What Causes Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
More than 90% of cases of SCC are associated with numerous DNAmutations in multiple somaticgenes. ;Mutations in the p53 tumour suppressor gene are caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation , especially UVB . Other signature mutations relate to cigarette smoking, ageing;and immune suppression . Mutations in signalling pathways affect the epidermalgrowth factorreceptor, RAS, Fyn, and p16INK4a signalling.;
Beta-genus human papillomaviruses are thought to play a role in SCC arising in immune-suppressed populations. -HPV and HPV subtypes 5, 8, 17, 20, 24, and 38 have also been associated with an increased risk of cutaneous SCC in immunocompetent individuals.;
Effective Options For Early Stage Scc
Most squamous cell carcinomas of the skin can be cured when found and treated early. Treatment should happen as soon as possible after diagnosis, since more advanced SCCs of the skin are more difficult to treat and can become dangerous, spreading to local lymph nodes, distant tissues and organs. Find out more about treatment options for advanced or recurring SCCs here.
If youve been diagnosed with an SCC that has not spread, there are several effective treatments that can usually be performed on an outpatient basis. The choices available to you depend on the tumor type, size, location and depth, as well as your age and overall health.
Options include:
What Should I Do If I Think I Have A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
If you notice a change to or growth on your skin, make an appointment to see your doctor straight away. Your doctor will assess the size, location and look of the growth. They will also ask you how long you have had it and whether it bleeds or itches.;
If your doctor thinks the growth may be cancer, they may take a small sample of tissue . The tissue sample will be sent to a laboratory and examined under a microscope. Your doctor will let you know whether the sample shows any cancer cells or not, and will recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.;
You May Like: How Do You Know If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has Spread
What Are The Types Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma develops when the flat cells in the toplayer of skin grow and divide in an uncontrolled way.
You can get an SCC wherever there are squamous cells which is in manydifferent parts of the body. However, typically they appear on parts of theskin that have been exposed to a lot of ultraviolet radiation from the sunor from tanning beds.
An early form of skin cancer, called Bowen’s disease, which looks like a red, scaly patch, can also develop into an SCC if nottreated.
An SCC can be quite an aggressive cancer if left untreated. If you evernotice a sore, scab or scaly patch of skin that doesnt heal within 2 months,see a doctor.
Skin Lesion Management Guidelines
If a patient presents with a suspicious lesion:
- Assess the likelihood of melanoma being present then provisionally identify the type of lesion.;See;skin cancer clinicians.
- Surgical excision with histology is the first-line treatment for all skin cancer. It has the highest cure rate among available treatments.;For squamous cell carcinoma the recommended margin for excision is 4mm for a well-defined low risk lesion, or 6mm for those with poor prognostic features .
- Referral, according to local guidelines, to a general practitioner with a special interest in skin lesions, a dermatologist, a plastic surgeon or an ENT surgeon may be appropriate for patients with;poor prognostic features, eg,
- large lesions 20mm
- lymphatic or vascular invasion
- fibrosing subtype.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
How Does This Cancer Typically Progress
In the skin form of the disease, although spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs is possible, it is very uncommon. With SCC of the nose, spread may occur to the lymph nodes under the chin .
Dogs with multicentric SCC often develop new lesions in other sites after surgical removal of lesions.
The digit form of SCC is far more aggressive. It can spread to the local lymph nodes and beyond. For this reason, your veterinarian may recommend staging . Staging may include bloodwork, urinalysis, X-rays of the lungs, and possibly an abdominal ultrasound. If any lymph nodes appear to be affected , samples may be taken via FNA to determine if the tumor has spread into them.
Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
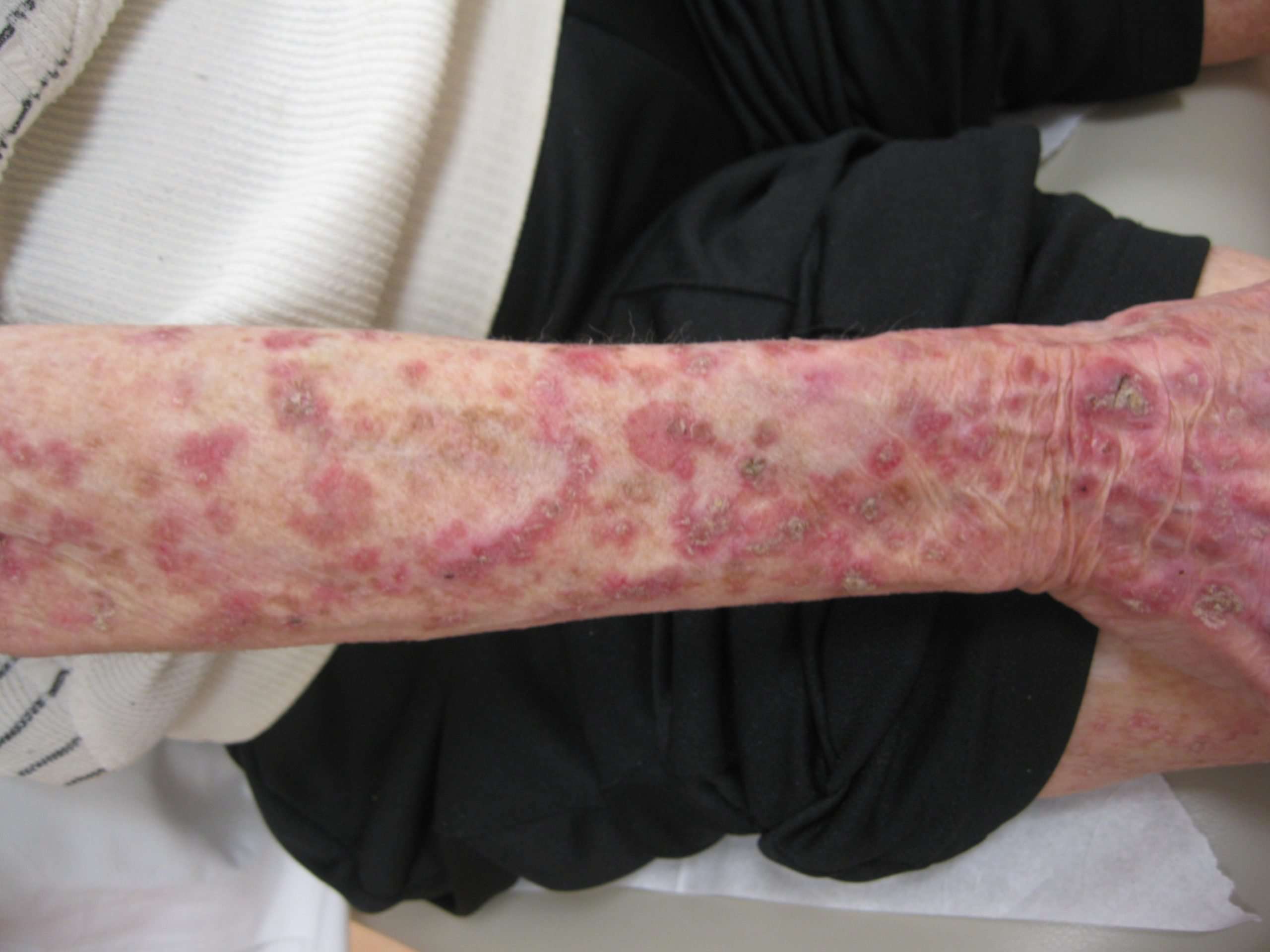
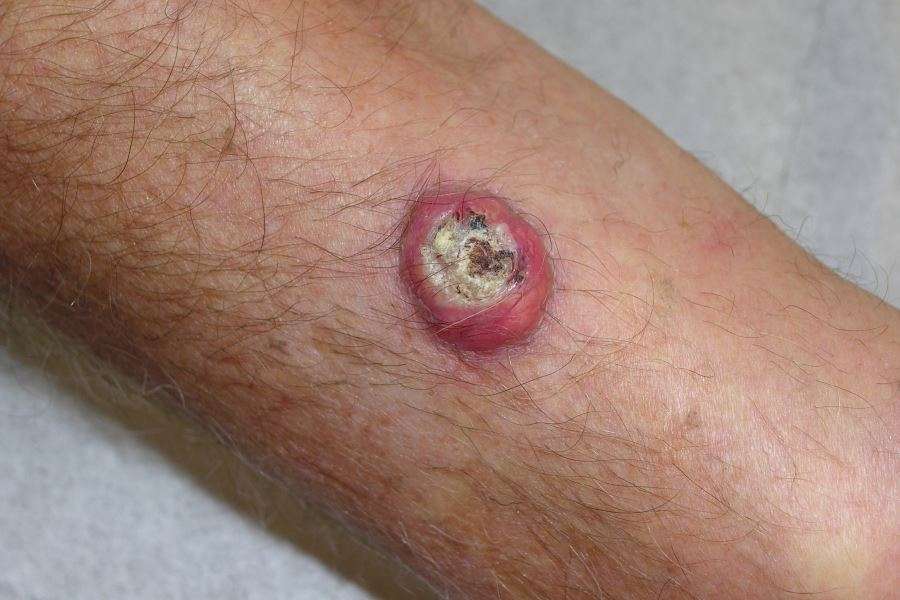
Squamous cell carcinoma is characterized by its thick, scaly, irregular appearance, but it can have various appearances, and a doctor may be suspicious of any sores on sun-exposed surfaces that do not heal.
Squamous cell carcinoma begins as a red area with a scaly, crusted surface. As it grows, the tumor may become somewhat raised and firm, sometimes with a wartlike surface. Eventually, the cancer becomes an open sore and grows into the underlying tissue.
Squamous cell carcinomas can have various appearances. This photo shows one that is raised, scaly, and crusted.
This red, irregular area on the arm was diagnosed as squamous cell carcinoma after a biopsy.
Squamous cell carcinomas can have various appearances. This photo shows an area that is scaly, crusted, and darker than the surrounding skin. It was diagnosed as squamous cell carcinoma after a biopsy.
This squamous cell carcinoma on the lip shows excess build up of keratin that has broken down to form an open sore.
Don’t Miss: How Aggressive Is Merkel Cell Carcinoma
What Survival Rates Mean
The survival rate is the percentage of people who live for a certain period of time with this cancer. The number is based on research done on large groups of people with the same stage of cancer.
Experts dont know the exact survival numbers for late-stage SCC, because cancer registries dont track statistics for this cancer. However, your doctor may be able to give you an estimate of your prognosis.
When it comes to surviving cancer, everyone is different. Your outcome will depend on the specific treatments you have and how well you respond to them. Talk to your doctor about your outlook and what it means.
What Are Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers are the most common types of skin cancer. They start in the top layer of skin , and are often related to sun exposure.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer cells. To learn more about cancer and how it starts and spreads, see What Is Cancer?
You May Like: How Bad Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Diagnosing Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The main way to diagnose squamous cell carcinoma is with a biopsy. This involves having a small piece of tissue removed from the suspicious area and examined in a laboratory.
In the laboratory, a pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope to determine if it is a skin cancer. He or she will also stage the cancer by the number of abnormal cells, their thickness, and the depth of penetration into the skin. The higher the stage of the tumor, the greater the chance it could spread to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma on sun-exposed areas of skin usually does not spread. However, squamous cell carcinoma of the lip, vulva, and penis are more likely to spread. Contact your doctor about any sore in these areas that does not go away after several weeks.
What Is Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is a common skin cancer that typically develops in chronic sun-exposed areas of your body. This type of skin cancer is usually not nearly as aggressive as melanoma and is uncontrolled growth of cells in the epidermis of your skin.
It can become disfiguring and sometimes deadly if allowed to grow. Squamous cell carcinomas are at least twice as frequent in men as in women. They rarely appear before age 50 and are most often seen in individuals in their 70s.
An estimated 700,000 cases of SCC are diagnosed each year in the United States, resulting in approximately 2,500 deaths.
You May Like: What Is Melanoma In The Brain
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The majority of skin cancers can be prevented. Besides the physician, the nurse and the pharmacist play a vital role in patient education. The patient must be told to avoid excessive sun exposure and use sunscreen when going out. Tanning beds should be avoided and one should wear protective clothing that covers the arms and upper body. Further, the patient must be told to avoid the sun between 10 am to 4 pm. Finally, all patients should be taught how to perform a skin examination and see a healthcare provider if there is any skin lesion that suddenly changes in its growth or shape. To date, there is no evidence that the use of herbs or other supplements can prevent skin cancer, and the patient should be told not to rely on these treatments.
Outcomes
Small squamous cell cancer lesions can be excised;and are not fatal but they can add significant morbidity depending on their location. Most squamous cell cancers around the head and neck region require complex surgery, which even in the best of hands can lead to poor cosmesis. Further, the cost of management of these cancers is escalating each year, and the patient is often burdened with huge copayments. Advanced squamous cell cancers have a poor prognosis with a 5-year survival rate below 40%. With larger lesions, tumor recurrence is also a problem despite wide excision. Local recurrences have;been reported in 10-18% of cases.
Is There Anything Else I Should Know
As UV rays/sunlight may play a role in the development of SCC, it is best to limit your dogs exposure to the sun, especially between the hours of 10am and 3pm, and especially in dogs with thin haircoats. Your dog should not be allowed to rub, scratch, lick, chew, or bite the affected area, as this may cause trauma and increase the risk of secondary infection. Secondary infections are common and treated with antibiotics as recommended by your veterinarian. Your veterinarian may also recommend medications for pain.
Don’t Miss: Do You Need Chemo For Melanoma
What Is Cutaneoussquamous Cell Carcinoma
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is a common type of keratinocytecancer, or non-melanomaskin cancer. It is derived from cells within the epidermis that make keratin the horny protein that makes up skin, hair and nails.
Cutaneous SCC is an invasive disease, referring to cancer cells that have grown beyond the epidermis. SCC can sometimes metastasise;and may prove fatal.
Intraepidermal carcinoma and mucosal SCC are considered elsewhere.
Ways To Protect Your Skin
- Avoid outdoor activities when the sun is strongest between 10am and 4pm from September to April in New Zealand.
- Wear sunscreen and lip balm daily that offer SPF 30 or higher sun protection.
- Use sunscreen that offers broad-spectrum protection and is water resistant.;
- Apply the sunscreen and lip balm to dry skin 15 minutes before going outdoors.;
- Apply the sunscreen to every part of your body that will not be covered by clothing.;Reapply it every 2 hours if you are swimming or sweating.
- Whenever possible, wear a wide-brimmed hat, long sleeves and long pants.;
- Wear sunglasses to protect the skin around your eyes.;
- Avoid getting a tan and never use a tanning bed or sun lamp.;
Skin cancer information;The Skin Cancer Foundation, US, 2015
Don’t Miss: Is Melanoma The Same As Skin Cancer
Management Of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Treatment options include the following:
-
Surgical excision with clear margins, as verified by frozen sections
-
Mohs micrographic surgery for;invasive cSCC in the facial region
-
Radiation therapy as an adjuvant to surgery, to provide improved locoregional control, or as primary therapy in patients who are unable to undergo surgical excision
-
Chemotherapy, such as treatment with;oral 5-fluorouracil and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors,;as adjuvant therapy for select highest-risk cases
-
Systemic chemotherapy for metastatic cSCC
What Are The Causes Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Vagina
The human papilloma virus infection is a major cause behind the development of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Vagina.
- Under normal circumstances, certain genes called tumor suppressor genes, keep a check on the growth and division of cervical cells
- HPV infection has been found to disrupt some tumor suppressor genes, thus allowing vaginal cells to grow and multiply uncontrollably
- Other factors that aid in cancer development are yet to be fully explained
Almost all histological subtypes are rare and linked to high-risk HPV; HPV-associated SCC subtypes include non-keratinizing, basaloid, warty, and papillary subtypes, which are linked to high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion . Even more rarely, vaginal cancer can occur without a preceding HPV infection. In such cases, the cause of the condition is unknown.
- HPVs are known to have carcinogenic potency, meaning they have the potential to cause cancer
- Of HPVs, HPV-16 and HPV-18 are most common, indicating that they have a more potent threat
- 7 in 10 cancers are due to these two virus types
- HPV-16 is causative for most cases of SCC, just as HPV-18 is for adenocarcinoma
Untreated squamous cell carcinoma in situ can result in invasive squamous cell carcinoma. Other factors that may contribute to the condition include compromised immune system, sexual promiscuity, smoking, and even poor hygiene.
Don’t Miss: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
Key Points On Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Patient Discussion About Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Q. what is the most accurate pathological test to identify the primary source of a cystic mass in the neck? the mass was removed. Pathologist was unable to identify the source and diagnosed the mass as a branchilogic carcinmoa . Therefore, I am looking for the most updated test and examinations that can be applied to blocks of the mass and determine their origin
A.
Also Check: What Is Soft Tissue Carcinoma
Scc Is Mainly Caused By Cumulative Uv Exposure Over The Course Of A Lifetime
If youve had a basal cell carcinoma you may be more likely to develop a squamous cell skin carcinoma, as is anyone with an inherited, highly UV-sensitive condition such as xeroderma pigmentosum.
Chronic infections, skin inflammation, HIV and other immune deficiency diseases, chemotherapy, anti-rejection drugs used in organ transplantation, and excessive sun exposure can all lead to a risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Occasionally, squamous cell carcinomas arise spontaneously on what appears to be normal, healthy skin. Some researchers believe the tendency to develop these cancers can be inherited.
SCCs may occur on all areas of the body including the mucous membranes and genitals, but are most common in areas frequently exposed to the sun:
- Ears
- Previous BCC or SCC
- Chronic inflammatory skin conditions or chronic infections
But anyone with a history of substantial sun exposure is at increased risk. Those whose occupations require long hours outside or who spend their leisure time in the sun are also at risk.
Other Key Molecular Markers Shared In Several Sccs
In addition to the shared cell cycle regulation , signal transduction , and protein metabolism molecular abnormalities, several other molecular abnormalities of gene expression, protein expression, gene mutation, and epigenetic regulation and their respective prognostic values have been characterized in SCCs . Key markers shared in two or three of the major SCCs involve several classes of genes including signal transduction , transcription factor , cell adhesion , and extracellular matrix degradation . Additional markers affecting only one of the SCCs can be found in and .
VEGF
VEGF is an important signal transduction protein involved in both vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Four subtypes have been described . VEGF alteration is involved in HNSCC and ESCC. In oral SCC, it was reported that overexpression as measured by immuno-histochemistry of subtypes A and B were correlated with tumor angiogenesis and subtypes C and D with metastases and poor prognosis . In ESCC, VEGF expression has historically ranged between 2493% , and recently elevated immunoexpression has been reported in 55% of ESSC tissues . Overexpression of VEGF has been significantly correlated with poorer prognosis of ESCC .
SOX2
CDH1
MMPs
Gene mutations
Methylation
miRNAs
You May Like: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
Prognosis Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Typically, the prognosis for small tumors that are removed early and adequately is excellent. Treatment is usually effective, and most people survive. Most squamous cell carcinomas affect only the area around them, penetrating into nearby tissues. However, some spread to distant parts of the body, nearby skin and lymph nodes, and eventually to nearby organs and can be fatal. Tumors that are more than 2 centimeters in diameter or grow more than 2 millimeters deep, or tumors that occur near the ears and lips, in scars, or around nerves are more likely to spread. About one third of cancers on the tongue or elsewhere in the mouth have metastasized before diagnosis .
If the cancer is treated before it metastasizes, the person is usually cured. However, if the cancer has metastasized, the chance of surviving the next 5 years, even with treatment, is only 34%.