How Can Uv Light Cause Skin Cancer
Every time UV light hits our skin, it can damage some of the DNA inside our skins cells. This happens every time we:
-
Spend time in the sun without sun protection
-
Use indoor tanning equipment
The body tries to repair this damage. When the body can no longer repair all the damage, changes called mutations develop in our skins cells. The mutated cells, which are cancer cells, can multiple quickly. As these cells pile up, a tumor develops.
When a tumor forms in skin cells called squamous cells, we get SCC of the skin. These cells are found in the outermost layer of our skin, which is called the epidermis. The following picture shows you where these cells live.
Treatment Of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-
Surgery, with postoperative radiation or chemoradiation as needed
For most oral cavity cancers, surgery is the initial treatment of choice. Radiation or chemoradiation is added postoperatively if disease is more advanced or has high-risk features.
Selective neck dissection is indicated if the risk of nodal disease exceeds 15 to 20%. Although there is no firm consensus, neck dissections are typically done for any lesion with a depth of invasion > about 3.5 mm.
Routine surgical reconstruction is the key to reducing postoperative oral disabilities; procedures range from local tissue flaps to free tissue transfers. Speech and swallowing therapy may be required after significant resections.
Radiation therapy is an alternative treatment. Chemotherapy is not used routinely as primary therapy but is recommended as adjuvant therapy along with radiation in patients with advanced nodal disease.
Treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the lip is surgical excision with reconstruction to maximize postoperative function. When large areas of the lip exhibit premalignant change, the lip can be surgically shaved, or a laser can remove all affected mucosa. Mohs surgery can be used. Thereafter, appropriate sunscreen application is recommended.
Delay In Diagnosis And Treatment Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Cristina Renzi1, Simona Mastroeni1, Thomas J. Mannooranparampil1, Francesca Passarelli2, Alessio Caggiati3, Clemente Potenza3 and Paolo Pasquini1
1Clinical Epidemiology Unit, 2Pathology Department, 3Department of Plastic Surgery, Istituto Dermopatico dellImmacolata , Rome, Italy
Advanced squamous cell carcinomas of the skin can cause significant tissue destruction and may metastasize. Understanding the determinants of patient delay could help prevent advanced presentation. The purpose of the present study was to examine patient- and healthcare-related factors associated with delay before the detection and treatment of SCC. A sample of 308 patients with SCC treated at a dermatological referral centre in Italy were interviewed. Clinical data were obtained from the medical records. The highest quartile patients reported > 9 months delay between noticing the lesion and the first medical visit . Multivariate analysis showed that SCC arising on pre-existing chronic lesions were associated with long patient delay . Controlling for confounders, the first physicians advice to remove the lesion immediately was associated with a shorter treatment delay . In conclusion, our work emphasizes the importance of seeing a doctor about any change in a pre-existing lesion, particularly in light of the fact that SCC on chronic lesions are at greater risk of metastasis and recurrence. Key words: skin cancer; cutaneous; squamous cell carcinoma; delay.
Acta Derm Venereol 2010; 90: 595601.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Basal Cell Carcinoma For Years
How Long Does It Take For A Scar To Morph Into Cancer
Typical malignant change may occur over decades in these cases, says Dr. Tung.
Signs that may alert you that your scar is no longer just a scar include pain, redness, bleeding or skin breakdown.
Scars and skin which has been persistently inflamed can turn into a type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma.
The Second Most Common Skin Cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is the second most common form of skin cancer, characterized by abnormal, accelerated growth of squamous cells. When caught early, most SCCs are curable.
SCC of the skin is also known as cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma . Adding the word cutaneous identifies it as a skin cancer and differentiates it from squamous cell cancers that can arise inside the body, in places like the mouth, throat or lungs.
You May Like: Is Melanoma Caused By The Sun
What Is Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is a common skin cancer that typically develops in chronic sun-exposed areas of your body. This type of skin cancer is usually not nearly as aggressive as melanoma and is uncontrolled growth of cells in the epidermis of your skin.
It can become disfiguring and sometimes deadly if allowed to grow. Squamous cell carcinomas are at least twice as frequent in men as in women. They rarely appear before age 50 and are most often seen in individuals in their 70s.
An estimated 700,000 cases of SCC are diagnosed each year in the United States, resulting in approximately 2,500 deaths.
Tests That May Be Done
The doctor will ask you questions about when the spot on your skin first showed up and if it has changed in size or the way it looks or feels. The rest of your skin will be checked. During the exam your doctor will check the size, shape, color and texture of any skin changes. If signs are pointing to skin cancer, more tests will be done.
Skin biopsy
In a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of tissue to check it for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have skin cancer and what kind it is.
There are many types of skin biopsies. Ask your doctor what kind you will need. Each type has pros and cons. The choice of which type to use depends on your own case.
In rare cases basal and squamous cell skin cancer can spread to the nearby lymph nodes Ask your doctor if your lymph nodes will be tested.
Basal and squamous cell cancers don’t often spread to other parts of the body. But if your doctor thinks your skin cancer might spread, you might need imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans.
Don’t Miss: What Is Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Squamous cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes , and when spreading does occur, it typically happens slowly. Indeed, most squamous cell carcinoma cases are diagnosed before the cancer has progressed beyond the upper layer of skin. There are various types of squamous cell carcinoma and some tend to spread more quickly than others.
Answer: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth
While it is said that most skin cancers grow slowly, the true answer is it depends. It depends on location of the skin cancer, your general health, the health of your skin and the cause of the skin cancer. Most squamous cell carcinomas arise in skin damaged by ultra violet light and, often, grow slowly. However, if the UV damage is severe or if the SCC arose from a burn or infection site, the cancer can grow rapidly and spread to other organs. Additionally, SCC, which grows contiguously will sometimes send seeds beyond the tissue containing the roots. These factors all have to be considered in determining how to deal with SCC. The best advice I can give you is to not delay and have this evaluated by a fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon. I hope I have answered your question. Best.;;;;;;;;; jlr
Don’t Miss: How Can You Get Skin Cancer
How Aggressive Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is not often considered to be life threatening. This form of skin cancer that affects the squamous cells tends to create slow-growing tumors. Although squamous cell carcinoma is more likely to invade deeper layers of the skin and spread to other parts of the body than basal cell carcinoma, this is still uncommon.
Only about 5 to 10 percent of squamous cell carcinoma tumors are considered to be aggressive.
What Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Look Like
Squamous cell carcinoma , also known as squamous cell cancer, is the second most common type of skin cancer following basal cell carcinoma. About 1 million cases are diagnosed each year in the United States. It begins in the squamous skin cells located in the top layer of skin called the epidermis. The DNA in squamous cells can become damaged from ultraviolet rays from the sun or tanning beds. When this occurs, they begin to grow at an out-of-control rate, leading to skin cancer.;
Fortunately, when caught early, most cases of squamous cell carcinoma are curable. Knowing the early warning signs is critical to receiving an early diagnosis and treatment.;
Unprotected exposure to UV rays is a major risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma. The more time you spend in the sun , the more likely you are to develop SCC. About 90% of non-melanoma skin cancers are related to exposure to UV rays. Other risk factors of SCC include light skin, age , male sex, immunosuppression, human papillomavirus, chronic scarring conditions, family history, and toxic exposures.
Don’t Miss: How Bad Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
The best way to prevent SCC is to avoid sunburn. Avoid going outin the sun when the UV Index is higher than 3, such as in the middle of theday. Seek shade, wear a hat, sunglasses and clothing that protects you from thesun, and always use an SPF30+ sunscreen. Do not go to tanningsalons.
If you are at very high risk of developing another skin cancer, yourdoctor may prescribe you specific vitamins.
When Should I Seek Care
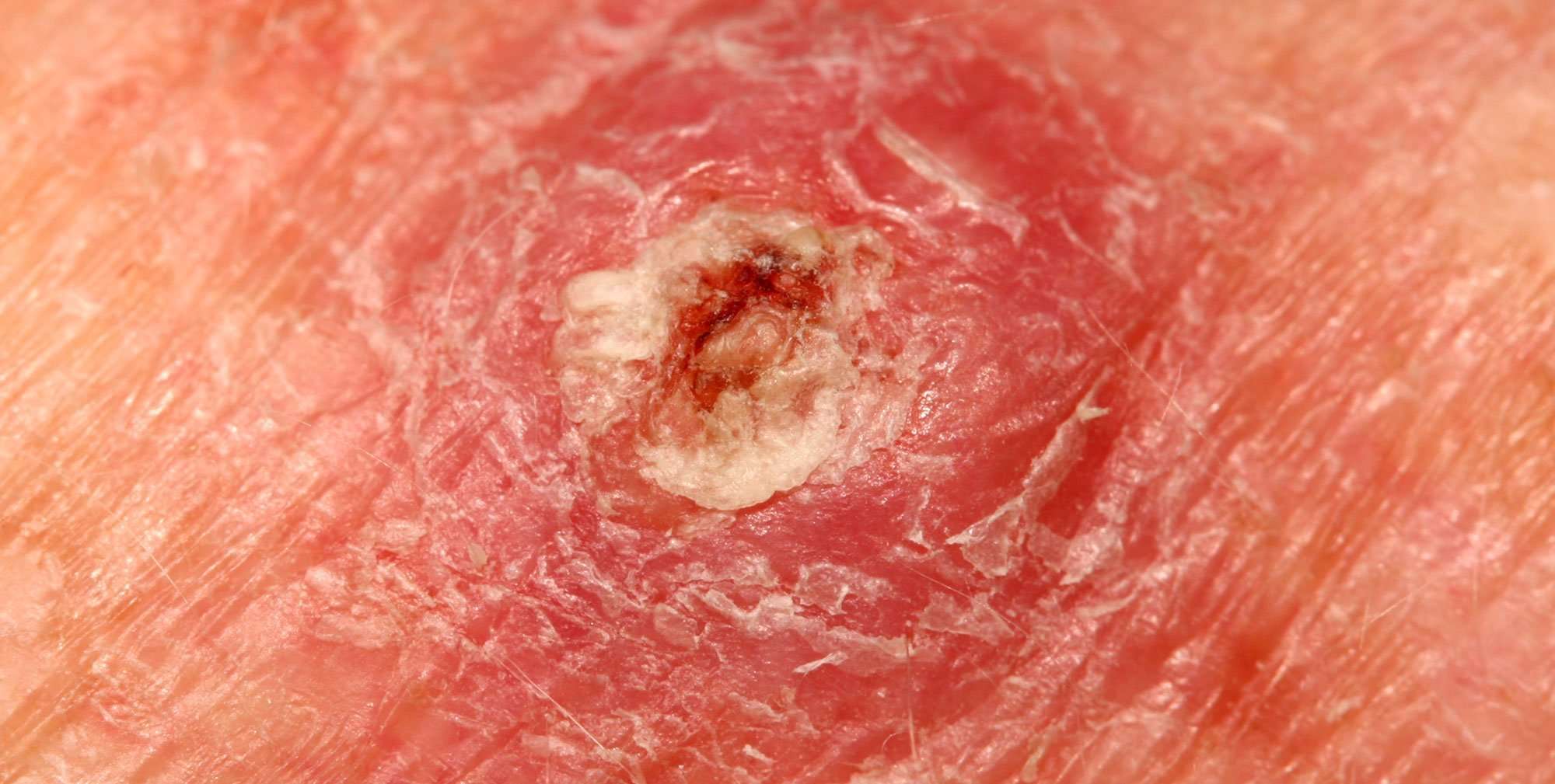
If you have a lesion that could be a skin cancer, please dont wait. Getting these treated early before they become aggressive is critical to a successful outcome.
Request an appointment online or call us today to see how we can help utilize the most advanced methods with the highest cure rates possible to treat any skin cancers that arise.
- 26732 Crown Valley Parkway Suite 571 Mission Viejo, CA 92691-7305
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
What Survival Rates Mean
The survival rate is the percentage of people who live for a certain period of time with this cancer. The number is based on research done on large groups of people with the same stage of cancer.
Experts dont know the exact survival numbers for late-stage SCC, because cancer registries dont track statistics for this cancer. However, your doctor may be able to give you an estimate of your prognosis.
When it comes to surviving cancer, everyone is different. Your outcome will depend on the specific treatments you have and how well you respond to them. Talk to your doctor about your outlook and what it means.
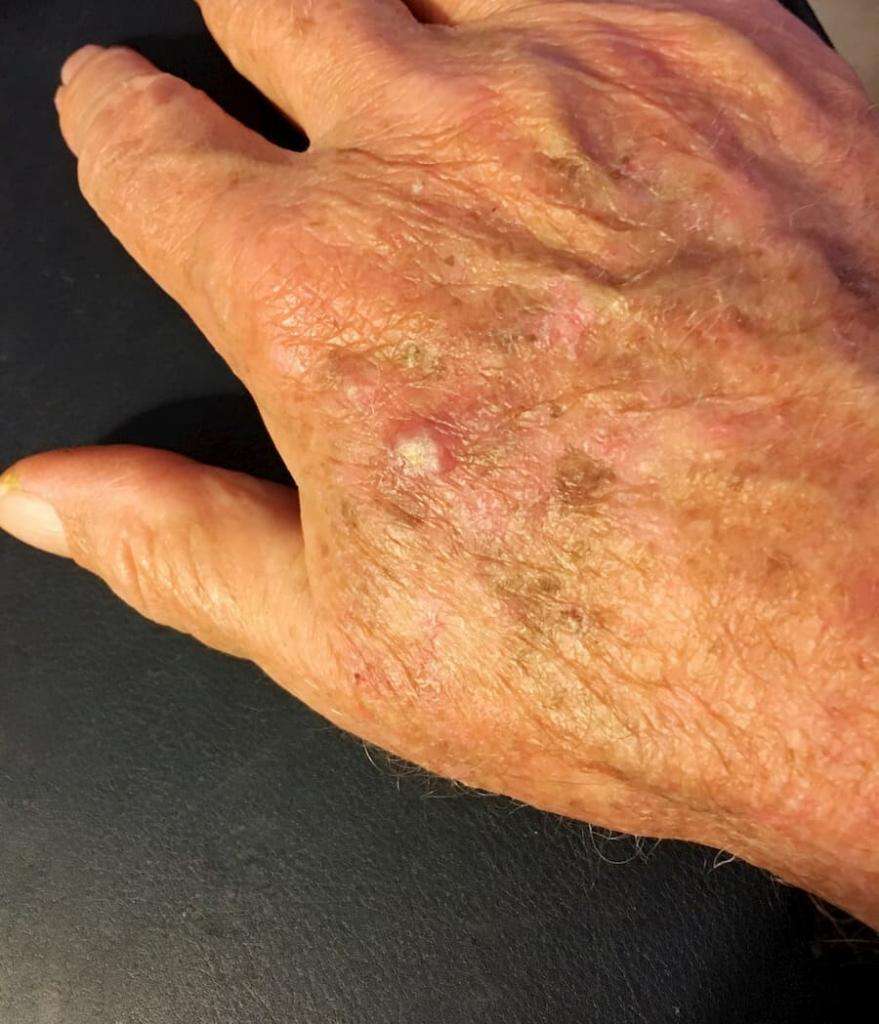
How To Spot An Scc
SCC of the skin can develop anywhere on the body but is most often found on exposed areas exposed to ultraviolet radiation like the face, lips, ears, scalp, shoulders, neck, back of the hands and forearms. SCCs can develop in scars, skin sores and other areas of skin injury. The skin around them typically shows signs of sun damage such as wrinkling, pigment changes and loss of elasticity.
SCCs can appear as thick, rough, scaly patches that may crust or bleed. They can also resemble warts, or open sores that dont completely heal. Sometimes SCCs show up as growths that are raised at the edges with a lower area in the center that may bleed or itch.
You May Like: What Causes Renal Cell Carcinoma Cancer
What Is Skin Cancer
Cancer can start any place in the body. Skin cancer starts when cells in the skin grow out of control.
Skin cancer cells can sometimes spread to other parts of the body, but this is not common. When cancer cells do this, its called metastasis. To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the skin.
Cancer is always named based on the place where it starts. So if skin cancer spreads to another part of the body, its still called skin cancer.
The skin
Ask your doctor to use this picture to show you where your cancer is
How Dangerous Is Scc
While the majority of SCCs can be easily and successfully treated, if allowed to grow, these lesions can become disfiguring, dangerous and even deadly. Untreated SCCs can become invasive, grow into deeper layers of skin and spread to other parts of the body.
Did you know?
Americans die each year from squamous cell carcinoma
Read Also: When Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreads
What Can I Do To Manage Or Prevent Scc
- Prevent skin cancer:
- Wear sunscreen when outdoors. Use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15 and UVA and UVB protection. Reapply after you swim or sweat. If you need to be in the sun, wear a hat and long-sleeved shirts and pants to cover your skin.
- Stay out of the sun between 10 am and 4 pm. This is when the sun is the strongest and most damaging to your skin.
- Do not use tanning booths. These can damage your skin as much as the sun.
- Examine your skin monthly. Watch for growths or moles that change size, shape, or color.
What Causes Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Repeated exposure to ultraviolet light, either from the sun or from tanning beds, is the main cause of SCC. Indoor tanning is linked to about 168,000 cases of SCC in the US each year.
People with light skin, light hair , and light eyes have a higher risk of skin cancer in general, as well as SCCs. However, most of the skin cancers that develop in African Americans are SCCs.
Other risk factors include:
- Having an impaired immune system, including:
- Cancers of the blood or bone marrow.
- Chronic infections like HIV.
- Taking immunosuppressive medications, including chemotherapy or some biologic medications.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Ignore Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treatments Your Physician May Prescribe
If your physician suspects squamous cell carcinoma, he or she will first want to establish the correct diagnosis by performing a biopsy of the lesion. The procedure involves:
- Numbing the skin with an injectable anesthetic.
- Sampling a small piece of skin by using a flexible razor blade, a scalpel, or a tiny cookie cutter . If a punch biopsy is taken, a suture or two may be placed and will need to be removed 6â14 days later.
- Having the skin sample examined under the microscope by a specially trained physician .
Cancer Stage Determines Risk Of Spreading And Line Of Treatment
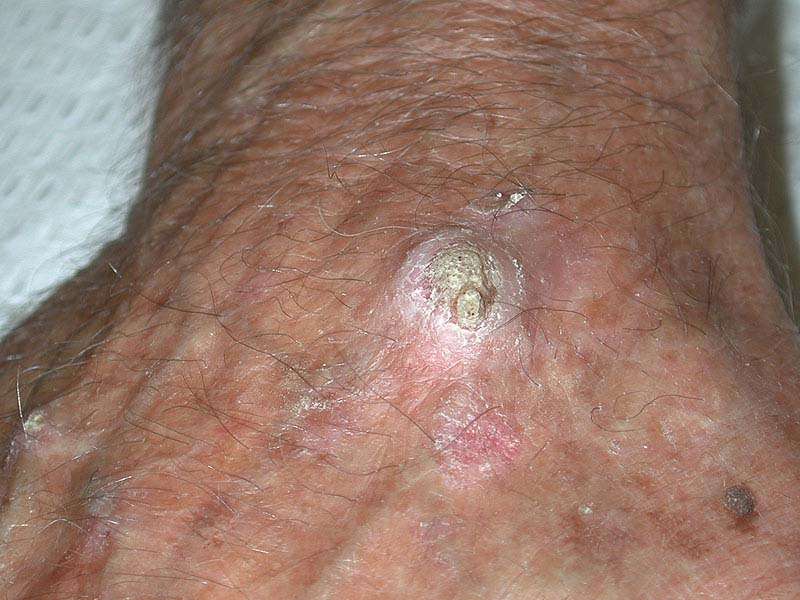
A cancer of the upper layers of the skin in the epidermis, SCC is the second most common form of skin cancer after basal cell carcinoma and affects an estimated 1 million new people every year in the United States alone. Cancer staging is done for SCC with the intention of categorizing the size of cancer and to judge how much it has grown. And theres a clear line of treatment and way forward for each stage.1
With skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma, the likelihood of cancer spreading to other parts of the body is very low and early diagnosis and treatment usually tackles the problem before it spreads. SCC, however, is a little trickier. While the risk of spreading is still quite small, there is a relatively higher chance of it progressing depending on what stage the cancer is at. For those with weakened immune systems, say, people whove had organ transplants or anyone infected with HIV, the risk is a little higher. Also, when the cancer is in the head and neck region, it may have a slightly higher risk of recurring or spreading.2
The actual stage of this form of cancer is determined based on the TNM protocol devised by the American Joint Commission on Cancer.3
- T : The size/extent of the tumor
- N : Whether it has spread to lymph nodes
- M : Whether it has spread to other parts of the body
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Melanoma Skin Cancer
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomasigns And Symptoms
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, especially a new growth or a sore that doesn’t heal. The cancer may start as a small, smooth, shiny, pale or waxy lump. It also may appear as a firm red lump. Sometimes, the lump bleeds or develops a crust.
Both basal and squamous cell cancers are found mainly on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun the head, face, neck, hands and arms. But skin cancer can occur anywhere.
An early warning sign of skin cancer is the development of an actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin lesion caused by chronic sun exposure. These lesions are typically pink or red in color and rough or scaly to the touch. They occur on sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the face, scalp, ears, backs of hands or forearms.
Actinic keratoses may start as small, red, flat spots but grow larger and become scaly or thick, if untreated. Sometimes they’re easier to feel than to see. There may be multiple lesions next to each other.
Early treatment of actinic keratoses may prevent them from developing into cancer. These precancerous lesions affect more than 10 million Americans. People with one actinic keratosis usually develop more. Up to 1 percent of these lesions can develop into a squamous cell cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most commonly diagnosed skin cancer. In recent years, there has been an upturn in the diagnoses among young women and the rise is blamed on sunbathing and tanning salons.
- Raised, dull-red skin lesion