How Do People Find Bcc On Their Skin
Many people find it when they notice a spot, lump, or scaly patch on their skin that is growing or feels different from the rest of their skin. If you notice any spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist. These doctors have the most training and experience in diagnosing skin cancer.
To find skin cancer early, dermatologists recommend that everyone check their own skin with a skin self-exam. This is especially important for people who have a higher risk of developing BCC. Youll find out what can increase your risk of getting this skin cancer at, Basal cell carcinoma: Who gets and causes.
Images used with permission of:
-
The American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
-
J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:303-17.
Dont Miss: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
Treating Advanced Squamous Cell Cancers
Lymph node dissection:Removing regional lymph nodes might be recommended for some squamous cell cancers that are very large or have grown deeply into the skin, as well as if the lymph nodes feel enlarged and/or hard. The removed lymph nodes are looked at under a microscope to see if they contain cancer cells. Sometimes, radiation therapy might be recommended after surgery.
Immunotherapy: For advanced squamous cell cancers that cant be cured with surgery or radiation therapy, one option might be using an immunotherapy drug such as cemiplimab or pembrolizumab . However, these drugs havent been studied in people with weakened immune systems, such as people who take medicines for autoimmune diseases or who have had an organ transplant, so the balance between benefits and risks for these people isnt clear.
Systemic chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy:Chemotherapy and targeted therapy drugs might be other options for patients with squamous cell cancer that has spread to lymph nodes or distant organs. These types of treatment might be combined or used separately.
Who Is Most Likely To Have A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The following groups of people are at greater risk of developing SCC:
- Immunosuppressed individuals either due to medical treatment, such as methotrexate, ciclosporin and azathioprine, or due to diseases which affect immune function, including inherited diseases of the immune system or acquired conditions such as leukaemia or HIV;
- Patients who have had an organ transplant because of the treatment required to suppress their immune systems to prevent organ rejection
- People who are more susceptible to sunburn;
- People who have had significant cumulative ultraviolet light exposure, for example:
- people who have lived in countries near to the equator, or who have been posted to work in these countries, e.g. military personnel, construction workers;
- outdoor workers, such as builders, farmers;
- people of advanced years, who have had a lifetime of frequent sun exposure;
Read Also: How Bad Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Squamous cell cancers are usually raised growths, ranging from the size of a pea to the size of a chestnut. They may appear as scaly red patches, open sores or protruding growths with a dented center, or they may look like a wart. Most are found in areas of the body that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the ears, lips, face, balding scalp, neck, hands, arms, and legs. Less commonly, they may appear on mucous membranes and genitals.;Regardless of what form the bumps take, they do;not heal or go away on their own.;
What Are The Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
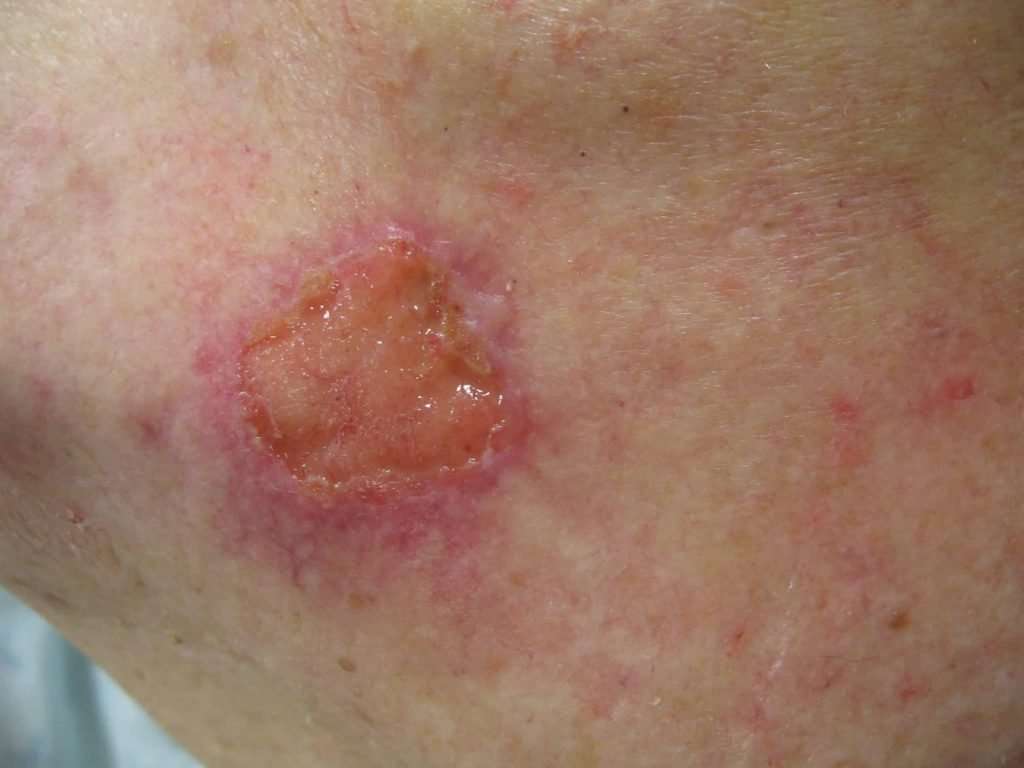
Squamous cell carcinoma is classified into the following stages, which are partly based on how far the cancer has spread throughout the body:
- Stage 0 Squamous cell carcinoma develops in the squamous cells, which are located in the epidermis . During Stage 0, the cancer hasnt spread beyond the epidermis.
- Stage 1 When squamous cell carcinoma progresses to Stage 1, it means that the cancer has spread deeper into the skin, but not into any lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 2 A Stage 2 classification means that, in addition to progressing deeper into the skin, the cancer also displays at least one high-risk feature. This might include metastasizing to the lower skin layers or the nerves. However, at this stage, the cancer still hasnt spread to lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 3 Once squamous cell carcinoma reaches Stage 3, the cancer has spread into lymph nodes but not any other tissues or organs.
- Stage 4 This is the final stage of squamous cell carcinoma, where the cancer has spread to at least one distant organ, whether that be the brain, the lungs or a separate area of skin.
If you think you might have squamous cell carcinoma, its important to seek prompt medical attention to minimize the risk of cancer spread. The specialists in Moffitt Cancer Centers Cutaneous Oncology Program can provide you with the comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services you need. Call or complete our new patient registration form online to request an appointment.
- BROWSE
Also Check: Do You Need Chemo For Melanoma
What Survival Rates Mean
The survival rate is the percentage of people who live for a certain period of time with this cancer. The number is based on research done on large groups of people with the same stage of cancer.
Experts dont know the exact survival numbers for late-stage SCC, because cancer registries dont track statistics for this cancer. However, your doctor may be able to give you an estimate of your prognosis.
When it comes to surviving cancer, everyone is different. Your outcome will depend on the specific treatments you have and how well you respond to them. Talk to your doctor about your outlook and what it means.
How Is Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated
Each patients ideal course of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma treatment will vary according to the location of the primary cancer, how far it has spread, the overall health of the patient and several other factors. Many treatment plans include a combination of surgery to remove skin lesions and affected lymph nodes, as well as chemotherapy and radiation therapy to help shrink or destroy cancer cells that have traveled to other parts of the body.; ;
Moffitt Cancer Centers Cutaneous Oncology Program offers a full spectrum of diagnostics and leading-edge treatment options to patients with squamous cell carcinoma of any stage. To speak with a Moffitt oncologist specializing in skin cancer, submit a new patient registration form online or call .
- BROWSE
You May Like: What Is The Deadliest Type Of Skin Cancer
Who Gets Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Vagina
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Vagina affects women who are above the age of 50 years , in over 70% of the cases
- Less than 15% cases are seen in women below 40 years; over 50% cases are noted in older women, above the age of 70 years
- The condition is uncommon; the global incidence rate of this cancer type is around 7 cases per million women
- No geographical, racial, or ethnic preference is generally noted, although dark-skinned women are affected more than white-skinned women. The incidence ratio between African and African-American women to Caucasian women is 1.7:1
How Can A Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Treated
Surgery is usually the recommended treatment. This involves removing the SCC with a margin of normal skin around it, using a local anaesthetic. The skin is then closed with stitches or sometimes a skin graft is needed. Sometimes other surgical methods are used such as curettage and cautery. This involves scraping the SCC away using local anaesthetic.
Radiotherapy can also be used to treat SCC. This involves shining a beam of X-rays onto the skin. Usually several sessions are required.
For advanced SCC, a combination of treatments may be used. For SCC that has spread to other parts of the body a combination of surgery, radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy may be used.
You May Like: How To Identify Skin Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatment
Squamous cell carcinomas detected at an early stage and removed promptly are almost always curable and cause minimal damage. However, left untreated, they may grow to the point of being very difficult to treat.
A small percentage may even metastasize to distant tissues and organs. Your doctor can help you determine if a particular SCC is at increased risk for metastasis and may need treatment beyond simple excision.
Fortunately, there are several effective ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma. The choice of treatment is based on the type, size, location, and depth of penetration of the tumor, as well as the patients age and general health. Squamous cell carcinoma treatment can almost always be performed on an outpatient basis.
Multiple Myeloma Shows No Signs Of Slowing Down
Almost all people with multiple myeloma will still relapse on or after treatments. Once these patients relapse, they become more difficult to treat.2 There is a need for new agents so that patients and physicians can have options as the disease progresses.
You May Like: Is Renal Cell Carcinoma Hereditary
How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Squamous cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes , and when spreading does occur, it typically happens slowly. Indeed, most squamous cell carcinoma cases are diagnosed before the cancer has progressed beyond the upper layer of skin. There are various types of squamous cell carcinoma and some tend to spread more quickly than others.
How Can I Prevent Scc
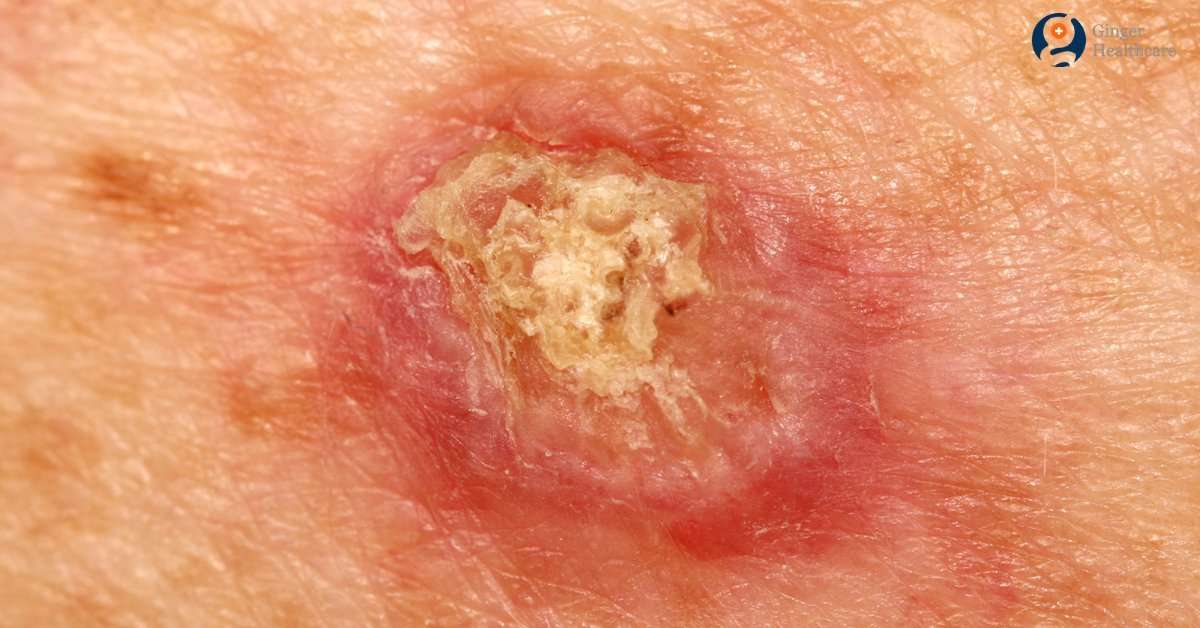
Reducing ultraviolet exposure will reduce the risk of getting an SCC.
Top sun safety tips
- Protect your skin with clothing, and dont forget to wear a hat that protects your face, neck and ears, and a pair of UV protective sunglasses.
- Spend time in the shade between 11am and 3pm when its sunny. Step out of the sun before your skin has a chance to redden or burn. Keep babies and young children out of direct sunlight.
- When choosing a sunscreen look for a high protection SPF to protect against UVB, and the UVA circle logo and/or 4 or 5 UVA stars to protect against UVA. Apply plenty of sunscreen 15 to 30 minutes before going out in the sun, and reapply every two hours and straight after swimming and towel-drying.
- Sunscreens should not be used as an alternative to clothing and shade, rather they offer additional protection. No sunscreen will provide 100% protection.
- It may be worth taking Vitamin D supplement tablets as strictly avoiding sunlight can reduce Vitamin D levels. You should consult your doctor about this.
Treatment of areas of scaly sun damage may reduce your risk of an SCC.
Read Also: How Bad Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
General Prognosis After Treatment
An individual’s prognosis depends on the type and stage of cancer, as well as their age and general health at the time of diagnosis. The majority of Squamous Cell Carcinoma cancers are successfully treated.
When small Squamous Cell Carcinomas are removed, the scars are usually cosmetically quite acceptable. If the tumours are very large, a skin graft or flap may be used to repair the wound in order to achieve the best cosmetic result and facilitate healing.
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
Read Also: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
What Are The Types Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma develops when the flat cells in the toplayer of skin grow and divide in an uncontrolled way.
You can get an SCC wherever there are squamous cells which is in manydifferent parts of the body. However, typically they appear on parts of theskin that have been exposed to a lot of ultraviolet radiation from the sunor from tanning beds.
An early form of skin cancer, called Bowen’s disease, which looks like a red, scaly patch, can also develop into an SCC if nottreated.
An SCC can be quite an aggressive cancer if left untreated. If you evernotice a sore, scab or scaly patch of skin that doesnt heal within 2 months,see a doctor.
Chemotherapy For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Superficial Squamous Cell Carcinoma may be able to be treated with topical chemotherapy that is applied to the skin as an ointment or cream. This type of treatment is only for skin cancers that biopsy-proven to affect only the top layer of skin.
5-fluorouracil is approved for the treatment of Superficial Squamous Cell Carcinoma, however, invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma should not be treated topically due to the risk of spread.
You May Like: How Often Does Melanoma Spread To Lymph Nodes
Who Gets Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Skin is generally uncommon and it affects elderly or older adults; some cases rarely develop in children too
- It can occur in both males and females
- The condition is prevalent worldwide, though dark-skinned individuals are affected less than lighter-skinned individuals
How To Improve Your Odds
Even if youve exhausted all of your treatment options, you dont have to give up. Researchers are always testing new SCC treatments in clinical trials. Getting into one of these studies could give you access to a drug or therapy that might slow or stop your cancer.
To avoid the worsening of your skin cancer or a new cancer in a different area, protect yourself from the suns damaging UV rays. Wear sun-protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat whenever you go outdoors. Apply a layer of broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
Also check your own skin for any new growths on a regular basis. Report any skin changes to your doctor right away.
Read Also: What Is Non Small Cell Carcinoma
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have skin cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging.
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers don’t spread as often as some other types of cancer, so the exact stage might not be too important. Still, your doctor might want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the growth or spread of the cancer through the skin. It also tells if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body that are close by or farther away.
Your cancer can be stage 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread beyond the skin. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
Other things can also help you and your doctor decide how to treat your cancer, such as:
- Where the cancer is on your body
- How fast the cancer has been growing
- If the cancer is causing symptoms, such as being painful or itchy
- If the cancer is in a place that was already treated with radiation
- If you have a weakened immune system
How Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Treated
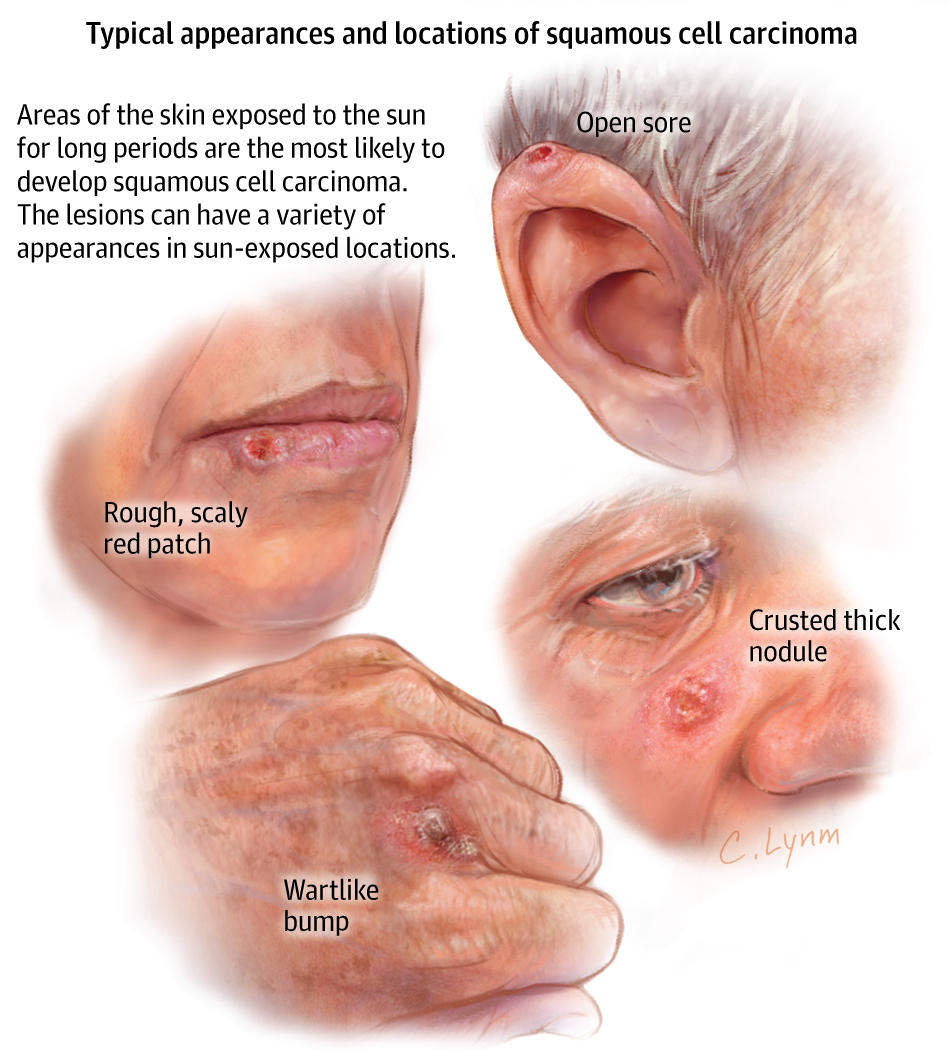
Although squamous cell cancers usually grow slowly,;it is important to see a dermatologist quickly. “The sooner you see your doctor and the cancer is diagnosed and treated, the less complicated the surgery to remove it will be, and the faster you will make a complete recovery, Dr. Leffell explains. The treatment for squamous cell cancer varies according to the size and location of the lesion. The surgical options are the same as those for basal cell cancer:;
- Surgical excision: Removing a squamous cell lesion is a simple procedure that typically;takes place in the dermatologist’s office. After numbing the cancer and the area around it with a local anesthetic, the doctor uses a scalpel to remove the tumor and some of the surrounding skin to make sure all cancer is eliminated. Estimating how much to take requires skill and expertise, Dr. Leffell notes. The risk of taking too little tissue is that some cancer remains; taking too much leaves a larger scar than is necessary. Shaped like a football, the wound is stitched together, using plastic surgery techniques. If dissolvable stitches are used, they will disappear on their own as the area heals. Though the procedure leaves some redness and a small scar, it tends to become less noticeable over time. “The cure rate for this type of excision is typically about 90 to 93 percent,” says Dr. Leffell. But, of course, this is dependent on the skill and experience of the doctor.”
Read Also: What Is The Leading Cause Of Skin Cancer
Radiotherapy For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Radiotherapy is generally used to treat Squamous Cell Carcinomas in areas near the eyes or on the nose or forehead, or other areas which are difficult to treat with surgery.
Radiotherapy Treatment Process – This treatment uses x-rays to target and kill cancer cells. X-ray beams are directed at the tumour, with no need for cutting or anesthesia.
Radiotherapy Treatment Recovery – Destruction of the tumour usually requires a series of treatments, administered several times a week for one to four weeks, or sometimes daily for one month.
Radiotherapy Treatment Prognosis – Cure rates range widely, from about 65 to 95 percent, since the technique does not provide precise control in identifying and removing residual cancer cells at the margins of the tumour. ;
The technique can involve long-term cosmetic problems and radiation risks, as well as multiple visits. For these reasons, though this therapy limits damage to adjacent tissue, it is mainly used for tumours that are hard to treat surgically, as well as patients for whom surgery is not advised, such as the elderly or those in poor health.