Looking For More About The Latest Research
If you would like additional information about the latest areas of research regarding head and neck cancer, explore these related items that take you outside of this guide:
-
To find clinical trials specific to your diagnosis, talk with your doctor or search online clinical trial databases now.
ON THIS PAGE: You will learn more about coping with the physical, emotional, social, and financial effects of cancer and its treatment. Use the menu to see other pages.
Every cancer treatment can cause side effects or changes to your body and how you feel. For many reasons, people do not experience the same side effects even when they are given the same treatment for the same type of cancer. This can make it hard to predict how you will feel during treatment. People who are being treated for head and neck cancer may find it helpful to reach out to support groups that specialize in helping people being treated for this type of cancer. If you do not live near a support group or prefer receiving support in a different way, many patient advocacy groups offer one-on-one matching programs for patients as well as caregivers.
The Molecular Pathogenesis Of Head And Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
Address correspondence to: Leif W. Ellisen, MGH Cancer Center, GRJ-904, 55 Fruit Street, Boston, Massachusetts 02114, USA. Phone: 617.726.4315; Fax: 617.726.8623; E-mail: .
Find articles byRothenberg, S.in: |PubMed |
Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
Address correspondence to: Leif W. Ellisen, MGH Cancer Center, GRJ-904, 55 Fruit Street, Boston, Massachusetts 02114, USA. Phone: 617.726.4315; Fax: 617.726.8623; E-mail: .
J Clin Invest.
-
As noted above, the relative lack of readily targeted oncogenes in these tumors has challenged traditional approaches to drug development for HNSCC. Nevertheless, the increasingly refined knowledge of epithelial biology and HNSCC genetics, combined with newer approaches aimed at targeting proteins previously thought undruggable, could lead to novel therapies with greater potency and less toxicity for these cancers . These conceptual advances will allow the development of ever-more-sophisticated animal models, which in turn will be essential for testing the emerging host of candidate targeted therapeutics, and for determining which of these may have the most clinical viability. A strong biologic rationale will be essential if progress against this disease is to be accelerated in the near term.
What Are Head And Neck Cancer Symptoms
Head and neck cancer symptoms may include a lump in the neck or a sore in the mouth or the throat that does not heal and may be painful, a sore throat that does not go away, difficulty in swallowing, and a change or hoarseness in the voice. These symptoms may also be caused by other, less serious conditions. It is important to check with a doctor or dentist about any of these symptoms.
Symptoms of cancers in specific areas of the head and neck include:
Oral cavity. A white or red patch on the gums, the tongue, or the lining of the mouth; a growth or swelling of the jaw that causes dentures to fit poorly or become uncomfortable; and unusual bleeding or pain in the mouth.
Throat . Pain when swallowing; pain in the neck or the throat that does not go away; pain or ringing in the ears; or trouble hearing.
Voice box . Trouble breathing or speaking, pain when swallowing or ear pain.
Paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity. Sinuses that are blocked and do not clear; chronic sinus infections that do not respond to treatment with antibiotics; bleeding through the nose; frequent headaches, swelling or other trouble with the eyes; pain in the upper teeth; or problems with dentures.
Salivary glands. Swelling under the chin or around the jawbone, numbness or paralysis of the muscles in the face, or pain in the face, the chin, or the neck that does not go away.
Don’t Miss: Can Melanoma Be Treated Successfully
Head And Neck: Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Overview
| 2011-09 | Audrey Rousseau, Cécile Badoual | |
| Universite d’Angers, Departement de Pathologie Cellulaire et Tissulaire, CHU Angers, 4 rue Larrey, 49100 Angers, France ; Universite Rene Descartes Paris 5, Service d’Anatomie Pathologique, Hopital Europeen Georges Pompidou, 20 rue Leblanc, 75015 Paris, France |
| 8070/3 Squamous cell carcinoma, NOS | |
| Atlas_Id | |
| Head and Neck::Squamous cell carcinoma | |
| WHO/OMS Classification | Head and Neck |
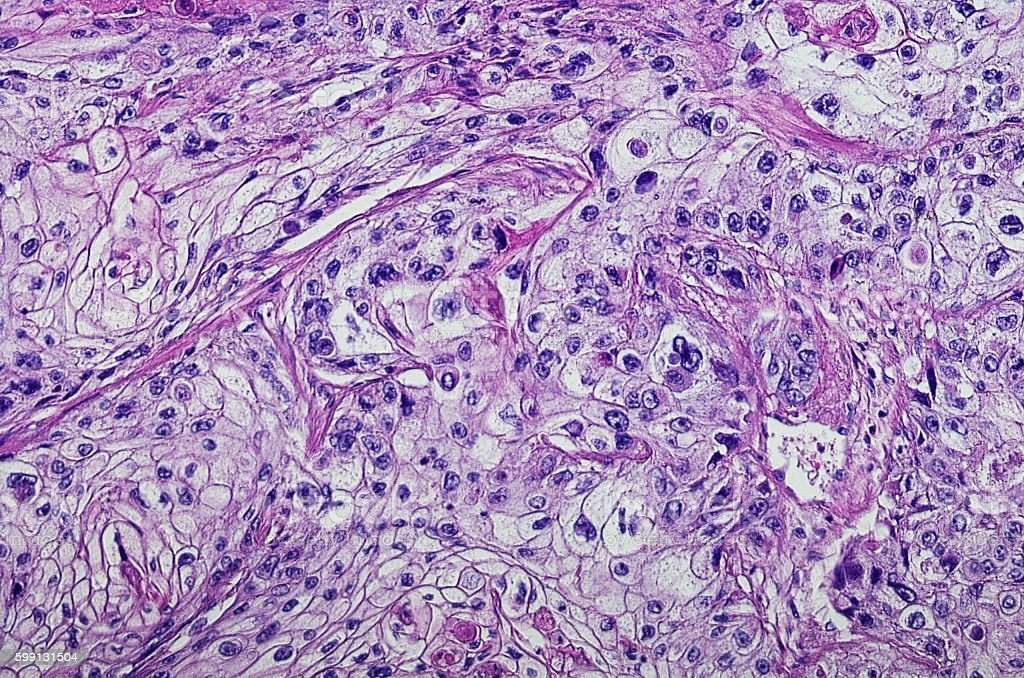
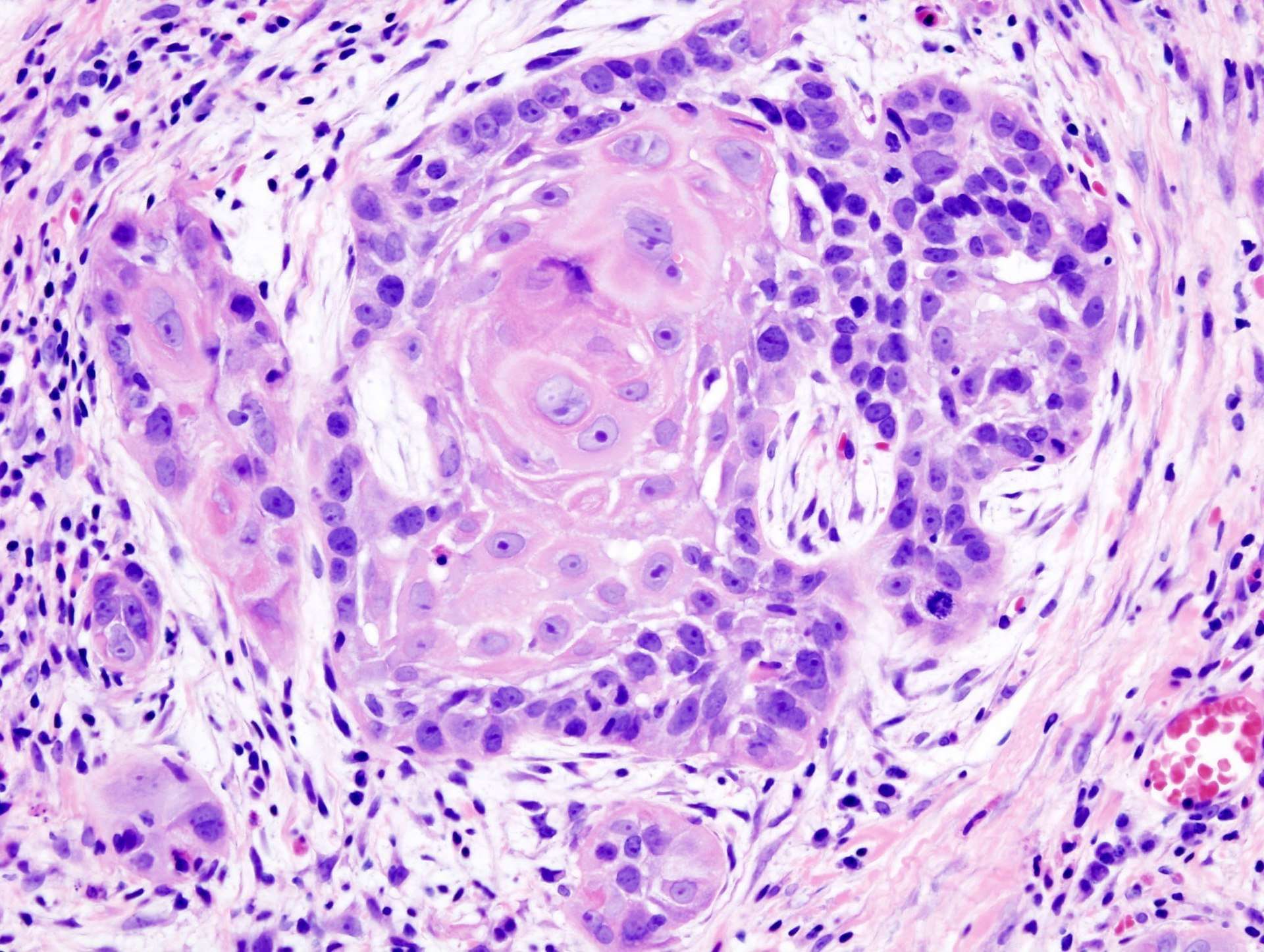
| Note | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma develops from the mucosal linings of the upper aerodigestive tract, comprising 1) the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, 2) the nasopharynx, 3) the hypopharynx, larynx, and trachea, and 4) the oral cavity and oropharynx. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most frequent malignant tumor of the head and neck region. HNSCC is the sixth leading cancer by incidence worldwide. There are 500000 new cases a year worldwide. Two thirds occur in industrialized nations. HNSCC usually develops in males in the 6th and 7th decade. It is caused by tobacco and alcohol consumption and infection with high-risk types of human papillomavirus . SCC often develops from preexisting dysplastic lesions. The five-year survival rate of patients with HNSCC is about 40-50%. |
| Classification |
| Clinics and Pathology |
The Ljubljana classification of squamous intraepithelial lesions has also been proposed .
2005 WHO Classification
SIN 3
Carcinoma in situ
| Bibliography |
How Do People Find Bcc On Their Skin
Many people find it when they notice a spot, lump, or scaly patch on their skin that is growing or feels different from the rest of their skin. If you notice any spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist. These doctors have the most training and experience in diagnosing skin cancer.
To find skin cancer early, dermatologists recommend that everyone check their own skin with a skin self-exam. This is especially important for people who have a higher risk of developing BCC. Youll find out what can increase your risk of getting this skin cancer at, Basal cell carcinoma: Who gets and causes.
Images used with permission of:
-
The American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
-
J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:303-17.
Dont Miss: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
Also Check: How Fast Does Melanoma Metastasis
What You Need To Know
According to the American Cancer Society, head and neck cancer affected over 61,000 patients in the United States in 2016. In fact, cancer of the mouth and throat was the eighth most common cancer diagnosed in men last year. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is the most frequent tumor of the head and neck region, developing in the mucous membrane of the mouth, nose and throat.
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Surgery is the preferred management method for the majority of squamous cell skin cancers. Low-risk, early stage, small squamous cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, which is a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Excision, curettage and desiccation, and cryosurgery can also be used to remove the cancer while sparing normal tissue. Radiation alone is an alternative for low-risk tumors when surgery is not desirable because of cosmetic concerns or medical reasons.
Large tumors and tumors with nerve or lymph node involvement are not suitable for Mohs surgery and require removal of at least 5-millimeter margins of normal tissue around the cancer and neck dissection for involved lymph nodes. Larger tumors require reconstruction, which can be done at the time of surgery if margin status is clear. Reconstruction should be staged when margins status is not clear.
Patients with high-risk tumors should meet with a radiation therapist to discuss postoperative radiation. Chemotherapy may be added to radiation for extensive lymph node involvement or positive margins that cannot be cleared with additional surgery. In patients with high-risk tumors who are not surgical candidates, systemic treatment with both radiation and chemotherapy is used. Such cases require multidisciplinary care by a team of surgeons, radiation oncologists and medical oncologists.
Recommended Reading: How Bad Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Diagnostic Tumor Markers In Head And Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma In The Clinical Setting
- 1Section of Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Attikon University Hospital, Athens, Greece
- 2Department of Head and Neck Surgical Oncology, UMC Utrecht Cancer Center, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma represents a group of tumors arising in the oral cavity, oropharynx, and larynx. Although HNSCC is traditionally associated with tobacco and alcohol consumption, a growing proportion of head and neck tumors, mainly of the oropharynx, are associated with Human Papilloma Virus . Recurrent/metastatic disease is characterized by dismal prognosis and there is an unmet need for the development of biomarkers for detection of early disease, accurate prediction of prognosis, and appropriate selection of therapy. Based on the REMARK guidelines, a variety of diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers are being evaluated in clinical trials but their clinical significance is doubtful. Herein, we will focus on biomarkers in HNSCC used in the clinical setting and we will illustrate their clinical relevance.
Patient Health And Supportive Care
Given the complex nature of everyday functions within the head and neck area, the inherent consequences of HNSCC and its treatment and the increasing choices of treatments have a large effect on the health-related QOL of patients with HNSCC.
The wide array and combinations of treatments all have their specific sequelae, including physical, emotional, functional, social, and occupational dysfunction, as well as a profound effect on the families of patients with HNSCC. Furthermore, HRQOL is significantly associated with survival,. For example, a clinically meaningful association exists between HRQOL scores measured at diagnosis and overall survival of patients after treatment . Depending on the primary tumour site, patients with HNSCC might be confronted with specific symptoms, such as oral dysfunction and swallowing and speech problems, during treatment, which often improve 6 months after treatment. However, long-term reduction in QOL in HNSCC survivors is common. On average, overall HRQOL deteriorated by 11% when compared with pre-treatment, and by 15% when compared with years 1 and 2 post-treatment.
You May Like: How To Identify Skin Cancer
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated
The treatment options depend on the stage and type of skin cancer. For localized cancers, the following treatment may be used
- Curettage and electrodessication : Scraping the cancerous ulcer with a curette and then searing the base of the cancer with an electric needle is one treatment method.
- Laser therapy: Laser treatment may be an option for very superficial skin lesions. It is used to burn down cancer cells.
- Freezing: Liquid nitrogen is used to freeze and kill the cancer cells. Freezing might be done after using a scraping instrument to remove the surface of the skin cancer.
- : The cancer cells are sensitized to light with chemicals and then exposed to light.
The most common treatment in large cancers include
- Excision: The removal of the tumor.
- Moh surgery: The removal of the tumor layer by layer and examination of each layer under a microscope until no cancer cells are seen.
- Surgery to remove cancerous lymph nodes as well as healthy lymph nodes in more invasive cancers. Complications of surgery include bleeding, infection or pneumonia.
- Radiation therapy:Radiation of high frequency destroys the cancerous cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses medications to kill cancerous cells.
You May Like: What Is Soft Tissue Carcinoma
Treatment For Head And Neck Cancers
Cancers affecting the head and neck are not common. People with this type of cancer are usually treated in specialist centres by a team of healthcare professionals.
A team of specialists will meet to discuss the best possible treatment for you. This is called a;multidisciplinary team .
Your doctor or cancer specialist or nurse will explain the different treatments and their side effects. They will also talk to you about things to consider when making treatment decisions.
Treatment for head and neck cancers may include:
We have more information about:
Don’t Miss: How To Remove Skin Cancer Yourself
Q: What Does Asco Recommend For Surgery For Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Unknown Primary In The Head And Neck
A: First, as part of diagnosis, all patients need a complete surgical evaluation of the upper aerodigestive path. The surgeon is able to better visualize all tissues and samples are taken from any places where there is suspicion of possible cancer.
The recommendations for surgery also include when to do tonsillectomies and what tonsillectomies to do. The recommendations are based on how much cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. Is there cancer in lymph nodes on both sides of the neck? Or on just one side? How big are the nodes? Is there a concern that there is cancer extending outside of the capsule of the lymph nodes? That all plays a role in the recommendations regarding surgical diagnostics or intervention.
If a primary tumor is identified and a therapeutic surgery is planned, there are clear recommendations and guidelines to make every effort to remove the tumor with negative margins; this means no cancer cells are found at the edge of the removed tumor. The reason we want to stress that negative margins are the goal is because we’re trying to avoid having to use 3 types of treatment, which is called trimodal therapy. If surgery leaves a positive margin, that is likely going to lead to recommendations for radiation therapy plus chemotherapy. We want to try to avoid the side effects that come with trimodal therapy.
Immunotherapeutic Strategies For Hpv Hnscc
Improved understanding of the role of the immune system in cancer has led to the identification of a range of novel therapeutic targets. Immuno-oncology is an evolving field of investigation that includes active immunotherapies that are designed to target and harness the patients own immune system directly to fight cancer. More specifically, it is designed to leverage the unique properties of the immune system .The primary goal of immunotherapy is to shift the balance in favor of an immune response against the tumor, allowing tumor eradication or long-term suppression of tumor growth, and the generation of immunological memory.
Also Check: How Often Does Melanoma Spread To Lymph Nodes
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck: Current Status And Future Directions
Although head and neck cancers include multiple histologies and primary sites, squamous cell carcinomas originating in the oropharynx, oral cavity, larynx, or hypopharynx are the most common. Today, we recognize different types of head and neck cancers, primarily those that are human papillomavirus -positive and those that are HPV-negative. In the locally advanced curative-intent setting, a good prognosis has driven the study of de-escalation therapy in the former group, whereas a poor prognosis has led to escalation of therapy trials in the latter. Additionally, there is recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck SCC , where all systemic therapy is palliative, regardless of HPV status, and there continues to be a great need for improvement in outcomes for all patients. Important progress has been made recently, driving the field in new directions.
In the field of head and neck cancer, we strive for the next big jump in the recurrent and/or metastatic setting, like the one we achieved with antiPD-1 monoclonal antibodies. Dan P. Zandberg, MDTweet this quote
HPV-Positive Oropharyngeal SCC
Over the past 3 decades, it has become apparent that HPV causes SCC in the oropharynx, with a continued rise in incidence of these cancers over time. HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer has a significantly better prognosis, with clinical risk stratification by smoking status and stage used to identify patients with low-risk cancer and intermediate-risk cancer.
HPV-Negative HNSCC
What Kind Of Treatment Follow
There are several reasons for follow-up examinations:
- To detect recurrent cancer and possibly try further treatment, such as an operation, if the radiation therapy is unsuccessful
- To treat the acute side effects of the radiation therapy
- To detect and treat late side effects or complications from the radiation therapy, should they occur
- To detect and treat additional, unrelated head and neck cancers that may arise
If the initial treatment for the cancer is successful and you are cured, there is still a relatively low risk of developing a new, completely unrelated head and neck cancer. Per the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, follow-up examinations usually take place:
- Every one to three months for the first year
- Every two months to six months for the second year
- Every four to eight months for the years three through five
- Annually thereafter
Thyroid functions are often checked annually to detect any occurrence of hypothyroidism , which is easily treatable.
Continued imaging follow-up is typically performed both to assess the response to treatment and to monitor for disease recurrence. CT scans are most commonly performed for this purpose, however, MRI and fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography may also be performed in certain situations.
Dental exams for oral cavity and sites exposed to significant intraoral radiation treatment.
Also Check: What Is The Main Cause Of Skin Cancer
Citation Doi And Article Data
Citation:DOI:Assoc Prof Frank GaillardRevisions:see full revision historySystems:
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Squamous carcinoma of the head and neck
- SCC of the head and neck
- Head and neck SCC
Head and neck squamous cell carcinomas ;are common, being the sixth most common cancer.;They can have a cutaneous or mucosal origin. As such there is a wide array of clinical and radiographic manifestations, and are separated into:
Finding A Clinical Trial
Research through clinical trials is ongoing for all types of cancer. For specific topics being studied for head and neck cancer, learn more in the Latest Research section.
ON THIS PAGE: You will read about the scientific research being done to learn more about head and neck cancer and how to treat it. Use the menu to see other pages.
Doctors are working to learn more about head and neck cancer, ways to prevent it, how to best treat it, and how to provide the best care to people diagnosed with this disease. The following areas of research may include new options for patients through clinical trials. Always talk with your doctor about the best diagnostic and treatment options for you.
Read Also: How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Removed From The Nose