What Are Causes And Risk Factors Of Renal Cell Carcinoma
The exact cause of renal cell cancer has not been determined. A number of different factors seem to contribute to renal cell cancer. These risk factors include the following:
- Cigarettesmoking doubles the risk of renal cell cancer and contributes to as many as one third of all cases. The more someone smokes, the greater the risk is of that person developing renal cell cancer.
- Obesity is a risk factor. As body weight increases, so does the risk of developing renal cell cancer. This is especially true in women.
- Occupational exposure to petroleum products, heavy metals, solvents, coke-oven emissions, or asbestos
- Cystic kidney disease associated with chronic renal insufficiency
- Cystic changes in the kidney and renal dialysis
- Tuberous sclerosis
In its early stages, renal cell cancer usually causes no noticeable symptoms. Symptoms may occur only when the cancer grows and begins to press on surrounding tissues or spread to other parts of the body. The symptoms vary considerably from person to person. Some people never develop any symptoms before the disease is discovered the cancer is found when they undergo imaging tests, such as a CT scan, for another reason. In a study in the Journal of Urology, approximately 53% of people with localized renal cell carcinoma had no symptoms.
Signs and symptoms of renal cell cancer may include the following:
- Malaise
- Anemia
- Weight loss
- Night sweats
Multidetector Ct Findings In The Diagnosis Of Metastatic Rcc
The metastasis of RCC has some specific features that are important to consider to achieve correct diagnosis and cancer staging and to detect recurrence. RCCs can grow to a large size before they become clinically evident because of their retroperitoneal location and the rich vascular supply of the kidneys. These characteristics help explain why patients with RCC are more likely to present with symptoms caused by metastatic disease rather than by the primary tumor, compared with patients with other types of primary tumors. In addition, patients with clinically evident RCC are also more likely to have a high frequency of metastases at the time of diagnosis. Recurrence of RCC may occur several years or decades after treatment of the primary tumor and in locations that are uncommon for other neoplasms .
Figure 1aFigure 1b
Lymphatic dissemination is the second major route by which RCC metastasizes. According to the TNM classification, the regional lymph nodes in RCC are the renal hilar and retroperitoneal nodes , which are most commonly affected. Metastasis to any other lymph node is coded as M1 . By invading the retroperitoneal lymphatics and traversing the thoracic duct, RCC can sometimes reach distant locations, such as the thoracic or supraclavicular nodes, and even the lung .
Figure 2
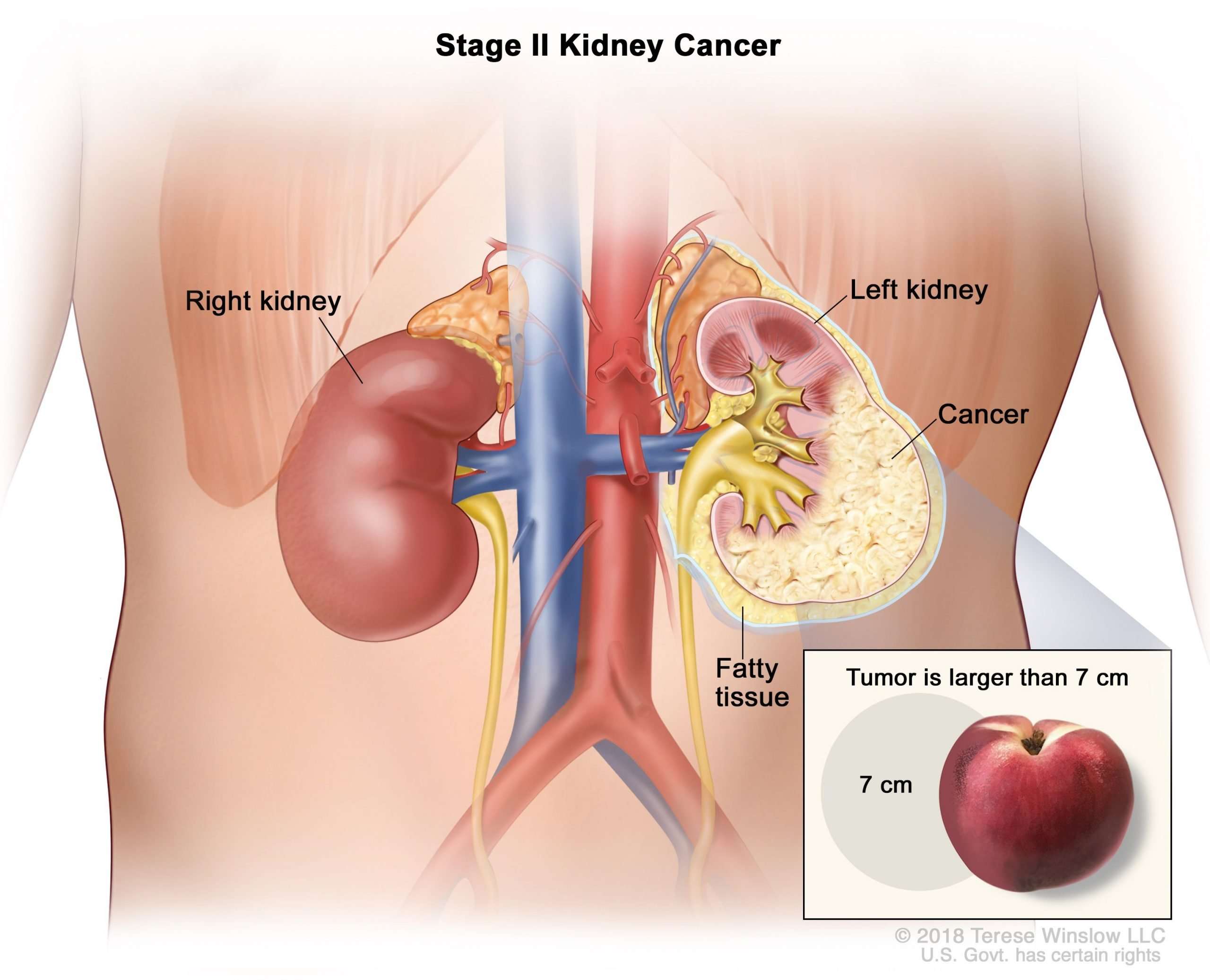
Renal Cell Carcinoma Tumor Stages
- Stage 1: The tumor is only in the kidney and it is smaller than 7 centimeters in size.
- Stage 2: The tumor is only in the kidney and it is larger than 7 cm in size.
- Stage 3: The tumor has spread beyond the kidney to adjacent areas, such as the adrenal gland.
- Stage 4: the tumor has spread beyond the kidney and adjacent structures to at least one other area of the body.
Read Also: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Understanding The Spread: Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma, also called kidney cancer, occurs when cancer cells form in the tubules of the kidney. Tubules are tiny tubes in your kidney that help filter waste products from your blood in order to make urine.
Smoking, hypertension, obesity, and hepatitis C all increase the risk of renal cell carcinoma. Renal cell carcinoma becomes metastatic renal cell carcinoma when it spreads beyond your kidney to your lymph system, bones, or other organs.
Renal cell carcinoma can spread from a mass of cancer cells or tumor to other parts of your body. This process is called metastasis. It occurs in one of three ways:
- Cancer cells spread into the tissue around the tumor in your kidney.
- The cancer moves from your kidney into your lymph system, which has vessels throughout the body.
- Kidney cancer cells enter the bloodstream and are carried and deposited to another organ or location in your body.
When renal cell carcinoma is in its early stages, its unlikely that youll experience obvious symptoms. Noticeable symptoms are often a sign that the disease has metastasized.
Symptoms typically include:
A physical exam and a review of your medical history may prompt further testing to determine the health of your kidneys.
Questions For Your Doctor
You and your healthcare provider need to work together. Here are some questions to start the conversation.
- Do I have kidney cancer?
- Has my cancer spread beyond my kidneys?
- Can my kidney cancer be cured?
- What are my treatment options?
- How long will treatment last?
- Are there any risks or side effects associated with my treatment?
- What will my recovery be like?
- How long will it take for me to recover from treatment?
- What are the chances of cancer coming back?
- Should I also see a nephrologist ?
- Will you be partnering with a nephrologist about my care?
- Should I get a second opinion?
- How much experience do you have treating this kind of cancer?
- Are there any clinical trials I should think about?
Don’t Miss: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Metastatic Disease To The Adrenal Gland
Certain cancers can spread from other parts of the body to the adrenal gland, including kidney cancer , melanoma , lung cancer, colon cancer, and lymphoma. The best treatment for metastatic cancer is usually systemic therapy like chemotherapy, however doctors will sometimes recommend removing the adrenal gland. Adrenalectomy may be recommended when the primary disease is well controlled and the adrenal is the only site of metastatic disease, if the patient is having significant symptoms from a large adrenal tumor, or if a diagnosis needs to be made and the adrenal is the easiest site to perform a biopsy. It is uncommon for metastatic cancer to appear in the adrenal gland before the primary site is known.
What Is The Prognosis For People With Ccrcc
The estimate of how a disease will affect you long-term is called prognosis. Every person is different and prognosis will depend on many factors, such as
- Where the tumor is in your body
- If the cancer has spread to other parts of your body
- How much of the tumor was taken out during surgery
If you want information on your prognosis, it is important to talk to your doctor. NCI also has resources to help you understand cancer prognosis.
Doctors estimate ccRCC survival rates by how groups of people with ccRCC have done in the past. Because there are so few pediatric ccRCC patients, these rates may not be very accurate. They also dont take into account newer treatments being developed.
With this in mind, ccRCC patients with smaller tumors have a better chance of survival than patients with larger tumors. The 5-year survival rate for patients with ccRCC is 50-69%. When ccRCC is already large or has spread to other parts of the body, treatment is more difficult and the 5-year survival rate is about 10%.
Related Resources
Also Check: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
New Potential Drug Targets
In the recent study, the team addressed this question by performing experiments in mouse models and cell lines, and by analyzing biological and clinical data from more than 700 patients with ccRCC, whose tumors had been analyzed in large-scale cancer genomics projects.
They discovered that two genes called CYTIP and CXCR4 are activated in metastatic tumor cells but inactive in non-metastatic cells. Their experiments suggest that the activation of the two genes might be essential for the spread of kidney cancer.
CXCR4 has been linked to metastasis before in this and other tumor types, including breast cancer, Dr. Vanharanta says. Now, our study shows that blocking CXCR4 function with a drug called plerixafor can reduce kidney cancer metastasis in mice. Plerixafor is currently used to stimulate blood stem cells in some cancer patients treated by bone marrow transplantation.
The researchers plan to investigate further whether CXCR4 and CYTIP, and other genes identified in the study, might offer new targets for the development of more-effective drugs for kidney cancer.
Signs Of Renal Cell Cancer Include Blood In The Urine And A Lump In The Abdomen
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by renal cell cancer or by other conditions. There may be no signs or symptoms in the early stages. Signs and symptoms may appear as the tumor grows. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- Blood in the urine.
- A lump in the abdomen.
- A pain in the side that doesn’t go away.
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
What Is Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma, or ccRCC, is a type of kidney cancer. The kidneys are located on either side of the spine towards the lower back. The kidneys work by cleaning out waste products in the blood. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma is also called conventional renal cell carcinoma.
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma is named after how the tumor looks under the microscope. The cells in the tumor look clear, like bubbles.
Treatment Of Stage Ii Renal Cell Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- Surgery , before or after radiation therapy.
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms in patients who cannot have surgery.
- Arterial embolization as palliative therapy.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
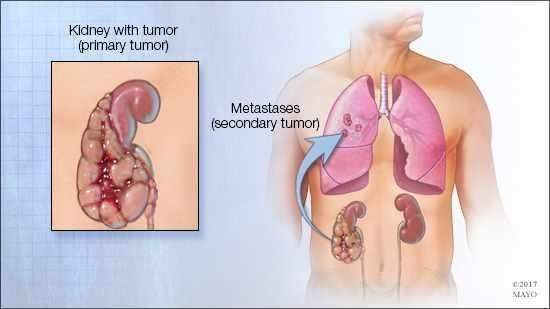
If Kidney Cancer Spreads
Cancer cells can spread from the kidney to other parts of the body. This spread is called metastasis.
Understanding how a type of cancer usually grows and spreads helps your healthcare team plan your treatment and future care. If kidney cancer spreads, it can spread to the following:
- lymph nodes around the kidney
- the main vein in the kidney
- the large vein in the abdomen leading to the heart
- the other kidney
- American Cancer Society. Kidney Cancer Stages. 2017: .
- Lane BR, Canter DJ, Rin BL, et al. Cancer of the kidney. DeVita VT Jr, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2015: 63:865-884.
- National Cancer Institute. Renal Cell Cancer Treatment Health Professional Version. 2018: .
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Kidney Cancer . .
Renal Cell Carcinoma Support Groups And Counseling

Living with cancer presents many new challenges, both for the people with cancer and for their family and friends.
- People with cancer probably have many worries about how the cancer will affect them and their ability to “live a normal life,” to care for their family and home, to hold their job, and to continue the friendships and activities they enjoy.
- Many people feel anxious and depressed. Some people feel angry and resentful others feel helpless and defeated.
For most people with cancer, talking about their feelings and concerns helps.
- Friends and family members can be very supportive. They may be hesitant to offer support until they see how someone is coping. If people with cancer want to talk about their concerns, they should let someone know.
- Some people do not want to “burden” their loved ones, or prefer talking about their concerns with a more neutral professional. A social worker, a counselor, or a member of the clergy can be helpful if they want to discuss their feelings and concerns about having cancer. A surgeon or an oncologist should be able to recommend someone.
- Many people with cancer are helped profoundly by talking to other people who have cancer. Sharing concerns with others who have been through the same thing can be remarkably reassuring. Support groups of people with cancer may be available through the medical center where treatment was received. The American Cancer Society also has information about support groups all over the United States.
Also Check: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
How Does Ccrcc Form
Scientists are always working to understand how cancer forms, but it can be hard to prove. Because ccRCC can run in families, we know that changes in the VHL gene are important in causing ccRCC. The VHL gene is also changed in ccRCC from people without a family history of Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. Scientists have learned a lot about what the VHL gene does in the body. This has given scientists clues about treatments to try for ccRCC.
Early And Advanced Kidney Cancer
Like most things in cancer, its also important to diagnose kidney cancer as early as possible because it is relatively easier to treat if caught early. On the other hand, its more difficult to treat if it has become advanced. Even at metastatic stage, the treatment goal is only to help relieve the symptoms and slow the progression of the cancer.
Early stage means the cancer is still completely inside the kidney. Advanced stage means the cancer has spread from its site of origin to another part of the body or if the cancer cells have found in more than one lymph node and it has grown into the surrounding tissues.
In addition, there is also a phase called locally advanced kidney cancer, the stage of when the cancer cells have been found in the adrenal gland or one of the nearby major blood vessels leading to the kidney. But there is no more than one lymph node affected.
For more detailed information about stages of kidney cancer, see this post! Cancer staging is important and required to determine the most effective cancer treatment.
Recommended Reading: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
Symptoms Of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Your renal cell cancer might not produce symptoms until it spreads outside your kidney. Your first symptoms may be caused by the effects of metastatic cancer in a different part of your body besides your kidney:
- Back pain can occur due to renal cell carcinoma metastasis to the spine
- Breathing problems or feeling faint can occur due to the spread of renal cell carcinoma to the lungs or heart
- Headaches or weakness on one side of the body
- Behavioral changes, confusion, or seizures can occur if renal cell carcinoma spreads to the brain
Rare Types Of Kidney Cancer
Rare kidney cancers occur most frequently in children, teenagers, and young adults.
Papillary renal cell carcinoma
- 15% of all renal cell carcinomas
- Tumor located in the kidney tubes
- Type 1 PRCC is more common and grows slowly
- Type 2 PRCC is more aggressive and grows more quickly
Translocation renal cell carcinoma
- Accounts for 1% to 5% of all renal cell carcinomas and 20% of childhood caces
- Tumor located in the kidney
- In children, TRCC usually grows slowly often without any symptoms
- In adults, TRCC tends to be agressive and fast-growing
Recommended Reading: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Other Aggressive Forms Of Kidney Cancer
Low grades of kidney cancer tend to be slow-growing, while high grades can multiply fast. The other types that are found to be more aggressive are papillary , chromophobe, medullary and oncocytic.
These variations of kidney cancer have a higher chance to metastasize, or spread, to other parts of the body. The most common places that kidney cancer can spread to are the lung and lymph nodes.
Does Kidney Cancer Spread Quickly Or Slowly
Actually, its not easy for the cancer to spread and create a new tumor in another part of the body . Because the body has its own defense system to inhibit the metastasis of cancer!
For instances, the journey of cancer cells through bloodstream and lymphatic system is quite a complicated process. Most of them are probably killed off by the body immune system or die because battered around by the quickly flowing blood. Mostly, they dont survive only a few will survive which then may form a secondary cancer.
In general, the chance of developing the secondary cancer is dependent on several factors. These include:
Recommended Reading: Soderstrom Skin Cancer Screening
Smoking And Misuse Of Certain Pain Medicines Can Affect The Risk Of Renal Cell Cancer
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for renal cell cancer include the following:
- Smoking.
- Having certain geneticconditions, such as von Hippel-Lindau disease or hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma.
Advanced Or Recurrent Kidney Cancer Treatment
For people with advanced kidney cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, treatment with a drug may be recommended along with surgery, or instead of surgery. Some of these drugs are given to you as a pill that you take by mouth others are given as an injection. Much progress has been made in recent years, and people with advanced kidney cancer are living much longer than ten years ago.
- Medicine is often used for advanced kidney cancer that has spread to other parts of the body or where surgery cannot be done.
- Immunotherapy uses the bodys defense system to stop or slow the growth of cancer cells
- Monoclonal antibodies attack a specific part of cancer cells
- Checkpoint inhibitors help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells
- Vaccines give an overall boost to the immune system
Recommended Reading: Basal Skin Cancer Survival Rates