skin. Keep an eye out for new growths. Some signs of cancer include areas of skin that are growing, changing, or bleeding. Check your skin regularly with a hand-held mirror and a full-length mirror so that you can get a good view of all parts of your body.
Avoid too much sun. Stay out of sunlight between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m., when the sun’s UVB burning rays are strongest.
Use sunscreen. The suns UVA rays are present all day long — thats why you need daily sunscreen. Make sure you apply sunscreen with at least a 6% zinc oxide and a sun protection factor of 30 to all parts of the skin that aren’t covered up with clothes every day. You also need to reapply it every 60 to 80 minutes when outside.
Dress right. Wear a broad-brimmed hat and cover up as much as possible, such as long-sleeved shirts and long pants.
Continued
You May Like: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
The Dangers Of Untreated Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the world. Brought on typically by overexposure of UV rays , skin cancer can be prevented and oftentimes easily treated. However, if left untreated, no matter which type of skin cancer you have, it will undoubtedly cause severe health complications and may even lead to death. Lets break it down a bit and walk you through what would happen if skin cancer were left untreated.
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Survival Rates
Because basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are lower-risk skin cancers, theres little information on survival rates based on stage.
Both types of cancer have a very high cure rate. According to the Canadian Cancer Society, the five-year survival rate for basal cell carcinoma is 100 percent. The five-year survival rate for squamous cell carcinoma is 95 percent.
Recommended Reading: What Race Is More Likely To Get Skin Cancer
Whats The Outlook For Stage 4 Melanoma
Once the cancer spreads, locating and treating the cancerous cells becomes more and more difficult. You and your doctor can develop a plan that balances your needs. The treatment should make you comfortable, but it should also seek to remove or slow cancer growth. The expected rate for deaths related to melanoma is 10,130 people per year. The outlook for stage 4 melanoma depends on how the cancer has spread. Its usually better if the cancer has only spread to distant parts of the skin and lymph nodes instead of other organs.
Also Check: What Are The Early Stages Of Skin Cancer