Diagnosis Of Skin Cancer
It is important to check your skin regularly and check with your doctor if you notice any changes.
In the majority of cases, your GP will examine you, paying attention to any spots that may look suspicious. Your GP may perform a biopsy . In some cases your GP may refer you to a specialist, such as a dermatologist, if necessary.
What You Can Do
Know your skin: If you have atypical moles, FAMMM or other melanoma risk factors, perform monthly self-checks and visit your dermatologist regularly for thorough head-to-toe skin exams. Talk to your doctor at length about self-monitoring steps you need to take. Advise family members to do the same.
Be on the lookout: See your dermatologist if you notice any of the ABCDE melanoma warning signs or any of the following changes on your skin:
- Itching, bleeding, crusting, oozing or swelling of a skin lesion
- Changes in color, size, shape, texture or elevation of a skin lesion
- Pain
Protect against UV rays: You can reduce the skin cancer risk posed by UV-radiation by taking simple protective measures. Safeguard your skin against the sun every day, even when its cloudy. Avoid indoor tanning entirely.; Get the details on how to make healthy skin a way of life: Your Daily Sun Protection Guide.
Reviewed by:
Looks Can Be Deceptive
Precancerous skin growths may look harmless. As you now know, their looks can be deceptive. Following your dermatologists recommendations can help protect your skin and your health.
Precancerous skin growths may look harmless
These arrows point to precancerous skin growths that are barely noticeable.
Related AAD resources
You May Like: What Does Early Squamous Skin Cancer Look Like
The Facts The Risks What You Can Do
Sunburn hurts you in more ways than one. The danger goes far beyond any short-term pain, redness and discomfort, because after the sunburn fades, lasting damage remains.
Sunburn accelerates skin aging and is a leading cause in the majority of cases of;basal cell carcinoma,;squamous cell carcinoma;and;melanoma, the deadliest form of;skin cancer.
Sunburn is bad news, but the good news is that its totally preventable. And the best time to start is today.
Dont feel the burn!
YOUR RISKof developing potentially deadly melanomaDOUBLESwith a history of 5 or more sunburns.
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
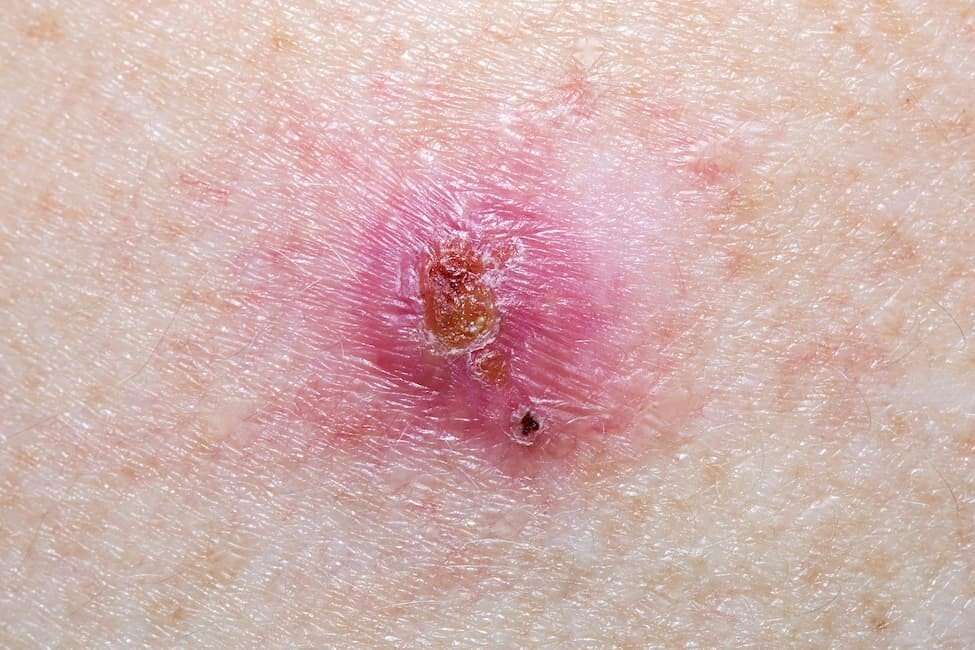
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, typically a new mole or skin lesion or a change in an existing mole.
- Basal cell carcinoma may appear as a small, smooth, pearly or waxy bump on the face, ears or neck, or as a flat pink, red or brown lesion on the trunk or arms and legs.
- Squamous cell carcinoma can appear as a firm, red nodule, or as a rough, scaly flat lesion that may bleed and become crusty. Both basal cell and squamous cell cancers mainly occur on areas of the skin frequently exposed to the sun, but can occur anywhere.
- Melanoma usually appears as a pigmented patch or bump but can also be red or white. It may resemble a normal mole, but usually has a more irregular appearance.
When looking for melanoma, think of the ABCDE rule that tells you the signs to watch for:
- Asymmetry — the shape of one half doesn’t match the other
- Border — edges are ragged or blurred
- Color — uneven shades of brown, black, tan, red, white or blue
- Diameter — A significant change in size , although any mole that is getting larger should be brought to the attention of your dermatologist; many melanomas are being diagnosed at much smaller diameters.
- Evolving — any new spot or mole that is changing in color, shape or size or itches or bleeds.
Continued
Recommended Reading: Can Skin Cancer Be Cured With Cream
What Are The Causes And Risk Factors Of Skin Cancer
Most basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are caused by ultraviolet radiation produced by the sun, but other risk factors also are linked to these skin cancers. Risk factors listed below can increase the risk for skin cancer.
Ultraviolet radiation:;Too much exposure to UV radiation is a risk factor for skin cancer. The main source of such radiation is sunlight and tanning lamps and booths.Race:;People with fair skin, freckling or red or blond hair have a higher risk. The risk of skin cancer is much higher for whites than for dark-skinned African Americans.Moles:;Certain types of moles, including some large moles, increase the chance of getting melanoma.Family history:;People with a family history of skin cancer are at increased risk . A person who has already had melanoma is at a higher risk of getting another melanoma.Exposure to chemicals:;Exposure to large amounts of arsenic, a heavy metal used in making some insecticides, increases the risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer.Radiation:;Radiation treatment increases the risk of developing nonmelanoma skin cancer in the area that was treated.Gender:;Men are more likely to develop skin cancer than women.Age:;More than 50 percent of all melanomas occur in people older than 50 years of age.
Different Types Of Cancer Start In The Skin
Skin cancer may form in basal cells or squamous cells. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of skin cancer. They are also called nonmelanoma skin cancer. Actinic keratosis is a skin condition that sometimes becomes squamous cell carcinoma.
Melanoma is less common than basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
This summary is about basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis. See the following PDQ summaries for information on melanoma and other kinds of cancer that affect the skin:
Recommended Reading: Do You Need Chemo For Melanoma
What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Although the number of skin cancers in the United States continues to rise, more and more skin cancers are being caught earlier, when they are easier to treat. Thus, illness and death rates have decreased.
When treated properly, the cure rate for both basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma approaches 95%. The remaining cancers recur at some point after treatment.
- Recurrences of these cancers are almost always local , but they often cause significant tissue destruction.
- Less than 1% of squamous cell carcinomas will eventually spread elsewhere in the body and turn into dangerous cancer.
In most cases, the outcome of malignant melanoma depends on the thickness of the tumor at the time of treatment.
- Thin lesions are almost always cured by simple surgery alone.
- Thicker tumors, which usually have been present for some time but have gone undetected, may spread to other organs. Surgery removes the tumor and any local spread, but it cannot remove distant metastasis. Other therapies, new targeted agents or older approaches such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy, are used to treat the metastatic tumors.
- Malignant melanoma causes more than 75% of deaths from skin cancer.
- Of the approximately 70,000 malignant melanomas diagnosed in the United States in 2007, the vast majority were cured. Still, thousands of people die of melanoma each year.
How Is Scalp Cancer Diagnosed
You might go to your doctor if you notice a suspicious spot on your scalp, or a doctor might notice it during a skin check. No matter how the spot is found, skin cancer diagnosis will happen roughly the same way.
First, your doctor will ask you about your family history of cancer, if you spend a lot of time in the sun, use protection in the sun, and if you use tanning beds. If you noticed the lesion, your doctor may ask if youve noticed any changes over time or if its a new growth.
Then your doctor will do a skin exam to look more closely at the lesion and determine if you need further testing. Theyll look at its size, color, shape, and other features.
If your doctor thinks it might be skin cancer on your scalp, theyll take a biopsy, or small sample, of the growth for testing. This testing can tell your doctor if you have cancer, and if you do, what type. A biopsy might be enough to completely remove a small cancerous growth, especially basal cell carcinoma.
If the spot is cancerous but not basal cell carcinoma, your doctor might recommend more testing to see if it has spread. This will usually include imaging tests of lymph nodes in your head and neck.
Read Also: What Does Melanoma Look Like On The Leg
Three Most Common Skin Cancers
It is estimated that one in seven people in the United States will develop some form of skin cancer during their lifetime. Although anyone can get skin cancer, people who burn easily and are fair-skinned are at higher risk. Researchers believe that one serious sunburn can increase the risk of skin cancer by as much as 50%. A yearly skin exam by a doctor is the best way to detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable. If you have a new growth or any change in your skin, be sure to see your doctor to have it examined. Remember, protecting yourself from the sun is the best way to prevent all forms of skin cancer.
How Often Does Scc Spread
Studies suggest that around 1.4% of people with SCC will experience metastasis.
As with BCC, the five-year survival rate is highhovering around 99%in the absence of metastasis. With metastasis, the three-year survival is roughly 29% in women and 46% in men.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
I Think I Have An Actinic Keratosis What Should I Do
If detected early, actinic keratoses can be treated before they develop into skin cancer.
See your dermatologist, who can accurately diagnose the lesion and recommend an effective treatment. Its best to diagnose and treat AKs early, before they become cancerous. This is especially true for AKs that arise on the head or neck, where skin cancers may be more aggressive.
Protect yourself to help prevent further sun damage. Seek shade and protect your skin against UV exposure every day, even when its cloudy, using broad-spectrum sunscreen and sun safe clothing, hats and eyewear. Avoid indoor tanning entirely and do not get sunburned.
Reviewed by:
What Is The Treatment For Skin Cancer
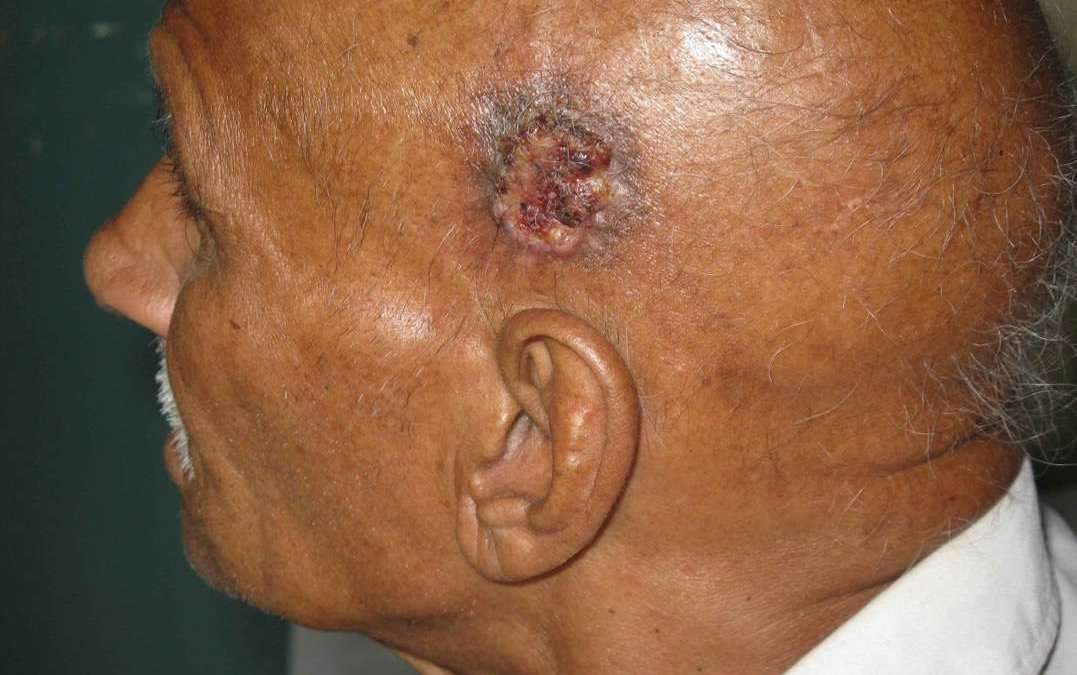
Treatment for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma is straightforward. Usually, surgical removal of the lesion is adequate. Malignant melanoma, however, may require several treatment methods, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy or immunotherapy or both. Because of the complexity of treatment decisions, people with malignant melanoma may benefit from the combined expertise of the dermatologist, a cancer surgeon, and a medical oncologist.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Recommended Reading: What Is Non Small Cell Carcinoma
What Causes Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet light exposure, most commonly from sunlight, is overwhelmingly the most frequent cause of skin cancer.
Other important causes of skin cancer include the following:
- Use of tanning booths
- Immunosuppression – This means impairment of the immune system. The immune system protects the body from foreign entities, such as germs or substances that cause an allergic reaction. This suppression may occur as a consequence of some diseases or can be due to medications prescribed to combat conditions such as autoimmune diseases or prevent organ transplant rejection.
- Exposure to unusually high levels of X-rays
- Contact with certain chemicals-arsenic , hydrocarbons in tar, oils, and soot
The following people are at the greatest risk:
- People with fair skin, especially types that freckle, sunburn easily, or become painful in the sun
- People with light hair and blue or green eyes
- Those with certain genetic disorders that deplete skin pigment such as albinism, xeroderma pigmentosum
- People who have already been treated for skin cancer
- People with numerous moles, unusual moles, or large moles that were present at birth
- People with close family members who have developed skin cancer
- People who had at least one severe sunburn early in life
A basal cell carcinoma usually looks like a raised, smooth, pearly bump on the sun-exposed skin of the head, neck, or shoulders.
A squamous cell carcinoma is commonly a well-defined, red, scaling, thickened patch on sun-exposed skin.
What Does A Common Mole Look Like
A common mole is usually smaller than about 5 millimeters wide . It is round or oval, has a smooth surface with a distinct edge, and is often dome-shaped. A common mole usually has an even color of pink, tan, or brown. People who have dark skin or hair tend to have darker moles than people with fair skin or blonde hair. Several photos of common moles are shown here, and more photos are available on the What Does a Mole Look Like? page.
Common Mole Photos
This common mole is 1 millimeter in diameter .
This common mole is 2;millimeters;in diameter .
This common mole is about 5 millimeters in diameter .
This common mole is about 5 millimeters in diameter .
This common mole is about 5 millimeters in diameter .
Recommended Reading: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
What You Need To Know About Sunburn
- Some people are more prone to sunburn: Skin type determines your susceptibility; people with fair skin run the greatest risk. But anyone can get burned.
- Even without a burn, sun exposure raises skin cancer risk. Even if you are tan or your skin type is dark and your skin does not redden, the sun can cause cellular damage that can lead to cancer.
- The UV index is a factor: The sun varies in intensity by season, time of day and geographic location. A high UV index means that unprotected skin will burn faster or more severely. Be careful, especially when the sun is strongest. But even when the index is low, the risk remains. Protect yourself every day of the year.
- You can burn on an overcast day:;Be careful even when the sun isnt shining. Up to 80 percent of UV rays can penetrate clouds.
- Light pink is still bad: No matter how mild, every burn is a sign of injury to your skin that can result in premature aging and skin cancer.
What Should People Do If They Have A Dysplastic Nevus
Everyone should protect their skin from the sun and stay away from sunlamps and tanning booths, but for people who have dysplastic nevi, it is even more important to protect the skin and avoid getting a suntan or sunburn.
In addition, many doctors recommend that people with dysplastic nevi check their skin once a month . People should tell their doctor if they see any of the following changes in a dysplastic nevus :
- The color changes.
- It gets smaller or bigger.
- It changes in shape, texture, or height.
- The skin on the surface becomes dry or scaly.
- It becomes hard or feels lumpy.
- It starts to itch.
- It bleeds or oozes.
Another thing that people with dysplastic nevi should do is get their skin examined by a doctor . Sometimes people or their doctors take photographs of dysplastic nevi so changes over time are easier to see . For people with many dysplastic nevi, doctors may conduct a skin exam once or twice a year because of the moderately increased chance of melanoma. For people who also have a family history of melanoma, doctors may suggest a more frequent skin exam, such as every 3 to 6 months .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Skin Cancer And Melanoma
Causes Of Skin Cancer
Australia has one of the highest rates of skin cancer in the world. Anyone can be at risk of developing skin cancer, though the risk increases as you get older.
The majority of skin cancers in Australia are caused by exposure to UV radiation in sunlight.
Some factors that increase your risk of skin cancer include:
-
sunburn
What Is The Treatment For Atypical Moles
If you have one or more atypical moles, talk to your dermatologist about an appropriate surveillance program and whether or not any moles need a biopsy to ensure they are not;melanomas. The more abnormal features moles have, the riskier they are. Frequent monitoring of these moles is especially crucial, so that if a melanoma arises, it can be detected and treated as early as possible. ;
If your doctor identifies a mole as suspicious, or if new moles appear after age 40, you may need a biopsy.
Don’t Miss: How Bad Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if skin cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually skin cancer cells. The disease is metastatic skin cancer, not lung cancer.
What Is A Dysplastic Nevus
A dysplastic nevus is a type of mole that looks different from a common mole. A dysplastic nevus may be bigger than a common mole, and its color, surface, and border may be different. It is usually more than 5 millimeters wide . A dysplastic nevus can have a mixture of several colors, from pink to dark brown. Usually, it is flat with a smooth, slightly scaly, or pebbly surface, and it has an irregular edge that may fade into the surrounding skin. Some examples of dysplastic nevi are shown here. More examples are on the What Does a Mole Look Like? page.
Dysplastic Nevi Photos
This dysplastic nevus has a raised area at the center that doctors may call a fried egg appearance.
This dysplastic nevus is more than 5 millimeters in diameter.
This dysplastic nevus is more than 10 millimeters wide .
A dysplastic nevus may occur anywhere on the body, but it is usually seen in areas exposed to the sun, such as on the back. A dysplastic nevus may also appear in areas not exposed to the sun, such as the scalp, breasts, and areas below the waist . Some people have only a couple of dysplastic nevi, but other people have more than 10. People who have dysplastic nevi usually also have an increased number of common moles.
Don’t Miss: How To Protect Your Self From Skin Cancer