How Fast Does Melanoma Spread
Melanoma is a deadly form of skin cancer because of its ability to metastasize to local lymph nodes and other organs. It is estimated that melanoma kills, on average, over 10,000 people in the United States every year.
The first sign of flat melanoma is usually a new spot or an existing mole or freckle that changes in appearance. Some changes can include:
- A spot that has grown in size
- A spot where the edges are looking irregular versus smooth and even
- A spot that has a range of colors such as brown, black, blue, red, white or light gray.
- A spot that has become itchy or is bleeding
According to Dr. Andrew Duncanson, board-certified dermatologist at Forefront Dermatology, It is important to know that melanoma can appear on areas of the skin not normally exposed to the sun such as under the arm, chest, and buttocks. It can also appear in areas that you are not able to see easily on your own including the ears, scalp, back of legs, and bottom of feet. I always recommend to my patients to look for the ugly duckling spot the new spot that doesnt look like any others. Additionally, ask a family member to look over the hard to see areas monthly, while also getting an annual skin cancer exam by a board-certified dermatologist to detect skin cancer early.
How Fast Does Melanoma Spread And What Should I Know About This Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most lethal and serious type of skin cancer, with the exception of certain rare skin cancers, due to melanoma being often likely to metastasize to the internal organs and lymph nodes. 77 percent of all skin cancer-related deaths are due to melanoma, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. Being able to recognize this cancer when it is in its very early stages is crucial in surviving this skin cancer.
Amelanotic Melanoma Risk Factors
Though these risk factors dont mean someone will develop melanoma, they are linked with increased risk of all forms of the cancer, including amelanotic melanoma.
Exposure to UV rays: Damage to DNA in your skin cells, from exposure to UV rays , is the No. 1 risk factor for all types of melanoma. Both natural sunlight and artificial tanning lamps increase the risk of developing this type of skin cancer. Getting many sunburns during childhood also has been associated with the development of melanoma on the chest, back and legs.
Moles: If you have a lot of moles or have atypical moles, youre at greater risk of developing melanoma. Additionally, patients with the inherited condition dysplastic nevus syndrome are at a high risk of developing melanoma during their lifetime.
Fair skin: People who have light-colored, freckled skin and blond or red hair with blue or green eyes are at a greater risk of developing melanoma. This is especially true if your skin tends to burn as opposed to tanning when exposed to UV rays.
Race: Melanoma is 20 times more likely for white people than it is for black people, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology .
Family and personal history: If your close relatives have a history of melanoma, youre at increased risk. If youve previously had melanoma or another type of skin cancer, the chance of developing it again is also greater.
Read Also: Can You Get Skin Cancer From Radiation Treatments
Are There Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
There are many types of skin cancer. Your doctor can tell you more about the type of skin cancer you have.
Basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are much more common than melanoma and dont often spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma is more deadly because it is more likely to spread to other parts of the body.
Whats The Outlook For Stage 4 Melanoma
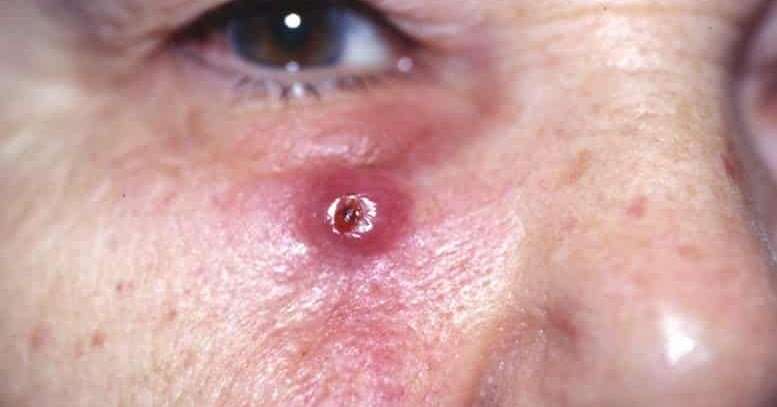
Once the cancer spreads, locating and treating the cancerous cells becomes more and more difficult. You and your doctor can develop a plan that balances your needs. The treatment should make you comfortable, but it should also seek to remove or slow cancer growth. The expected rate for deaths related to melanoma is 10,130 people per year. The outlook for stage 4 melanoma depends on how the cancer has spread. Its usually better if the cancer has only spread to distant parts of the skin and lymph nodes instead of other organs.
You May Like: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Where Else Does Melanoma Spread To
When melanoma advances to stage 3, it means the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes or the skin around the primary tumor and lymph nodes. In stage 4, the cancer has moved to other areas far beyond the lymph nodes, like your internal organs. The most common places melanoma spreads to are the:
- lungs
- brain
- stomach, or abdomen
These growths will cause different symptoms, depending on which areas it has spread to. For example, you may feel breathless or constantly cough if the cancer has spread to your lungs. Or you may have a long-term headache that wont go away if it has spread to your brain. Sometimes the symptoms for stage 4 melanoma may not appear for many years after the original tumor was removed.
Talk to your doctor if youre feeling new pains and aches or symptoms. Theyll be able to help diagnose the cause and recommend treatment options.
How Fast Does Melanoma Grow
Some types of melanoma can grow very quickly, becoming life-threatening in as little as six weeks. If left untreated it can spread to other parts of the body.
Nodular melanoma is a highly dangerous form of melanoma that looks different from common melanomas and can grow in just a few weeks. Raised and even in color, nodular melanoma are often red, pink, brown, or black. It can be life-threatening if not detected and removed quickly. See your doctor immediately if you notice any of these changes.
Its also important to note that while sun exposure is a major risk factor in melanoma, the disease can develop in parts of the body that get little or no sun exposure.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If Skin Cancer Is Melanoma
Symptoms Of Subungual Melanoma
The symptoms of subungual melanoma are often difficult to diagnose, because their incidence is in a relatively unknown place. Subungual melanomas often appear as a dark line below the nail. However, since the predisposition of the condition happens in people with dark color skin, such lines underneath the nails are usually normal and benign. In the event that the stripe changes shape or color, or if a new stripe appears, it is advisable to consult the medical professional. Other indications of advanced subungual melanoma are damaged nail beds, or skin hyperpigmentation. The first signs and symptoms of subungual melanoma are often the development of a new pigmented growth or unusual appearance on the skin or nails.
Melanomas can grow in areas of the body with little or no exposure to the sun. They are named occult melanomas. When melanoma arises in people with darker skin, it is more likely to happen in a hidden area of the body. Subungual melanoma begins under the nail, and it can affect hands or feet. The first sign of a subungual melanoma is usually a brown or black coloration, often confused with a contusion.
What Is Superficial Spreading Melanoma
Superficial spreading melanoma is the most common type of melanoma, a potentially serious skin cancer that arises from melanocytes along the basal layer of the epidermis.
Superficial spreading melanoma is a form of melanoma in which the malignant cells tend to stay within the epidermis for a prolonged period . At first, superficial spreading melanoma grows horizontally in the skin this is known as the radial growth phase, presenting as a slowly-enlarging flat area of discoloured skin.
An unknown proportion of superficial spreading melanoma become invasive, that is, the melanoma cells cross the basement membrane between the epidermis and dermis and malignant melanocytes enter the dermis. A rapidly-growing nodular melanoma can arise within superficial spreading melanoma and proliferate deeply within the skin.
Melanocytes, a layer of cells in the skin produce melanin, a brown-black skin pigment that determines skin and hair color and protect against the damaging rays of the sun. These melanocytes spread as the person ages and form clusters.
Read Also: What Is Precancerous Skin Cancer
What Is Subungual Melanoma
Nails are adjoining structures of the skin located in the distal regions of the limbs, consisting primarily of hardened dead cells that contain a fibrous protein called keratin. Nails can be affected by pathologies of the skin and the integumentary system, but they can also be affected as part of systemic diseases.
Subungual melanomaacral lentiginous melanoma
We must differentiate the following categories:
- Ungual melanoma: melanoma that originates from below the surface of the nail.
- Subungual melanoma: melanoma from the matrix of the nail.
- Periungual melanoma: melanoma that originates from the skin next to the nail plate.
Could It Just Be A Bruise
Just for some reference, here are some images of bruises of the toe and toenail for you to compare.
The marking on this toenail is a bruise. Note the mark goes across the nail and you can see some bruising on the skin too.
This bruised toenail has a white mark where the damage was caused and the mark looks like blood.
Where there is a marking at the base of the nail like in this image, this is usually caused by impact damage kicking something for example.
Read Also: How Does Skin Cancer Develop
Have You Checked Your Nails Lately
Did you know that melanoma and other skin cancers can form under the fingernails and toenails? Melanoma of the nail is not widely known about, and it usually comes as a surprise that people with dark skin are affected by this type of melanoma. In fact, famous musician Bob Marley died in 1981 from an acral lentiginous melanoma, which spread to his lungs and brain from under his toenail.
In recent weeks, Dr Helena was privileged enough to not only attend but also address skin cancer doctors at the Skin Cancer College of Australasia annual congress. The Skin Cancer College Australasia a non-profit, peak body representing more than 1,000 skin cancer practitioners in both Australia and New Zealand. Around 400 doctors were in attendance during the conference.
Dr Helenas topic for this lecture was on how to diagnose melanoma and other cancers that have grown under the nail. Below is a recap of some of the key points, with tips on what to look for.
These cancers are often diagnosed late because they are relatively rare, and the biopsy is challenging. There are different types of nail-related melanoma. Subungual melanoma comes from the nail matrix . Other nail-related cancers include ungula melanoma, which occurs underneath the nail plate, and periungual melanoma, which comes from the skin next to the nail plate.
How Fast Can Melanoma Spread
![How fast does Bladder Cancer Grow [Read 5 Step]](https://img.healthyskinworld.com/wp-content/uploads/how-fast-does-bladder-cancer-grow-read-5-step.jpeg)
A second factor that plays an important role in how fast melanoma can spread is the genetic factor. Certain gene abnormalities encourage melanoma to invade the surrounding tissue. This means that certain ways of how cells are composed can affect the speed of the melanoma spreading. This process, though, can vary significantly from one person to another.
If you have been diagnosed with melanoma skin cancer, talk with your doctor about your personal situation and treatment options.
You May Like: How Does Skin Cancer Occur
Red Flag #: Headaches Or Visual Changes
Just like the liver, not everyone will notice symptoms of melanoma spreading to the brain. But when symptoms do show up, its usually in the form of headaches, problems with eyesight, paralysis on one side of the body, or seizures. If someone simply has a headache, that doesnt mean they have advanced stage melanoma, Dr. Yushak says. But if its a headache thats not going away after a week, and you never have headaches, then thats something that definitely needs to be checked out.
Read Also: What Does Advanced Skin Cancer Look Like
Tests To Check Your Lymph Nodes
If you are diagnosed with melanoma, your doctor may suggest some tests to check the lymph nodes. Not everyone needs these test. Whether you have them depends on the size of the melanoma and if the lymph nodes look or feel swollen. These tests include:
- A sentinel lymph node biopsy
A sentinel lymph node biopsy is a way of checking the lymph nodes closest to the melanoma
- Ultrasound
An ultrasound scan uses sound waves to make up a picture of an area of the body.
- Fine needle aspiration
If the ultrasound scan of the lymph nodes is abnormal, the doctor will do a fine needle aspiration.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Metastatic Melanoma
Its A Fact That Melanoma Can Be Well Under Six Millimeters And In Fact Can Be Only One Millimeter In Diameter
The ABCD rules for melanoma certainly do not apply to all such skin cancers.
Some dermatologists even refer to very small melanomas as micromelanomas, meaning, they are much smaller than a pencil eraser .
Time It Takes for a Tiny Melanoma to Grow to Two Millimeters
A tumor that does not arise from a pre-existing mole doesnt grow from one cancer cell to two millimeters overnight.
It is completely unknown how long it takes for melanoma to achieve a size of two mm, says Dr. Steven Musick, MD, a board certified dermatologist who runs Musick Dermatology, LLC, in Swansea, IL, which provides state-of-the-art medical and surgical care for all disorders of the skin, hair and nails.
Though there are, on record, serial images of progressing superficial spreading melanomas, these do not tell how long it took for the tumor to get to two millimeters.
Instead, such images show increase in lateral growth usually from a starting point of over two millimeters, e.g., from three to five millimeters in 12 months.
Prior imaging records are not available because the patient didnt begin noticing the lesion until it was over two millimeters.
And even if, by chance, a 0.2 mm spot was photographed, and looked benign, and then 12 months later it was two millimeters and looked suspicious, and a biopsy confirmed melanoma, this one particular example would not speak for melanoma in general.
The fastest growing melanoma is the nodular type. It is not flat, hence its name.
Steven Musick, MD
When Melanoma Can’t Be Cured
If your cancer has spread and it is not possible to cure it by surgery, your doctor may still recommend treatment. In this case, treatment may help to relieve symptoms, might make you feel better and may allow you to live longer.Whether or not you choose to have anti-cancer treatment, symptoms can still be controlled. For example, if you have pain, there are effective treatments for this. General practitioners, specialists and palliative care teams in hospitals all play important roles in helping people with cancer.
Recommended Reading: Can Skin Cancer Look Like Psoriasis
Symptoms Of Melanoma Spread
A mole developing the following characteristics at a fast pace, within days or weeks could show melanoma:
- Asymmetry, or both sides of the hole looking different
- Border or moles with blurry or jagged edges
- Color, or moles darkening, loosing color, or spotting multiple colors such as blue, red, white, pink, purple or gray
- Diameter, or a mole larger than 1/4 inch in diameter
- Elevation, or a mole raised above the skin and with a rough surface.
The bleeding or itching of such moles reinforces the possibility of melanoma. Apart from moles, speedy development of a scaly or crusted growth on the skin could also show spread of melanoma.
What Are The Symptoms Of Subungual Melanoma
When you hear the word melanoma, your first thought might be irregular-shaped moles on the skin caused by sun damage. But since subungual melanoma affects the nail matrix, the signs and symptoms dont look like a typical mole on the skin.
Symptoms of this condition include:
- a light- to dark-brown colored band on the nail thats usually vertical
- a dark band on the nail that slowly expands and covers more of the nail
- dark nail pigmentation that expands to the surrounding skin
- a nodule underneath the nail with or without a pigmentation band
- nail brittleness and cracking
- bleeding at the site of pigmentation
Its important to note that not all cases of this condition cause pigmentation changes in the nail. While this can make the melanoma more challenging to detect, a telltale sign of the condition is that it usually affects one nail at a time.
You May Like: How Do You Know If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has Spread
Don’t Miss: What Is Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- How far has the melanoma spread under my skin?
- Has it spread anywhere else?
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- Will I need other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- What can I do about side effects that I might have?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- How soon do I need to start treatment?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
What Kind Of Treatment Will I Need
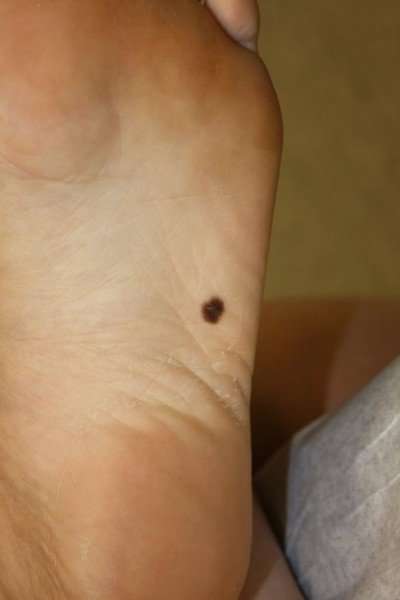
There are many ways to treat melanoma. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
Most early stage melanomas can be treated with surgery alone. More advanced cancers need other treatments.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage of the cancer
- The results of lab tests on the cancer cells
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the melanoma or help in some way
- Your age
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Read Also: How Fast Does Renal Cell Carcinoma Grow