What Are The Chances Of Breast Cancer Recurrence After Treatment For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
In women who have breast-conserving treatment, the chance of recurrence is about 3-15% in 10 years, depending on tumor characteristics and margins. Distant recurrence in those who had mastectomy is most influenced by axillary lymph node involvement. When axillary lymph nodes are not cancerous, the recurrence rate is 6% in 5 years. When axillary lymph nodes are cancerous, the recurrence rate is 23% in 5 years with mastectomy but no radiation.
What Is Invasive Breast Cancer
Invasive breast cancer is the most common type of breast cancer.
Invasive means the cancer cells have spread outside the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue.
NST stands for no special type.
Its called no special type because the cancer cells have no features that class them as a special type of breast cancer when examined under the microscope.
You may also hear it called:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast
- Breast cancer not otherwise specified
Sometimes invasive breast cancer is found mixed with other types of breast cancer.
Although its rare, men can get breast cancer. Invasive breast cancer is the most common type of breast cancer in men.
Breast cancer is Invasive when cancer cells have spread outside the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue.
Hormone Receptor Status Influences Breast Cancer Survival Rates
The hormone receptor status of a breast tumour is not usually included in formal discussions of prognosis.
Each breast tumour will potentially have a different hormone receptor status. When a breast cancer tumour tests positive for the hormones estrogen and progesterone, it implies two things:-
Therefore, due to improvements in treatments, overall survival rates will be higher for hormone receptor positive breast tumors than for those that are hormone negative.
Read Also: Life Expectancy Metastatic Melanoma
Causes Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Unfortunately, doctors have yet to figure out the exact cause of invasive ductal carcinoma. When you get this type of cancer, it means something damaged your cells’ DNA and caused it to change. The result is that the cells grow abnormally and uncontrollably in your breast tissue.
Doctors are still looking for genetic and environmental factors that damage the DNA. They have determined that caffeine, deodorant, microwaves and cell phone use do not lead to this type of cancer.
How Can I Protect Myself From Breast Cancer
Follow these three steps for early detection:
- Get a mammogram. The American Cancer Society recommends having a baseline mammogram at age 35, and a screening mammogram every year after age 40. Mammograms are an important part of your health history. Recently, the US Preventive Services Task Force came out with new recommendations regarding when and how often one should have mammograms. These include starting at age 50 and having them every two years. We do not agree with this, but we are in agreement with the American Cancer Society and have not changed our guidelines, which recommend yearly mammograms starting at age 40.
- Examine your breasts each month after age 20. You will become familiar with the contours and feel of your breasts and will be more alert to changes.
- Have your breast examined by a healthcare provider at least once every three years after age 20, and every year after age 40. Clinical breast exams can detect lumps that may not be detected by mammogram.
Recommended Reading: Large Cell Cancers
Hormone Therapy After Breast Surgery
If the DCIS is hormone receptor-positive , treatment with tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor, such as exemestane or anastrozole, for 5 years after surgery can lower the risk of another DCIS or invasive cancer developing in either breast. If you have hormone receptor-positive DCIS, discuss the reasons for and against hormone therapy with your doctor.
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:
Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Mammary Carcinoma Survival Rate
Treatment For Invasive Breast Cancer
Treatment for invasive breast cancer usually involves some combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy and/or HER2-targeted therapy.
The order of therapies and the specific treatments depend on the cancer stage and the characteristics of the tumor .
Learn more about treatment.
Prognosis And Survival Rate
The prognosis depends on each patients factors like tumor size, histological considerations and biological factors. However, tumor that has bigger sizes are most likely with higher mortality rate. Tumor size that is 5 cm has 50-60% survival rate. With tumor sizes less than 1 cm has 90-98% plus 20 years survival rate.
- Mastectomy removal of affected breast where the malignant carcinoma has invaded the breast tissues.
- Supportive care after the success of the surgery, care is needed when providing wound dressing, changing of surgical patch and maintaining integrity of the skin.
- Continuous education to be fully aware when the carcinoma regresses and the medication regimen already available.
Don’t Miss: Skin Cancer Mayo
Stages And Types Of Breast Cancer
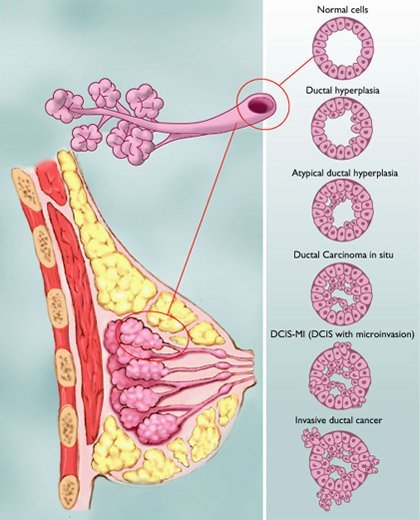
There are numerous forms of breast cancer and numerous methods to define them. Its easy to become perplexed after receiving a breast cancer diagnosis.The exact cells in the breast that are impacted determine the type of breast cancer. The majority of breast cancers are carcinomas, which are tumours that begin in the epithelial cells that line the organs and tissues of the body.When carcinomas originate in the breast, they are frequently a kind known as adenocarcinoma, which begins in cells in the ducts or lobules .Breast cancer can start in a variety of places, including the ducts, lobules, and, in some circumstances, the tissue in between. This part will teach you about the various types of breast cancer, such as non-invasive, invasive, and metastatic breast cancers, as well as the intrinsic or molecular subtypes of breast cancer.The type of breast cancer might also indicate whether or not the cancer has spread. In situ breast cancer is a type of cancer that begins in a milk duct but does not spread to the rest of the breast tissue.
The phrase invasive breast cancer refers to any type of breast cancer that has spread into the surrounding breast tissue.
Ductal cancer in situ
Because there is no way to predict which DCIS will progress to invasive cancer and which will not, practically all women with DCIS will be treated.
Invasive ductal carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma
Triple negative breast cancer
Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Paget Disease of the Breast
Stages of cancer
Genetic Variation In Stromal Proteins Decorin And Lumican With Breast Cancer: Investigations In Two Case
The stroma is the supportive framework of biologic tissue in the breast, consisting of various proteins such as the proteoglycans, decorin and lumican. Altered expression of decorin and lumican is associated with breast tumors. We hypothesized that genetic variation in the decorin and lumican genes may contribute to breast cancer.
You May Like: Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Diagnosing Invasive Breast Cancer
Invasive breast cancer is diagnosed using a range of tests. These may include:
- A mammogram
- An ultrasound scan
- A core biopsy of the breast and sometimes lymph nodes
- A fine needle aspiration of the breast and sometimes lymph nodes
When there is a change to the skin or nipple a punch biopsy of the skin may be performed. This involves taking a very small cylindrical piece of tissue from the changed area.
M Categories For Breast Cancer
M followed by a 0 or 1 indicates whether the cancer has spread to distant organs — for example, the lungs, liver, or bones.
M0: No distant spread is found on x-rays or by physical exam.
cM0: Small numbers of cancer cells are found in blood or bone marrow , or tiny areas of cancer spread are found in lymph nodes away from the underarm, collarbone, or internal mammary areas.
M1: Cancer has spread to distant organs as seen on imaging tests or by physical exam, and/or a biopsy of one of these areas proves cancer has spread and is larger than 0.2mm.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Cancer Prognosis
What Is Breast Cancer
Cells in the body normally divide only when new cells are needed. Sometimes, cells in a part of the body grow and divide out of control, which creates a mass of tissue called a tumor. If the cells that are growing out of control are normal cells, the tumor is called benign. If, however, the cells that are growing out of control are abnormal and don’t function like the body’s normal cells, the tumor is called malignant .
Cancers are named after the part of the body from which they originate. Breast cancer originates in the breast tissue. Like other cancers, breast cancer can invade and grow into the tissue surrounding the breast. It can also travel to other parts of the body and form new tumors, a process called metastasis.
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Inflammatory breast cancer can be difficult to diagnose. Often, there is no lump that can be felt during a physical exam or seen in a screening mammogram. In addition, most women diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer have dense breast tissue, which makes cancer detection in a screening mammogram more difficult. Also, because inflammatory breast cancer is so aggressive, it can arise between scheduled screening mammograms and progress quickly. The symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer may be mistaken for those of mastitis, which is an infection of the breast, or another form of locally advanced breast cancer.
To help prevent delays in diagnosis and in choosing the best course of treatment, an international panel of experts published guidelines on how doctors can diagnose and stage inflammatory breast cancer correctly. Their recommendations are summarized below.
Minimum criteria for a diagnosis of inflammatory breast cancer include the following:
- A rapid onset of erythema , edema , and a peau d’orange appearance and/or abnormal breast warmth, with or without a lump that can be felt.
- The above-mentioned symptoms have been present for less than 6 months.
- The erythema covers at least a third of the breast.
- Initial biopsy samples from the affected breast show invasive carcinoma.
Imaging and staging tests include the following:
Read Also: Melanoma On Face Prognosis
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Treated
Inflammatory breast cancer is generally treated first with systemic chemotherapy to help shrink the tumor, then with surgery to remove the tumor, followed by radiation therapy. This approach to treatment is called a multimodal approach. Studies have found that women with inflammatory breast cancer who are treated with a multimodal approach have better responses to therapy and longer survival. Treatments used in a multimodal approach may include those described below.
More About Invasive Breast Cancer With Central Necrosis
Sometimes medics refer to an infiltrative breast carcinoma with central necrosis as a centrally necrotizing breast carcinoma, . Historically, centrally necrotizing breast carcinomas have an aggressive course.
Histologically, the composition of infiltrating ductal carcinoma with central necrosis is a well-circumscribed nodule with an extensive region of central necrosis. This area of necrosis is usually surrounded by a narrow rim of high-grade tumor cells. But these tumor cells usually show only minimal if any ductal differentiation, ie. they tend not to form into tubules.
The average age of development of an infiltrative ductal carcinoma with central necrosis is hard to estimate, but generally occurs in the mid 50s. Most infiltrative breast carcinomas with central necrosis are estrogen and progesterone receptor negative, making them more resistant to treatment.
Don’t Miss: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Most invasive ductal carcinomas are the general type. However, there are four additional sub-types that are much less common:
- Medullary ductal carcinoma – these tumors look aggressive, but are often slow-growing. They are named because they look similar to a part of the brain called the medulla. They are often found in women whose ages are the late 40s to early 50s. The BRCA1 gene raises the risk for this kind of tumor.
- Mucinous ductal carcinoma – this is a less aggressive tumor where cancer cells are surrounded by a puddle of mucin . This cancer most often develops in women in their 60s and beyond.
- Papillary carcinoma – these are very rare kinds of IDC that have a tumor with fingers that grow out and reach toward nearby healthy cells. They most often occur in women after menopause. Sometimes the cells are abnormal and grow very quickly.
- Tubular ductal carcinoma – a less aggressive, slow-growing tumor that grows in very small tube shapes. It is most often found in women in their early 50s.
How A Breast Cancers Stage Is Determined
Your pathology report will include information that is used to calculate the stage of the breast cancer that is, whether it is limited to one area in the breast, or it has spread to healthy tissues inside the breast or to other parts of the body. Your doctor will begin to determine this during surgery to remove the cancer and look at one or more of the underarm lymph nodes, which is where breast cancer tends to travel first. He or she also may order additional blood tests or imaging tests if there is reason to believe the cancer might have spread beyond the breast.
The breast cancer staging system, called the TNM system, is overseen by the American Joint Committee on Cancer . The AJCC is a group of cancer experts who oversee how cancer is classified and communicated. This is to ensure that all doctors and treatment facilities are describing cancer in a uniform way so that the treatment results of all people can be compared and understood.
In the past, stage number was calculated based on just three clinical characteristics, T, N, and M:
- the size of the cancer tumor and whether or not it has grown into nearby tissue
- whether cancer is in the lymph nodes
- whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body beyond the breast
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M give more details about each characteristic. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Jump to more detailed information about the TNM system.
Jump to a specific breast cancer stage to learn more:
Also Check: Large Cell Carcinoma Definition
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
DCIS is the most common type of noninvasive breast cancer, with about 60,000 new cases diagnosed in the United States each year. About one in every five new breast cancer cases is ductal carcinoma in situ.
Also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer, its considered a noninvasive breast cancer. With DCIS, abnormal and cancerous cells havent spread from the ducts into nearby breast tissue nor anywhere else, such as the lymph nodes.
DCIS is divided into several subtypes, mainly according to the appearance of the tumor. These subtypes include micropapillary, papillary, solid, cribriform and comedo.
Patients with ductal carcinoma in situ are typically at higher risk for seeing their cancer return after breast cancer treatment, although the chance of a recurrence is less than 30 percent. Most recurrences occur within five to 10 years after the initial breast cancer diagnosis and may be invasive or noninvasive. DCIS also carries a heightened risk for developing a new breast cancer in the other breast. A recurrence of ductal carcinoma in situ would require additional treatment.
The type of therapy selected may affect the likelihood of recurrence. Treating DCIS with a lumpectomy , and without radiation therapy, carries a 25 percent to 35 percent chance of recurrence. Adding breast cancer radiation therapy to the treatment decreases this risk to about 15 percent. Currently, the long-term survival rate for women with ductal carcinoma in situ is nearly 100 percent.
Is Inoperable Breast Cancer Still Treatable
Although stage 3C breast cancer is defined as either operable or inoperable, an inoperable diagnosis doesnt necessarily mean that it cant be treated.
The term inoperable may mean that all the cancer in the breast and surrounding tissue cant be removed through simple surgery. When breast cancer is removed, a rim of healthy tissue around the tumor, called a margin, is also removed.
For breast cancer to be successfully removed, there needs to be healthy tissue in all margins of the breast, from your clavicle down to a few inches below the breast mound.
It is possible for inoperable breast cancer to become operable following a treatment to shrink the cancer.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Bone Cancer Symptoms
Side Effects And Complications
All treatments have some side effects that range from mild to severe. Most clear up when treatment ends, but there can be some lasting complications.
Its important to tell your oncologist about all symptoms, even if they seem minor. Your healthcare team will work with you to ease side effects and deal with complications.
Lumpectomy With Radiation Therapy
In this procedure, the surgeon will remove the tumor and some healthy breast tissue close by as a precaution.
Sometimes they may also remove the lymph nodes and request a biopsy to confirm that the cancer has not spread. Healthcare professionals call this a sentinel lymph node biopsy . They are more likely to do this if the tumor is large.
After surgery a person will receive radiation therapy to destroy any remaining cells.
You May Like: Melanoma Cancer Prognosis