How Widespread Is Scc
While SCC is less common than basal cell carcinoma , the number of reported SCC cases in the U.S. has steadily increased.
- An estimated;1.8 million cases of SCC are diagnosed each year, which translates to about 205 cases diagnosed every hour.
- SCC incidence has increased up to 200 percent in the past three decades.
Reviewed by:
How To Improve Your Odds
Even if youve exhausted all of your treatment options, you dont have to give up. Researchers are always testing new SCC treatments in clinical trials. Getting into one of these studies could give you access to a drug or therapy that might slow or stop your cancer.
To avoid the worsening of your skin cancer or a new cancer in a different area, protect yourself from the suns damaging UV rays. Wear sun-protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat whenever you go outdoors. Apply a layer of broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
Also check your own skin for any new growths on a regular basis. Report any skin changes to your doctor right away.
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Surgery is the preferred management method for the majority of squamous cell skin cancers. Low-risk, early stage, small squamous cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, which is a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Excision, curettage and desiccation, and cryosurgery can also be used to remove the cancer while sparing normal tissue. Radiation alone is an alternative for low-risk tumors when surgery is not desirable because of cosmetic concerns or medical reasons.
Large tumors and tumors with nerve or lymph node involvement are not suitable for Mohs surgery and require removal of at least 5-millimeter margins of normal tissue around the cancer and neck dissection for involved lymph nodes. Larger tumors require reconstruction, which can be done at the time of surgery if margin status is clear. Reconstruction should be staged when margins status is not clear.
Patients with high-risk tumors should meet with a radiation therapist to discuss postoperative radiation. Chemotherapy may be added to radiation for extensive lymph node involvement or positive margins that cannot be cleared with additional surgery. In patients with high-risk tumors who are not surgical candidates, systemic treatment with both radiation and chemotherapy is used. Such cases require multidisciplinary care by a team of surgeons, radiation oncologists and medical oncologists.
Don’t Miss: How Often Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Spread
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
The best way to prevent SCC is to avoid sunburn. Avoid going outin the sun when the UV Index is higher than 3, such as in the middle of theday. Seek shade, wear a hat, sunglasses and clothing that protects you from thesun, and always use an SPF30+ sunscreen. Do not go to tanningsalons.
If you are at very high risk of developing another skin cancer, yourdoctor may prescribe you specific vitamins.
Is Poorly Differentiated Carcinoma Curable
Many early empiric chemotherapy trials of CUP included patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma in addition to the more common adenocarcinomas of unknown primary origin, since these patients were assumed to have the same poor response to treatment and short survival It is now clear that some patients with poorly
Don’t Miss: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Most of squamous cell carcinomas can be cured if they are treated early. Once squamous cell carcinoma has spread beyond the skin, though, less than half of people live five years, even with aggressive treatment.
There are many ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma that has not spread. These include:
- cutting away the cancer and a small amount of healthy tissue around it. If a large area of skin is removed, a skin graft may be necessary.
- scraping away the cancer with a surgical tool. An electric probe is used to kill any cancerous cells left behind.
- freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen. This treatment is usually used only for very small tumors or for a patch of skin that looks abnormal but isn’t yet cancerous.
- destroying the tumor with radiation.
- shaving away the cancer, one thin layer at a time. Each layer is examined under the microscope as it is removed. This technique helps the doctor preserve as much healthy skin as possible.
- applying drugs directly to the skin or injecting them into the tumor
- using a narrow laser beam to destroy the cancer.
The treatment that is best for you depends on the size and location of the cancer, whether it has returned after previous treatment, your age, and your general health.
Once your treatment is finished, it’s important to have regular follow-up skin exams. Your doctor may want to see you every three months for the first year, for example, and then less often after that.
Laser Surgery Is Not Fda
Laser surgery is not currently used as a standard treatment for basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It can, however, be an effective secondary treatment. Laser treatment is sometimes used after Mohs surgery to complete the removal of cancer cells. Lasers are effective at removing precancerous lesions, but have not been proven effective at treating cancer yet.;
Don’t Miss: What Does Advanced Skin Cancer Look Like
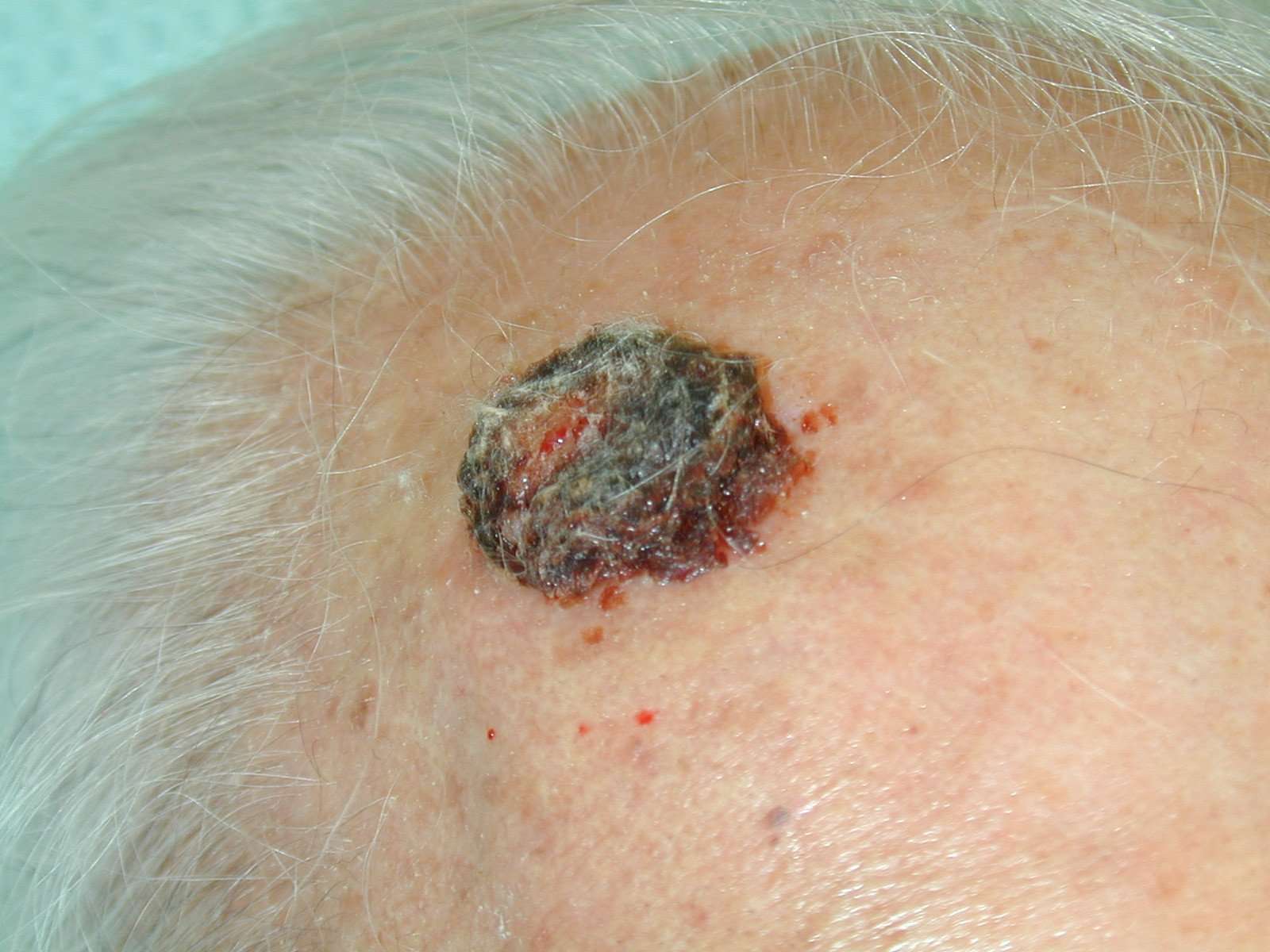
What Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Look Like
Squamous cell carcinomas most often affect areas with lot of sun exposure such as the face, scalp, neck, ears, backs of hands, forearms, and shins. Squamous cell carcinomas can occur in many other areas of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma often looks like a rough scaly spot, scab or sore that just will not heal. They tend to bleed easier than normal skin.
Scabs and scratches typically heal within 4 weeks. Skin cancer does not heal because the cells are abnormal. If you have a non-healing scab or sore, and it has been more than 4 weeks you should call your dermatologist to have this spot examined.
It is very important to note that while these characteristics are some of the most common signs of squamous cell carcinoma, there is no substitute for your skin concern being examined in person by a Board-Certified Dermatologist. This is the gold standard for having any of your skin concerns addressed. Your Board-Certified Dermatologist will perform a comprehensive examination and is the expert when it comes to diagnosis and treating skin cancers.
What causes squamous cell carcinoma?
How is squamous cell carcinoma diagnosed?
When Should I Seek Care
If you have a lesion that could be a skin cancer, please dont wait. Getting these treated early before they become aggressive is critical to a successful outcome.
Request an appointment online or call us today to see how we can help utilize the most advanced methods with the highest cure rates possible to treat any skin cancers that arise.
- 26732 Crown Valley Parkway Suite 571 Mission Viejo, CA 92691-7305
Read Also: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
Is Carcinoma Cancer Deadly
Untreated squamous cell carcinoma of the skin can destroy nearby healthy tissue, spread to the lymph nodes or other organs, and may be fatal, although this is uncommon. The risk of aggressive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin may be increased in cases where the cancer: Is particularly large or deep.
Are Skin Cancers Dangerous
Yes. As with all skin cancers, early diagnosis and treatment is critical. More than 1 million people will be diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma this year in the United States. And at least 15,000 people will die of it this year. That is more than twice as many people as those who die from melanoma.
Read Also: Can Skin Cancer Be Cured With Cream
When To Seek Help
Not all sores on the skin are skin cancer. But if you do develop a skincancer, the earlier it is treated, the better the outcome for you.
Most people find SCCs by checking their own skin. Check your skin regularly so you notice any changes. See a doctor if:
- you have a sore that doesn’t heal in 2 months
- you notice a new and unusual looking spot
- an existing spot changes in colour, size or shape
- you have a spot that is asymmetrical
- you have a spot with an uneven border
- you have a spot with an unusual or uneven colour
- you have a spot that is larger than 7 mm
Treatment Of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
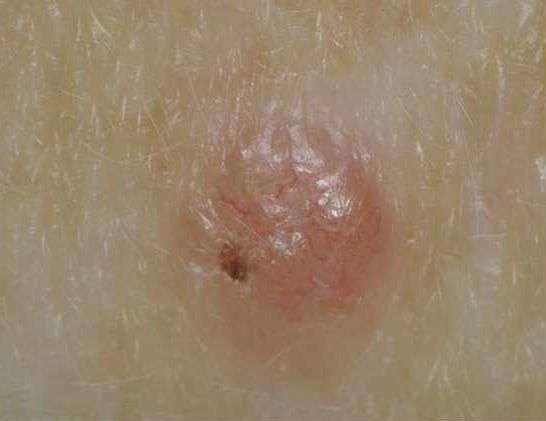
-
Surgery, with postoperative radiation or chemoradiation as needed
For most oral cavity cancers, surgery is the initial treatment of choice. Radiation or chemoradiation is added postoperatively if disease is more advanced or has high-risk features.
Selective neck dissection is indicated if the risk of nodal disease exceeds 15 to 20%. Although there is no firm consensus, neck dissections are typically done for any lesion with a depth of invasion > about 3.5 mm.
Routine surgical reconstruction is the key to reducing postoperative oral disabilities; procedures range from local tissue flaps to free tissue transfers. Speech and swallowing therapy may be required after significant resections.
Radiation therapy is an alternative treatment. Chemotherapy is not used routinely as primary therapy but is recommended as adjuvant therapy along with radiation in patients with advanced nodal disease.
Treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the lip is surgical excision with reconstruction to maximize postoperative function. When large areas of the lip exhibit premalignant change, the lip can be surgically shaved, or a laser can remove all affected mucosa. Mohs surgery can be used. Thereafter, appropriate sunscreen application is recommended.
Read Also: Are There Stages Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Is A Squamous Cell
One of three main types of cells in the top layer of the skin , squamous cells are flat cells located near the surface of the skin that shed continuously as new ones form.
SCC occurs when DNA damage from exposure to ultraviolet radiation or other damaging agents trigger abnormal changes in the squamous cells.
How Often Does Scc Spread
Studies suggest that around 1.4% of people with SCC will experience metastasis.
As with BCC, the five-year survival rate is highhovering around 99%in the absence of metastasis. With metastasis, the three-year survival is roughly 29% in women and 46% in men.
Recommended Reading: How Fast Can You Get Skin Cancer From The Sun
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Cancer
SCC often occurs in areas exposed to UV radiation, such as the face, ears, and hands. However, it can also appear in the mouth, in the anal area, and on the genitals.
In its early stages, SCC often presents itself as a scaly, reddish patch of skin. As it progresses, it can turn into a raised bump that continues to grow. The growth may also crust or bleed. In the mouth, this cancer will take on the appearance of a mouth ulcer or a white patch.
In some cases, youll notice a new growth on a preexisting scar, mole, or birthmark. Any existing lesions or sores that arent healing can also indicate SCC.
Make an appointment with your doctor or dermatologist right away if you notice any of these symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for preventing complications.
What Causes Squamous Cell Cancer
Skin cancer is caused by mutations that occur in skin cell DNA. These changes cause abnormal cells to multiply out of control. When this occurs in the squamous cells, the condition is known as SCC.
UV radiation is the most common cause of the DNA mutations that lead to skin cancer. UV radiation is found in sunlight as well as in tanning lamps and beds.
While frequent exposure to UV radiation greatly increases your risk of skin cancer, the condition can also develop in people who dont spend much time in the sun or in tanning beds.
These people may be genetically predisposed to skin cancer, or they may have weakened immune systems that increase their likelihood of getting skin cancer.
Those who have received radiation treatment may also be at greater risk of skin cancer.
Risk factors for SCC include:
- having fair skin
- having light-colored hair and blue, green, or gray eyes
- having long-term exposure to UV radiation
- living in sunny regions or at a high altitude
- having a history of multiple severe sunburns, especially if they occurred early in life
- having a history of being exposed to chemicals, such as arsenic
Don’t Miss: Can Cancer Cause Skin Rash
What Happens If Precancers Go Untreated
As the name suggests, precancers are damaged skin cells that arent considered cancerous, but if they are left untreated, these lesions are at high risk to become skin cancer. There are two main types of precancerous skin conditions: actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi. Actinic keratosis looks like a rough, scaly patch of the skin that is usually red or brown. This condition may develop into squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Nevi are moles, and dysplastic nevi is a term that means a mole is abnormal. Dysplastic nevi may develop into melanoma without proper treatment. While precancerous skin cancers are not malignant on their own, the potential to develop into life-threatening forms of this condition means they need to be evaluated regularly.
Prognosis Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Typically, the prognosis for small tumors that are removed early and adequately is excellent. Treatment is usually effective, and most people survive. Most squamous cell carcinomas affect only the area around them, penetrating into nearby tissues. However, some spread to distant parts of the body, nearby skin and lymph nodes, and eventually to nearby organs and can be fatal. Tumors that are more than 2 centimeters in diameter or grow more than 2 millimeters deep, or tumors that occur near the ears and lips, in scars, or around nerves are more likely to spread. About one third of cancers on the tongue or elsewhere in the mouth have metastasized before diagnosis .
If the cancer is treated before it metastasizes, the person is usually cured. However, if the cancer has metastasized, the chance of surviving the next 5 years, even with treatment, is only 34%.
Read Also: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
What Happens If Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare but aggressive and potentially fatal form of skin cancer. It typically affects people above the age of 50 and those who have weakened immune systems. In most cases, Merkel cell carcinoma begins as a skin-toned growth that may bleed easily. The bumps or nodules may also have blue, purple, or red coloring. Because the Merkle cells are near nerve endings, this form of cancer has numerous health risks, and if left untreated, Merkle cell cancer may spread to the brain, lungs, or bones, becoming fatal.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
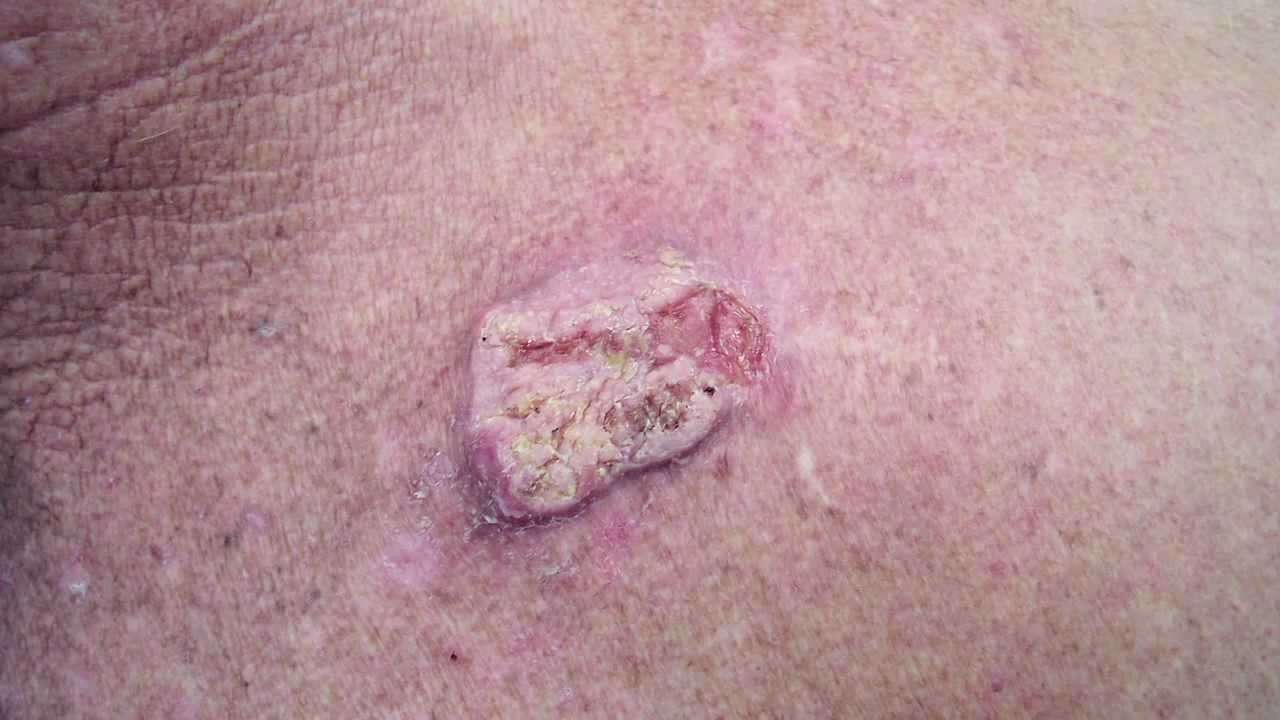
In general, the squamous cell carcinoma survival rate is very highwhen detected early, the five-year survival rate is 99 percent. Even if squamous cell carcinoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes, the cancer may be effectively treated through a combination of surgery and radiation treatment. Nevertheless, a patient who has been treated for squamous cell carcinoma in the past always faces the possibility of a recurrence, so lifelong monitoring to increase the chance of early detection is highly encouraged.
Recommended Reading: How Bad Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
What Survival Rates Mean
The survival rate is the percentage of people who live for a certain period of time with this cancer. The number is based on research done on large groups of people with the same stage of cancer.
Experts dont know the exact survival numbers for late-stage SCC, because cancer registries dont track statistics for this cancer. However, your doctor may be able to give you an estimate of your prognosis.
When it comes to surviving cancer, everyone is different. Your outcome will depend on the specific treatments you have and how well you respond to them. Talk to your doctor about your outlook and what it means.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2;basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage;3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones;or other organs in the body.
Don’t Miss: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomasigns And Symptoms
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, especially a new growth or a sore that doesn’t heal. The cancer may start as a small, smooth, shiny, pale or waxy lump. It also may appear as a firm red lump. Sometimes, the lump bleeds or develops a crust.
Both basal and squamous cell cancers are found mainly on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun the head, face, neck, hands and arms. But skin cancer can occur anywhere.
An early warning sign of skin cancer is the development of an actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin lesion caused by chronic sun exposure. These lesions are typically pink or red in color and rough or scaly to the touch. They occur on sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the face, scalp, ears, backs of hands or forearms.
Actinic keratoses may start as small, red, flat spots but grow larger and become scaly or thick, if untreated. Sometimes they’re easier to feel than to see. There may be multiple lesions next to each other.
Early treatment of actinic keratoses may prevent them from developing into cancer. These precancerous lesions affect more than 10 million Americans. People with one actinic keratosis usually develop more. Up to 1 percent of these lesions can develop into a squamous cell cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most commonly diagnosed skin cancer. In recent years, there has been an upturn in the diagnoses among young women and the rise is blamed on sunbathing and tanning salons.
- Raised, dull-red skin lesion