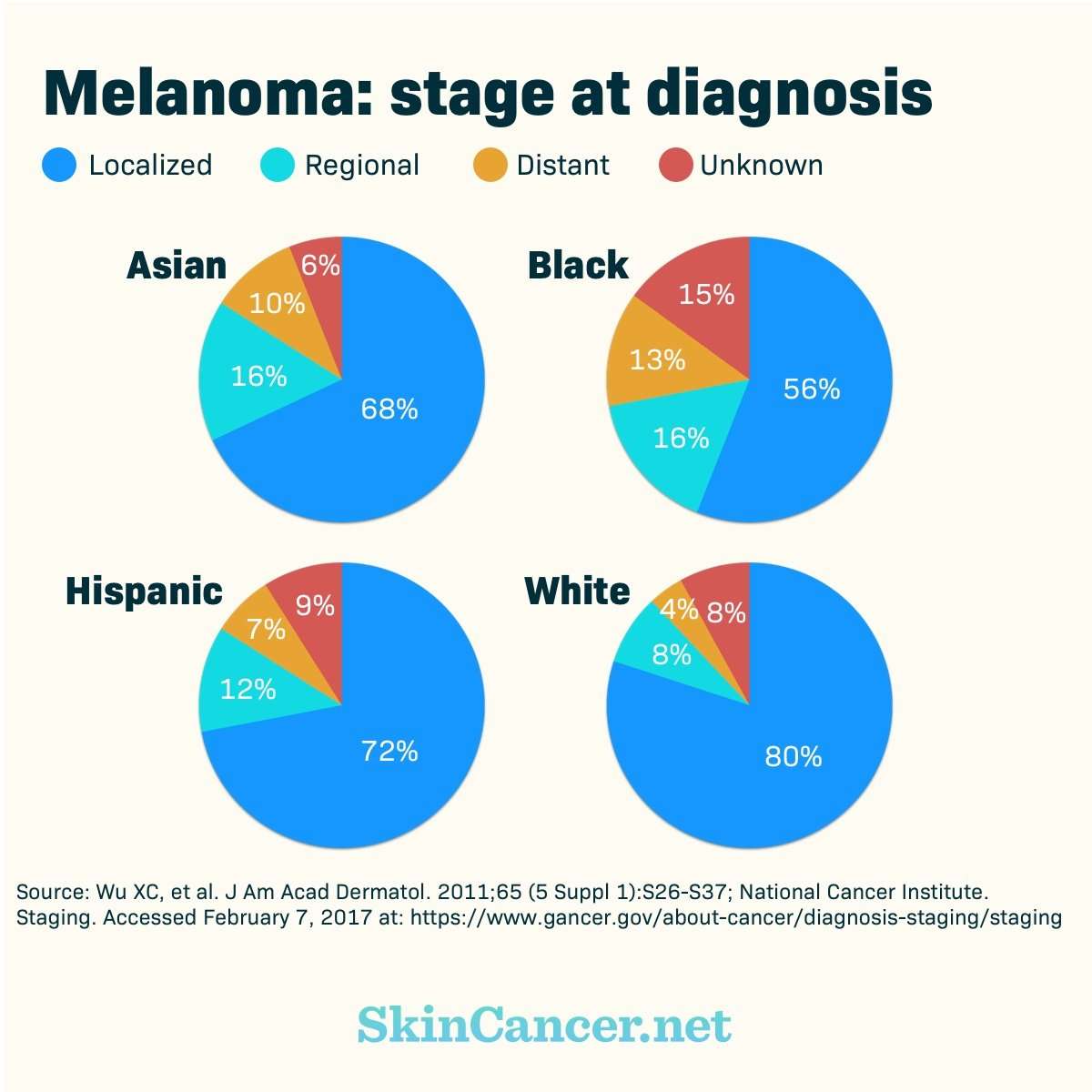
Is Ethnicity A Factor
The American Cancer Society estimates Caucasians are 20 times more likely to develop skin cancer than people of African descent. In fact, they note lifetime risk of getting melanoma is significantly higher for non-Hispanic Caucasians:
- 2.6 percent for Caucasians
- 0.58 percent for Hispanics
- 0.10 percent for African-Americans
In their lifetime, 1 in 27 white men and 1 in 42 white women will develop melanoma, says the Skin Cancer Foundation.
While skin cancer is more common in white people, this population also has the best rate of survival. People of Hispanic, Asian, Native American, Pacific Islander, and African descent follow.
The five-year survival rate of melanoma for white people with skin cancer is 94 percent, compared to only 69 percent survival in black people, notes the American Cancer Society.
A 2006 investigation found this is due, in part, to people of African descent being to receive a diagnosis of melanoma after the cancer has progressed to an advanced stage or spread to other parts of the body.
Other reasons for the discrepancy include that nearly say they werent trained on diagnosing cancer on black skin.
Generally, skin cancers in people of color may be
Until theyre 49, women have a higher risk for developing melanoma than men. In fact, the Skin Cancer Foundation reports that up until age 49, women have a higher probability of developing melanoma than every other cancer except breast cancer.
Study: Lack Of Education About Melanoma May Contribute To Black
Skin that makes more melanin is naturally darker and provides more protection from the suns UV radiation than light skin. But not all types of melanoma are related to UV radiation exposure. Your genes or other factors may have a role in your risk for it.
Its true that people with darker skin have a lower risk of melanoma. But as a recent study of non-Hispanic Black Americans showed, its also true that non-Hispanic Black Americans are more likely to have lower survival rates when they are diagnosed. Thats partly because compared with non-Hispanic whites, people with darker skin are more often diagnosed with later-stage melanoma . Its also because the most common type of melanoma among non-Hispanic Blacks called acral lentiginous melanoma has a lower survival rate.
This type of melanoma tends to occur on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, or under the nails. Those are not obvious places people think to check for skin cancer. The co-authors of the study, MaryBeth B. Culp, MPH, from the American Cancer Society and Natasha Buchanan Lunsford, PhD, from the Centers for Disease Control, believe education could lead Blacks to get skin checks from their doctors more regularly. They also hope better education will help health care providers spot potential skin cancers faster.
The study found:
- Five years after their diagnosis of melanoma, about 90 out of every 100 non-Hispanic whites were still alive, compared with about 66 out of every 100 non-Hispanic Blacks .
Melanoma In Mori Pacific And Asian People
Skin cancer, including melanoma, occurs much less commonly in Mori, Pacific and Asian people from New Zealand compared with New Zealand Europeans.
- Ethnic groups with naturally darker skin produce more melanin. Melanin absorbs the ultraviolet radiation that comes from the sun, preventing it from harming skin cells.
- Cultural and behavioural differences relating to clothing and activities may also account for varied risks of melanoma in different populations.
Even though less than 1% of Mori are diagnosed with melanoma, they tend to have thicker melanomas, which are more dangerous and more difficult to treat. Three Mori men and three Mori women died of melanoma in 2010.
- Melanoma in ethnic skin is often on the sole of the foot or under a nail.
- Take a new or growing skin spot seriously see your doctor straight away.
- Skin that burns easily and tans poorly
- Using sunbeds or tanning salons
These relative risk factors are less important for the less common types of melanoma . These arise sporadically.
Don’t Miss: What Does Skin Cancer On Your Lip Look Like
Q: What Other Skin Cancer Precautions Do You Recommend To Patients Of Color
I constantly stress the importance of monthly self-examinations of the skin that include not just sun-exposed areas but also the soles of the feet, the palms, the toenail and fingernail beds and also the genital areas places that one might not even think to look. Thats really where the biggest learning gap is. And everyone should get a full-body examination from a dermatologist once a year or any time they see something unusual, such as a new or changing growth or mole or, particularly in skin of color, a sore that doesnt heal. Unfortunately, most people of color are not doing this.
However, Ive observed growing awareness of the dangers of skin cancer among populations of color. We have a long way to go, but the interest is there. I think in the next phase were going to see larger-scale change that results in actual reduction of some of the disparities. Im very optimistic about the future. Interview by Lorraine Glennon
About the Expert:
Andrew Alexis, MD, MPH, is chair of the Department of Dermatology at Mount Sinai St. Lukes and Mount Sinai West in New York City. He is also professor of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. As director of the Skin of Color Center in New York City, he is actively involved in advancing patient care, research and education pertaining to dermatologic disorders prevalent in ethnic skin.
Can Black People Get Skin Cancer
Yes, Black people can develop skin cancer. This is because they can be exposed to the same environmental risk factors, such as ultraviolet rays, as people of other races or ethnicities.
Overall, skin cancer is less common in Black people. Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found that in 2018 , 1 case of melanoma occurred per 100,000 Black people, compared with 25 cases per 100,000 white people.
Recommended Reading: Can Laser Hair Removal Cause Skin Cancer
People With A Weak Immune System
Your immune system is your bodys defense system. It fights off germs. It also helps you fight off cancer. If your immune system is weak, it can’t do that as well. You may have a weak immune system if:
- You have had an organ transplant.
- You need to take a medication that suppresses your immune system.
Skin Cancer In People Of Color
As a person of color, you might question whether skin cancer ought to be one of your top health concerns. If you’re African-American, you may not even think you can getskin cancer. But youâd be surprised.
“Anyone can get skin cancer,” says Lisa Chipps, MD, director of dermatologic surgery at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center. It is less common in people of color, but itâs often more serious. That’s because it’s usually found later, when it’s harder to treat.
If you know what to look for and how to protect yourself, you can prevent it or catch it early.
You May Like: Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Deadly
What Are The Risk Factors For Skin Cancer
People burn or tan depending on their skin type, the time of year, and how long they are exposed to UV rays.
Anyone can get skin cancer, but people with certain characteristics are at greater risk
- A lighter natural skin color.
- Skin that burns, freckles, reddens easily, or becomes painful in the sun.
- Blue or green eyes.
- Certain types and a large number of moles.
- A family history of skin cancer.
- A personal history of skin cancer.
- Older age.
How People Of Color Can Reduce Their Skin Cancer Risk
Dermatologists in the United States tell their patients with skin of color to reduce their risk of getting skin cancer by doing the following:
Seek shade whenever possible. The sun causes many skin cancers.
Wear clothing that protects your skin from the sun. A wide-brimmed hat can shade your face and neck. You also want to wear shoes that cover the entire foot. African Americans often develop skin cancer on their feet.
Wear sunscreen. Yes, people of color should wear sunscreen. Dermatologists recommend that people of color use sunscreen that has:
Apply sunscreen to dry skin 15 to 30 minutes before going outdoors. You want to apply sunscreen to skin that will be bare. Be sure to apply sunscreen every day even on cloudy days.
When outdoors, reapply sunscreen. You want to reapply:
Never use tanning beds or sunlamps. These emit harmful UV rays, which can cause skin cancer.
Skin of color: How to prevent and detect skin cancer
Although people of color have a lower risk of developing skin cancer than Caucasians, when skin cancer develops in people of color, it is often diagnosed at a more advanced stage making it more difficult to treat.
Follow these tips from dermatologists to protect your skin from the sun and reduce your risk of skin cancer.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Skin Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer In Black People
The main symptom of skin cancer is a change in an area of skin. This sounds very general, so lets dive deeper into some general qualities to look for.
Not all skin cancers appear the same. Its possible that a cancerous area could have one, a few, or all the characteristics listed below.
Whats important is that you make an appointment with a dermatologist if you have concerns about a certain area. They can evaluate the area to help determine whether it may be skin cancer.
How Race/ethnicity Can Increase The Risk Of Getting Cancer
There are several risk factors that can increase a persons chance of developing cancer, and one of them is race/ethnicity. Statistics show us that certain racial groups are more likely to get some types of cancer than other groups are. It helps to understand these statistics, so that you can better determine your own personal risk. Below, RCCA explores some of the most common racial and ethnic disparities for cancer.
Also Check: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
Q: Prevention Is Key What Are The Challenges
Multiple studies show much less frequent use of sunscreen among people of color. The most important rule, as with everyone, is simply to make sure you use it. Nuances arise in helping darker-skinned patients overcome some of the aesthetic barriers to use. The mineral-based sunscreens that are least irritating often create an ashen look, with residue, and thats a big obstacle. Patients constantly ask, What sunscreen can I use thats going to be acceptable for my skin? Ive found that the sophisticated formulations that have nanoparticles, where the zinc oxide and titanium dioxide have been micronized to limit the chalky look, tend to work well on darker skin tones. Theres been a general call to action in the industry to test sunscreen formulations on diverse populations in order to establish cosmetic acceptability across a range of skin types and complexions.
Risk Factors: Everyone Is At Risk
Studies have shown that even at low levels, ultraviolet radiation damages all types of skin.1Melanin is a pigment that gives skin its tan or brown color. Darker skin has larger, more productive melanocytes.1 Melanin protects skin from UV radiation. Dark skin recovers from UV damage more quickly than light skin. Nevertheless, no one is immune to UV damage. Sun protection is important for everyone, regardless of skin tone.
Non-UV risk factors contribute to skin cancer in people with dark skin tones.1 These risk factors include:
- Scarring
- Weakened immune system
- Human papilloma virus infection
The risk factors for some skin cancers are unknown. For example, no one knows why some people develop melanoma on parts of the body that rarely get sun.
Don’t Miss: Is Melanoma Caused By The Sun
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed
Skin cancer is often diagnosed by a dermatologist. This is a type of doctor who specializes in conditions affecting the skin. The first steps include getting your medical history and performing a physical exam.
The physical exam will include a skin exam, during which your dermatologist checks your skin for spots or bumps that appear abnormal. If they find an area that has a concerning color, size, or shape, theyll perform a skin biopsy.
During a skin biopsy, all or a portion of the abnormal-looking area is carefully removed using a sterile instrument. Local anesthesia is used to numb the area, so you wont feel pain during the procedure.
The biopsy sample is sent to a lab where its checked under a microscope for signs of cancer. When the analysis is complete, your dermatologist will receive a report of the results, which theyll then communicate to you.
Skin Exams Can Reduce Mens Risk Of Dying Of Melanoma
Found early, melanoma is highly treatable. Skin self-exams can help men find skin cancer early. Of course, it helps to have your partner check hard-to-see areas like your backside.
Getting your partner involved can also make skin exams more fun. With a partners help, a skin exam may even become something that you look forward to.
Youll find a video that shows how a partner can help you check your skin for signs of skin cancer at, Skin self-exam: How to do.
If youve never been screened for skin cancer, now is an excellent time to start. Screenings can help find early signs of skin cancer.
The AAD offers free SPOTme® skin cancer screenings. Most take place in the spring. If you dont find a free screening in your area, you can sign up for an e-mail alert, which will let you know when a screening is scheduled in your area.
You can find out whether a screening is being offered in your area at, Find a free skin cancer screening.
Also Check: How Do You Remove Skin Cancer
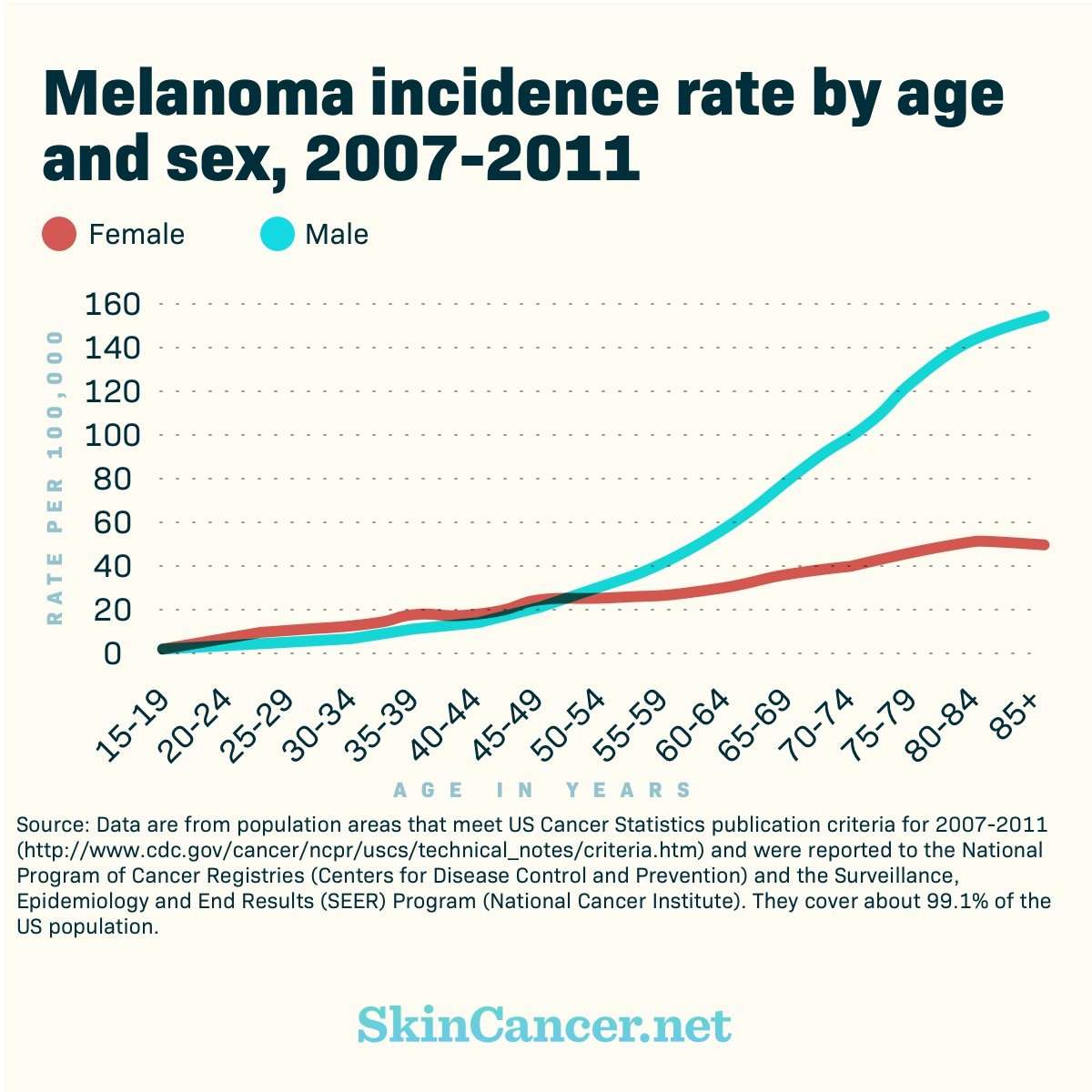
Melanoma Skin Cancer Incidence By Age
Melanoma skin cancer incidence is related to age, with the highest incidence rates being in older people. In the UK in 2016-2018, on average each year more than a quarter of new cases were in people aged 75 and over. In contrast to most cancer types, melanoma skin cancer also occurs relatively frequently at younger ages.
Age-specific incidence rates increase steadily from around age 20-24 and more steeply in males from around age 55-59. The highest rates are in in the 85 to 89 age group for females and males.
Incidence rates are significantly higher in females than males in the younger age groups and significantly lower in females than males in the older age groups. The gap is widest at age 20 to 24, when the age-specific incidence rate is 2.7 times higher in females than males.
Melanoma skin cancer , Average Number of New Cases per Year and Age-Specific Incidence Rates per 100,000 Population, UK, 2016-2018
For melanoma skin cancer, like most cancer types, incidence increases with age. This largely reflects cell DNA damage accumulating over time. Damage can result from biological processes or from exposure to risk factors. A drop or plateau in incidence in the oldest age groups often indicates reduced diagnostic activity perhaps due to general ill health.
Skin Cancer In Asians
Non-melanoma skin cancer is uncommon in Asians, but it has been reported. SCC and BCC may be pigmented in Asians, leading to misdiagnosis as melanoma. Melanoma is diagnosed in 1.6 per 100,000 Asians and Pacific Islanders.5 Women are slightly more likely than men to be diagnosed.3 Twenty-two percent of melanomas in Asians are superficial spreading melanoma.3 Melanoma is most likely to develop on the lower limbs and hips.3
The 5-year survival rate for Asians with local melanoma is 95.3%.3 The 5-year survival rates for regional and distant melanoma are 65.5% and 27.5%.3
Also Check: Is Melanoma The Same As Skin Cancer
Differences In Diagnosis And Outcomes
Although minority groups may be at a lower risk of developing skin cancer, they are disproportionately affected by worse outcomes and diagnoses. Overall:
- Black and Latino people are more likely to die than White people for all skin cancers.
- When it comes to melanoma specifically, Black people are more likely to be diagnosed at later stages or with distant metastasis when compared to White people.
- One study found that 91 percent of White people are diagnosed with earlier stage melanoma, compared to 74 percent and 48 percent of Latino and Black people, respectively.1,2
How Common Is Skin Cancer
You may think places with sunnier, hotter weather have more cases of skin cancer. This isnt necessarily the case. In fact, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes California and Florida had fewer cases per 100,000 people than states with cooler climates, like Wyoming, Montana, and Idaho, in 2015.
The states with the fewest cases of skin cancer are:
- Alaska
- Wyoming
Read Also: How Do You Treat Skin Cancer
Skin Color And Skin Cancer
The three most common skin cancers are:
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Melanoma
Getting too much ultraviolet light is linked to all of these cancers. But it is just one cause and may not even be a factor in melanoma in people of color. Some other things that can raise your risk of skin cancer are:
- Skin conditions that lead to scarring or chronic swelling and redness, like discoid lupus
- An infection that doesn’t heal
- Injury, such as a bad bruise or burn
- Having moles, especially on the palms, soles of your feet, and mouth
Cancer Incidence By Major Ethnic Group
Age-standardised incidence rates for White males with cancer range from 408.2 to 416.8 per 100,000. Rates for Black males are similar, ranging from 316.7 to 488.3 per 100,000 whereas the rates for Asian males are significantly lower, ranging from 168.3 to 258.9 per 100,000.
For females there is a different pattern the AS rates for White females range from 351.0 to 358.4 per 100,000, while rates for Asian and Black females are significantly lower ranging from 168.4 to 249.8 per 100,000 and 215.0 to 322.0 per 100,000 respectively.
Ranges are given because of the analysis methodology used to account for missing and unknown data. A total of 1,192,585 cancer cases were identified 24% had no known ethnicity.
Don’t Miss: How Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Start