What Causes Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet radiation from the sun is the number one cause of skin cancer, but UV light from tanning beds is just as harmful. Exposure to sunlight during the winter months puts you at the same risk as exposure during the summertime.
Cumulative sun exposure causes mainly basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer, while episodes of severe blistering sunburns, usually before age 18, can cause melanoma later in life. Other less common causes are repeated X-ray exposure, scars from burns or disease, and occupational exposure to certain chemicals.
Ultraviolet A and Ultraviolet B rays also affect the eyes and the skin around the eyes. Sun exposure may lead to cataracts, cancer of the eyelids, and possibly macular degeneration.
Skin Cancer Pictures: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Skin cancer images by skin cancer type. Skin cancer can look different than the photos below.
Basal Cell Carcinoma;|;Squamous Cell Carcinoma;|;Bowens Disease;|;Keratoacanthoma;|;Actinic Keratosis;|;Melanoma
Skin cancer often presents itself as a change in the skins appearance. This could be the appearance of a new mole or other mark on the skin or a change in an existing mole.
Please remember that you should always seek advice from your doctor if you have any concern about your skin. Skin cancers often look different from skin cancer images found online.
How Are Moles Evaluated
If you find a mole or spot that has any ABCDE’s of melanoma — or one that’s tender, itching, oozing, scaly, doesn’t heal or has redness or swelling beyond the mole — see a doctor. Your doctor may want to remove a tissue sample from the mole and biopsy it. If found to be cancerous, the entire mole and a rim of normal skin around it will be removed and the wound stitched closed. Additional treatment may be needed.
You May Like: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Who Is At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest in people who have fair or freckled skin that burns easily, light eyes and blond or red hair. Darker-skinned individuals are also susceptible to all types of skin cancer, although their risk is lower.
In addition to complexion, other risk factors include having a family history or personal history of skin cancer, having an outdoor job, and living in a sunny climate. A history of severe sunburns and an abundance of large and irregularly shaped moles are risk factors unique to melanoma.
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed
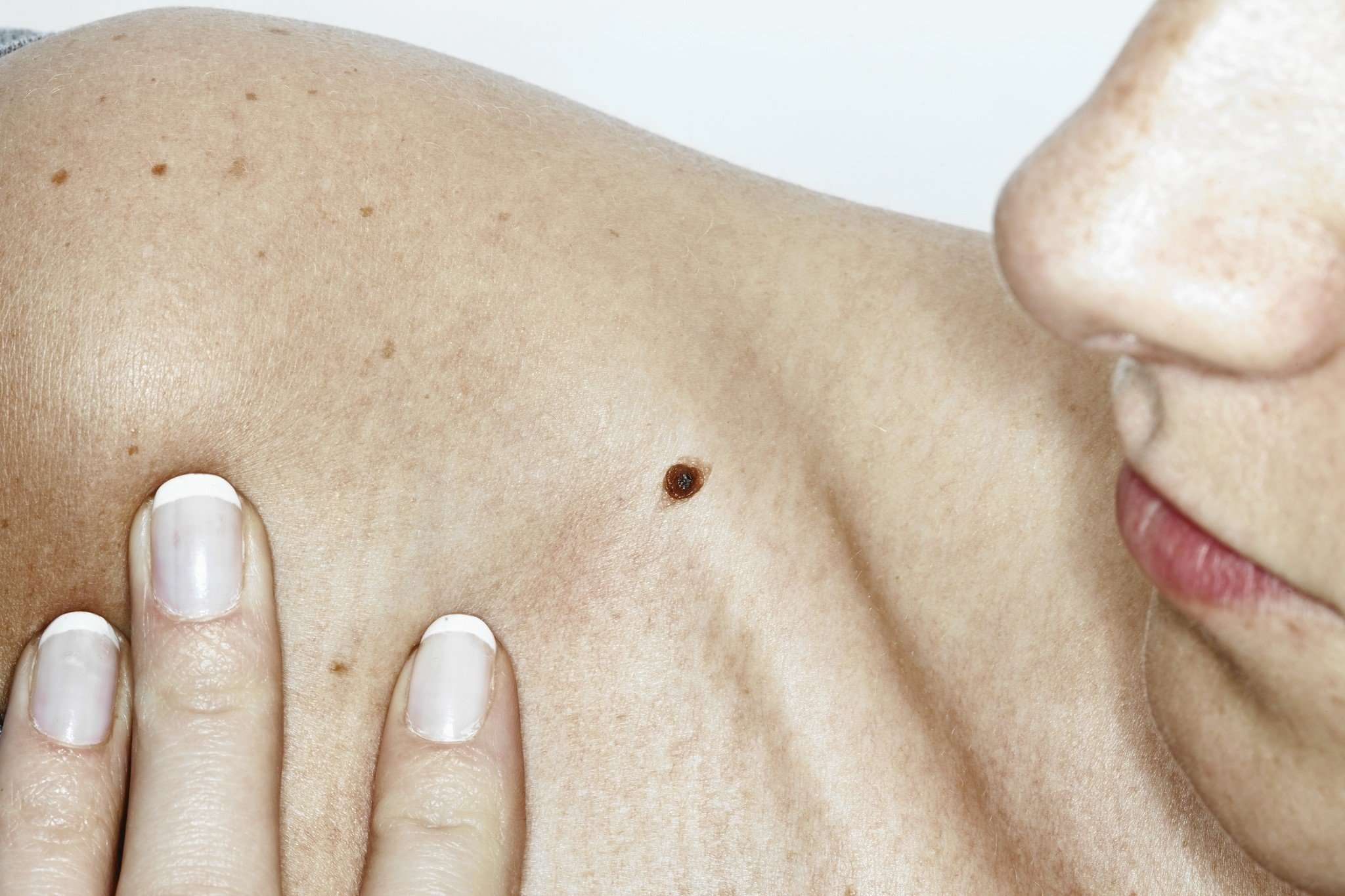
Many people do not show symptoms of cancer in the skin unless their condition has advanced. However, through regular skin examinations, you can tell whats normal and whats not, so you can seek professional advice once you see any suspicious growth.
When seeking professional help, you can get a total body skin exam from a certified dermatologist. We will review your medical history and ask you about the suspicious growths in your skin. To see your skin structures clearly, we might use a dermatoscope and take photographs of your lesions or abnormal growths. If you have a high risk of skin cancer, regular screening can help you detect the appearance of cancers much sooner.
Also Check: What Is Melanoma In The Brain
The Warning Signs Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancers — including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma — often start as changes to your skin. They can be new growths or precancerous lesions — changes that are not cancer but could become cancer over time. An estimated 40% to 50% of fair-skinned people who live to be 65 will develop at least one skin cancer. Learn to spot the early warning signs. Skin cancer can be cured if it’s found and treated early.
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Also Check: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
Who Gets Skin Cancer And Why
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation treatment, and even heredity may play a role. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive sun exposure or blistering sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Melanoma
A new spot on your skin or a spot thats changing in size, shape, or color may be a warning sign of melanoma. If you have any of these changes, have your skin checked by a doctor.
The doctor will ask you questions about when the spot on your skin first showed up and if it has changed in size or the way it looks. The rest of your skin will be checked. During the exam your doctor will check the size, shape, color and texture of any skin changes. If signs are pointing to melanoma, more tests will be done.
Also Check: Can Melanoma Be Treated Successfully
You May Like: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
How Can I Help Prevent Sun Damage And Ultimately Skin Cancer
Nothing can completely undo sun damage, although the skin can sometimes repair itself. So, it’s never too late to begin protecting yourself from the sun. Your skin does change with age; for example, you sweat less and your skin can take longer to heal, but you can delay these changes by limiting sun exposure.
Maintaining healthy skin
- Stop smoking: People who smoke tend to have more wrinkles than nonsmokers of the same age, complexion, and history of sun exposure. The reason for this difference is unclear. It may be because smoking interferes with normal blood flow in the skin.
- Apply sunscreen with a sun protection factor of 30 or greater 30 minutes before sun exposure and then every 2 to 3 hours thereafter. Reapply sooner if you get wet or perspire significantly.
- Select cosmetic products and contact lenses that offer UV protection.
- Wear sunglasses with total UV protection.
- Avoid direct sun exposure as much as possible during peak UV radiation hours between 10 am and 4 pm.
- Perform skin self-exams regularly to become familiar with existing growths and to notice any changes or new growths.
- Relieve dry skin using a humidifier at home, bathing with soap less often , and using a moisturizing lotion.
- Become a good role model and foster skin cancer prevention habits in your child. Eighty percent of a person’s lifetime sun exposure is acquired before age 18.
Understanding UV index
0-2: Low
3-5: Moderate
6-7: High
8-10: Very high
11 or higher : Extreme
Types Of Skin Cancer:
Basal Cell found mainly in areas exposed to the sun, very common and usually very treatable. Detected at an early stage and removed promptly are almost always curable and cause minimal damage.Squamous Cell typically develops in chronic sun-exposed areas of your body.Melanoma more likely to grow and spread than the more common typesMerkel Cell very rare and tends to grow quickly, may be hard to treat if it spreads past beyond the skin
Also Check: What Is Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome
This rare inherited condition, which is also known as Gorlin syndrome, increases your risk of developing basal cell cancer, as well as other types of tumors. The disease can cause clusters of basal cell carcinoma, especially on areas like your face, chest, and back. You can learn more about basal cell nevus syndrome here.
What Is The Follow
Most skin cancer is cured surgically in the dermatologist’s office. Of skin cancers that do recur, most do so within three years. Therefore, follow up with your dermatologist as recommended. Make an appointment immediately if you suspect a problem.
If you have a more deeply invasive or advanced malignant melanoma, your oncologist may want to see you every few months. These visits may include total body skin examinations, regional lymph node checks, and periodic chest X-rays. Over time, the intervals between follow-up appointments will increase. Eventually these checks may be done only once a year.
Also Check: Is Melanoma Skin Cancer Hereditary
Curettage Electrodesiccation And Cryotherapy
Some dermatologists perform curettage, electrodesiccation, and cryotherapy to treat skin cancer. These are considered to be destructive techniques that are best suited for small, superficial carcinomas with definite borders. During the procedure, layers of skin cells are scraped away using a curette. Any remaining cancer cells are destroyed with the use of an electric needle.
In some cases, liquid nitrogen or cryotherapy is used to freeze the margins of the treatment area. Extremely low temperatures kill the malignant skin cells and create a wound, which will heal in a few weeks. The treatment may leave scars that are flat and round, similar to the size of the skin cancer lesion.
What Kind Of Treatment Will I Need
There are many ways to treat melanoma. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
Most early stage melanomas can be treated with surgery alone. More advanced cancers need other treatments.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage of the cancer
- The results of lab tests on the cancer cells
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the melanoma or help in some way
- Your age
Read Also: Can Melanoma Be Treated Successfully
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If Something Is Skin Cancer
How Do I Know If I Just Have Age Spots
Age spots are often called liver spots or sunspots. They usually occur in people over 50 and in areas that are exposed to the sun.
Age spots can definitely look like cancerous growths but even if they are not diagnosed as cancer, they are clear signs that you have spent a lot of time in the sun. The age spots are the skins attempt to protect it from even further sun damage.
Age spots do not require medical care but it is still important to be looked at by a physician. They also will not fade over time but can be removed for cosmetic reasons if you should decide. It may be a sign of melanoma if spots are black, irregular, or have changed. Please contact your doctor for an evaluation if you have noticed any concerning changes.
The Early Stages Of Skin Cancer
Some forms of cancer, especially melanoma, may appear suddenly and without warning. Most people become alarmed only when they develop a crust or sore that refuses to heal. Did you know that the early stages of cancer do not always look or feel so bad? Harmless-looking moles, skin lesions, or unusual skin growths may also be the signs of early stages.
Regular skin examination can help you spot these early clues. If you see anything suspicious or observe unusual appearances in your skin, we can help you get the right diagnosis and treatment immediately. Some forms of cancer in the skin can be life-threatening and spread without being given urgent attention.
Also Check: How Serious Is Melanoma Cancer
What Is The Treatment For Skin Cancer
Treatment for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma is straightforward. Usually, surgical removal of the lesion is adequate. Malignant melanoma, however, may require several treatment methods, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy or immunotherapy or both. Because of the complexity of treatment decisions, people with malignant melanoma may benefit from the combined expertise of the dermatologist, a cancer surgeon, and a medical oncologist.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
How Reduce Your Risk For Cancer
Factors like genetics can influence your risk of getting skin cancer, but the number-one culprit is still the sun. Naturally, the biggest thing you can do is use sun protection all the time. “You really have to wear sunscreen every single day,” Karen says. When you’re actually at the beach or spending a lot of time outside in the sun’s rays, make sure to reapply every two hours, she says.
As much as we love our SPF, Karen stresses sunscreen alone isn’t enough. “It should be one component of a smart sun strategy that includes hats, long sleeves, sun-protective clothing, and sitting in the shade,” she explains.
“If you don’t go in the sun, it doesn’t guarantee that you’ll never get skin cancer, but it does greatly decrease your risk of the big three,” Day adds.
Be sure to keep up with yearly skin checks. If you have a history of skin cancer, either personally or in your family, your dermatologist might recommend upping them to every six months. And in the meantime, don’t be afraid to see your derm about something that looks weird.
McNeill recommends making an appointment to see your dermatologist if a spot a weird bump, sore, mole, or pimple that just won’t go away is not healing after a month. “You should not have a pimple or a scab or new bump for a month,” she says.
For more on how to prevent skin cancer:
Also Check: What Causes Renal Cell Carcinoma Cancer
Cancerous: Basal Cell Carcinoma
What it is: Basal cell carcinomas are usually found on sun-exposed areas, such as the face and neck. They also tend to grow so slowly that they rarely cause any harm.
What it looks like: According to Dr. Rosen, basal cells look like a raised bump on the skin or a red scaly patch that doesnt go away. How its treated: Some basal cell carcinomas can be treated with a cream thats applied daily for several weeks, while others are below the surface and need to be surgically removed. Basal cell carcinoma is really curable, says Dr. Rosen, but it can leave you with a scar that can be quite noticeable.
Skin Color And Being Exposed To Sunlight Can Increase The Risk Of Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesnt mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include the following:
- Being exposed to natural sunlight or artificial sunlight over long periods of time.
- Having a fair complexion, which includes the following:
- Fair skin that freckles and burns easily, does not tan, or tans poorly.
- Blue, green, or other light-colored eyes.
- Red or blond hair.
Although having a fair complexion is a risk factor for skin cancer, people of all skin colors can get skin cancer.
Older age is the main risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
You May Like: How Can Skin Cancer Kill You
Preventing Skin Cancer In Dogs
Some types of diseases are preventable, while others are not. As in humans, many cancers are the result of a genetic predisposition. In other cases, cancer is the result of a variety of factors coming together in an unlucky configuration, but there are a few things you can do to lower your dogs risk.
The risk factor most in your control is exposure to sunlight. If you have a light-skinned, short-haired dog breed, limiting your dogs exposure to direct sunlight, especially during the peak daylight hours, may help lower his risk of skin cancer.
The most important thing you can do to help your dog avoid skin cancer, however, is to familiarize yourself with all your dogs lumps, bumps, and rashes, perhaps during your daily grooming routine, and consult your veterinarian if you notice anything suspicious.
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin depends mostly on the following:
- Stage of the cancer.
- Whether the patient is immunosuppressed.
- Whether the patient uses tobacco.
- The patient’s general health.
Treatment options for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin depend on the following:
- The type of cancer.
- The stage of the cancer, for squamous cell carcinoma.
- The size of the tumor and what part of the body it affects.
- The patients general health.
Read Also: How Often Does Melanoma Spread To Lymph Nodes
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomasigns And Symptoms
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, especially a new growth or a sore that doesn’t heal. The cancer may start as a small, smooth, shiny, pale or waxy lump. It also may appear as a firm red lump. Sometimes, the lump bleeds or develops a crust.
Both basal and squamous cell cancers are found mainly on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun the head, face, neck, hands and arms. But skin cancer can occur anywhere.
An early warning sign of skin cancer is the development of an actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin lesion caused by chronic sun exposure. These lesions are typically pink or red in color and rough or scaly to the touch. They occur on sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the face, scalp, ears, backs of hands or forearms.
Actinic keratoses may start as small, red, flat spots but grow larger and become scaly or thick, if untreated. Sometimes they’re easier to feel than to see. There may be multiple lesions next to each other.
Early treatment of actinic keratoses may prevent them from developing into cancer. These precancerous lesions affect more than 10 million Americans. People with one actinic keratosis usually develop more. Up to 1 percent of these lesions can develop into a squamous cell cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most commonly diagnosed skin cancer. In recent years, there has been an upturn in the diagnoses among young women and the rise is blamed on sunbathing and tanning salons.
- Raised, dull-red skin lesion