Expert Review And References
- Christensen SR, Leffell DJ. Cancer of the skin. DeVita VT Jr, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 10th ed. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2015: 92:1314-1336.
- National Cancer Institute. Skin Cancer Treatment for Health Professionals . 2015: .
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Basal Cell Skin Cancer . 2015.
- Zloty D, Guenther LC, Sapijaszko M et al. Non-melanoma skin cancer in Canada chapter 4: management of basal cell carcinoma. Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 2015.
Thinking About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
Clinical trials;are carefully controlled research studies that are done to get a closer look at promising new treatments or procedures. Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they’re not right for everyone.
If you would like to learn more about clinical trials that might be right for you, start by asking your doctor if your clinic or hospital conducts clinical trials.;
Skin Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Skin
The skin is the bodys largest organ. It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D. The skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells:
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Skin cancer can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most common in skin that is often exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, and hands.
You May Like: How Fast Does Subungual Melanoma Grow
Topical 5% Imiquimod Cream
Imiquimod is an immune response modifier. It acts by binding to toll-like receptor. This induces proinflammatory cytokine production and subsequent cytotoxic T cell mediated cell death. It is licensed for use in the treatment of sBCCs.
Vehicle-controlled studies in the treatment of small sBCC by Geisse et al. have reported reasonable results. Twelve weeks following the 6 week treatment course the clearance rates were 82% , 79% and 3% . Moderate to severe local site reactions occurred in 87% with erosions and ulceration in 36% and 22%, respectively. However, it is worth noting that facial BCCs were not included in this study. Schulze et al. found similar clearance rates following a 6 weeks course of 7x/week topical imiquimod, with a 80% histological clearance compared to 6% for vehicle alone. However, long term clearance rates are lower. A prospective study of 182 patients who received topical imiquimod applied 5x/week for 6 weeks gave clearance rates of 69% at 5-years .
There is some data to suggest that imiquimod may be used in the treatment of nBCCs. A randomized dose-response study reported that 6 weeks after treatment with either a 6- or 12-week course of 7x/week imiquimod histological clearance rates were 71% and 76%, respectively . A further randomized trial on nBCCs reported complete clinical clearance in 78% following 3x/week imiquimod. However, 8 weeks later excision revealed residual BCC in 13% of the patients considered to have shown complete clinical clearance .
The Most Common Skin Cancer
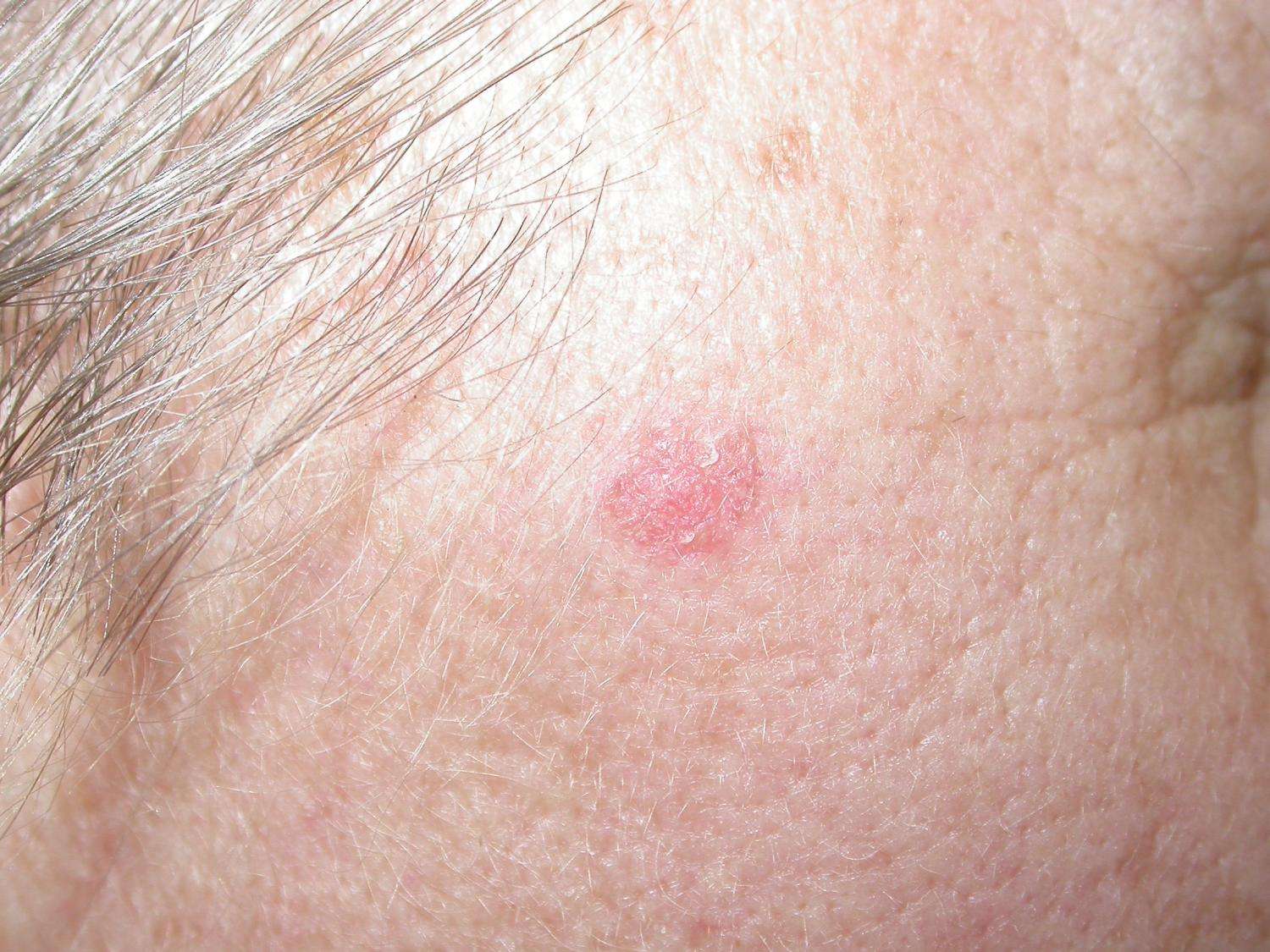
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer and the most frequently occurring form of all cancers. In the U.S. alone, an estimated 3.6 million cases are diagnosed each year. BCCs arise from abnormal, uncontrolled growth of basal cells.
Because BCCs grow slowly, most are curable and cause minimal damage when caught and treated early. Understanding BCC causes, risk factors and warning signs can help you detect them early, when they are easiest to treat and cure.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Deadliest Type Of Skin Cancer
What Is Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is a common skin cancer that typically develops in chronic sun-exposed areas of your body. This type of skin cancer is usually not nearly as aggressive as melanoma and is uncontrolled growth of cells in the epidermis of your skin.
It can become disfiguring and sometimes deadly if allowed to grow. Squamous cell carcinomas are at least twice as frequent in men as in women. They rarely appear before age 50 and are most often seen in individuals in their 70s.
An estimated 700,000 cases of SCC are diagnosed each year in the United States, resulting in approximately 2,500 deaths.
How Dangerous Is Bcc
While BCCs rarely spread beyond the original tumor site, if allowed to grow, these lesions can be disfiguring and dangerous. Untreated BCCs can become locally invasive, grow wide and deep into the skin and destroy skin, tissue and bone. The longer you wait to have a BCC treated, the more likely it is to recur, sometimes repeatedly.
There are some highly unusual, aggressive cases when BCC spreads to other parts of the body. In even rarer instances, this type of BCC can become life-threatening.
Read Also: What Are The Chances Of Getting Skin Cancer
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
JONATHON M. FIRNHABER, MD, East Carolina University, Brody School of Medicine, Greenville, North Carolina
Am Fam Physician.;2012;Jul;15;86:161-168.
Nonmelanoma skin cancer, which includes basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, is the most common cancer in the United States. Approximately 80 percent of nonmelanoma skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma and 20 percent are squamous cell carcinoma. Although the National Cancer Institute does not formally track the incidence and prevalence of nonmelanoma skin cancers, multiple longitudinal studies indicate that the incidence has risen sharply over the past two decades.1
Curettage With And Without Cautery
Curettage is widely used in management of BCC. The tumour is scraped off with a curette and then the base and wound margin is often treated with electrocautery to control bleeding and destroy any residual tumour. This may be repeated. As excision margins are being destroyed it is advisable to confirm the diagnosis and determine the histological subtype with a preoperative biopsy, especially for facial lesions, unless a very confident clinical diagnosis can been made.
For standard curettage and electrocautery recurrence rates have been reported to be between 7.7% and 19% at 5 years. Recurrence rates have been found to be much higher for facial lesions and recurrent disease . A prospective study of 69 re-excised BCC wounds immediately after curettage and electrocautery found residual tumour in 47% of head and neck wounds and 8.3% of trunk and limb wounds . Curettage is very operator dependant; however, a retrospective study of curettage alone reported a 5-year cure rate of 96% for nonaggressive BCC, and tumours involving more than 50% of the deep edge of the specimen were found to have an increased risk of recurrence .
Given the disproportionate amount of residual tumour on head and neck wounds and higher recurrence rates curettage and electrocautery is not considered first line treatment for BCCs on the face.
You May Like: What Is Melanoma In The Brain
Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Increase Risk For Other Cancers
People who develop abnormally frequent cases of a skin cancer known as basal cell carcinoma appear to be at significantly increased risk for developing of other cancers, including blood, breast, colon and prostate cancers, according to a preliminary study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine.
After Squamous Cell Cancer Of The Skin Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Skin Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the skin or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
Basal cell carcinoma of the skin rarely spreads to other parts of the body. Staging tests to check whether basal cell carcinoma of the skin has spread are usually not needed.
The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin:
Read Also: Can Cancer Cause Skin Rash
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in.;Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.;
Whether you are thinking about treatment, getting treatment, or not being treated at all,; you can still get;supportive care;to help with pain or other symptoms.;Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to;maintain or improve your quality of life.;;
Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help.
The American Cancer Society also;has programs and services; including rides to treatment, lodging, and more to help you get through treatment. Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists.
The Best Natural Treatments And Remedies For Basal Cell Carcinoma
The basal cell carcinoma is not considered as a life threatening by the doctors, but any kind of cancer poses an important threat to the health. If you have any type of cancer, you have to search for a holistic treatment options that will manage the symptoms effectively and your condition too, and include needed medical supervision. Some natural cures for the basal cell carcinoma include hydrogen peroxide, apple cider vinegar, and baking soda.
Read Also: What Is Soft Tissue Carcinoma
Health & Wellnesshow To Avoid Squamous Cell Carcinoma This Summer
This type of cancer is much more common in people who have light skin. One of the things thats tricky about basal cell carcinoma is that it can show up as skin-colored or pink, said Dr. Ivy Lee, a board-certified dermatologist with Pasadena Premier Dermatology in California and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology. A lot of patients mistake them as warts or witchs moles.
According to the ACS, you should watch for:
- Scar-like flat, firm areas
Prognosis Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
The prognosis of basal cell carcinoma is relatively good; it can be completely cured, especially when it is detected in the initial stages. The following is the prognosis in different situations:
- Basal cell carcinomas rarely metastasize, for this reason the mortality is low.
- Recurrent tumors, however, have poorer cure rates when compared to primary tumors.
- Patients are at an increased risk for developing subsequent basal cell carcinomas at other sites after the initial development at a primary site.
- Patients with tumor clusters and with truncal BCC are at a high risk groups for developing Basal cell carcinoma in the future.
- Patients having basal cell carcinoma are also at an increased risk for developing squamous cell carcinoma and malignant melanoma.
- There is a slightly increased risk for other malignancies, such as lung cancer, thyroid cancer, mouth cancer, breast cancer, and cervical cancer and also non-Hodgkins lymphoma.
| Written, Edited or Reviewed By:Pramod Kerkar, M.D., FFARCSI, DA Pain Assist Inc.This article does not provide medical advice. See disclaimerLast Modified On: March 19, 2019 |
You May Like: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
What Does Bcc Look Like
BCCs can look like open sores, red patches, pink growths, shiny bumps, scars or growths with slightly elevated, rolled edges and/or a central indentation. At times, BCCs may ooze, crust, itch or bleed. The lesions commonly arise in sun-exposed areas of the body. In patients with darker skin, about half of BCCs are pigmented .
Its important to note that BCCs can look quite different from one person to another. For more images and information on BCC signs, symptoms and early detection strategies, visit our BCC Warning Signs page.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these photos serve as a general reference to what they can look like. If you see something new, changing or unusual on your skin, schedule an appointment with your dermatologist.
An open sore that does not heal
A shiny bump or nodule
A reddish patch or irritated area
A scar-like area;that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
A small pink growth;with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
Basal Cell Carcinoma Prevention
The best way to reduce your risk for basal cell or any type of skin cancer is to:
- Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, making sure to cover all exposed areas and reapply it frequently.
- Avoid the sun when its strongest.
- Wear wide-brimmed hats and long sleeves or long pants when out under the sun’s rays.
- Wear sunglasses that block UV light, which can prevent damage to the thin skin around your eyes.
- Skip indoor tanning.
- Schedule yearly skin cancer checks with a dermatologist.
- Conduct monthly self-checks for skin changes.
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
When Should I See A Healthcare Provider About Basal Cell Carcinoma
It is important to contact a healthcare provider any time you have a skin problem that does not resolve. This means developing any new or larger mole, lump or sore, or new symptoms such as pain or itchiness. If you have had BCC or another type of skin cancer, you will probably be given a recommended schedule of needed appointments. You should follow up on these appointments as directed.
Infiltrated Basal Cell Carcinoma
This version of basal cell carcinoma is presented as thin bundles of basaloid cells with nest-like configuration located between the collagenous fibers on the dermis and infiltrating in the depth. Clinically, it is a whitish, compact, not-well defined plaque . The most common localization is in the upper part of the trunk or the face. Seldom had the paresthesia or hyperesthesia as a symbol of perineural infiltration appeared, especially when the tumor is localized on face. This clinical version is often underestimated when the borders of surgical excision are estimated. Histologically this variant is presented as thin, nest-like bundles of basaloid cells infiltrating in the dermal collagenous fibers .
Infiltrated basal cell carcinoma. Thin bundles of basaloid cells invade the dermis
Read Also: How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Removed From The Nose
Also Check: Is Melanoma Skin Cancer Hereditary
Epidemiology Risk Factors And Subtypes
With around 2 million new tumors annually, BCC is the most common non-benign tumor in individuals with fair skin type . It accounts for 80% of non-melanoma skin cancer and is increasingly seen in younger patients although the average age at first diagnosis is 60 years . A recently published metaanalysis showed regional differences in annual incidence rates/100 000 population: 115 BCC in Great Britain; 7080 BCC in Germany, Switzerland and Italy; 170 BCC in the USA; and >800 BCC in Australia. In the past 30 years the incidence has at a minimum increased 23 fold . The site of predilection is the chronically sun-exposed skin of the head and neck region, but multicentric-superficial BCC frequently are found on the trunk. In addition to skin type and exposure to UV irradiation, other risk factors include immunosuppression, exposure to arsenic, scars and hereditary disorders such as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome and xeroderma pigmentosum .
Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
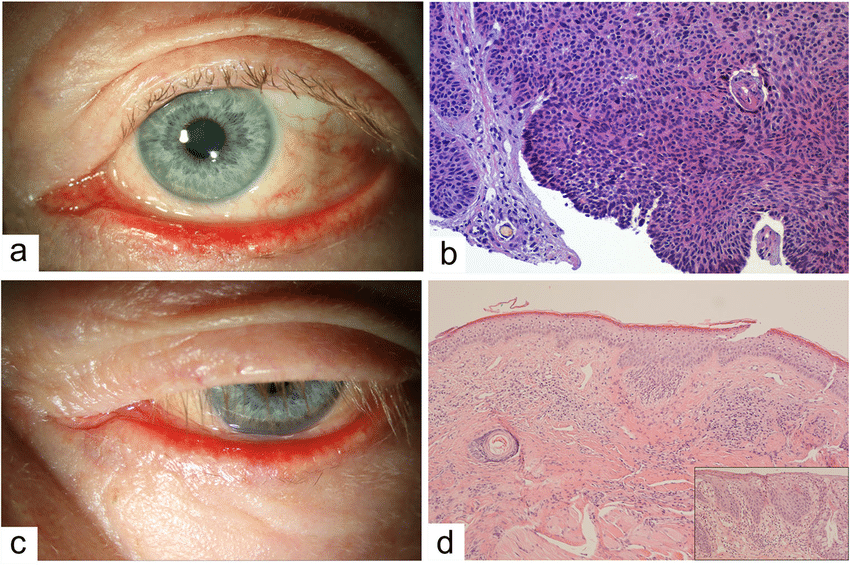
Mohs micrographically controlled surgery involves examining carefully marked excised tissue under the microscope, layer by layer, to ensure complete excision.
- Very high cure rates achieved by trained Mohs surgeons
- Used in high-risk areas of the face around eyes, lips and nose
- Suitable for ill-defined, morphoeic, infiltrative and recurrent subtypes
- Large defects are repaired by flap or skin graft
Also Check: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
How Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
The most important way to prevent BCC is to avoid sunburn. This is especially important in childhood and early life. Fair skinned individuals and those with a personal or family history of BCC should protect their skin from sun exposure daily, year-round and lifelong.
- Stay indoors or under the shade in the middle of the day
Meet The Woman Who’s Had 86 Skin Cancer Surgeries
The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends an annual skin exam by a dermatologist, and you may need more frequent screening if you are at higher risk.
More advanced tumors can still be treated, but the procedures are more complex. The SCF reports that basal cell carcinoma is rarely deadly.
You need to watch for changes in your skin to spot basal cell carcinoma tumors typically dont show signs like pain, itching or bleeding until theyve been progressing for a while.
Recommended Reading: Can You See Skin Cancer
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas can appear anywhere on the body but the most common sites are sun exposed areas such as the face and arms. Its important to keep a close eye on your skin to try and identify early basal cell carcinoma, as its easier to treat if identified early on.
Typical Basal cell carcinoma symptoms are:
- New skin lesion
- Change in colour of a lesion
The typical lesions to watch out for are as follows:
- Pink or translucent, shiny bumps or pearly nodules, sometimes with dark spots or black, blue, or brown surface
- Growths, pink in color, with raised edges and sunken center, usually with irregular blood spoke-wheel vessels on its surface
- Pale or yellow scar-like areas
- Elevated reddish patches