Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma usually begins as a painless bump or nodule that grows slowly. Later, it becomes an open ulcer with a hard edge. Nearly 90% of basal cell carcinomas occur on the face, but they can appear on any part of the body that is sometimes exposed to the sunthe face, ears, neck, back, chest, arms, and legs.
Although basal cell carcinoma almost never spreads to other organs and is rarely fatal, it can invade surrounding tissue and be disfiguring if not treated.
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Because basal cell carcinoma is often caused by sun exposure, people can help prevent this cancer by doing the following:
-
Avoiding the sun: For example, seeking shade, minimizing outdoor activities between 10 AM and 4 PM , and avoiding sunbathing and the use of tanning beds
-
Wearing protective clothing: For example, long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats
-
Using sunscreen: At least sun protection factor 30 with UVA and UVB protection used as directed and reapplied every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating but not used to prolong sun exposure
In addition, any skin change that lasts for more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a doctor.
Who Is At The Greatest Risk
Anyone can develop this type of cancer but it is more common in light-skinned individuals with blonde or red hair and light green or blue eyes. It most frequently occurs in elderly males, but it can also occur in younger males and females. If a family has a history of basal cell naevus syndrome, Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome, Rombo syndrome, Oley syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum they are at greater risk for developing basal cell carcinoma.
Recommended Reading: What Does Different Types Of Skin Cancer Look Like
What Are The Symptoms
One common symptom of a basal cell carcinoma is a wound or sore that will not heal. Typically, the wound or sore may bleed or ooze and remain unhealed for an abnormal length of time before eventually healing. It will then reopen and start to ooze or bleed. This process can repeat itself several times.Basal cell carcinomas present themselves as reddish areas of skin on the parts of the body that are exposed to the sun, including the face, neck, arms and legs. Itching is an occasional side effect.Basal cell carcinomas can also appear as a scar, pink growths, or as shiny bumps that appear red, pink or white. These shiny bumps are often mistaken for moles.
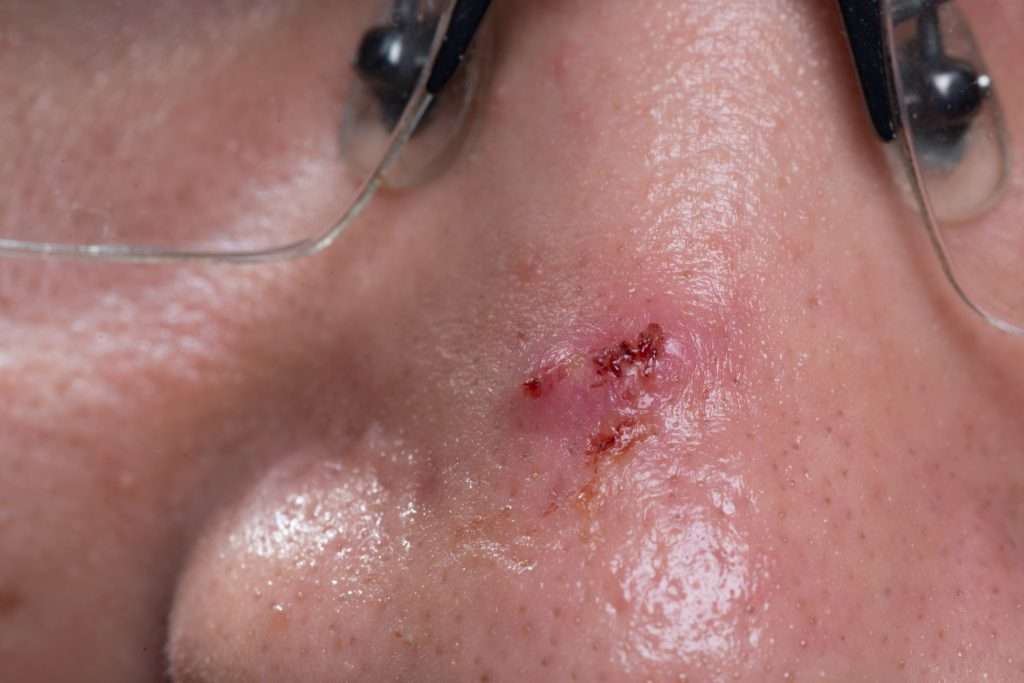
Pigment Basal Cell Carcinoma
The pigmentation can be found in different clinical versions of basal cell carcinoma including nodular, micronodular, multifocal and superficial BCC, and the color varies from dark brown to black . Histology showed nests of basaloid cells, abundance of melanin and melanophages, and moderate inflammatory infiltrate. The melanocytes are located among tumor nests, while the melanophages are present in the stroma. The differential diagnosis has to be made with malignant melanoma.
An irregular, periphery spreading erosive pigmented plaque on head of a 78 years old woman
Donât Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Basal Cell Carcinoma
Recommended Reading: Can I Donate Blood If I Had Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Common
If youve been diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma or BCC, you have plenty of company. As the most common type of cancer in the world, doctors diagnose millions of people with BCC every year. In the United States alone, its estimated that about 2 million Americans hear, You have basal cell carcinoma, each year.1
Most people who develop this skin cancer have fair skin that they seldom protected with sunscreen or sun-protective clothing. Before they developed skin cancer, they often noticed signs of sun damage on their skin, such as age spots, patches of discolored skin, and deep wrinkles.
Dermatologist examining patient for signs of skin cancer
You have a greater risk of developing this skin cancer if youve seldom protected your skin from the sun throughout your life or used tanning beds.
Although BCC is most common in people who have fair skin, people of all colors get this skin cancer.
For most people, BCC is not life-threatening. It tends to grow slowly. It seldom spreads to another part of the body. Even so, treatment is important.
When found early, this skin cancer is highly treatable. An early BCC can often be removed during an appointment with your dermatologist.
Given time to grow, this skin cancer can grow deep, injuring nerves, blood vessels, and anything else in its path. As the cancer cells pile up and form a large tumor, the cancer can reach into the bone beneath. This can change the way you look, and for some people the change may be disfiguring.
Professional Skin Cancer Diagnosis And Treatment At Brentwood Dermatology
If youve noticed a suspicious spot or an atypical mole, or simply would like to schedule your annual skin cancer screening, contact Brentwood Dermatology!
Our board-certified dermatologists are here to help you with professional skin cancer detection, diagnosis, and treatment.;
If youre interested in learning more about basal cell carcinoma or need to schedule your annual skin cancer screening, the expert team of board-certified dermatologists at Brentwood Dermatology are here to help. Schedule an appointment online or give us a call today at 615-377-3448!;
Don’t Miss: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like On Your Head
What Happens When Skin Cancer Goes Untreated
If you notice an abnormality on your skin you may be tempted to ignore it. However, if it is skin cancer you could be putting your health at risk by waiting to get a skin and mole check. There are three main types of skin cancer in Australia with melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, and they each have their own set of unique characteristics. The most important thing to remember is that if you delay treatment of skin cancer it could have life threatening consequences:
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of cancer, but also the least likely to spread. In particular, BCCs rarely spread beyond the initial tumor site. However, left untreated, BCCs can grow deeper into the skin and damage surrounding skin, tissue, and bone. Occasionally, a BCC can become aggressive, spreading to other parts of the body and even becoming life threatening. Also, the longer you wait to have your BCC treated, the more likely it is to return after treatment. Like BCCs, SCCs are highly curable when caught and treated early. However, if left to develop without treatment, an SCC can become invasive to skin and tissue beyond the original skin cancer site, causing disfigurement and even death. Over 15,000 Americans die each year from SCCs. And even if untreated carcinomas dont result in death, they can lead to large, open lesions on the skin that can cause discomfort, embarrassment, and infection.
Read Also: How Fast Does Subungual Melanoma Grow
What You Can Do
If youve already had a BCC, you have an increased chance of developing another, especially in the same sun-damaged area or nearby.
A BCC can recur even when it has been carefully removed the first time, because some cancer cells may remain undetectable after surgery and others can form roots that extend beyond whats visible. BCCs on the nose, ears and lips are more likely to recur, usually within the first two years after surgery.
Heres what you can do to detect a recurrence and safeguard yourself against further skin damage that can lead to cancer:
Reviewed by:
The Risks The Causes What You Can Do
Basal cell carcinoma is caused by damage and subsequent DNA changes to the basal cells in the outermost layer of skin. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun and indoor tanning is the major cause of BCCs and most skin cancers.
Understanding what causes BCC and the factors that increase your risk of getting it can help you prevent the disease or detect it in its earliest stages, when its easiest to treat.
These factors increase your BCC risk:
Recommended Reading: How Does Skin Cancer Feel
Is Stage 4 Basal Cell Carcinoma Serious
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma is the fifth and final phase of development of the cancer, so it’s the most serious stage. Basal cell carcinoma isn’t often life-threatening, but by the time it reaches stage 4, it’s already begun to spread to bones, lymph nodes, and other organs. This means treatment is more difficult by the time the cancer has reached this stage. Because of this, it’s important to see a doctor if you notice symptoms of stage 4 basal cell carcinoma.
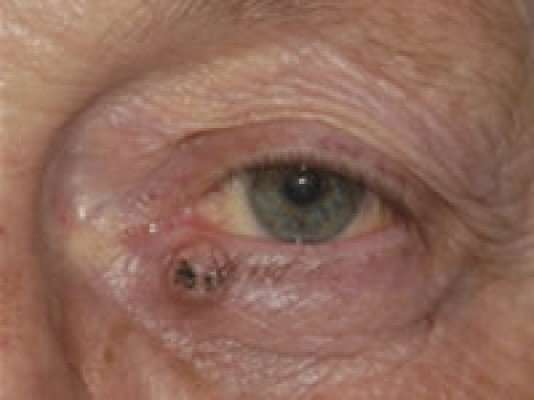
Eyelid Basal Cell Carcinoma
Eyelid basal cell carcinoma is the most common cancer of the skin around the eye. It most frequently originates in the lower eyelid and is more common in fair-skinned adults between 50 and 80 years of age. The lesion appears as a nodule or it can appear as a simply thickened eyelid with eyelash loss. Sometime it hides under a skin abrasion or ulcer. This can be invasive and grow deep into the soft tissues around the eye and into the brain where it becomes life-threatening
The goal of management of eyelid basal cell carcinoma is complete tumor control. This means that the tumor should be surgically removed completely. This is accomplished in the operating room and with pathologic proof of tumor-free frozen section margins. The eyelid then needs to be reconstructed so that it functions normally and covers the eye. This requires great skill and the need to borrow tissue from the opposite eyelid, neck, ear, or sometimes the mouth. Occasionally the eyelids must be sewn shut for two months so that the eye is protected as the eyelids heal. Sometimes eyelid basal cell carcinoma is treated with a cream that is used for several months or it can be treated with an injection of chemotherapy.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has Spread
How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed
The first step in diagnosing BCC will be a visual inspection from a dermatologist. Theyll check your skin head-to-toe to look for any skin growths or discolorations. Theyll also ask about your medical history, including family history of skin cancers.
If your dermatologist finds any discolorations or growths of concern, theyll take a biopsy of the skin. To do this, theyll inject a numbing agent into the skin before removing a small sample of the lesion for testing. The biopsy will be viewed under a microscope to look for skin cancer.
Your dermatologist will remove the growth if BCC is found. If you have an aggressive form of BCC, your doctor may take a biopsy of your lymph nodes to check for metastasis.
Treatment for basal cell carcinoma involves removing the growth. Your doctor will recommend a treatment depending on the type of BCC you have, the size of the lesion, and the location of the lesion. Treatment options include:
What Are The Clinical Features Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is a locally invasive skin tumour. The main characteristics are:
- Slowly growing plaque or nodule
- Skin coloured, pink or pigmented
- Varies in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter
- Spontaneous bleeding or ulceration
BCC is very rarely a threat to life. A tiny proportion of BCCs grow rapidly, invade deeply, and/or metastasise to local lymph nodes.
Donât Miss: How Deadly Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Read Also: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common kind of skin cancer. It can develop almost anywhere on the body.
BCCs typically form in sun-exposed areas. They vary greatly in how they lookpink or red bumps, open sores, or waxy patches. For people with brown or black skin, BCCs may appear brown or almost black.
What Are Basal Cells
Human skin is made up;of two main;layers:;the epidermis, which;forms the top layer of skin, and;the dermis, which forms the bottom;layer.
The epidermis functions as;the protective outer shell, while the dermis contains;blood vessels, hair follicles,;melanocytes, and other specialized biological structures.
Within the two layers of skin, several different types of cells can be found. Each type of cell serves a different;role in the normal;functioning of the skin.
Basal cells can be found in the deepest;layer of the epidermis.;While their specific purpose isnt completely clear, scientist believe basal cells serve as a type of stem cellbasal cells start out as relatively undifferentiated, but rapidly reproduce and aid in the process of creating new skin cells.
Recommended Reading: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma Staging
Staging;is the process of determining whether cancer has spread and, if so, how far. The stage of the disease may affect the treatment plan.
The stage is based on the size of the tumor, how deeply into the skin it has grown, and whether cancer has spread beyond the tumor to the lymph nodes. Your doctor will look at the results of the biopsy to determine the stage.;In rare cases, your doctor may recommend imaging such as CT or PET-CT scan to see if the cancer has spread beyond the skin
Stages are numbered in Roman numerals between 0 and IV.
Most non-melanoma skin cancers are Stage 0 or Stage 1. Stage 3 and 4 are relatively rare. Based on the type of cancer, the stage of cancer, your overall health, and other factors, your doctor works with you to develop a treatment plan.
High risk features for primary tumor staging
- Depth/invasion: >2 mm thickness , Clark level IV, Perineural invasion
- Anatomic: Primary site ear
- Location: Primary site hair-bearing lip
- Differentiation: Poorly differentiated or undifferentiated
Causes Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Pro Tip
Newer treatments for severe, advanced basal cell carcinoma target the PTCH gene. PTCH is a tumor suppressor gene that normally prevents uncontrolled cell growth but has malfunctioned in many basal cell carcinomas, causing abnormal cell replication. Dr. MacCormack
Cancers develop because of abnormal, uncontrolled cell growth. BCCs are caused by an overgrowth of basal cells. Often, the overgrowth occurs because cell DNA has been damaged.
The most likely reason you have a BCC is from being exposed to sunlight. Exposure to UV radiation, especially severe, intermittent sunburns, increases the risk of developing BCC. People with pale skin, blue eyes, and blond hair are a greater risk of BCC than individuals with darker complexions.
Basal cell DNA can also be damaged by other UV light exposure, such as from tanning beds, by ionizing radiation , and from chemicals like arsenic, which can be found in well water.
Some genetic syndromes, diseases , and medical treatments that suppress the immune system, like chemotherapy, may impair cell DNA repair, increasing the likelihood of getting BCCs.
Recommended Reading: When Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreads
The Clinical Course Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Although most patients who develop SCCs have localized disease that can be cured, tumor recurrence, tumor spread to other parts of the body, and death occasionally occurs.
Larger tumors may cause disfigurement as they may penetrate into the underlying tissues causing nerve or muscle damage. SCCs that have spread into the underlying tissue have been resistant to previous therapy or have reoccurred are considered advanced SCCs.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment
After a doctor examines the carcinoma, a biopsy is needed to confirm the cancer. If tumor cells are visible, treatment is required. Treatment will vary based on the type, size, depth, and location of the carcinoma as well as individual patient concerns. The cancer is most commonly treated through surgery on an outpatient basis in a physicians clinic or office.
A doctor will usually choose from the following main forms of treatment:
You May Like: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
This is a type of excision that uses a microscope to remove the lesion layer by layer until no signs of cancer are present. The microscope allows the doctor to pinpoint the cancerous areas of skin to better target removal and save healthy skin. This is a very effective form of removal with a success rate of 99 percent or higher.
Donât Miss: Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Malignant
How Dangerous Is A Basal Cell Carcinoma
While melanoma rightly deserves the attention it receives as the most dangerous form of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma isnt something to brush off as harmless. Yes, this most common form of skin cancer rarely causes fatalities, but it can become quite disfiguring.
While basal cell carcinoma lesions rarely spread beyond the original tumor site, they should not be allowed to grow freely. These lesions can grow widely, penetrating deeply into the skin destroying skin, tissue, and bone. Plus, the longer you leave a basal cell carcinoma untreated, the more likely it is to come back. And because it will usually return in the same area, this can create problems removing the lesions without overly disfiguring the patient.
Read Also: Should I Be Worried About Basal Cell Carcinoma
More Information About Basal Cell Carcinoma
The following are some English-language resources that may be useful. Please note that THE MANUAL is not responsible for the content of these resources.
See the following sites for comprehensive information about basal cell carcinoma, including detection, prevention, treatment options, and other resources:
Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatments
Basal cell carcinoma can be treated;in several different ways depending on the size of the cancer, its location, how long you have had the tumor and how much scarring is likely to occur with each treatment.
Options for treating basal cell carcinoma include:
- Cryosurgery, in which the lesion is frozen with liquid nitrogen
- Curettage, in which the;skin cancer;is removed by scraping the area with a sharp looped-edged instrument called a curette. The cancerous area is then treated with an electrocautery needle to destroy any remaining cancer cells and help control bleeding. This process may be repeated a few times with a deeper layer of tissue being scraped and cauterized each time to help destroy all of the cancer cells.
- Simple excision, in which the cancerous tissue and some surrounding healthy skin is cut out.
- Mohs surgery. This is a procedure in which your doctor removes the cancer layer by layer and examines each layer under the microscope until no abnormal cells remain.
- Radiation therapy, which uses high-energy beams such as X-rays to kill cancer cells. This is more common for deeper tumors.
If the cancer has spread to other parts of your body, or if it has come back after surgery, your doctor may prescribe certain medications.;In some cases, your doctor may also recommend the use of a prescription cream for several weeks.
If you are diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma, your dermatologist will discuss options with you to determine the best treatment plan.
Read Also: Can Renal Cell Carcinoma Be Benign