Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Melanoma Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
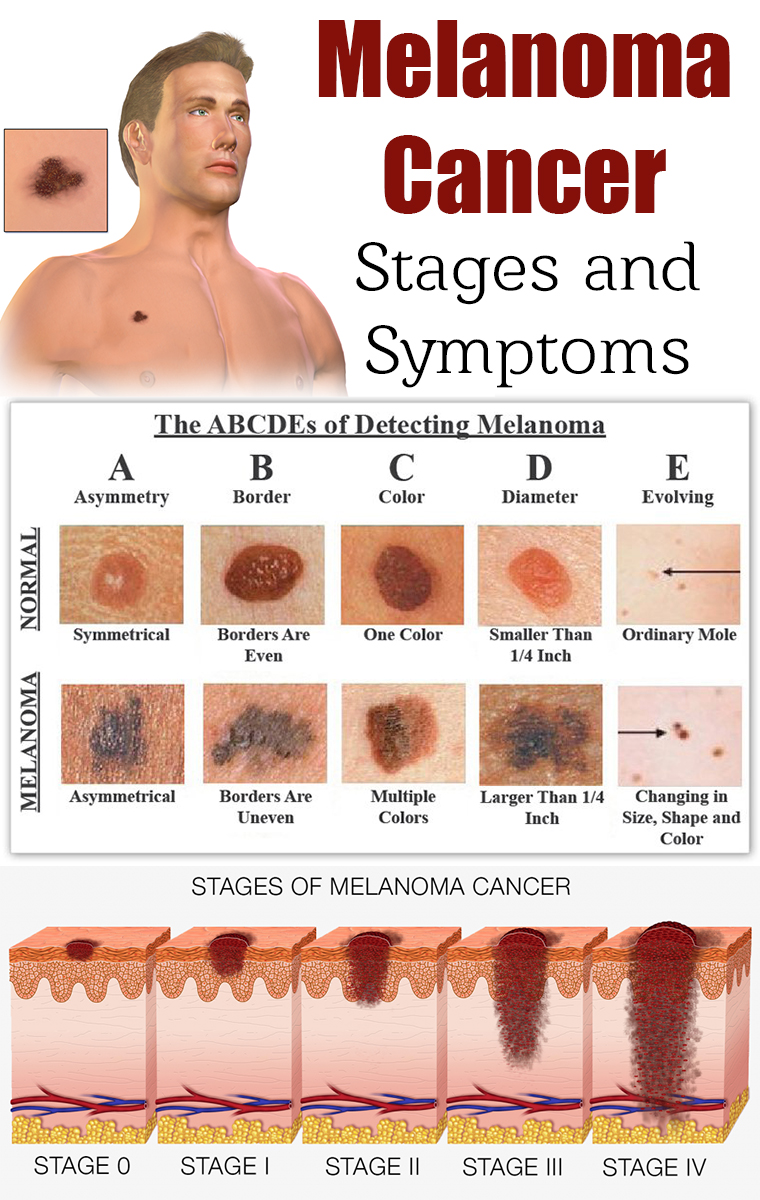
How Do Dermatologists Diagnose Melanoma
When you see a board-certified dermatologist, your dermatologist will:
-
Examine your skin carefully
-
Ask questions about your health, medications, and symptoms
-
Want to know if melanoma runs in your family
If any spot on your skin looks like skin cancer, your dermatologist will first numb the area and then remove all of it. This can be done during an office visit and is called a skin biopsy. This is a simple procedure, which a dermatologist can quickly, safely, and easily perform.
Having a skin biopsy is the only way to know for sure whether you have skin cancer.
The tissue that your dermatologist removes will be sent to a lab, where a doctor, such as a dermatopathologist, will examine it under a high-powered microscope. The doctor is looking for cancer cells.
What this doctor sees while looking at your tissue will be explained in the pathology report, including whether cancer cells were seen. If melanoma cells are seen, the report will include many important details, including:
-
The type of melanoma
-
How deeply the melanoma tumor has grown into the skin
-
How quickly the melanoma cells are growing and dividing
If its possible to tell the stage of the melanoma, the report will include this information.
Stages of melanoma
Heres an explanation of what each stage of melanoma means:
Stages of melanoma
Stage 0
The melanoma has spread to either: One or more nearby lymph node Nearby skin
Once the stage is known, the next step is treatment.
How Can I Prevent Malignant Melanoma
Now that you know what is melanoma, what is next? Checking your skin is the most important thing you can do to find malignant melanomas early. So it is important that you understand the signs of melanoma that you should point out to your doctor. These include any unusual moles that are irregular in shape or color, that are bleeding or itchy or have grown at any time over the age of 30.
You should also be aware of your own personal risk factors to prevent melanoma. These include a family history of melanoma, exposure to high degrees of sunlight in your early life , fair or easily burned skin and if you have more than 11 moles on one arm this indicates that you have more than the average number of moles across your body.
Knowing how to check your moles and avoiding the harmful sun can ensure that you are unlikely to be caught out by a malignant melanoma that you didnt know was there.
But regular checks by your doctor or a dermatologist make great sense for anyone who has any of the risk factors stated above.
Read more about Malignant melanoma symptoms
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
The Following Stages Are Used For Melanoma:
Stage 0
Stage I
- Stage IA: The tumor is not more than 1millimeter thick, with or without ulceration.
- Stage IB: The tumor is more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Enlarge Stage I melanoma. In stage IA, the tumor is not more than 1 millimeter thick, with or without ulceration . In stage IB, the tumor is more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body.
Stage II
- Stage IIA: The tumor is either:
- more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, with ulceration or
- more than 2 but not more than 4 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Enlarge Stage IIA melanoma. The tumor is more than 1 but not more than 2 millimeters thick, with ulceration OR it is more than 2 but not more than 4 millimeters thick, without ulceration. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body.
Stage III
Stage III is divided into stages IIIA, IIIB, IIIC, and IIID.
After Melanoma Has Been Diagnosed Tests May Be Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Skin Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out whether cancer has spread within the skin or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment.
For melanoma that is not likely to spread to other parts of the body or recur, more tests may not be needed. For melanoma that is likely to spread to other parts of the body or recur, the following tests and procedures may be done after surgery to remove the melanoma:
The results of these tests are viewed together with the results of the tumor biopsy to find out the stage of the melanoma.
Don’t Miss: Treatment For Stage 3 Melanoma
Combined Nivolumab And Ipilimumab
Nivolumab and ipilimumab have complementary activity in metastatic melanoma. In the CheckMate 067 study, a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, phase 3 trial in 945 previously untreated patients with metastatic melanoma, nivolumab combined with ipilimumab and nivolumab alone resulted in significantly longer progression-free survival than ipilimumab alone in those patients with PD-L1negative tumors, combination therapy was more effective than either agent alone.
On 5-year follow-up of CheckMate 067 patients, overall survival was 52% in the nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group, compared with 44% in the nivolumab group and 26% in the ipilimumab group. Median overall survival was more than 60.0 months in the nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group, 36.9 months in the nivolumab group, and 19.9 months in the ipilimumab group. Hazard ratios for death were 0.52 with nivolumab plus ipilimumab vs. ipilimumab, and 0.63 with nivolumab vs. ipilimumab.97 Current National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines include nivolumab plus ipilimumab as one of the preferred first-line therapeutic options for unresectable or malignant melanoma.
How Do You Stage Malignant Melanoma
The staging system most often used for melanomas is based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system. The TNM staging system is a very detailed system.
- T: The T refers to the size and extent of the primary tumor.
- N: Refers to the number of nearby lymph nodes where cancer is detected on pathologic exam.
- M: Whether the tumor has metastasized to spread to regional lymph nodes or to other organs or areas of the body.
Physicians and cancer registries often refer to a five-stage system that groups the TNM stages into a less-detailed staging system.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Forms Of Skin Cancer
Recurrence In Other Parts Of The Body
Melanoma can also come back in distant parts of the body. Almost any organ can be affected. Most often, the melanoma will come back in the lungs, bones, liver, or brain. Treatment for these recurrences is generally the same as for stage IV melanoma . Melanomas that recur on an arm or leg may be treated with isolated limb perfusion/infusion chemotherapy.
Melanoma that comes back in the brain can be hard to treat. Single tumors can sometimes be removed by surgery. Radiation therapy to the brain may help as well. Systemic treatments might also be tried.
As with other stages of melanoma, people with recurrent melanoma may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial.
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor. Your doctor may have reasons for suggesting a treatment plan different from these general treatment options. Don’t hesitate to ask him or her questions about your treatment options.
Skin Exam And Physical
If youve been diagnosed with melanoma, youve already had a skin biopsy. This biopsy was taken when you had part of the suspicious spot removed. After it was removed, a doctor looked at the spot under a microscope to find out if it contained cancer cells. This is currently the only way to tell if someone has skin cancer.
After getting the diagnosis, the next step is to get a complete skin exam and physical.
During the physical, your dermatologist will feel your lymph nodes. This is where melanoma usually goes when it begins to spread. It usually travels to the lymph nodes closest to the melanoma.
If there is a risk the cancer could have spread, your dermatologist may recommend that you have a lymph node biopsy. If a sentinel lymph node biopsy is recommended, it can be performed at the time of your surgery for melanoma.
After the skin exam and physical, your dermatologist may recommend testing, such as a CAT scan, MRI, or a blood test. These can also help detect spread.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take Melanoma To Metastasize
There Are Different Types Of Treatment For Patients With Melanoma
Different types of treatment are available for patients withmelanoma. Some treatments arestandard , and some are being tested inclinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
If Treatment Does Not Work
Recovery from melanoma is not always possible. If the cancer cannot be cured or controlled, the disease may be called advanced or terminal.
This diagnosis is stressful, and for many people, advanced cancer is difficult to discuss. However, it is important to have open and honest conversations with your health care team to express your feelings, preferences, and concerns. The health care team has special skills, experience, and knowledge to support patients and their families and is there to help. Making sure a person is physically comfortable, free from pain, and emotionally supported is extremely important.
People who have advanced cancer and who are expected to live less than 6 months may want to consider hospice care. Hospice care is designed to provide the best possible quality of life for people who are near the end of life. You and your family are encouraged to talk with the health care team about hospice care options, which include hospice care at home, a special hospice center, or other health care locations. Nursing care and special equipment can make staying at home a workable option for many families. Learn more about advanced cancer care planning.
After the death of a loved one, many people need support to help them cope with the loss. Learn more about grief and loss.
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Prognostic Factors For Metastatic Melanoma
Many factors have been proposed to influence the prognosis in patients with metastatic melanoma. The impact of the initial site of metastasis on survival was studied in a multivariate analysis of 1,521 patients with stage IV melanoma. Three groups of patients were identified: those with cutaneous, nodal, or gastrointestinal tract metastases those with isolated pulmonary metastases and those with liver, brain, or bone metastases. The median survivals in these three groups were 12.5, 8.3, and 4.4 months, respectively. The 5-year actuarial survivals were 14%, 4%, and 3%, respectively. In addition to the site of disease, the presence of an elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase has also been associated with poor prognosis. The 2002 American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system of cutaneous melanoma classifies patients with metastatic disease into three categories based on the site of metastases and serum LDH level .
Ipilimumab For Advanced Melanoma
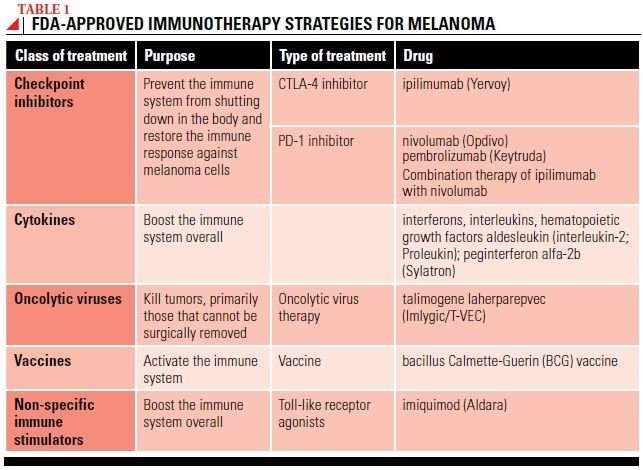
Ipilimumab can be effective for people with metastatic melanoma and stage III melanoma that cannot be removed completely with surgery. Ipilimumab works by blocking an immune molecule called CTLA-4.
In 2004, MSK patients were among the first in the world to receive ipilimumab treatment. MSK led the first clinical studies showing that ipilimumab could prolong the overall survival of people with metastatic melanoma. The US Food and Drug Administration approved the drug for general use in 2011. Clinical trials gave MSK patients the opportunity to receive ipilimumab years before the FDA approved it.
You May Like: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis and treatment options depend on the following:
- The thickness of the tumor and where it is in the body.
- How quickly the cancer cells are dividing.
- Whether there was bleeding or ulceration of the tumor.
- How much cancer is in the lymph nodes.
- The number of places cancer has spread to in the body.
- The level of lactate dehydrogenase in the blood.
- Whether the cancer has certain mutations in a gene called BRAF.
- The patients age and general health.
Surgical Removal Of The Melanoma
Treating early melanoma
Stage 0 in situ and stage I
Tumors discovered at an early stage are confined to the upper layers of the skin and have no evidence of spread. These melanomas are treated by excisional surgery. Usually, this is the only treatment required. The first step was a biopsy, where the physician removed part or all of the lesion and sent it to a lab for analysis, where the melanoma was diagnosed and staged. For the excisional surgery, the surgeon removes more tissue from the site.
Melanoma in situ is localized to the outermost layer of skin . Stage I melanoma has invaded the second layer of skin . In both stage 0 and stage I melanoma cases, the physician uses a scalpel to remove any remaining tumor plus a safety margin of surrounding normal tissue. The margin of normal skin removed depends on the thickness and location of the tumor. After surgery the margins are checked to make sure they are cancer-free. If the margins are cancer-free, no further surgery is necessary.
Surgeons may, under certain circumstances, recommend removal of melanoma by Mohs surgery. The procedure is done in stages over a few days to remove all of the cancer cells in layers while sparing healthy tissue and leaving the smallest possible scar. One layer at a time is removed and examined until the margins are cancer-free. New advances in this technique make it easier for the surgeon to spot melanoma cells in the margins.
Treating intermediate, high-risk melanomas
Stage II
Don’t Miss: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
Treating Stage Iii Melanoma
These cancers have already reached the lymph nodes when the melanoma is first diagnosed. Surgical treatment for stage III melanoma usually requires wide excision of the primary tumor as in earlier stages, along with lymph node dissection.
After surgery, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or with targeted therapy drugs may help lower the risk of the melanoma coming back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines may also be recommended as part of a clinical trial to try to reduce the chance the melanoma will come back. Another option is to give radiation therapy to the areas where the lymph nodes were removed, especially if many of the nodes contain cancer.
If melanoma tumors are found in nearby lymph vessels in or just under the skin , they should all be removed, if possible. Other options include injections of the T-VEC vaccine , Bacille Calmette-Guerin vaccine, or interleukin-2 directly into the melanoma radiation therapy or applying imiquimod cream. For melanomas on an arm or leg, another option might be isolated limb perfusion or isolated limb infusion . Other possible treatments might include targeted therapy , immunotherapy, or chemotherapy.
Some people with stage III melanoma might not be cured with current treatments, so they may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial of newer treatments.
Can Changing My Diet Help Prevent Melanoma
The American Cancer Society advocates eating a plant-based diet over an animal-based diet as part of a healthy plan to avoid all cancers. Growing evidence suggests that plants pack a powerful punch in any fight against cancer because they’re nutritious, cholesterol-free and fiber-rich.
Theres no doubt that a healthy diet can protect your immune system. Having a strong immune system is important to help your body fight disease. Some research has shown that a Mediterranean diet is a healthy choice that may help prevent the development of cancer. Talk to your healthcare provider about the role food plays in lowering your cancer risks.
Some skin and immune-system healthy foods to consider include:
- Daily tea drinking: The polyphenols in tea help strengthen your immune system. Green tea contains more polyphenols than black tea.
- High vegetable consumption: Eating carrots, cruciferous and leafy vegetables is linked to the prevention of cutaneous melanoma.
- Weekly fish intake: Study participants who ate fish weekly seemed to avoid developing the disease when compared to those who did not eat fish weekly.
Recommended Reading: What Is Braf Melanoma