Benign Tumors That Develop From Other Types Of Skin Cells
- Seborrheic keratoses: tan, brown, or black raised spots with a waxy texture
- Hemangiomas: benign blood vessel growths, often called strawberry spots
- Lipomas: soft growths made up of fat cells
- Warts: rough-surfaced growths caused by some types of human papilloma virus
Most of these tumors rarely, if ever, turn into cancers. There are many other kinds of benign skin tumors, but most are not very common.
What Are The Treatment Options For Melanoma
Surgery performed to remove the melanoma while leaving as much nearby skin intact as possible. The surgeon may also remove one or more nearby lymph nodes to look for signs that the cancer has spread.
Targeted therapy uses drugs directed at specific abnormal proteins in cancer cells. Patients whose melanoma carries a mutation in the BRAF gene may be treated with drugs that target the altered BRAF protein or the associated MEK proteins. Three drug combinations have been FDA-approved for metastatic and high-risk melanoma with a BRAF mutation: dabrafenib and trametinib; encorafenib and binimetinib; and vemurafenib and cobimetinib
Immunotherapy uses the bodys immune system to fight cancer cells. Dana-Farber scientists have led clinical trials of the drug ipilimumab, one of a class of immunotherapy drugs that are helping some patients with advanced melanoma survive 10 years or longer. In other Dana-Farber-led trials, the immunotherapy agent nivolumab achieved three-year survival rates of more than 40% in patients with metastatic melanoma. Dana-Farber investigators have also found that initially treating advanced melanoma patients a combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab results in a much higher response rate than treatment with ipilimumab alone. A range of other clinical trials testing various immunotherapies is also under way for patients with advanced melanoma.
What Are Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell cancer can occur anywhere on the skin, but it tends to develop on sun-exposed areas of the body such as the face, ear, scalp, shoulders, neck, lips, backs of the hands, and forearms.;
Squamous cell cancers may look like:
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Raised growths or lumps, sometimes with a depressed area in the center
- Open sores that dont completely heal, or that heal and return
- A flat area that is only slightly different from normal skin
Recommended Reading: What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
There Are Four Common Types Of Skin Biopsies:
The dermatologist will never shave off or cauterize a growth that might be melanoma. An excisional biopsy will be performed, or, if the growth is too large to be removed entirely, a tissue sample will be taken.
The Great Millennial Skin Cancer Crisis
Melanoma isnt just an older mens issue anymore. Its now killing young guys at an alarming rate.
Around the time that Dustin Allen, a soft-spoken electrical engineer, turned 27, he noticed a small red spot on his right temple. He thought it was nothing, maybe an acne scar. But it didnt fade away. In fact, it kept getting darker, and he started to see splotches of dark brown popping up inside it, too. He asked his primary-care physician if he should be concerned.She said it just looked like sun damage and they typically dont worry about that until it gets to about nine millimeters, he says. His father had had melanoma, though, so he knew he was at higher risk for this most dangerous form of skin cancerhaving a first-degree relative with it can push up your odds by 50 percent. And with his red hair and freckle-prone complexion, another risk factor, he couldnt shake the bad feeling he had about that spot.
Of the things that keep dermatologists up at night, melanoma is at the top of that list, says Jonathan Ungar, M.D., medical director of the new Kimberly and Eric J. Waldman Melanoma and Skin Cancer Center at Mount Sinai in New York City. The fifth most common cancer for men and among the top three for young adults, its been on the rise.
Don’t Miss: How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Removed From The Nose
How Do You Prevent Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell skin cancers may be prevented in some cases.;
- Limit exposure to ultraviolet rays
- Stay in the shade
- Wear a shirt and hat
- Wear sunglasses to protect eyes
- Avoid tanning beds and sun lamps
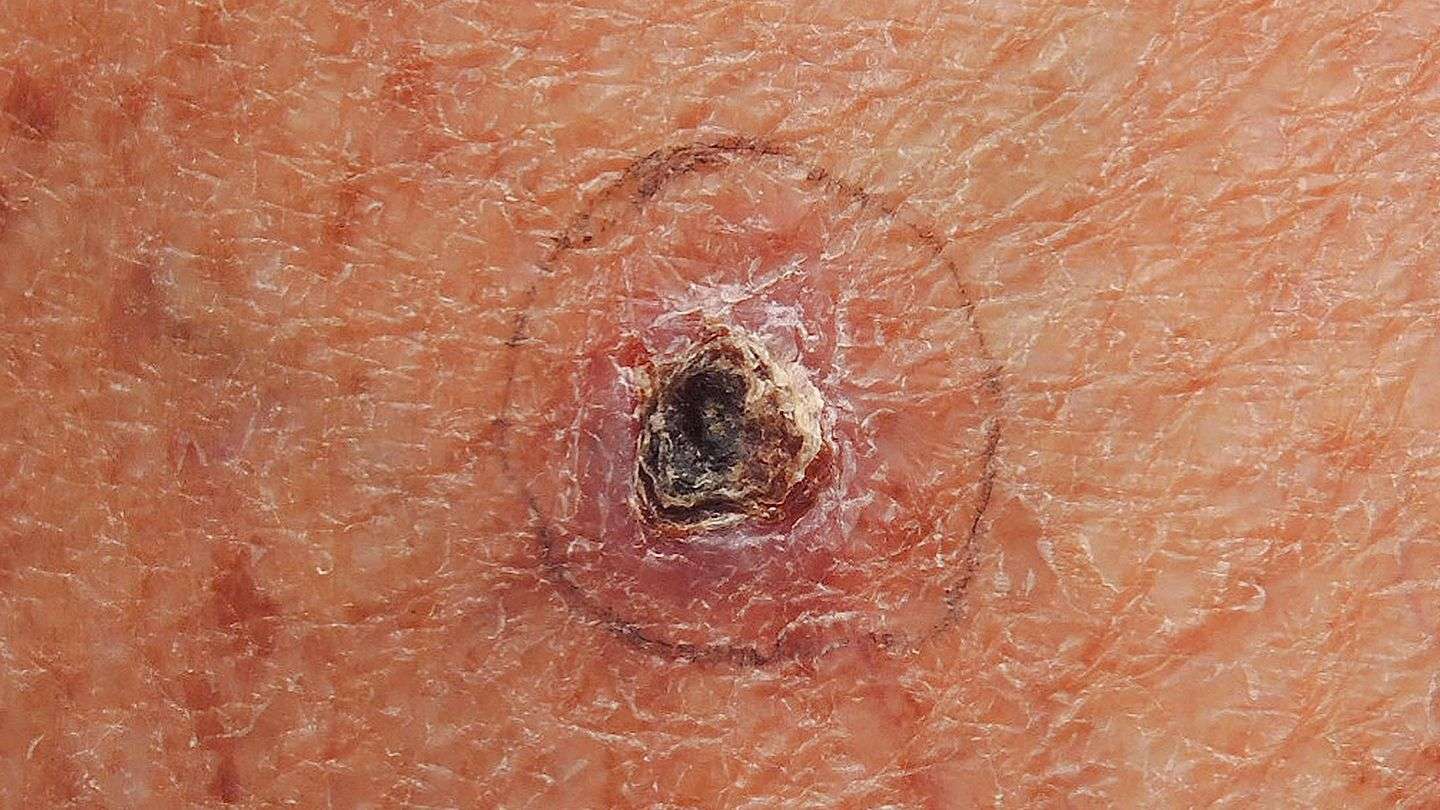
Possible Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
The most important warning sign of melanoma is a new spot on the skin or a spot that is changing in size, shape, or color.
Another important sign is a spot that looks different from all of the other spots on your skin .
If you have one of these warning signs, have your skin checked by a doctor.
The ABCDE rule is another guide to the usual signs of melanoma. Be on the lookout and tell your doctor about spots that have any of the following features:
- A is for Asymmetry: One half of a mole or birthmark does not match the other.
- B is for Border:The edges are irregular, ragged, notched, or blurred.
- C is for Color:The color is not the same all over and may include different shades of brown or black, or sometimes with patches of pink, red, white, or blue.
- D is for Diameter:The spot is larger than 6 millimeters across , although melanomas can sometimes be smaller than this.
- E is for Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape, or color.
Some melanomas dont fit these rules. Its important to tell your doctor about any changes or new spots on the skin, or growths that look different from the rest of your moles.
Other warning signs are:
- A sore that doesnt heal
- Spread of pigment from the border of a spot into surrounding skin
- Redness or a new swelling beyond the border of the mole
- Change in sensation, such as itchiness, tenderness, or pain
- Change in the surface of a mole scaliness, oozing, bleeding, or the appearance of a lump or bump
You May Like: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
Whats The Difference Between Melanoma And Non
Monday, January 11th, 2016 | Written by Premier Surgical Staff
With the skin as the largest organ of the body, it is understandable skin cancer is the most common type of human cancer. The American Cancer Society estimates there will be approximately 73,000 new cases of melanoma diagnosed in 2015 and 3.5 million cases of basal and squamous cell skin cancer. In its basic form, cancer occurs when a previously normal cell undergoes a transformation and begins to grow abnormally and multiply. As the abnormal cells multiply they form a mass or tumor. If the tumor is malignant it will begin to invade neighboring tissues, restricting oxygen and vital nutrients needed for the surrounding tissues to survive. Malignant tumors may also metastasize or travel via the blood stream to other organs.
Many people consider skin cancer and melanoma to be synonymous when in fact melanoma is only one form of skin cancer. Melanoma is by far the most aggressive and deadly, and perhaps the most universally known. Melanoma begins in the cells found in the lowest layer of the epidermis referred to as the melanocytes. These cells are responsible for pigment within the skin giving it a brown color. Melanoma most often is found on the skin, even on areas normally not exposed to the sun, and can also start in other parts of the body such as the eyes or mouth. The risk of melanoma increases as people age.
To learn more about surgical oncology at Premier Surgical Associates visit our website.
Recurrent Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas are the most common type of skin cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. These cancers develop within the basal cell layer of the skin, in the lowest part of the epidermis.
Patients who have had basal cell carcinoma once have an increased risk of developing a recurrent;basal cell cancer. Basal cell cancers may recur in the same location that the original cancer was found or elsewhere in the body. As many as 50 percent of cancer patients are estimated to experience basal cell carcinoma recurrence within five years of the first diagnosis.
Basal cell carcinomas typically grow slowly, and it is rare for them to metastasize or spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. But early detection and treatment are important.
After completing treatment for basal cell carcinoma, it is important to perform regular self-examinations of the skin to look for new symptoms, such as unusual growths or changes in the size, shape or color of an existing spot. Skin cancers typically develop in areas of the body that are exposed to the sun, but they may also develop in areas with no sun exposure. Tell your oncologist or dermatologist about any new symptoms or suspicious changes you may have noticed.
- Have a history of eczema or dry skin
- Have been exposed to high doses of UV light;
- Had original carcinomas several layers deep in the skin
- Had original carcinomas larger than 2 centimeters
You May Like: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
Prevention And Early Detection
The exact cause of subungual melanoma is unknown, meaning that patients cannot take specific steps to prevent this condition. However, because it may be associated with trauma to the hands and feet, you may want to keep yours hands and feet protected.2 For example, you can protect your hands and feet by wearing gloves during heavy labor, or wearing protective gear and sturdy shoes during sports.
Early detection is crucial to the treatment of subungual melanoma, so be sure to tell your doctor about any changes to your nails.1 You can regularly check your nails, fingers, and toes for any bruising, streaking, or changes.3
When To Seek Medical Care For Skin Cancer
Many people, especially those who have fair coloring or have had extensive sun exposure, periodically check their entire body for suspicious moles and lesions.
Have your primary health care provider or a dermatologist check any moles or spots that concern you.
See your health care provider to check your skin if you notice any changes in the size, shape, color, or texture of pigmented areas .
If you have skin cancer, your skin specialist or cancer specialist will talk to you about symptoms of metastatic disease that might require care in a hospital.
You May Like: What Is The Main Cause Of Skin Cancer
Medical Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of skin cancer treatment for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more information, see Surgery.People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the use of a small beam of radiation targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy can cause irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It can also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, topical chemotherapy creams have been FDA approved for the treatment of certain low-risk nonmelanoma skin cancers. Patients with advanced or many basal cell carcinomas are sometimes prescribed oral pills to block the growth of these cancers. Side effects include muscle spasms, hair loss, taste changes, weight loss and fatigue.
In advanced cases of melanoma, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work better than existing therapies.
Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
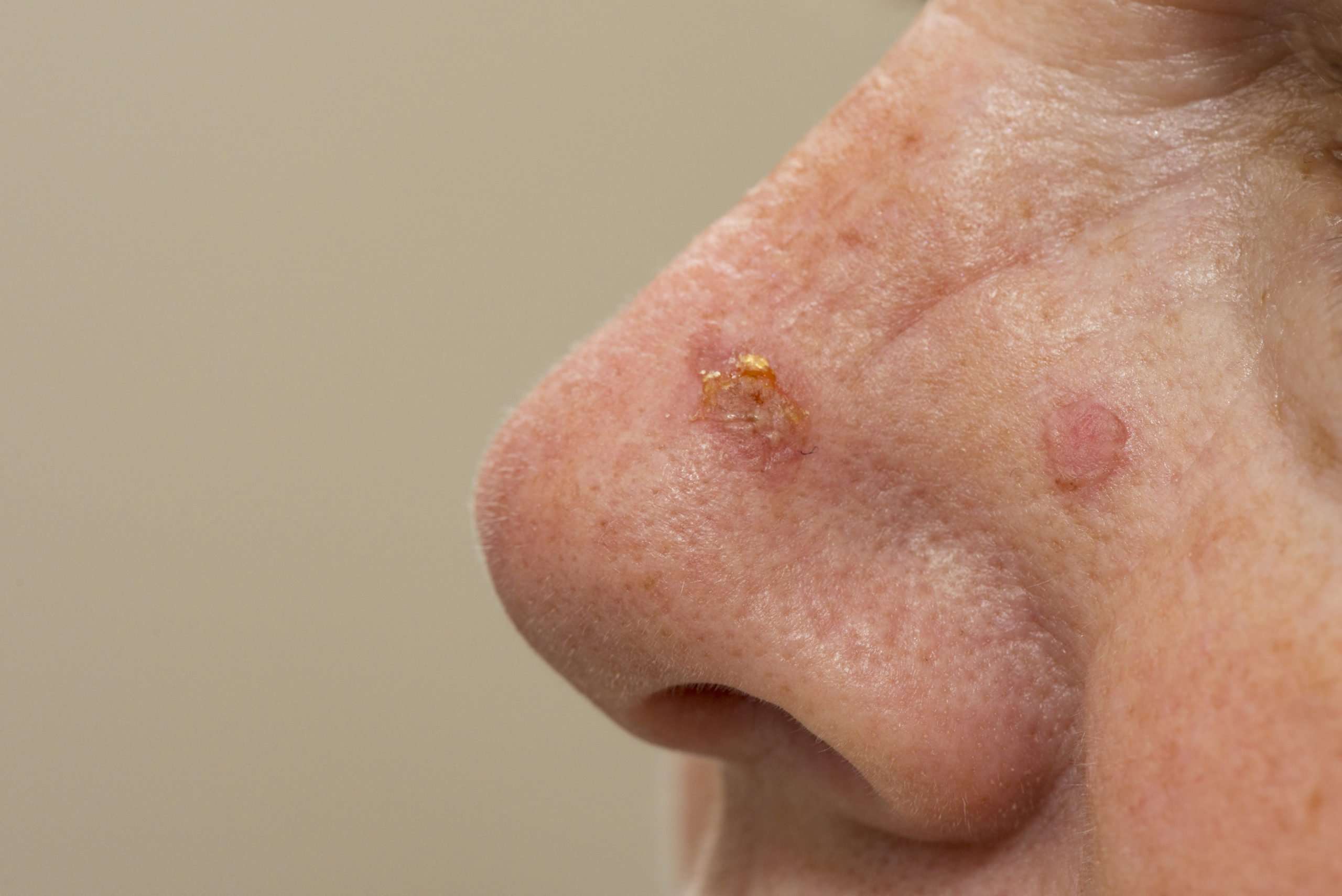
The most common sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new;mole or a change in an existing mole.
This can happen anywhere on the body, but the;most commonly affected areas are;the back in men and the legs in women.;
Melanomas are uncommon in areas that are protected from sun exposure, such as the buttocks and the scalp.
In most cases, melanomas have an irregular shape and are more than 1 colour.
The mole may also be larger than normal and can sometimes be itchy or bleed.
Look out for a mole that gradually changes shape, size or colour.
Superficial spreading melanoma are the most common type of melanoma in the UK.
They’re more common in people with pale skin and freckles, and much less common in people with darker skin.
They initially tend to grow outwards rather than downwards, so they do not pose a problem.
But if they grow downwards into the deeper layers of skin, they can spread to other parts of the body.
You should see a GP if you have a mole that’s getting bigger, particularly if it has an irregular edge.
You May Like: What Is Soft Tissue Carcinoma
Lymph Nodes As A Stopover On A Cancer Cells Journey
Movement of melanoma cells into lymph nodes is not necessarily an endpoint, but rather a stopover on the cells journey elsewhere, wrote Barbara Grüner, Ph.D., of University Hospital Essen in Germany, and Sarah-Maria Fendt, Ph.D., of the Leuven Center for Cancer Biology in Belgium, in .
These results provide a first step towards understanding the protective environment of lymph, Drs. Grüner and Fendt wrote. To what extent findings apply to tumor types other than melanoma, and to humans, remains to be determined. If the results are relevant to human disease, innovative ways must be found for them to have a therapeutic impact.
Dr. Morrisons team is already looking into existing drugs that might make cancer cells more vulnerable to ferroptosis and block the protective effects of lymph, he said. The idea would be to see if such a drug could be given early in the disease course of melanoma to prevent it from spreading.
If we can find a therapy that blocks disease progression in mice, then we would go into clinical trials to see if it works in humans, he added.
Dr. Salnikow said multiple approaches will likely be needed to prevent the spread of melanoma, because different biological factors may be important for metastasis in different people.
One of the interesting questions to answer is whether MCT1 is also helping to protect these melanoma cells metastasizing through lymph, and were doing those experiments now, Dr. Morrison said.
What Causes Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma skin cancer is a type of cancer that usually develops on the skin from melanocytes, or cells that produce melanin. Melanoma can also develop from exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds. The signs of melanoma are orange-to-brown spots, moles that do not change in size and shape over time, a change in pigmentation, a new mole or lesion that appears disfiguring, or a mole that changes color.
Skin cancer is a serious problem, and it can be preventable. The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and melanoma. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, although it tends to grow slowly and is often not as dangerous as melanoma. Melanoma is the second most common type of skin cancer, but it is the fastest growing and the deadliest form.
Many people do not know that skin cancer can be detected by changes in the color and texture of the skin. The signs that one may have a melanoma are very visible and can be identified from a distance. Melanoma skin cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the cells that produce melanin, which is the pigment that gives your skin its color. People with dark skin are more likely to develop melanoma than people with light-colored skin. Melanoma is most common in adults over age 50, but it can occur at any age if you have risk factors like a history of chronic sun exposure or a family history of melanoma.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Worst Skin Cancer To Have
Mouse Models Mimic Metastasis Of Human Melanoma
Metastasis is a highly inefficient process in that the vast majority of cancer cells that try to migrate die before they ever have an opportunity to form a tumor, Dr. Morrison said.
Dr. Morrisons team found previously that one factor limiting the survival of melanoma cells circulating in the blood is that the cells experience a high level of oxidative stress. Oxidative stressan imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the bodycauses chemical reactions that can damage proteins, DNA, and lipids in cells and disrupt normal cell processes. However, precisely how oxidative stress kills circulating melanoma cells was not known.
For their studies, the team used a mouse model of metastasis created by transplanting melanoma cells from humans beneath the skin of specially bred mice with weakened immune systems. These mice were used to avoid having the transplanted human cells seen as foreign and attacked by the immune system. The team also used a second mouse model created by transplanting mouse melanoma cells into mice with normal immune systems.
Comparing these two mouse models let the researchers control for potential effects of the immune system on the spread of melanoma, Dr. Salnikow explained.
The study was supported in part by NCIs Patient-Derived Models of Cancer program, which promotes the development of animal models that more closely mirror how tumor cells behave in humans.